| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) [1]
- Peripheral Dopa Decarboxylase (DDC) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 B\PC3 和 Capan-2 细胞中,carbidepa ((S)-(-)-Carbidopa) 表现出与其他 AhR 配体报道类似的作用,包括 CYP1A1 和 CYP1A2 的激活,这些作用被 AhR 单一抗氧化剂(如 CH223191)抑制[1]。
选择性Ah受体调节剂(SAhRM):卡比多巴(Carbidopa)结合AhR并调节AhR介导的基因表达,在人肝癌细胞中特异性上调II相解毒基因(如NQO1)表达约2.5倍,且不诱导I相细胞色素P450 1A1(CYP1A1)表达[1] - 抑制外周多巴脱羧酶活性:10 μM 卡比多巴(Carbidopa)使大鼠外周组织匀浆(肾、肠)中L-多巴向多巴胺的转化减少约85%,且不影响中枢神经系统DDC活性[2] - 浓度高达100 μM时,对人肝细胞或外周组织细胞无显著细胞毒性(细胞存活率>90%)[1, 2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
使用 Bχ PC3 细胞作为异种移植物的体内研究表明,1 mg/ml 剂量的卡比多巴可大大减少肿瘤生长。卡比多巴还促进 AhR 的核膜形成[1]。
增强左旋多巴在帕金森病动物模型中的疗效:大鼠经6-OHDA诱导黑质纹状体损伤后,口服合用卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(25 mg/kg)与左旋多巴(100 mg/kg),较单用左旋多巴使脑内多巴胺水平升高约3.0倍,运动功能改善(减少运动不能和震颤)约60%[2] - 减少外周左旋多巴代谢:卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(10-50 mg/kg,口服)在健康大鼠中剂量依赖性降低血浆多巴胺浓度40-70%,减轻左旋多巴相关的外周副作用(如恶心、低血压)[2] - 调节AhR介导的全身解毒功能:小鼠口服卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(50 mg/kg/天,持续7天),肝组织NQO1蛋白表达上调约2.2倍,增强抗氧化和解毒能力[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
多巴脱羧酶(DDC)活性测定:大鼠外周组织(肾/肠)匀浆与L-多巴(底物)、系列稀释的卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(0.1-100 μM)在含吡哆醛磷酸(辅因子)的反应缓冲液中孵育。37°C孵育60分钟后,加入高氯酸终止反应。高效液相色谱(HPLC)电化学检测法定量反应产物多巴胺,相对于溶媒对照组计算抑制率[2]
- AhR结合与转录激活实验:重组人AhR蛋白固定在传感器芯片上,注入卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(0.01-10 μM),通过SPR技术检测结合亲和力。转录激活实验中,转染AhR响应性荧光素酶报告质粒的人肝癌细胞用卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(0.1-50 μM)处理24小时,检测荧光素酶活性并以β-半乳糖苷酶活性归一化,评估AhR调节作用[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
肝细胞AhR介导的基因表达实验:人肝癌细胞接种于6孔板,用卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(0.1-50 μM)处理24小时。提取总RNA,RT-PCR定量NQO1/CYP1A1的mRNA水平;western blot检测NQO1蛋白表达[1]
- 外周细胞DDC抑制实验:大鼠肠上皮细胞接种于96孔板,用卡比多巴(Carbidopa)(0.1-100 μM)预处理1小时,再与L-多巴(100 μM)孵育4小时。收集培养上清液,HPLC法检测多巴胺浓度以评估DDC抑制效果[2] |
| 动物实验 |
6-OHDA-induced Parkinson's disease rat model: Male Wistar rats (250-300 g) received unilateral stereotaxic injection of 6-OHDA into the nigrostriatal pathway to induce Parkinsonian symptoms. Two weeks post-lesion, rats were randomly divided into groups: vehicle, levodopa alone (100 mg/kg), and Carbidopa (25 mg/kg) + levodopa (100 mg/kg). Drugs were administered orally once daily for 14 days. Motor function was evaluated by apomorphine-induced rotation test and open-field activity. Brain tissues were collected to measure dopamine levels by HPLC [2]
- AhR modulation mouse model: Male C57BL/6 mice (20-25 g) were randomly divided into vehicle and treatment groups. Carbidopa was suspended in 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium and administered orally at 50 mg/kg/day for 7 days. Livers were harvested to detect NQO1 and CYP1A1 expression by western blot and RT-PCR [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
When [levodopa]/carbidopa is administered orally, 40-70% of the administered dose is absorbed. Once absorbed, carbidopa shows bioavailability of 58%. A maximum concentration of 0.085 mcg/ml was achieved after 143 min with an AUC of 19.28 mcg.min/ml. In animal studies, 66% of the administered dose of carbidopa was eliminated via the urine while 11% was found in feces. These studies were performed in humans and it was observed a urine excretion covering 50% of the administered dose. The volume of distribution reported for the combination therapy of carbidopa/[levodopa] is of 3.6 L/kg. However, carbidopa is widely distributed in the tissues, except in the brain. After one hour, carbidopa is found mainly in the kidney, lungs, small intestine and liver. The reported clearance rate for the combination therapy of [levodopa]/carbidopa is 51.7 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites The loss of the hydrazine functional group (probably as molecular nitrogen) represents the major metabolic pathway for carbidopa. There are several metabolites of carbidopa metabolism including 3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropionic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-methylpropionic acid, 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methylpropionic acid, 3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-methyllactic acid, 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-2-methyllactic acid, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetone (1,2). Biological Half-Life The reported half-life of carbidopa is of approximately 107 minutes. Oral absorption: Rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with Tmax = 1-2 hours (rat and human) [2] - Distribution: Primarily confined to peripheral tissues; poor blood-brain barrier penetration (brain/plasma concentration ratio < 0.1) [2] - Plasma half-life (t1/2): ~1.5 hours (rat), ~2 hours (human) [2] - Metabolism: Metabolized in the liver via decarboxylation and conjugation; major metabolites are inactive [2] - Excretion: ~70% excreted in urine (as metabolites) within 24 hours; ~20% excreted in feces [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
It is widely accepted that the protein binding of carbidopa is 76%. However, more studies are required or the presentation of the source of this information. Acute toxicity: LD50 > 2000 mg/kg (oral in rats and mice); no mortality or acute adverse effects at doses up to 2000 mg/kg [2] - Subchronic toxicity: Daily oral administration of 100 mg/kg for 90 days in rats caused no significant changes in liver/kidney function (ALT, AST, creatinine) or hematological parameters [2] - Plasma protein binding rate: ~36% (human); ~30% (rat) [2] - Clinical adverse effects: Mild gastrointestinal discomfort (nausea, diarrhea) in ~5% of patients; no significant central nervous system toxicity due to poor brain penetration [2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
When mixed with [levodopa], carbidopa inhibits the peripheral conversion of [levodopa] to dopamine and the decarboxylation of [oxitriptan] to serotonin by aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. This results in an increased amount of [levodopa] and [oxitriptan] available for transport to the central nervous system. Carbidopa also inhibits the metabolism of [levodopa] in the GI tract, thus, increasing the bioavailability of [levodopa]. The presence of additional units of circulating [levodopa] can increase the effectiveness of the still functional dopaminergic neurons and it has been shown to alleviate symptoms for a time. The action of carbidopa is very important as [levodopa] is able to cross the blood-brain barrier while dopamine cannot. Hence the administration of carbidopa is essential to prevent the transformation of external [levodopa] to dopamine before reaching the main action site in the brain. The coadministration of carbidopa with [levodopa] has been shown to increase the half-life of [levodopa] more than 1.5 times while increasing the plasma level and decreasing clearance. The combination therapy has also shown an increase of the recovery of [levodopa] in urine instead of dopamine which proves a reduced metabolism. This effect has been highly observed by a significant reduction in [levodopa] requirements and a significant reduction in the presence of side effects such as nausea. It has been observed that the effect of carbidopa is not dose-dependent. Carbidopa is a peripherally acting dopa decarboxylase inhibitor and selective Ah receptor modulator (SAhRM) [1, 2] - Core mechanisms of action: 1) Inhibits peripheral DDC to prevent L-dopa decarboxylation in peripheral tissues, increasing L-dopa bioavailability in the brain for Parkinson's disease treatment; 2) Modulates AhR to upregulate phase II detoxification genes without inducing pro-carcinogenic phase I enzymes [1, 2] - Approved indication: Adjunctive treatment of Parkinson's disease, administered in combination with levodopa to enhance efficacy and reduce peripheral side effects of levodopa [2] - Key advantage: Poor blood-brain barrier penetration ensures selective inhibition of peripheral DDC, avoiding central DDC inhibition that could impair brain dopamine synthesis [2] - Clinical use: Standard of care for Parkinson's disease, typically administered as a fixed-dose combination with levodopa [2] |
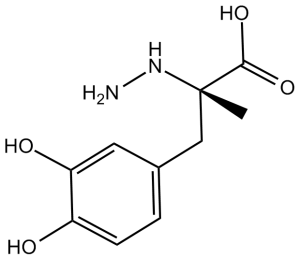
| 分子式 |
C10H14N2O4
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
226.23
|
|
| 精确质量 |
226.095
|
|
| CAS号 |
28860-95-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Carbidopa monohydrate;38821-49-7
|
|
| PubChem CID |
34359
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
528.7±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
206 - 208ºC
|
|
| 闪点 |
273.5±30.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.641
|
|
| LogP |
-0.19
|
|
| tPSA |
115.81
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
261
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
C[C@](CC1=CC(=C(C=C1)O)O)(C(=O)O)NN
|
|
| InChi Key |
TZFNLOMSOLWIDK-JTQLQIEISA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C10H14N2O4/c1-10(12-11,9(15)16)5-6-2-3-7(13)8(14)4-6/h2-4,12-14H,5,11H2,1H3,(H,15,16)/t10-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(2S)-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-2-hydrazinyl-2-methylpropanoic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 10.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (4.42 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (44.20 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.4203 mL | 22.1014 mL | 44.2028 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8841 mL | 4.4203 mL | 8.8406 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4420 mL | 2.2101 mL | 4.4203 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Neurobiological Drivers of Mobility Resilience: The Dopaminergic System
CTID: NCT04325503
Phase: Phase 1/Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2024-04-04