| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
β-lactam
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
克拉维酸和氨苄西林表现出协同抗菌活性(针对产生 β-内酰胺酶的微生物)[2]。
Ab11 和 Ab51 菌株在 MIC 为 2–8 μg/mL 时被克拉维酸抑制[3]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
克拉维酸(13 mg/kg,腹腔注射)可降低鲍曼不动杆菌感染的 C57BL/6 小鼠肺炎模型的肺部细菌负荷[3]。克拉维酸(13 mg/kg,ip)在 Ab51 感染的 C57BL/6 小鼠肺炎模型中的 t1/2 为 6.69 h,AUC 为 4.03 mg·h/L[3]。
角叉菜胶 (HY-125474) 引起的爪水肿在用克拉维酸(100–300 mg/kg,腹腔注射)治疗时表现出抗炎作用[4]。 |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Clavulanic acid, when taken orally, is well absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. After administration of radiolabeled clavulanic acid to four human subjects, a minimum of 73% absorption and the average absolute bioavailability was calculated at 64%. The mean Cmax in a group of 8 healthy research volunteers was 2.098 ± 0.441 micrograms/ml in a pharmacokinetic study. The same study reported a mean Tmax of 1.042 ± 0.80 hours. Tmax is reported to be 40-120 minutes according to another pharmacokinetic study. About 40 to 65% of the clavulanic acid is excreted as unchanged drug in urine during the first 6 hours following ingestion. The metabolites of clavulanic acid are found to be excreted in the urine and feces and as carbon dioxide in expired air. Clavulanate is cleared by both renal and non-renal processes. About 17% of radiolabeled dose of clavulanic acid was found to be exhaled in expired air and 8% of a dose was found to be excreted in the feces. A study in 4 healthy volunteers administered a radiolabeled dose of clavulanic acid determined a volume of distribution of 12L.Clavulanic acid is distributed to various tissues and interstitial fluid. Clinically significant concentrations have been measured in the gallbladder, abdomen, skin, fat, and muscle tissues. Bile, pus, synovial and peritoneal fluids are also found to have therapeutic concentrations of clavulanic acid. Studies of animals have demonstrated that clavulanic crosses the placenta. The clearance of clavulanic acid in a pharmacokinetic study of 4 healthy volunteers administered a radiolabeled dose of clavulanic acid was 0.21 l/min. Another resource indicates the average clearance of clavulanic acid is 12.20 liters/h/70 kg. Dose adjustments may be required in patients with renal failure. Metabolism / Metabolites Clavulanic acid is heavily metabolized to form the metabolites 2,5-dihydro-4-(2- hydroxyethyl)-5-oxo-1H-pyrrole-3-carboxylic acid and 1-amino-4-hydroxy-butan-2-one. The first metabolite was found to account for 15.6% of the dose while the second metabolite was reported to account for 8.8% of the dose in one pharmacokinetic study. Biological Half-Life The half-life of clavulanic acid is reported to be similar to amoxicillin, and last 45-90 minutes. A study of radiolabeled clavulanic acid administered to 4 healthy volunteers determined a half-life of 0.8 h. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
The plasma protein binding of amoxicillin is about 25%. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Clavulanic acid is antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces clavuligerus. It acts as a suicide inhibitor of bacterial beta-lactamase enzymes. It has a role as an antibacterial drug, a bacterial metabolite, an anxiolytic drug and an EC 3.5.2.6 (beta-lactamase) inhibitor. It is a conjugate acid of a clavulanate.
Clavulanic acid is a beta-lactamase inhibitor that is frequently combined with [Amoxicillin] or [Ticarcillin] to fight antibiotic resistance by preventing their degradation by beta-lactamase enzymes, broadening their spectrum of susceptible bacterial infections. Clavulanic acid is derived from the organism Streptomyces clavuligerus.When it is combined with amoxicillin, clavulanic acid is frequently known as Augmentin, Co-Amoxiclav, or Clavulin. Clavulanic acid is a beta Lactamase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of clavulanic acid is as a beta Lactamase Inhibitor. Clavulanic acid has been reported in Streptomyces cattleya and Streptomyces clavuligerus with data available. Clavulanic Acid is a semisynthetic beta-lactamase inhibitor isolated from Streptomyces. Clavulanic acid contains a beta-lactam ring and binds strongly to beta-lactamase at or near its active site, thereby hindering enzymatic activity. This protects other beta-lactam antibiotics from beta-lactamase catalysis, thereby enhancing their antibacterial effects. This agent is used in conjunction with beta-lactamase susceptible antibiotics, such as penicillins and cephalosporins, to treat infections caused by beta-lactamase producing organisms. A beta-lactam antibiotic produced by the actinobacterium Streptomyces clavuligerus. It is a suicide inhibitor of bacterial beta-lactamase enzymes. Administered alone, it has only weak antibacterial activity against most organisms, but given in combination with other beta-lactam antibiotics it prevents antibiotic inactivation by microbial lactamase. Drug Indication Clavulanic acid combined with other antibiotics is indicated to prevent the development of drug-resistant strains of bacteria and promotes their therapeutic antibacterial effects. The following conditions, when they produced beta-lactamases, have been treated with a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid or ticarcillin and clavulanic acid: Acute otitis media caused by H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis Sinusitis due to H. influenzae and M. catarrhalis Lower respiratory tract infections due to Haemophilus influenzae, S.aureus, Klebsiella species, and Moraxella catarrhalis Skin and skin structure infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella species Urinary Tract Infections due to E. coli, Klebsiella species of bacteria, and Enterobacter species of bacteria, S.marcescens, or S.aureus Gynecologic infections due to a variety of bacteria, including P.melaninogenicus, Enterobacter species, E.Coli species, Klebsiella species, S. aureus, S.epidermidis Septicemia due to a variety of bacteria, including Klebsiella species, E.Coli species, S.aureus, or Pseudomonas species Bone and joint infections due to S.aureus Intraabdominal infections due to E.Coli, K.pnemoniae, or B.fragilis group **A note on susceptibility** It should be noted that it is only to be administered in infections that are confirmed or highly likely to be caused by susceptible bacteria. Culture and susceptibility tests should be performed if possible and used in selecting whether this antibiotic is prescribed. When beta-lactamase enzyme production is not detected during microbiological testing, clavulanic acid should not be used. When these tests are not available patterns of local infection and susceptibility may be used to determine the appropriateness of using clavulanic acid. Ticarcillin with clavulanate has shown particular efficacy in mixed infections in addition to empiric therapy before determining the susceptibility of causative organisms. The ticarcillin-clavulanic acid combination may prove to be an effective single-agent antibiotic therapy to treat infections where a regimen of several drugs may normally be used. Mechanism of Action Clavulanic acid contains a beta-lactam ring in its structure that binds in an irreversible fashion to beta-lactamases, preventing them from inactivating certain beta-lactam antibiotics, with efficacy in treating susceptible gram-positive and gram-negative infections. |
| 精确质量 |
199.048
|
|---|---|
| CAS号 |
58001-44-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Potassium clavulanate cellulose;Clavulanate lithium;61177-44-4;Clavulanate potassium;61177-45-5
|
| PubChem CID |
5280980
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
545.8±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
117.5-118
117.5 - 118 °C |
| 闪点 |
283.9±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.3 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.644
|
| LogP |
-1.98
|
| tPSA |
87.07
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
14
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
324
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
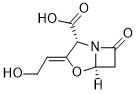
C(=C/1\[C@H](C(=O)O)N2C(=O)C[C@H]2O1)/CO
|
| InChi Key |
HZZVJAQRINQKSD-PBFISZAISA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H9NO5/c10-2-1-4-7(8(12)13)9-5(11)3-6(9)14-4/h1,6-7,10H,2-3H2,(H,12,13)/b4-1-/t6-,7-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2R,3Z,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid
|
| 别名 |
Clavulanate; Acide clavulanique; Acido clavulanico; Clavulansaeure; Antibiotic MM 14151; acidum clavulanicum;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 (2). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~13.89 mg/mL (~69.74 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (12.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (12.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 10% DMSO+90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline): ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (12.55 mM) 配方 4 中的溶解度: 12.5 mg/mL (62.76 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶 (<60°C). 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02563769 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Clavulanic acid Drug: Intravenous cocaine Drug: Placebo |
Cocaine Abuse Cocaine Addiction Cocaine Dependence Cocaine-Related Disorders |
Temple University | 2016-10-24 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00603317 | COMPLETED | Drug: Firstly : Amoxicillin-Clavulanic acid and secondly : Placebo Drug: Firstly : Placebo and secondly : Amoxicillin-Clavulanic acid |
Atrial Fibrillation Deep Venous Thrombosis Oral Anticoagulation Pulmonary Embolism |
Assistance Publique - Hôpitaux de Paris | 2008-03 | Phase 4 |
| NCT05562349 | ACTIVE, NOT RECRUITING | Drug: Clavulanic Acid Only Product Drug: Placebo |
Cocaine Dependence | Temple University | 2023-05-03 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04411914 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Clavulanic Acid Other: Placebo |
Cocaine Dependence | Temple University | 2020-09-01 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01772238 | COMPLETED | Drug: 400 mg Amoxicillin + 57 mg Clavulanic Acid/ 5 ml Drug: 400 mg Amoxicillin + 57 mg Clavulanic Acid/ 5 ml |
Infections, Respiratory Tract | GlaxoSmithKline | 2011-03-22 | Phase 1 |
|
|
|
|