| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Mitochondrial metabolism
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GPM-2 胃癌细胞在接触 demistat 时会发生凋亡。 Devimistat 专门针对肿瘤细胞使用的线粒体能量代谢的改良版本。 Devimistat 会引起细胞氧化还原状态和线粒体酶活性的改变,从而导致细胞死亡,包括细胞凋亡 [1]。
ARID1A与Harakiri在癌症细胞凋亡中的关系[1] Harakiri(也称为死亡蛋白5,DP5)的特征是通过线粒体改变与凋亡抑制剂Bcl-2和Bcl-XL相互作用来促进凋亡Devimistat是一种最近开发的硫辛酸拮抗剂,可消除线粒体能量代谢,诱导各种癌症细胞凋亡。在本研究中,Devimistat还诱导GPM-2胃癌癌症细胞凋亡。有趣的是,siRNA介导的ARID1A下调赋予了GPM-2细胞对脱维司他诱导的凋亡的抵抗力。值得注意的是,即使ARID1A下调,Harakiri的外源性表达也显著恢复了GPM-2癌症细胞对脱错诱导的凋亡的敏感性。代表性数据如图3所示。这些发现暗示了ARID1A与Harakiri介导的癌症细胞凋亡途径之间的关系 |
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
CPI-613 (25 mg/kg) 在胰腺肿瘤细胞 (BxPC-3) 的人类肿瘤异种移植模型中具有有效的抗癌活性。同样,CPI-613 (10 mg/kg) 也在小鼠模型中对 H460 人非小细胞肺癌产生显着的肿瘤生长抑制作用。此外,CPI-613在大型动物模型的预期治疗剂量范围内几乎不产生副作用毒性,并且小鼠的最大耐受剂量为100 mg/kg。
Devismat(CPI-613)治疗对富含CSC的球体产生负面影响,导致体内致瘤性降低[2] 许多研究提供了证据,表明球体形成条件在体外富集了CSCs。为了确认CPI-613对CSC群体的靶向作用,我们在低粘附板中在球体促进培养条件下孵育UWB1.289 MUT和OVCAR3球体14天后对这些细胞进行了处理(图2A)。与之前单层实验中观察到的相反,在这些球体形成培养条件下,用作阳性对照的卡铂/紫杉醇治疗对CD133+和CD117+细胞频率没有影响(p值>0.05),与载体相比,这些球体形成的培养条件优先富集CSC,间接证实了CSC对细胞毒性的抵抗力。有趣的是,CPI-613治疗降低了富含CSC球体中CD133+和CD117+细胞的频率(p值<0.01),证实了其对CSC人群的靶向作用。与单独使用载体或卡铂/紫杉醇治疗相比,在富含CSC的球体上结合CPI-613和卡铂/红豆杉醇导致CD133+和CD117+细胞频率降低(图2A,p值<0.001)。在UWB1.289细胞的CD117群体中观察到CPI-613与卡铂/紫杉醇联合使用的唯一相加效应。 Devimistat(CPI-613)体内治疗诱导CD133+和CD117+细胞频率降低[2] CPI-613在体外对CSC群体的靶向作用促使我们研究是否会在体内观察到类似的作用。在NOD/SCID(NOD.CB17-Prkdcscid/NCrCrl先天性免疫缺陷)小鼠中皮下注射OVCAR3细胞,一旦肿瘤体积达到200 mm3,每周用浓度为12.5 mg/kg的CPI-613对小鼠进行腹腔注射。在第二次注射后48小时,即开始治疗后的第9天,对小鼠实施安乐死(图3A)。此时,肿瘤细胞的流式细胞术分析显示,与赋形剂治疗的小鼠相比,CPI-613治疗的小鼠CD133+和CD117+肿瘤细胞频率降低(p值<0.001)(图3B下图)。这种对CD133+和CD117+细胞群的影响与体外分析中观察到的相似,证实了CPI-613降低肿瘤中CSC频率的能力。 与CPI-613单一药物相比,联合Devimistat(CPI-613)和卡铂/紫杉醇治疗会影响肿瘤生长[2] 联合药物治疗在癌症治疗中发挥了特别突出的作用,因为它靶向多种癌症细胞存活,促进了延缓治疗耐药性发生的途径。我们证明了CPI-613和卡铂/紫杉醇在体外的组合对培养中化疗耐药细胞的富集产生了负面影响(图1B)。为了在体内评估CPI-613与卡铂/紫杉醇的联合应用,我们在NOD/SCID小鼠中注射了OVCAR3细胞,以比较每周一次单独或与卡铂-紫杉醇联合给药的12.5mg/kg CPI-613的抗肿瘤活性(分别为25mg/kg和7mg/kg,每周腹腔注射一次)。每3天评估一次肿瘤体积。尽管与其他体内实验方案相比,我们使用了较低剂量的CPI-613,但与载体治疗组相比,CPI-613单药对肿瘤生长的抑制作用是明显的(p值<0.01)。正如预期的那样,与CPI-613单药和赋形剂组相比,卡铂/紫杉醇治疗组和卡铂/红豆杉醇CPI-613联合治疗组显示出肿瘤负担减轻(p值<0.001;图4A)。更重要的是,在治疗期结束时采集的肿瘤的流式细胞术分析显示,与载体治疗的对照组相比,CPI-613治疗的肿瘤中CD133+和CD117+细胞的频率降低,再次表明CPI-613优先靶向CSC(p值<0.01)。然而,令人感兴趣的是联合治疗对CSC频率的影响。尽管与CPI-613单药治疗相比,CD133+和CD117+细胞没有显著差异,但CPI-613和卡铂/紫杉醇的组合否定了卡铂/红豆杉诱导的CD133+与CD117+的细胞频率富集(p值<0.001)(图4B)。对收获的肿瘤中细胞的Annexin/PI分析证实,联合治疗组坏死增加(图S2),表明CPI-613与经典细胞毒性联合使用具有额外益处。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
线粒体膜电位(MMP)的JC-1分析[2]
MMP通过JC-1荧光探针进行测量。CPI-613处理或未处理的细胞与JC-1(1:1000稀释)一起孵育20 最小37 °C。PBS洗涤后,在具有红色荧光的荧光显微镜下观察细胞(550 nm激发/600 nm发射)和绿色荧光通道(485 nm激发/535 nm发射)。通过NIH ImageJ软件测量红/绿荧光比的定量分析 ROS水平的测量[2] 使用氧化剂感应荧光探针DCFH-DA测定细胞内ROS的产生 μM的DCFH-DA用于20 最小37 °C,并使用荧光显微镜拍摄图像。如我们之前所述,通过NIH Image J软件对随机选择的场中至少100个细胞的中位荧光强度进行量化。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
透射电子显微镜(TEM)[2]
约1.0 × 107个细胞用200处理 μM CPI-613或载体用2%戊二醛在0.1 M二碳酸钠(NaCAC)缓冲液(pH 7.4)对于45 min。将样品后固定在NaCAC中的2%四氧化锇中,用2%乙酸铀酰染色,用分级乙醇系列脱水,并包埋在Epon Araldite树脂中。用Leica EM UC6超微切片机切割薄片,收集在铜网格上,并用乙酸铀酰和柠檬酸铅染色。在Hitachi HT7700透射电子显微镜中观察细胞,并用UltraScan 4000 CCD相机和First Light数码相机控制器成像。 三维(3D)细胞培养[2] 简而言之,1 × 将105个细胞接种到提供有完全培养基的48孔SeedEZ支架中。3之后 培养天后,在SeedEZ支架中生长的细胞用200 μM CPI-613用于5 天,并通过alamarBlue在545/590测量细胞活力 nm ex/em,然后如我们之前所述进行鬼笔肽染色和成像。 脂解分析[2] 测量释放到胰腺癌症细胞培养基中的脂滴和游离脂肪酸(FFA)以评估脂解。AsPC-1和PANC-1细胞用200 μM CPI-613用于48 h进行脂解评估。为了测定脂滴,用4%多聚甲醛固定细胞,并用染料Oil-Red-O染色30 min,然后进行苏木精染色处理。根据制造商的说明,通过游离脂肪酸定量试剂盒测量释放的FFA水平。570nm处的吸光度 随后立即在微板读取器上测量。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Background: This article describes the development and validation of a bioanalytical assay to quantify CPI-613 and its major metabolites, CPI-2850 and CPI-1810, in human plasma matrix using LC-MS/MS. Methodology: Sample extraction procedure following protein precipitation with acetonitrile was optimized to extract all three analytes from plasma with maximum recovery. The final extracted supernatants were diluted with water and injected onto an Xbridge C18 (50 × 2.1 mm; 5 μm) column for analysis. The analytes were separated by a gradient elution, and detection was performed on a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (Sciex API 5000) operating in the negative ion mode. Results: The assay was linear over a range of 50-50,000 ng/ml for CPI-613, 250-250,000 ng/ml for CPI-2850 and 10-10,000 ng/ml for CPI-1810. Benchtop stability was established for 24 h, and four freeze-thaw cycles were evaluated for CPI-613 and its metabolites. Long-term freezer (-60 to -80°C) stability for about 127 days was established in this validation. Mean matrix recovery was more than 80% for all analytes. Conclusion: A robust LC-MS/MS method was developed for the quantification of CPI-613 and its major metabolites. The current assay will be used to support ongoing and future CPI-613 clinical trials. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35172610/
|
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Devimistat (CPI-613) has been used in trials studying the treatment of Cancer, Lymphoma, Solid Tumors, Advanced Cancer, and Pancreatic Cancer, among others.
Devimistat is a racemic mixture of the enantiomers of a synthetic alpha-lipoic lipoic acid analogue with potential chemopreventive and antineoplastic activities. Although the exact mechanism of action is unknown, devimistat has been shown to inhibit metabolic and regulatory processes required for cell growth in solid tumors. Both enantiomers in the racemic mixture exhibit antineoplastic activity. This study was designed to unravel the pathobiological role of impaired ARID1A expression in gastric carcinogenesis. We examined ARID1A expression immunohistochemically in 98 gastric cancer tissue specimens with regard to the clinicopathological features. Based on the proportion and intensity of ARID1A immunoreactivity at the cancer invasion front, we subdivided the specimens into low- and high-expression ARID1A groups. Notably, low ARID1A expression was significantly correlated with overall survival of the patients. Subsequently, we determined the molecular signature that distinguished ARID1A low/poor prognosis from ARID1A high/good prognosis gastric cancers. A comprehensive gene profiling analysis followed by immunoblotting revealed that a mitochondrial apoptosis mediator, Harakiri, was less expressed in ARID1A low/poor prognosis than ARID1A high/good prognosis gastric cancers. siRNA-mediated ARID1A downregulation significantly reduced expression of the Harakiri molecule in cultured gastric cancer cells. Interestingly, downregulation of ARID1A conferred resistance to apoptosis induced by the mitochondrial metabolism inhibitor, devimistat. In contrast, enforced Harakiri expression restored sensitivity to devimistat-induced apoptosis in ARID1A downregulated gastric cancer cells. The present findings indicate that impaired ARID1A expression might lead to gastric carcinogenesis, putatively through gaining resistance to the Harakiri-mediated apoptosis pathway.[1] One of the most significant therapeutic challenges in the treatment of ovarian cancer is the development of recurrent platinum-resistant disease. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are postulated to contribute to recurrent and platinum-resistant ovarian cancer (OvCa). Drugs that selectively target CSCs may augment the standard of care cytotoxics and have the potential to prevent and/or delay recurrence. Increased reliance on metabolic pathway modulation in CSCs relative to non-CSCs offers a possible therapeutic opportunity. We demonstrate that treatment with the metabolic inhibitor CPI-613 (devimistat, an inhibitor of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle) in vitro decreases CD133+ and CD117+ cell frequency relative to untreated OvCa cells, with negligible impact on non-CSC cell viability. Additionally, sphere-forming capacity and tumorigenicity in vivo are reduced in the CPI-613 treated cells. Collectively, these results suggest that treatment with CPI-613 negatively impacts the ovarian CSC population. Furthermore, CPI-613 impeded the unintended enrichment of CSC following olaparib or carboplatin/paclitaxel treatment. Collectively, our results suggest that CPI-613 preferentially targets ovarian CSCs and could be a candidate to augment current treatment strategies to extend either progression-free or overall survival of OvCa.[2] |
| 分子式 |
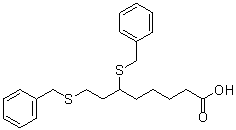
C22H28O2S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
388.59
|
| 精确质量 |
388.153
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 68.00; H, 7.26; O, 8.23; S, 16.50
|
| CAS号 |
95809-78-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Devimistat-d10;2586055-61-8
|
| PubChem CID |
24770514
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.1±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
553.0±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
63-65℃
|
| 闪点 |
288.3±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.595
|
| LogP |
5.66
|
| tPSA |
87.9
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
| 重原子数目 |
26
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
363
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(CCCCC(CCSCC1C=CC=CC=1)SCC1C=CC=CC=1)O
|
| InChi Key |
ZYRLHJIMTROTBO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C22H28O2S2/c23-22(24)14-8-7-13-21(26-18-20-11-5-2-6-12-20)15-16-25-17-19-9-3-1-4-10-19/h1-6,9-12,21H,7-8,13-18H2,(H,23,24)
|
| 化学名 |
6,8-bis(benzylthio)octanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
CPI613; CPI-613; Devimistat; CPI 613
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.35 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.35 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.35 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2 mg/mL (5.15 mM) in 2% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 53% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (5.15 mM) (饱和度未知) in 2% DMSO 98% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 6 中的溶解度: 1% DMSO+30% polyethylene glycol+1% Tween 80:30 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5734 mL | 12.8670 mL | 25.7341 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5147 mL | 2.5734 mL | 5.1468 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2573 mL | 1.2867 mL | 2.5734 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05926206 | Withdrawn | Drug: Devimistat Drug: Modified FOLFIRINOX |
Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma | University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center |
July 2023 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT05070104 | Withdrawn | Drug: CPI-613 Drug: modified FFX |
C04.588.274.476.411.307 | Cornerstone Pharmaceuticals | March 30, 2023 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05733000 | Recruiting | Procedure: Computed Tomography Drug: Devimistat |
Advanced Biliary Tract Carcinoma Advanced Colorectal Carcinoma |
Northwestern University | March 8, 2023 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05325281 | Recruiting | Drug: CPI-613® (Dose level - 1.0 250 mg/m^2) |
Pancreas Adenocarcinoma | Medical College of Wisconsin | October 31, 2022 | Phase 1 |