| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 100mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
- 人外周血单个核细胞 (PBMCs):diABZI STING agonist-1 剂量依赖性激活STING通路,表现为IRF3磷酸化增加以及IFN-β和CXCL10生成增多。IFN-β诱导的EC₅₀为130 nM。该化合物对人STING的选择性超过小鼠STING 100倍以上[1]。
- THP-1细胞:diABZI STING agonist-1 处理后显著激活STING-TBK1-IRF3信号轴,通过Western blot检测到磷酸化IRF3和TBK1水平升高。同时,IFN-β和促炎细胞因子的mRNA表达显著上调[1]。 diABZI STING agonist-1 是选择性干扰素基因 (STING) 受体的刺激剂,对小鼠的 EC50 值分别为 186 nM,对人类的 EC50 值分别为 130 nM。化合物 3(diABZI STING agonist-1)在 1 μM 浓度下对超过 350 种研究的激酶表现出优异的选择性 [1]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
- CT-26同基因小鼠模型:瘤内注射diABZI STING agonist-1 (100 μg) 显著抑制肿瘤生长 (TGI: 94%) 并延长生存期。静脉 (80% TGI) 或腹腔 (62% TGI) 全身给药同样显示强效抗肿瘤活性。该化合物诱导系统性免疫应答,表现为肿瘤内CD8⁺ T细胞浸润增加以及血清IFN-γ和TNF-α水平升高[1]。
- B16黑色素瘤模型:静脉和腹腔注射diABZI STING agonist-1后,第11天平均肿瘤体积分别减少77%和56%[1]。 在体内,diABZI STING 激动剂-1(皮下注射;2.5 mg/kg)可诱导 I 型干扰素和促炎细胞因子的 STING 依赖性激活 [1]。 ? DiABZI STING Agonist-1(静脉注射;3 mg/kg)产生的全身浓度高于小鼠 STING(200 ng/ml)的半最大有效浓度(EC50),并且显示出全身暴露,半衰期为 1.4 小时[1 ]。 diABZI STING Agonist-1(静脉注射;1.5 mg/kg;第 1、4 和 8 天;第 43 天)的作用可显着减少肿瘤发展并提高生存率。 [1]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
重组人STING结合实验:采用表面等离子体共振 (SPR) 评估diABZI STING agonist-1与人STING的结合亲和力,KD为25 nM,表明高亲和力结合。实验将重组人STING固定在传感器芯片上,注射系列稀释的化合物以测量结合动力学[1]。
为了及早发现任何潜在的脱靶缺陷,对化合物2 (diABZI STING激动剂-1)采用了基于亲和富集的化学蛋白质组学策略。化合物5是一种具有伯胺功能的活性类似物,被共价固定在蔗糖珠上,用于从THP1细胞裂解液中亲和捕获潜在的靶蛋白。下拉实验在没有游离化合物2的情况下进行,以从背景中描绘目标蛋白,或者在化合物2存在的浓度范围内。在不同条件下捕获的所有蛋白质都被洗脱,随后通过色氨酸同位素标记进行定量,然后进行LC-MS /MS分析,建立竞争结合曲线并确定半最大抑制(IC50)值。在这些实验中获得的IC50值代表了靶亲和力的量度,但也受到靶对头固定配体亲和力的影响。后一种效应可以通过测定靶蛋白被小珠消耗来推断,这样就可以确定表观解离常数,这在很大程度上与小珠配体无关(详见补充方法)。值得注意的是,在1000倍的窗口内,只有两种蛋白质被捕获并以剂量依赖的方式竞争,即STING和orosomucoid1 (ORM1, α -1-酸性糖蛋白1前体)。STING的平均值为1.6 nM,表明化合物2不仅在截断蛋白的人工生化检测系统中对目标蛋白具有高效能,而且对全长内源人蛋白也具有高效能。唯一鉴定出的脱靶蛋白ORM1的平均值为79 nM,选择性窗口约为40倍。ORM1是一种急性期反应物,是一种丰富的血浆蛋白,已知具有药物结合特性,已知在单核细胞中表达[1]。 |
| 细胞实验 |
- 人PBMC激活实验:从健康供体分离PBMC,用0.1至1000 nM的diABZI STING agonist-1处理24小时,ELISA检测培养上清中IFN-β和CXCL10水平。MTT法评估细胞活力,确认有效浓度下无细胞毒性[1]。
- THP-1信号实验:THP-1细胞转染IFN-β荧光素酶报告质粒,处理后检测荧光素酶活性以量化STING通路激活。Western blot验证下游信号蛋白磷酸化[1]。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Wild and Sting−/− C57Blk6 mice[1]
Doses: 2.5 mg/kg Route of Administration: subcutaneous injection; 2.5 mg/kg Experimental Results: The secretion of IFNβ, IL-6, TNF and CXCL1 was activated in wild-type mice, but Sting None in −/− mice. BALB/c mouse colorectal tumor syngeneic mouse model (CT-26) [1] Doses: 3 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) (iv)injection; 3 mg/kg Experimental Results: Half-life is 1.4 hrs (hrs (hours)), systemic concentration is greater than the EC50 of mouse STING (200 ng/ Animal/Disease Models: BALB/c mouse colorectal tumor syngeneic mouse model (CT-26) [1] Doses: 1.5 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) (iv)injection; 1.5 mg/kg; 43-day Experimental Results: Dramatically inhibited tumor growth and improved survival rate. - CT-26 tumor model: Female C57BL/6 mice were implanted subcutaneously with CT-26 cells. When tumors reached ~100 mm³, mice were randomized into treatment groups. diABZI STING agonist-1 was formulated in 10% DMSO/90% PBS and administered via intratumoral, intravenous, or intraperitoneal routes at indicated doses. Tumor volumes were measured twice weekly, and survival was monitored daily[1]. - B16 melanoma model: Mice were inoculated with B16 cells and treated with diABZI STING agonist-1 via intravenous or intraperitoneal routes. Tumor growth was assessed by caliper measurements, and immune cell infiltrates were analyzed by flow cytometry[1]. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
- Plasma pharmacokinetics: Following intravenous administration in mice, diABZI STING agonist-1 exhibited a half-life (t₁/₂) of 2.1 hours and a volume of distribution (Vd) of 0.8 L/kg. The compound demonstrated moderate plasma protein binding (~75%)[1].
- Tissue distribution: Biodistribution studies revealed significant accumulation of diABZI STING agonist-1 in tumors, spleen, and liver. The compound was rapidly cleared from the bloodstream, with >80% eliminated within 24 hours[1]. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
- Acute toxicity: Single-dose intravenous administration of diABZI STING agonist-1 in mice up to 100 mg/kg did not result in mortality or significant adverse effects. Clinical signs, body weight, and organ weights were monitored for 14 days post-treatment[1].
- Chronic toxicity: Repeat-dose toxicity studies in rats (daily intraperitoneal injections for 28 days) showed no dose-limiting toxicities. Hematology, clinical chemistry, and histopathology analyses revealed no significant abnormalities[1]. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is a receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum that propagates innate immune sensing of cytosolic pathogen-derived and self DNA. The development of compounds that modulate STING has recently been the focus of intense research for the treatment of cancer and infectious diseases and as vaccine adjuvants. To our knowledge, current efforts are focused on the development of modified cyclic dinucleotides that mimic the endogenous STING ligand cGAMP; these have progressed into clinical trials in patients with solid accessible tumours amenable to intratumoral delivery3. Here we report the discovery of a small molecule STING agonist that is not a cyclic dinucleotide and is systemically efficacious for treating tumours in mice. We developed a linking strategy to synergize the effect of two symmetry-related amidobenzimidazole (ABZI)-based compounds to create linked ABZIs (diABZIs) with enhanced binding to STING and cellular function. Intravenous administration of a diABZI STING agonist to immunocompetent mice with established syngeneic colon tumours elicited strong anti-tumour activity, with complete and lasting regression of tumours. Our findings represent a milestone in the rapidly growing field of immune-modifying cancer therapies.[1]
- Mechanism of action: diABZI STING agonist-1 is a small-molecule STING agonist that binds to the ligand-binding domain of STING, triggering conformational changes that activate the TBK1-IRF3 signaling pathway, leading to the production of type I interferons and pro-inflammatory cytokines[1]. - Development rationale: The compound was designed to overcome limitations of cyclic dinucleotide (CDN) STING agonists, such as poor stability and systemic delivery challenges. Its amidobenzimidazole scaffold provides enhanced potency, selectivity, and oral bioavailability[1]. - Preclinical efficacy: diABZI STING agonist-1 demonstrated robust antitumor activity in multiple syngeneic mouse models, both as monotherapy and in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors[1]. |
| 分子式 |
C42H51N13O7
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
849.937247514725
|
| 精确质量 |
849.403
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 59.35; H, 6.05; N, 21.42; O, 13.18
|
| CAS号 |
2138299-33-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
diABZI STING agonist-1 trihydrochloride;2138299-34-8;diABZI STING agonist-1 (Tautomerism);2138498-18-5
|
| PubChem CID |
131986624
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as White to off-white solids
|
| LogP |
1.9
|
| tPSA |
247Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
12
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
18
|
| 重原子数目 |
62
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1570
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
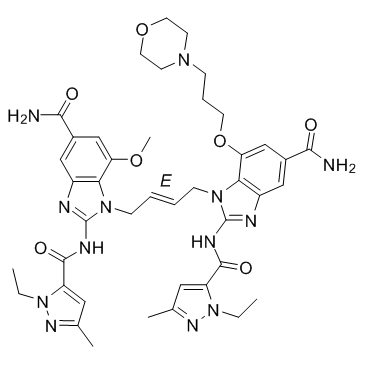
CCN1C(=CC(=N1)C)C(=O)NC2=NC3=C(N2C/C=C/CN4C5=C(C=C(C=C5OCCCN6CCOCC6)C(=O)N)N=C4NC(=O)C7=CC(=NN7CC)C)C(=CC(=C3)C(=O)N)OC
|
| InChi Key |
JGLMVXWAHNTPRF-CMDGGOBGSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C42H51N13O7/c1-6-54-31(19-25(3)49-54)39(58)47-41-45-29-21-27(37(43)56)23-33(60-5)35(29)52(41)12-8-9-13-53-36-30(46-42(53)48-40(59)32-20-26(4)50-55(32)7-2)22-28(38(44)57)24-34(36)62-16-10-11-51-14-17-61-18-15-51/h8-9,19-24H,6-7,10-18H2,1-5H3,(H2,43,56)(H2,44,57)(H,45,47,58)(H,46,48,59)/b9-8+
|
| 化学名 |
1-[(E)-4-[5-carbamoyl-2-[(2-ethyl-5-methylpyrazole-3-carbonyl)amino]-7-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)benzimidazol-1-yl]but-2-enyl]-2-[(2-ethyl-5-methylpyrazole-3-carbonyl)amino]-7-methoxybenzimidazole-5-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
diABZI STING agonist-1; 2138498-18-5; diABZI STING agonist-3; 2138299-33-7; STING agonist 3; diABZI STING agonist-1; 2138498-18-5; diABZI STING agonist-3; 2138299-33-7; Tautomerism; STING agonist 3; diABZI STING agonist-1 (Tautomerism); L7DUG75C36; diABZI STING agonist-1 (Tautomerism); diABZI STING agonist-1 Tautomerism; L7DUG75C36;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~117.66 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 3.5 mg/mL (4.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 35.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 3.5 mg/mL (4.12 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 35.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1766 mL | 5.8828 mL | 11.7655 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2353 mL | 1.1766 mL | 2.3531 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1177 mL | 0.5883 mL | 1.1766 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。