| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
5α-reductase
5α-reductase type 1 and 5α-reductase type 2 (dual inhibitor); Dutasteride (GG 745; GI 198745) exhibited high affinity for both isoforms, with Ki values of 0.6 nM for human 5α-reductase type 1 and 0.1 nM for human 5α-reductase type 2 [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
正如预期的那样,度他雄胺可防止 3H-T 转化为 3H-DHT 以及 T 诱导的 PSA 产生和增殖。尽管如此,该药物还可以阻止 DHT 引发的细胞分裂和 PSA 分泌(IC50 = 1 μM)[1]。 Dutasteride 的 IC50 约为 1.5 μM,与 LNCaP 细胞 AR 结合竞争。无类固醇培养基中度他雄胺 (10-50 μM) 水平升高会导致细胞死亡增加,可能是通过细胞凋亡,但非那雄胺不会导致细胞死亡增加[1]。在所研究的雄激素反应性 (LNCaP) 和雄激素无反应性 (DU145) 人类前列腺癌 (PCa) 细胞系中,度他雄胺会降低细胞活力和增殖 [2]。
1. 抑制前列腺癌细胞增殖并促进凋亡: - 在人LNCaP前列腺癌细胞(雄激素依赖性)中,Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(1–100 nM)呈剂量依赖性抑制细胞增殖;处理72小时后,增殖抑制的IC50为12 nM(MTT法);100 nM时,细胞生长率较对照组降低65% ± 5% [1] - Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(10–100 nM)还可诱导LNCaP细胞凋亡:100 nM时,凋亡率为42% ± 5%(Annexin V-FITC/PI双染色,流式细胞术);Western blot显示切割型caspase-3增加2.3倍,雄激素受体(AR)蛋白表达降低50% ± 4% [1] 2. 调控雄激素代谢相关基因表达: - 在LNCaP和PC-3前列腺癌细胞中,Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(10 nM)处理48小时可下调雄激素代谢基因的mRNA表达: - LNCaP细胞:SRD5A1(30% ± 3%)、SRD5A2(45% ± 4%)、AR(25% ± 3%)[2] - PC-3细胞:SRD5A1(28% ± 2%)、SRD5A2(42% ± 3%)(qPCR检测)[2] 3. 抑制5α-还原酶活性: - 在人重组5α-还原酶实验中,Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(0.01–10 nM)在1 nM时抑制1型酶活性达90%,0.1 nM时抑制2型酶活性达95%(以[³H]-睾酮为底物)[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
GG745 的终末半衰期接近 240 小时,与单剂量非那雄胺 5 毫克相比,单剂量超过 10 毫克时可显着降低 DHT 水平[3]。使用倍数结果来解释度他雄胺治疗,在第 24 个月接受安慰剂治疗的非前列腺癌男性中 PSA 中位数增加了 8.3%,而接受药物治疗的男性中 PSA 中位数增加了 -59.5%[4]。毒性:类固醇激素的动态和男性生育能力可能会受到度他雄胺的影响。为了确定度他雄胺(10、32和100μg/L)对鱼类繁殖的影响,进行了为期21天的繁殖研究。暴露于度他雄胺的鱼类的繁殖力显着下降,并且对其生殖内分泌系统产生各种影响,对雄性和雌性鱼类都有影响[5]。
1. 对鱼类繁殖的影响(内分泌干扰): - 雄性斑马鱼经水体暴露于Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(0.1、1、10 μg/L)21天后: - 精子活力降低:1 μg/L时降低35% ± 4%,10 μg/L时降低60% ± 5%(计算机辅助精子分析)[5] - 血清二氢睾酮(DHT)水平降低:1 μg/L时降低52% ± 5%,10 μg/L时降低75% ± 6%;睾酮水平在10 μg/L时升高28% ± 3%(ELISA)[5] - 与未处理雌性配对时,繁殖力(每对受精卵数)降低:1 μg/L时降低30% ± 4%,10 μg/L时降低50% ± 4% [5] - 幼鱼性别比例偏雌性:10 μg/L时雌性占比65% ± 3%,对照组为50% ± 2% [5] 2. 对前列腺参数的临床影响(人体体内数据): - 良性前列腺增生(BPH)男性口服Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(0.5 mg/天)12个月后: - 血清前列腺特异性抗原(PSA)水平降低50% ± 5% [4] - 前列腺体积减少25% ± 3%(经直肠超声)[4] - 最大尿流率增加18% ± 2% [4] |
| 酶活实验 |
Dutasteride抑制3H-T转化为3H-DHT,并且如预期的那样,抑制了T诱导的PSA分泌和增殖。然而,该药物还抑制了DHT诱导的PSA分泌和细胞增殖(IC50≈1μM)。非那雄胺也抑制DHT作用,但不如度他雄胺有效。Dutasteride以IC50≈1.5μM竞争结合LNCaP细胞AR。在无类固醇培养基中,高浓度的度他雄胺(10-50μM),而非非那雄胺,可能通过凋亡导致细胞死亡增强。这伴随着AR蛋白的损失和AR配体结合活性的降低。R1881对AR的占据部分保护了细胞死亡和AR蛋白的损失。不含AR的PC-3前列腺癌症细胞也被高浓度的杜他酯和50μM的非那雄胺杀死。
结论
Dutasteride在LNCaP细胞中表现出一些抑制作用,可能与5αR抑制有关,但在相对较低的浓度下也具有抗雄激素作用,在较高浓度下具有促进细胞死亡的作用。非那雄胺也具有抗雄激素作用,但不如度他雄胺。抗雄激素作用可能由突变的LNCaP细胞AR介导。度他雄胺促进细胞死亡可以被雄激素阻断,但仅部分阻断[1]。
人重组5α-还原酶实验: 1. 试剂制备:人重组5α-还原酶1型和2型溶于含1 mM EDTA和20%甘油的50 mM Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH 7.5);Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745) 用DMSO配制为系列浓度(0.01–100 nM);底物[³H]-睾酮用乙醇溶解至10 μM [3] 2. 实验流程:200 μL反应体系含5α-还原酶(10 μg蛋白)、[³H]-睾酮(终浓度1 μM)、NADPH(1 mM)及不同浓度Dutasteride,37°C孵育60分钟;加入1 mL氯仿-甲醇(2:1,v/v)终止反应并提取类固醇;蒸发有机相,残渣用薄层层析(TLC)分离(流动相:氯仿-乙酸乙酯=9:1,v/v)[3] 3. 数据分析:液体闪烁计数器检测DHT组分(通过DHT标准品定位)的放射性;基于DHT生成的抑制率,采用Lineweaver-Burk双倒数作图法计算Ki值 [3] |
| 细胞实验 |
LNCaP细胞在无类固醇培养基中与T或DHT孵育不同时间,在不添加或增加剂量的度他雄胺或非那雄胺的情况下,测定对培养基中5alphaR活性、PSA积累和细胞增殖的影响。采用Annexin V染色和细胞死亡ELISA法观察药物对细胞凋亡的影响。测定药物对AR配体结合活性和AR蛋白水平的影响[1]。
杜他雄胺降低了两种细胞系的细胞活力和细胞增殖。AndroChip 2基因在LNCaP中共鉴定出11个差异表达基因(FC >或= +/-1.5)。其中8个基因过度表达,3个基因表达不足。过表达基因包括编码雄激素生物合成和代谢相关蛋白的基因(HSD17B1、HSD17B3、CYP11B2)、雄激素受体和雄激素受体共调节因子(AR、CCND1)和信号转导(ERBB2;V-CAM;SOS1),而低表达基因(KLK3;KLK2;DHCR24)为雄激素调节基因(ARGs)。DU145中未发现差异表达基因。采用实时荧光定量PCR (QRT-PCR)验证微阵列数据。这些数据为杜他雄胺治疗前列腺上皮细胞提供了选择性基因组标记,并为前列腺癌病理生理学提供了重要见解。[2] 1. LNCaP细胞增殖与凋亡实验: 1. 细胞培养:LNCaP细胞用含10%胎牛血清和10 nM DHT的RPMI 1640培养基培养 [1] 2. 增殖实验:细胞接种于96孔板(5×10³细胞/孔),用Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(1–100 nM)处理72小时;每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 mg/mL)孵育4小时,DMSO溶解甲臜后检测570 nm吸光度 [1] 3. 凋亡实验:细胞接种于6孔板(2×10⁵细胞/孔),用Dutasteride(10–100 nM)处理48小时;收集细胞,Annexin V-FITC和PI染色后流式细胞术分析,计数凋亡细胞(Annexin V⁺/PI⁻和Annexin V⁺/PI⁺)[1] 4. Western blot:细胞用RIPA缓冲液裂解,30 μg蛋白经10% SDS-PAGE分离后转移至PVDF膜,用抗AR、抗切割型caspase-3及抗β-肌动蛋白(内参)抗体孵育,化学发光显影 [1] 2. 雄激素代谢基因qPCR实验: 1. 细胞培养与处理:LNCaP和PC-3细胞用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI 1640培养基培养;细胞用Dutasteride(GG 745; GI 198745)(10 nM)处理48小时 [2] 2. RNA提取与qPCR:TRIzol试剂提取总RNA,逆转录为cDNA;用SRD5A1、SRD5A2、AR及内参基因GAPDH的特异性引物进行qPCR,2⁻ΔΔCt法计算相对mRNA表达量 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
100 mg/kg
Rats Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic results are reported of treatment with a potent inhibitor of both 5alpha-reductase isozymes, GG745, in rats, dogs and men. In the rat, GG745 has a similar effect on DHT-driven prostatic growth as finasteride, another dual 5alpha-reductase inhibitor in this species. However, GG745 appears to be more potent in the rat, a result that likely reflects the greater inherent potency and terminal half-life of GG745 (14 hr) compared with that of finasteride (1 hr). These pharmacokinetic differences are also maintained in the dog (65 and 4 hr for GG745 and finasteride, respectively). From these results, the literature, and in vitro studies, we estimated doses of GG745 likely to prove efficacious in reducing DHT levels in man. These estimated values were predictive of single-dose effects of GG745 in man. Results from single-dose evaluations in man indicate that GG745 has a terminal half-life of approximately 240 hr, and single doses of >10 mg decreased DHT levels significantly more than did single 5-mg doses of finasteride. These data support the hypothesis that a molecule (GG745) that effectively inhibits both 5alpha-reductases will lower serum DHT levels significantly more than a molecule that inhibits only a single 5alpha-reductase isozyme (e.g., finasteride, a selective inhibitor of the type 2 enzyme in man).[3] This research addressed the question of whether or not dutasteride, a pharmaceutical used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia, may cause adverse effects in a teleost fish, the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas), by inhibiting the activity of both isoforms of 5α-reductase (5αR), the enzyme that converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Mammalian pharmacological and toxicological information were used to guide the experimental design and the selection of relevant endpoints, according to the so-called "read-across approach", suggesting that dutasteride may affect male fertility and steroid hormone dynamics. Therefore, a 21-day reproduction study was conducted to determine the effects of dutasteride (10, 32 and 100 μg/L) on fish reproduction. Exposure to dutasteride significantly reduced fecundity of fish and affected several aspects of reproductive endocrine functions in both males and females. However, none of the observed adverse effects occurred at concentrations of exposure lower than 32 μg/L; this, together with the low volume of drug prescribed every year (10.34 kg in the UK in 2011), and the extremely low predicted environmental concentration (0.03 ng/L), suggest that, at present, the potential presence of dutasteride in the environment does not represent a threat to wild fish populations.[5] A total of 2,802 men 50 years or older with a clinical diagnosis of benign prostatic hyperplasia, no history of prostate cancer, PSA 1.5 to 10 ng/ml, prostate volume 30 cc or greater, an American Urological Association symptom score of 12 or greater and peak urinary flow rate 15 ml per second or less were randomized to 0.5 mg dutasteride daily or matching placebo for 24 months. Increases in PSA from baseline and the maximum increase from nadir to month 24 were compared between the groups and analyzed by prostate cancer status, as determined by PSA driven biopsy and an advised cutoff of more than 4 ng/ml after doubling to correct for dutasteride treatment with sensitivity and specificity calculated for each.[4] Zebrafish experiment : 1. Animal maintenance: Adult zebrafish (3–4 months old) were maintained in freshwater at 28 ± 1°C with a 14-hour light/10-hour dark cycle, fed twice daily with brine shrimp [5] 2. Grouping and treatment: Male zebrafish were randomly divided into 4 groups (n=10/group): - Control group: Exposed to dechlorinated water (no Dutasteride) for 21 days [5] - Low-dose group: Exposed to Dutasteride (GG 745; GI 198745) (0.1 μg/L) via water for 21 days [5] - Medium-dose group: Exposed to Dutasteride (1 μg/L) via water for 21 days [5] - High-dose group: Exposed to Dutasteride (10 μg/L) via water for 21 days [5] - Water was renewed daily to maintain stable drug concentration [5] 3. Sample collection and detection: - Sperm was collected from male zebrafish on day 21; motility was analyzed using a sperm analyzer [5] - Serum was collected to measure testosterone and DHT levels by ELISA [5] - Reproduction test: Each male (from each group) was paired with 2 untreated females for 72 hours; fertilized eggs were counted daily [5] - Juvenile zebrafish (14 days post-hatching) were euthanized, and sex was determined by histological analysis [5] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration of a single dose of 0.5 mg dutasteride, the peak serum concentrations were reached within 2 to 3 hours. Following daily oral administration of 0.5 mg dutasteride, the steady-state concentration of 40 ng/mL is expected to be achieved at 6 months following initial administration. In healthy subjects, the absolute bioavailability was 60%, ranging from 40% to 94%. While food intake reduced the maximum serum concentrations by 10 to 15%, food intake is reported to have a negligible effect on the bioavailability of the drug. Dutasteride and its metabolites mainly undergo fecal excretion. About 1-15% of the dose is excreted as the unchanged parent compound, while 2-90% of the total dose is excreted in the form of dutasteride-related metabolites in the feces. Trace amounts of unchanged dutasteride, with less than 1%, can also be detected in the urine. Therefore, on average, the dose unaccounted for approximated 55%, with a range between 5% and 97%. Dutasteride displays a large volume of distribution ranging from 300 to 500 L. Following daily oral administration of 0.5 mg dutasteride healthy subjects for 12 months, the semen dutasteride concentrations averaged 3.4 ng/mL (range: 0.4 to 14 ng/mL) with 11.5% of serum dutasteride concentrations being partitioned into semen. In a study of healthy volunteers receiving single oral doses of dutasteride ranging from 0.01 to 40 mg, dutasteride displayed a low linear clearance of 0.58 L/h. The estimated inter-individual variability for the linear clearance was high. Metabolism / Metabolites Dutasteride undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism mediated by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. 4′-hydroxydutasteride, 6-hydroxydutasteride, 6,4′-dihydroxydutasteride, 1,2-dihydrodutasteride, and 15-hydroxydutasteride metabolites are formed. 2 minor metabolites - 6,4′-dihydroxydutasteride and 15-hydroxydutasteride - can also be detected. According to _in vitro_ studies, 4′-hydroxydutasteride and 1,2-dihydrodutasteride mediated inhibitory actions against both isoforms of 5α-reductase but with lower potency when compared to the parent drug. The activity of 6β-hydroxydutasteride is comparable to that of dutasteride. Biological Half-Life The terminal elimination half-life of dutasteride is approximately 5 weeks at steady state. This long half-life accounts for the serum concentrations remaining detectable for up to 4 to 6 months after discontinuation of treatment. Absorption: The oral bioavailability of Dutasteride (GG 745; GI 198745) in rats was approximately 60%; food intake did not affect absorption. Peak plasma concentration (Cmax) of 40 ± 5 ng/mL was reached 2 hours after oral administration of 1 mg/kg [3] - Distribution: The volume of distribution (Vd) in rats was 80 ± 10 L/kg; it distributed widely in tissues, with high concentrations in the prostate (prostate/plasma ratio = 15 ± 2 at 4 hours post-dosing) [3] - Metabolism: Dutasteride (GG 745; GI 198745) was minimally metabolized in the liver (≤10% of the dose) to inactive metabolites via CYP3A4; no active metabolites were detected [3] - Excretion: The elimination half-life (t1/2) in rats was 35 ± 5 days (long half-life due to high tissue binding). Approximately 70% of the dose was excreted in feces and 30% in urine within 7 days, mainly as unchanged drug [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Dutasteride has been associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations that, in controlled trials, was no higher than with placebo therapy. These elevations were transient and rarely required dose modification. There have been no published reports of clinically apparent liver injury due to dutasteride therapy. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding Dutasteride is about 99% bound to albumin and 96.6% bound to α-1 acid glycoprotein in the serum. Acute toxicity: The median lethal dose (LD50) of Dutasteride (GG 745; GI 198745) was >2000 mg/kg in mice (oral) and >1500 mg/kg in rats (oral) [3] - Chronic toxicity: In rats treated with Dutasteride (1 mg/kg/day) for 6 months, no significant changes in liver function (ALT/AST) or kidney function (creatinine/BUN) were observed. Prostate weight was reduced by 40% ± 3% (due to androgen deprivation) [3] - Plasma protein binding: Dutasteride (GG 745; GI 198745) had a high plasma protein binding rate of 99% ± 0.5% in human plasma and 98.5% ± 0.6% in rat plasma [3] - Clinical adverse effects: In men treated with Dutasteride (0.5 mg/day) for 12 months, common adverse effects included decreased libido (3% incidence) and breast tenderness (2% incidence) [4] - Endocrine toxicity in fish: Dutasteride (10 μg/L) caused female-biased sex ratio in juvenile zebrafish but no mortality or growth retardation [5] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Dutasteride is a synthetic 4-azasteroid compound that selectively inhibits both the type I and type II isoforms of steroid 5α-reductase, an intracellular enzyme that converts testosterone to 5α-dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Dutasteride works by reducing the levels of circulating DHT. It was also shown to reduce the size of the prostate gland, improve urinary flow, and symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia alone or in combination with tamsulosin. The effect of the reduction of DHT by dutasteride is dose-dependent, with the maximum effect observed within 1-2 weeks following initial administration. After 1 and 2 weeks of daily dosing with dutasteride 0.5 mg, median serum DHT concentrations were reduced by 85% and 90%, respectively. The serum concentrations of DHT were maintained to be decreased by more than 90% in 85% of patients following 1 years' administration of oral dutasteride 0.5 mg/day. As evident from the clinical studies, dutasteride may also cause decreases in serum PSA in the presence of prostate cancer. 1. Dutasteride (GG 745; GI 198745) is a dual 5α-reductase inhibitor that blocks the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT) — the primary androgen driving prostate growth and prostate cancer progression [1][3] 2. Unlike finasteride (a selective 5α-reductase type 2 inhibitor), Dutasteride inhibits both type 1 and type 2 isoforms, leading to a more significant reduction in serum DHT (up to 90% vs. 70% with finasteride) [3] 3. Therapeutic indications include benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) (to reduce prostate volume and improve urinary symptoms) and adjuvant treatment of androgen-dependent prostate cancer [4] 4. In clinical practice, serum PSA levels in men taking Dutasteride need to be doubled for prostate cancer screening (due to PSA reduction by ~50%) to avoid false-negative results [4] 5. Its long elimination half-life (3–5 weeks in humans) requires continuous dosing for 3–6 months to achieve maximum therapeutic effect [3] |
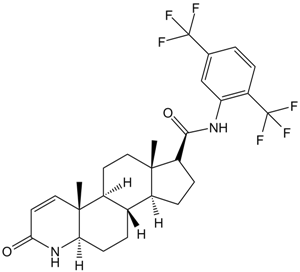
| 分子式 |
C27H30F6N2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
528.53
|
| 精确质量 |
528.221
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 61.36; H, 5.72; F, 21.57; N, 5.30; O, 6.05
|
| CAS号 |
164656-23-9
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Dutasteride-13C6;1217685-27-2
|
| PubChem CID |
6918296
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
620.3±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
242-250ºC
|
| 闪点 |
329.0±31.5 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.523
|
| LogP |
5.61
|
| tPSA |
58.2
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
37
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
964
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
7
|
| SMILES |
C[C@]12CC[C@H]3[C@H]([C@@H]1CC[C@@H]2C(=O)NC4=C(C=CC(=C4)C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F)CC[C@@H]5[C@@]3(C=CC(=O)N5)C
|
| InChi Key |
JWJOTENAMICLJG-VYZSUTEISA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C27H30F6N2O2/c1-24-11-9-17-15(4-8-21-25(17,2)12-10-22(36)35-21)16(24)6-7-19(24)23(37)34-20-13-14(26(28,29)30)3-5-18(20)27(31,32)33/h3,5,10,12-13,15-17,19,21H,4,6-9,11H2,1-2H3,(H,34,37)(H,35,36)/t15-,16-,17?,19+,21+,24-,25+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(4aR,6aS,7S,9aS,9bS,11aR)-N-(2,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-4a,6a-dimethyl-2-oxo-2,4a,4b,5,6,6a,7,8,9,9a,9b,10,11,11a-tetradecahydro-1H-indeno[5,4-f]quinoline-7-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
GI-198745, GG-745; GI198745, GG745; GI 198745, GG 745; LS-173584; LS 173584; LS173584; trade names: Avodart; Avidart; Avolve; Duagen; Dutas; Dutagen; Duprost.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.73 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8920 mL | 9.4602 mL | 18.9204 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3784 mL | 1.8920 mL | 3.7841 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1892 mL | 0.9460 mL | 1.8920 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。