| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
对羟基苯甲酸乙酯 (0-20 mg/mL) 对多种病原体具有抗菌和抗真菌特性 [1]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
对羟基苯甲酸乙酯(0-40 mg/kg,灌胃)会提高雌激素反应基因的水平和 SD 雌激素的雌激素重量 [1]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
By the oral route, parabens are rapidly absorbed, metabolized, and excreted. The metabolic reactions and conversions in mammals vary with the chain length of the ester, the animal species, route of administration, and quantity tested. The metabolism of parabens in humans appears to be most closely related to that of dogs. The rate of metabolite excretion appears to decrease with increasing molecular weight of the ester. /4-Hydroxybenzoates (Parabens)/ ... Deposition of parabens in dogs. Urine recoveries ranged from 50-95% except for butyl ester for which recoveries were 40%. /It/... was concluded that esters are well absorbed and that hydrolysis of ester linkage and metabolic conjugation constitute chief route of elimination. Similar metabolic scheme ... in man. /Parabens/ The permeation of methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, and butylparaben through untreated and lipid-depleted excised guinea pig dorsal skin, and the effects of 3 penetration enhancers, N-dodecyl-2-pyrrolidone (lauryl pyrrolidone), ethyl alcohol (ethanol), and a mixture of menthol (l-menthol) and ethyl alcohol, on the permeation of the parabens were studied; the relationship between the permeability and octyl alcohol (n-octanol)/water partition coefficients of the parabens, and the effect of the penetration enhancers on the fluidity of the lipid bilayer of liposomes containing stratum corneum lipids were also examined. Permeability coefficients of the parabens correlated with their octyl alcohol/water partition coefficients in untreated guinea pig skin. In lipid-depleted guinea pig skin, permeability coefficients of the parabens increased and did not correlate with their octyl alcohol/water partition coefficients. The effect of the penetration enhancers on the permeation of the parabens was variable. The penetration enhancers increased the fluidity of liposome lipid bilayers. After ethyl paraben is intravenously infused into the dog, unhydrolyzed ethyl paraben is found only in the brain. In liver, kidney, and muscle, it is immediately hydrolyzed to p-hydroxybenzoic acid. Six hours after oral administration of 1.0 g/kg to dogs, the peak plasma concentration of free and total ethyl paraben (427 and 648 ug/cu cm, respectively) is reached. After 48 hr, all ethyl paraben is completely eliminated. Metabolism / Metabolites Yields p-hydroxybenzoic acid in pig and in Aspergillus. /from table/ /Paraben/ ... esters are well absorbed and hydrolysis of ester linkage and metabolic conjugation constitute chief route of elimination /in dogs/. Similar metabolic scheme was observed in man. /Paraben esters/ Urine from cats who had received (14)C-labeled ethyl-p-hydroxybenzoate, orally contained 2 major metabolites, p-hydroxyhippuric acid and free p-hydroxybenzoic acid. In mice, rats, rabbits, pigs, or dogs, ethyl paraben is excreted in the urine as unchanged benzoate, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, p-hydroxyhippuric acid (p-hydroxybenzoylglycine), ester glucuronides, ether glucuronides, or ether sulfates. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for ETHYLPARABEN (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Ethyl-4-hydroxybenzoate has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-(4-ethoxycarbonylphenoxy)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Ethylparaben forms small colorless crystals, or white powder. Ethylparaben inhibits the growth of fungi and bacteria and is used as a preservative for pharmaceuticals, adhesives, and various cosmetic preparations. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Ethylparaben was a skin irritant in man. It gave no evidence of sensitizing potential in a human study. The paraben esters as a generic class are rare sensitizers when applied to the intact skin of man. Application to the damaged skin is a more common cause of sensitization. A methyl:ethyl:propylparaben mixture has been shown on oral administration to exacerbate pre-existing skin complaints. ANIMAL STUDIES: Ethylparaben was an eye irritant in rabbits. A low acute oral toxicity has been demonstrated for ethylparaben in laboratory animals. Limited long-term studies in rats have also indicated a low toxicity and have generated no evidence of carcinogenic activity. Ethylparaben in the diet produced cell proliferation in the forestomach of rats. No evidence of mutagenicity was reported in limited Ames Bacterial tests. Ethylparaben did increase chromosomal aberrations in a Chinese Hamster ovary cell assay, but similar effects were not seen in rats treated with ethylparaben. Fetal toxicity at maternally toxic dose levels occurred in female rats treated orally during pregnancy. Ethylparaben was nonteratogenic in rats. In one in vitro study, sperm were not viabile at concentrations as low as 8 mg/mL for Ethylparaben, but an in vivo study of 0.1% or 1.0% for Ethylparaben in the diet of mice reported no spermatotoxic effects. Interactions The biological fates of ethyl paraben after the simultaneous administration with salicylic acid were different from those of ethyl paraben alone as reported in the previous reports. The excretion of unconjugated p-hydroxybenzoic acid, which is a hydrolyzed product of ethyl paraben, increased and those of p-hydroxyhippuric acid, glycine conjugate of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, and p-hydroxybenzoyl glucuronide, its ester type glucuronide, decreased. The blood concentration patterns were considerably different from those of ethyl paraben alone, especially the elimination of every metabolite was delayed. Pharmacokinetic analyses on the data of blood concentration were carried out and the results also show the interaction of salicylic acid on the biological fate of ethyl paraben. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat (female) oral 4.30 g/kg LD50 Rat oral 11.0 g/kg LD50 Guinea pig oral 2.0 g/kg /From table/ LD50 Rabbit oral 5.0 g/kg /From table/ For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for ETHYLPARABEN (9 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
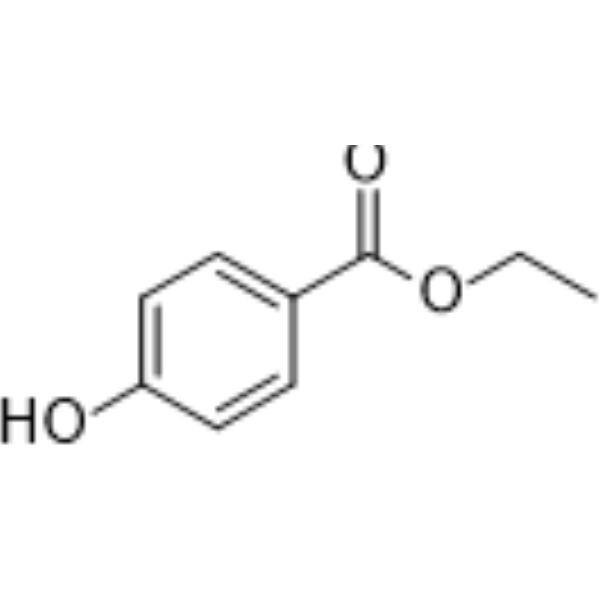
Ethylparaben is an ethyl ester resulting from the formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-hydroxybenzoic acid with ethanol, It has a role as an antimicrobial food preservative, an antifungal agent, a plant metabolite and a phytoestrogen. It is a paraben and an ethyl ester.
Ethylparaben is a Standardized Chemical Allergen. The physiologic effect of ethylparaben is by means of Increased Histamine Release, and Cell-mediated Immunity. Ethylparaben has been reported in Aeschynanthus bracteatus, Inula salsoloides, and other organisms with data available. Ethylparaben is found in alcoholic beverages. Ethylparaben is an antimicrobial agent, preservative. Ethylparaben is present in red wine, white wine and sake. Ethylparaben belongs to the family of Hydroxybenzoic Acid Derivatives. These are compounds containing an hydroxybenzoic acid (or a derivative), which is a benzene ring bearing a carboxylic acid. Ethyl-4-hydroxybenzoate is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. |
| 分子式 |
C9H10O3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
166.18
|
| 精确质量 |
166.062
|
| CAS号 |
120-47-8
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ethylparaben-d4;1219795-53-5
|
| PubChem CID |
8434
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
297.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
114-117 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
120.3±12.6 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.539
|
| LogP |
2.4
|
| tPSA |
46.53
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
12
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
148
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
NUVBSKCKDOMJSU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C9H10O3/c1-2-12-9(11)7-3-5-8(10)6-4-7/h3-6,10H,2H2,1H3
|
| 化学名 |
ethyl 4-hydroxybenzoate
|
| 别名 |
NSC23514; NSC 23514; Ethylparaben
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~601.79 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (15.04 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (15.04 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (15.04 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.0176 mL | 30.0879 mL | 60.1757 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.2035 mL | 6.0176 mL | 12.0351 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6018 mL | 3.0088 mL | 6.0176 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。