| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
非索罗定可增加排尿时产生的尿液量,同时减少急迫性尿失禁发作的频率、强度和持续时间[1]。口服摄入后,非特异性酯酶快速、彻底地水解血浆中的非索罗定,产生 Desfesoterodine(5-羟甲基托特罗定;SPM 7605;非索罗定的活性代谢物)[3][4]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
非索罗定(0.01-1 mg/kg;静脉注射)在研究的最低剂量 0.01 mg/kg 下可降低排尿压力并增加膀胱容量和 ICI(间期收缩间隔)[3]。
|
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Female SD (SD (Sprague-Dawley)) rat bladder (225-275 g) [3]
Doses: 0.01, 0.1 and 1 mg/kg Route of Administration: intravenous (iv) (iv)injection Experimental Results: At the lowest dose tested, micturition pressure diminished, bladder Capacity and ICI increased by 0.01 mg/kg. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Tmax (5-HMT): 5 hours post-adminitration of fesoterodine. AUC (0,∞)= 49.5 ng·h/ ml Bioavailability, 5-HMT = 52% Renal: 70% of fesoterodine was recovered in urine as 5-HMT; 35% carboxy metabolite; 18% carboxy-N-desisopropylmetabolite, and 1% N-desisopropyl metabolite Fecal: 7% Hepatic: fesoterodine elimination via CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 IV, 5-HMT: 169 L 5-HMT, healthy subjects: 14.4 L/h 5-HMT is also secreted into the nephron. Metabolism / Metabolites Metabolized by ubiquitous, nonspecific esterases to transform fesoterodine into 5-HMT Extensive metabolism via CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 into inactive metabolites Biological Half-Life 7-8 hours for the active metabolite 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Like most anticholinergic agents, fesoterodine has not been linked to episodes of liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent liver injury. In prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled trials of fesoterodine in overactive bladder syndrome, serum aminotransferase elevations were rare, arising in less than 1% of recipients, rates similar to those in placebo recipients. Since its approval, there have been no published case reports of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to fesoterodine. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of fesoterodine during breastfeeding. Long-term use of fesoterodine might reduce milk production or milk letdown. During long-term use, observe for signs of decreased lactation (e.g., insatiety, poor weight gain). ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information in nursing mothers was not found as of the revision date. Anticholinergics can inhibit lactation in animals apparently by inhibiting growth hormone and oxytocin secretion. Anticholinergic drugs can also reduce serum prolactin in nonnursing women. The prolactin level in a mother with established lactation may not affect her ability to breastfeed. Protein Binding 5-HMT: 50% to albumin and alpha1-acid glycoprotein |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
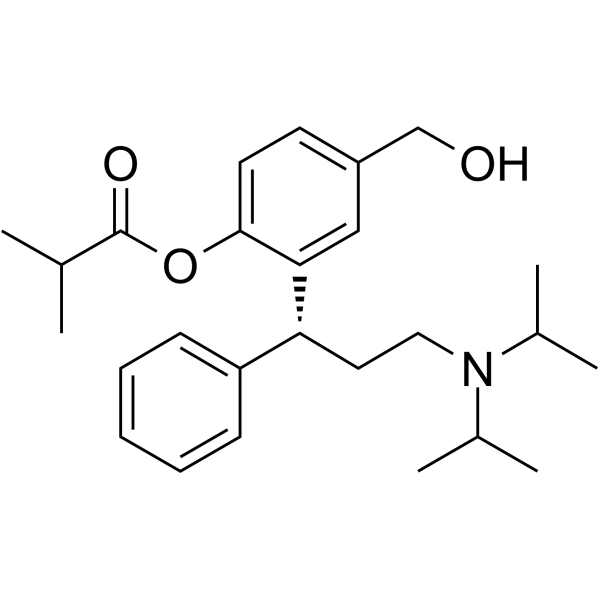
Fesoterodine is a diarylmethane.
Fesoterodine is an antimuscarinic prodrug for the treatment of overactive bladder syndrome. Fesoterodine is an anticholinergic and antispasmotic agent used to treat urinary incontinence and overactive bladder syndrome. Fesoterodine has not been implicated in causing liver enzyme elevations or clinically apparent acute liver injury. Fesoterodine is a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist with muscle relaxant and urinary antispasmodic properties. Fesoterodine is rapidly hydrolyzed in vivo into its active metabolite 5-hydroxy methyl tolterodine, which binds and inhibits muscarinic receptors on the bladder detrusor muscle, thereby preventing bladder contractions or spasms caused by acetylcholine. This results in the relaxation of bladder smooth muscle and greater bladder capacity, in addition to a reduction in involuntary muscle contractions and involuntary loss of urine. The active metabolite does not interact with alpha-adrenergic, serotonergic, histaminergic and excitatory amino acid receptors and is eliminated via renal excretion. See also: Fesoterodine Fumarate (has salt form). Drug Indication Fesoterodine is indicated for the treatment of overactive bladder in adult patients with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and frequency. It is also indicated in the treatment of neurogenic detrusor overactivity in pediatric patients ≥6 years old weighing >25 kg. FDA Label Treatment of the symptoms (increased urinary frequency and / or urgency and / or urgency incontinence) that may occur in patients with overactive-bladder syndrome. Mechanism of Action Fesoterodine, once converted to its active metabolite, 5-hydroxymethyltolterodine, acts as a competitive antagonists at muscarinic receptors. This results in the inhibition of bladder contraction, decrease in detrusor pressure, and an incomplete emptying of the bladder. Pharmacodynamics In-vivo the fesoteridine prodrug is broken down into its active metabolite, 5-hydroxymethyl tolterodine (5-HMT), by plasma esterases. The 5-hydroxymethyl metabolite, which exhibits an antimuscarinic activity. Both urinary bladder contraction and salivation are mediated via cholinergic muscarinic receptors. Therefore, acting as a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist, fesoterodine ultimately acts to decrease the detrusor pressure by its muscarinic antagonism, thereby decreasing bladder contraction and consequently, the urge to urinate. |
| 分子式 |
C26H37NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
411.5769
|
| 精确质量 |
412.285
|
| CAS号 |
286930-02-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Fesoterodine L-mandelate;1206695-46-6;Fesoterodine fumarate;286930-03-8
|
| PubChem CID |
6918558
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow viscous liquid
|
| 密度 |
1.043
|
| 沸点 |
518.9ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
267.6ºC
|
| LogP |
5.488
|
| tPSA |
49.77
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
4
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
491
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
| SMILES |
O(C(C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)C1C([H])=C([H])C(C([H])([H])O[H])=C([H])C=1[C@@]([H])(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
DCCSDBARQIPTGU-HSZRJFAPSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H37NO3/c1-18(2)26(29)30-25-13-12-21(17-28)16-24(25)23(22-10-8-7-9-11-22)14-15-27(19(3)4)20(5)6/h7-13,16,18-20,23,28H,14-15,17H2,1-6H3/t23-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
[2-[(1R)-3-[di(propan-2-yl)amino]-1-phenylpropyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl] 2-methylpropanoate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 (2). 该产品在溶液状态不稳定,请现配现用。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~242.97 mM)
Ethanol : ~50 mg/mL (~121.48 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (6.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 27.5 mg/mL的澄清EtOH储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中并混合均匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (6.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 27.5 mg/mL 澄清乙醇储备液加入 900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (6.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% EtOH + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL 生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4297 mL | 12.1483 mL | 24.2966 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4859 mL | 2.4297 mL | 4.8593 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2430 mL | 1.2148 mL | 2.4297 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Study of Fesoterodine and Oxybutynin on Cognitive Function in Mild Cognitive Impairment
CTID: NCT02240459
Phase: Phase 2 Status: Completed
Date: 2020-02-19