| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Met (IC50 = 0.4 nM); KDR (IC50 = 0.86 nM); Tie-2 (IC50 = 1.1 nM); VEGFR3/FLT4 (IC50 = 2.8 nM); RON (IC50 = 3 nM)
1. Foretinib (GSK-1363089; XL-880; EXEL2880; GSK-089) is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor with the following IC50 values: MET: 0.4 nM, VEGFR2 (KDR): 0.9 nM, VEGFR3 (Flt-4): 1.3 nM, AXL: 2.1 nM, RON: 2.5 nM [1] 2. It inhibits Tie2 with an IC50 of 3.2 nM and shows no significant inhibition (IC50 > 1 μM) against EGFR, HER2, and Src kinases [2] 3. For mutant MET (MET Y1230H), Foretinib exhibits an IC50 of 0.6 nM, comparable to its activity against wild-type MET [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:XL880 抑制 HGF 受体家族酪氨酸激酶,Met 的 IC50 值为 0.4 nM,Ron 的 IC50 值为 3 nM。 XL880 还抑制 KDR、Flt-1 和 Flt-4,IC50 值分别为 0.9 nM、6.8 nM 和 2.8 nM。 XL880 抑制 B16F10、A549 和 HT29 细胞的集落生长,IC50 分别为 40 nM、29 nM 和 165 nM。最近的一项研究表明,XL880 对胃癌细胞系 MKN-45 和 KATO-III 的细胞生长影响不同。 XL880 抑制 MKN-45 细胞中 MET 和下游信号分子的磷酸化,同时靶向 KATO-III 细胞中的 GFGR2。激酶测定:使用三种测定形式之一研究激酶抑制:[33P]磷酰基转移、荧光素酶偶联化学发光或 AlphaScreen 酪氨酸激酶技术。使用 XLFit 通过非线性回归分析计算 IC50。33P -磷酸基转移激酶测定反应在 384 孔白色、透明底部、高结合微量滴定板(Greiner,Monroe,NC)中进行。板在 50 μL 体积的包被缓冲液中包被 2 μg/孔的蛋白质或肽底物,其中包被缓冲液含有 40 μg/mL 底物(聚(Glu,Tyr)4:1、22.5 mM Na2CO3、27.5 mM NaHCO3、50 mM NaCl 和3 mM NaN 3. 在室温 (RT) 下过夜孵育后,用 50 μL 测定缓冲液清洗包被板一次。测试化合物和酶与 33P-γ-ATP (3.3 μCi/nmol) 混合,总体积为 20 μL.反应混合物在室温下孵育2小时并通过抽吸终止。随后用0.05%Tween-PBS缓冲液(PBST)洗涤微量滴定板6次。添加闪烁液(50μL/孔)并掺入33P荧光素酶偶联化学发光测定反应在 384 孔白色中等结合微量滴定板 (Greiner) 中进行。第一步将酶和化合物混合并孵育 60 分钟;反应在通过在最终体积 20 μL 中添加 ATP 和肽底物(聚(Glu,Tyr)4:1)开始,并在室温下孵育 2-4 小时。激酶反应后,添加 20 μL 等份的激酶 Glo(Promega,麦迪逊,威斯康星州),并使用 Victor 酶标仪测量发光信号。总 ATP 消耗限制为 50%。 AlphaScreenTM 酪氨酸激酶测定 使用涂有链霉亲和素的供体珠和涂有 PY100 抗磷酸酪氨酸抗体的受体珠。使用生物素化聚(Glu,Tyr) 4:1 作为底物。底物磷酸化通过在供体-受体珠复合物形成后通过发光添加供体/受体珠来测量。将激酶和测试化合物混合并预孵育 60 分钟,然后在 384 孔白色中等结合微量滴定板 (Greiner) 中添加 ATP 和生物素化聚 (Glu, Tyr),总体积为 20 μL。将反应混合物在室温下孵育1小时。通过添加 10 μL 15-30 μg/mL AlphaScreen 珠悬浮液(含有 75 mM Hepes、pH 7.4、300 mM NaCl、120 mM EDTA、0.3% BSA 和 0.03% Tween-20)来猝灭反应。在室温下孵育 2-16 小时后,使用 AlphaQuest 读数器读取板的读数。细胞测定:将 B16F10、A549 和 HT29 细胞(每孔 1.2×103 个)与软琼脂混合,并接种到基底琼脂层上含有 10% FBS 和 EXEL-2880 的 96 孔板中。对于常氧条件,将板在 21% 氧气、5% CO2 和 74% 氮气中孵育 (37°C) 12 至 14 天,而在低氧条件下孵育 (37°C) 在低氧室中进行 1 % 氧气、5% 二氧化碳和 94% 氮气。添加 50% Alamar Blue 并进行荧光检测后,评估每种条件下的菌落数量。
1. MET扩增的MKN45胃癌细胞中:福瑞替尼(0.1-10 μM)抑制细胞增殖,IC50为0.2 μM。1 μM处理72小时后,细胞活力较对照组降低约80% [2] 2. VEGFR2依赖的人脐静脉内皮细胞(HUVECs)中:福瑞替尼(0.01-0.5 μM)呈剂量依赖性抑制VEGF诱导的管形成。0.1 μM浓度下,管长度较VEGF刺激组降低约75% [1] 3. A549肺癌细胞(MET过表达)中:Western blot显示,福瑞替尼(0.5 μM)使MET(Tyr1234/1235)磷酸化水平降低约90%,下游p-AKT(Ser473)和p-ERK1/2分别降低约85%和80% [1] 4. SNU-5胃癌细胞(MET突变)中:福瑞替尼(10-100 nM)诱导凋亡。50 nM处理48小时后,凋亡率(Annexin V阳性细胞)从对照组的约4%升至约42% [2] 5. I期临床研究来源的患者肿瘤细胞(MET阳性)中:福瑞替尼(1 μM)较未处理组抑制克隆形成约70% [3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
单次口服 100 mg/kg 灌胃剂量的 XL880 可显着抑制 B16F10 肿瘤 Met 的磷酸化和配体(例如 HGFor VEGF)诱导的肝脏中 Met 受体磷酸化和肺中 Flk-1/KDR 受体磷酸化,并且这种磷酸化均持续存在24小时。 XL880(30-100 mg/kg,每日一次,口服强饲)治疗可减少肿瘤负荷。 30 mg/kg XL880 和 100 mg/kg XL880 治疗后,肺表面肿瘤负荷分别减少 50% 和 58%。 XL880 对携带 B16F10 实体瘤的小鼠进行治疗,在 30 毫克/千克和 100 毫克/千克剂量下,也可分别产生 64% 和 87% 的剂量依赖性肿瘤生长抑制作用。对于这两项研究,XL880 的给药耐受性良好,没有明显的体重减轻。 XL880 旨在通过 Met 靶向 HGF 的异常信号传导,同时靶向参与肿瘤血管生成的几种受体酪氨酸激酶。 XL880在2至4小时内引起人类异种移植物的肿瘤出血和坏死,并在96小时(每日五次给药后)观察到最大的肿瘤坏死,从而导致完全消退。
1. 裸鼠MKN45胃癌异种移植模型:口服福瑞替尼(30 mg/kg,每日1次,持续28天)的肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)为75%,处理组肿瘤重量约为溶媒对照组的25% [2] 2. SCID小鼠SNU-5胃癌腹腔移植模型:福瑞替尼(40 mg/kg,灌胃,每日1次,持续21天)延长小鼠生存期,中位生存期从对照组的22天延长至39天,7只小鼠中有2只存活超过60天 [2] 3. 大鼠HepG2原位肝癌模型:福瑞替尼(50 mg/kg,口服,每日1次,持续35天)抑制原发肿瘤生长(TGI约65%),并减少肺转移(转移结节数降低约80%)[1] 4. I期临床研究(n=25例MET阳性实体瘤患者):福瑞替尼(120 mg/天,口服,持续给药)在6例患者(24%)中达到部分缓解(PR),12例患者(48%)达到疾病稳定(SD),中位无进展生存期(PFS)为5.2个月 [3] |
| 酶活实验 |
三种检测形式之一——[33P]磷酰基转移、荧光素酶偶联化学发光或 AlphaScreen 酪氨酸激酶技术——用于研究激酶抑制。 XLFit 用于非线性回归分析来计算 IC50。 33P - 激酶磷酰基测定的转移 384 孔白色、透明底部、高结合微量滴定板(Greiner,Monroe,NC)用于反应。在含有 40 μg/mL 底物(聚(Glu,Tyr))的 50 μL 包被缓冲液中,将 2 μg/孔的蛋白质或肽底物施加到板中。 3 mM NaN3、50 mM NaCl、27.5 mM NaHCO3 和 4:1 均可找到。在室温下孵育整晚后,再次用 50 μL 测定缓冲液 (RT) 清洗包被板。在总体积为 20 μL 的情况下,将测试化合物和酶与33P-γ-ATP (3.3 μCi/nmol) 混合。 RT 孵育两小时后,通过抽吸结束反应混合物。之后,使用 0.05% Tween-PBS 缓冲液 (PBST) 将微量滴定板清洗六次。闪烁液的添加和掺入(50 μL/孔) MicroBeta 闪烁计数器用于液体闪烁光谱测定33P。使用荧光素酶偶联微量滴定板(Greiner)进行化学发光测定,测量 384 个孔,用于进行反应。第一步是将酶和化合物混合并静置 60 分钟。第二步涉及添加 ATP 和肽底物(聚(Glu,Tyr)4:1),最终体积为 20 μL,然后让它们在室温下静置两到四个小时。激酶反应后,使用 Victor 读板仪测量发光信号,并添加 20 μL 等份的激酶 Glo(Promega,麦迪逊,威斯康星州)。 ATP 总体消耗量有 50% 的上限。 ALPHAScreen 酪氨酸激酶测定使用的是涂有 PY100 抗磷酸酪氨酸抗体的受体珠和涂有链霉亲和素的供体珠。底物是生物素化的聚(Glu,Tyr) 4:1。添加供体/受体珠以及随后形成供体-受体珠复合物用于测量底物磷酸化。在 384 孔白色中等结合微量滴定板 (Greiner) 中,将激酶和测试化合物混合并预孵育 60 分钟。接下来,添加 ATP 和生物素化聚(Glu、Tyr),总体积为 20 μL。将反应混合物在室温下静置一小时。将含有 75 mM Hepes、pH 7.4、300 mM NaCl、120 mM EDTA、0.3% BSA 和 0.03% Tween-20 的 AlphaScreen 珠悬浮液添加到 10 L 中以淬灭反应。在室温下孵育 2-16 小时后,使用 AlphaQuest 读数器读取板。
1. 重组MET激酶活性测定:反应缓冲液含50 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)、10 mM MgCl2、1 mM DTT、20 μM ATP及1 μg/well GST-MET激酶结构域。不同浓度福瑞替尼(0.05 nM-5 nM)与激酶在30°C预孵育15分钟,加入底物(GST-Gab1肽)启动反应,30°C孵育45分钟。用磷酸特异性抗体和化学发光法检测磷酸化底物,通过非线性回归拟合抑制曲线计算IC50 [1] 2. VEGFR2(KDR)激酶测定:重组VEGFR2激酶(5 ng/well)与福瑞替尼(0.1 nM-10 nM)在含25 mM HEPES(pH 7.4)、5 mM MnCl2、1 mM DTT、10 μM ATP及0.5 μg/well Poly(Glu,Tyr)4:1底物的缓冲液中混合。37°C反应60分钟后,加入3%磷酸终止反应,将混合物转移至P81板,用0.5%磷酸洗涤,通过闪烁计数器检测[γ-32P]ATP的放射性信号以确定IC50 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
在含有 10% FBS 和 EXEL-2880 的 96 孔板中,将 B16F10、A549 和 HT29 细胞(每孔 1.2 x 103)与软琼脂混合并接种在基础琼脂顶部层。将板在 37°C、21% 氧气、5% CO2 和 74% 氮气、含氧量正常的条件下孵育 12 至 14 天。相反,板在含 1% 氧气、5% CO2 和 94% 氮气的缺氧室中于 37°C 缺氧条件下孵育。添加 50% Alamar Blue 并检测荧光后,评估每种条件下的菌落数量。
Met受体酪氨酸激酶及其配体肝细胞生长因子(HGF)在多种人类恶性肿瘤中过表达和/或活化。血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)受体在血管内皮细胞表面表达,与Met协同诱导肿瘤侵袭和血管化。EXEL-2880(XL880,GSK1363089)是一种小分子激酶抑制剂,靶向HGF和VEGF受体酪氨酸激酶家族的成员,对KIT、Flt-3、血小板衍生生长因子受体β和Tie-2具有额外的抑制活性。EXEL-2880与Met和VEGF受体2(KDR)的结合速度非常慢,这与X射线晶体学数据一致,表明抑制剂在Met激酶活性位点裂缝中深度结合。EXEL-2880抑制细胞HGF诱导的Met磷酸化和VEGF诱导的细胞外信号调节激酶磷酸化,并防止HGF诱导肿瘤细胞的反应和HGF/VEGF诱导内皮细胞的反应。此外,EXEL-2880可防止肿瘤细胞在常氧和缺氧条件下的锚定非依赖性增殖。在体内,这些效应在肺转移的实验模型中对肿瘤负荷产生了显著的剂量依赖性抑制。总的来说,这些数据表明,EXEL-2880可能通过直接影响肿瘤细胞增殖和抑制HGF和VEGF受体介导的侵袭和血管生成来预防肿瘤生长。[1] 为了探索foretinib(GSK1363089)(一种已知靶向MET、RON、AXL和血管内皮生长因子受体(VEGFR)的口服多激酶抑制剂)在癌症中的作用机制,我们评估了该药物对以下癌症细胞系(KATO-III、MKN-1、MKN-7、MKN-45和MKN-74)中细胞生长和细胞信号传导的影响。其中,只有分别携带MET和成纤维细胞生长因子受体2(FGFR2)扩增的MKN-45和KATO-III对普罗替尼高度敏感。在MKN-45中,1μM的foretinib或PHA665752(另一种MET激酶抑制剂)如预期的那样抑制了MET和下游信号分子的磷酸化。然而,在KATO-III中,PHA665752独立于下游分子抑制MET的磷酸化。此外,1μM的foretinib或PD173074,一种选择性FGFR激酶抑制剂,抑制FGFR2和下游分子的磷酸化,表明foretinib靶向KATO-III中的FGFR2。我们在另一种FGFR2扩增的癌症细胞系OCUM-2M中证实了foretinib对FGFR2的这种新活性。使用磷酸受体酪氨酸激酶阵列,我们发现foretinib通过抑制MKN-45中的MET来抑制表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)、HER3和FGFR3的磷酸化,并通过抑制KATO-III中的FGFR2来抑制EGFR、HER2和MET的磷酸化。用siRNA敲除MKN-45的HER3和FGF R3导致细胞信号传导和细胞生长的部分抑制。总之,foretinib似乎对不仅含有MET而且含有FGFR2扩增的癌症细胞有效,并通过阻断以MET或FGFR2为核心的RTK间信号网络发挥其抑制作用[2]。 1. MKN45细胞增殖测定(MTT法):MKN45细胞以2×10³个/孔接种于96孔板,培养过夜。加入福瑞替尼(0.01 nM-10 μM),37°C孵育72小时。每孔加入MTT试剂(5 mg/mL,10 μL),继续孵育4小时。用DMSO(100 μL/孔)溶解甲瓒结晶,在570 nm处测吸光度。细胞活力以对照组的百分比表示,从剂量-反应曲线推导IC50 [2] 2. HUVEC管形成实验:Matrigel冰上融化后铺于24孔板(500 μL/孔),37°C聚合30分钟。HUVECs(2×10⁴个/孔)悬浮于含福瑞替尼(0.01-0.5 μM)和VEGF(50 ng/mL)的培养基中,接种于Matrigel上。6小时后拍摄管状结构,用图像分析软件定量每孔管总长度,计算相对VEGF对照组的抑制率 [1] 3. SNU-5细胞凋亡测定(Annexin V-FITC/PI染色):SNU-5细胞(1×10⁵个/mL)用福瑞替尼(10-100 nM)处理48小时。收集细胞,PBS洗涤,按试剂盒说明用Annexin V-FITC和PI染色。流式细胞仪分析凋亡细胞,计算凋亡率 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice without tumors or mice carrying B16F10 tumors are used in in vivo target modulation experiments. Oral gavage with 10 mL/kg of foretinib or vehicle (0.9% normal saline) is used. HGF (10 μg/mouse) is given intraperitoneally 10 minutes prior to harvesting in order to assess Met phosphorylation in the liver. Thirty minutes prior to harvest, or half an hour later, mice receive an intravenous injection of VEGF (10 μg/mouse) to assess Flk-1/KDR phosphorylation in the lung. Immunoblot analysis is used to determine receptor phosphorylation.
Forty patients were treated in eight dose cohorts. The maximum tolerated dose was defined as 3.6 mg/kg, with a maximum administered dose of 4.5 mg/kg. Dose-limiting toxicities included grade 3 elevations in aspartate aminotransferase and lipase. Additional non-dose-limiting adverse events included hypertension, fatigue, diarrhea, vomiting, proteinuria, and hematuria. Responses were observed in two patients with papillary renal cell cancer and one patient with medullary thyroid cancer. Stable disease was identified in 22 patients. Foretinib pharmacokinetics increased linearly with dose. Pharmacodynamic evaluation indicated inhibition of MET phosphorylation and decreased proliferation in select tumor biopsies at submaximal doses. Conclusions: The recommended dose of foretinib was determined to be 240 mg, given on the first 5 days of a 14-day cycle. This dose and schedule were identified as having acceptable safety and pharmacokinetics, and will be the dose used in subsequent phase II trials.[3] 1. Nude mouse MKN45 xenograft model: Female athymic nude mice (6-8 weeks old) are subcutaneously injected with 5×10⁶ MKN45 cells (suspended in 100 μL PBS/Matrigel 1:1) into the right flank. When tumors reach ~100 mm³, mice are randomized into 2 groups (n=6/group): vehicle control (0.5% methylcellulose + 0.1% Tween 80) and Foretinib (30 mg/kg). The drug is administered by oral gavage once daily for 28 days. Tumor volume (V = length×width²/2) is measured every 3 days, and body weight is monitored to assess toxicity [2] 2. Rat orthotopic HepG2肝癌模型: Male Wistar rats (200-220 g) are anesthetized, and 1×10⁶ HepG2 cells are injected into the liver parenchyma. Two weeks after tumor implantation, rats are randomized into 2 groups (n=5/group): vehicle (0.2% Tween 80 in saline) and Foretinib (50 mg/kg, oral gavage once daily for 35 days). Rats are euthanized at the end of treatment; primary tumors are excised and weighed, and lung tissues are fixed to count metastatic nodules [1] 3. Phase I clinical study protocol: Adult patients (≥18 years old) with MET-positive advanced solid tumors (refractory to standard treatment) are enrolled. Foretinib is administered orally at doses of 30 mg/day, 60 mg/day, 90 mg/day, 120 mg/day, and 150 mg/day (3+3 dose-escalation design). Treatment is continued until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Tumor response is evaluated every 8 weeks using RECIST 1.0 criteria, and adverse events are graded per CTCAE v3.0 [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. In mice: After oral administration of Foretinib (30 mg/kg), the oral bioavailability (F) is 48%, peak plasma concentration (Cmax) is 1.6 μg/mL, time to Cmax (Tmax) is 2 hours, and terminal half-life (t1/2) is 7.2 hours [1]
2. In dogs: Oral administration of Foretinib (10 mg/kg) results in F=35%, Cmax=0.9 μg/mL, Tmax=2.5 hours, and t1/2=9.8 hours. Plasma protein binding rate is >95% (measured by ultrafiltration) [1] 3. In phase I clinical study (120 mg/day oral dose): Human Cmax is 2.1 μg/mL, Tmax is 3 hours, t1/2 is 10.5 hours, and oral bioavailability is estimated to be ~40% [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute toxicity in mice: Single oral administration of Foretinib (up to 200 mg/kg) does not cause mortality within 7 days, but mice in the 150-200 mg/kg group show transient weight loss (5-8% at 48 hours) and reduced food intake, which recover within 10 days [1]
2. Subchronic toxicity in rats (28-day oral administration): - 25 mg/kg group: No significant changes in body weight, organ weight, or serum biochemical parameters (ALT, AST, creatinine) [1] - 50 mg/kg group: Mild weight loss (4-6%), slight increase in liver weight (10-12%), and a 15% decrease in platelet count; no histopathological changes in liver/kidneys [1] - 100 mg/kg group: Significant weight loss (9-11%), increased serum ALT (2.2-fold) and AST (2.0-fold), and severe thrombocytopenia (45% decrease); mild hepatic necrosis is observed in 2 out of 5 rats [1] 3. Phase I clinical study adverse events (120 mg/day): The most common grade 1-2 adverse events are fatigue (68%), diarrhea (52%), and hypertension (44%); grade 3 adverse events include elevated ALT (8%) and thrombocytopenia (4%); no grade 4-5 adverse events are reported [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
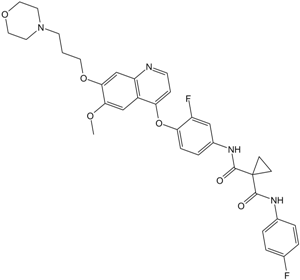
N1'-[3-fluoro-4-[[6-methoxy-7-[3-(4-morpholinyl)propoxy]-4-quinolinyl]oxy]phenyl]-N1-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide is an aromatic ether.
Foretinib has been used in trials studying the treatment of Cancer, Breast Cancer, Carcinoma, Renal Cell, Recurrent Breast Cancer, and Neoplasms, Head and Neck, among others. Foretinib is an orally available small molecule compound designed to target multiple RTKs implicated in the development, progression and spread of cancer. It inhibits the activation of MET, RON, ERK and AKT, decreased proliferation and increased apoptosis. Foretinib is an orally bioavailable small molecule with potential antineoplastic activity. Foretinib binds to and selectively inhibits hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) receptor c-MET and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2), which may result in the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, tumor cell proliferation and metastasis. The proto-oncogene c-MET has been found to be over-expressed in a variety of cancers. VEGFR2 is found on endothelial and hematopoietic cells and mediates the development of the vasculature and hematopoietic cells through VEGF signaling. Mechanism of Action Activation of MET by mutation is the causative factor in an inherited kidney cancer syndrome, hereditary papilliary renal cell carcinaoma. Mutational activation of MET has also been found in sporadic kidney cancer, lung carcinomas and head and neck carcinomas. MET is a key driver of tumor cell growth, motility, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Foretinib has attractive pharmaceutical properties with high solubility and oral bioavailability and demonstrates nanomolar potency against its targets, VEGFR, MET, which translates to potent activity in cellular assays. In preclinical studies, Foretinib, developed as a balanced inhibitor of these receptor tyrosine kinases, potently inhibited both MET and VEGFR, including mutant activated forms of MET found in hereditary papillary renal carcinomas. The compound also demonstrated dose-dependent growth inhibition in tumor models of breast, colorectal, non-small cell lung cancer and glioblastoma and has been shown to cause substantial tumor regression in all models tested. 1. Foretinib exerts dual antitumor effects: inhibiting MET signaling to block tumor cell proliferation and survival, and suppressing VEGFR2 to inhibit angiogenesis [1][2] 2. It is effective in tumor models resistant to MET-targeted monotherapies due to its ability to co-target VEGFR2 and overcome adaptive resistance [2] 3. In phase I clinical study, Foretinib shows promising activity in MET-positive solid tumors (e.g., gastric cancer, non-small cell lung cancer), supporting further development in phase II trials [3] |
| 分子式 |
C34H34F2N4O6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
632.65
|
| 精确质量 |
632.244
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 64.55; H, 5.42; F, 6.01; N, 8.86; O, 15.17
|
| CAS号 |
849217-64-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1226999-07-0 (phosphate);849217-64-7;
|
| PubChem CID |
42642645
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
828.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
454.8±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.649
|
| LogP |
5.12
|
| tPSA |
116.45
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
| 重原子数目 |
46
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1010
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1(CC1)C(NC1C=C(F)C(OC2C3C(=CC(=C(C=3)OC)OCCCN3CCOCC3)N=CC=2)=CC=1)=O)NC1C=CC(F)=CC=1
|
| InChi Key |
CXQHYVUVSFXTMY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C34H34F2N4O6/c1-43-30-20-25-27(21-31(30)45-16-2-13-40-14-17-44-18-15-40)37-12-9-28(25)46-29-8-7-24(19-26(29)36)39-33(42)34(10-11-34)32(41)38-23-5-3-22(35)4-6-23/h3-9,12,19-21H,2,10-11,13-18H2,1H3,(H,38,41)(H,39,42)
|
| 化学名 |
1-N'-[3-fluoro-4-[6-methoxy-7-(3-morpholin-4-ylpropoxy)quinolin-4-yl]oxyphenyl]-1-N-(4-fluorophenyl)cyclopropane-1,1-dicarboxamide
|
| 别名 |
EXEL 2880, XL-880; GSK1363089; GSK 1363089; GSK1363089, EXEL-2880,XL-880; XL880; XL 880; GSK-1363089; GSK089; EXEL2880
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.95 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.95 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.95 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.5807 mL | 7.9033 mL | 15.8065 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3161 mL | 1.5807 mL | 3.1613 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1581 mL | 0.7903 mL | 1.5807 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00920192 | Completed | Drug: Foretinib | Carcinoma, Hepatocellular | GlaxoSmithKline | August 12, 2009 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01147484 | Completed | Drug: Foretinib | Recurrent Breast Cancer | NCIC Clinical Trials Group | September 2, 2010 | Phase 2 |
| NCT01138384 | Completed | Drug: Foretinib Drug: Lapatinib |
Breast Cancer | NCIC Clinical Trials Group | October 27, 2010 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT00742131 | Completed | Drug: GSK1363089 | Solid Tumours | GlaxoSmithKline | March 17, 2005 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00742261 | Completed | Drug: GSK1363089 | Solid Tumours | GlaxoSmithKline | August 11, 2008 | Phase 1 |
EXEL-2880 (XL880, GSK1363089), inhibits migration, invasion, and anchorage-dependent growth of B16F10 cells. Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 15;69(20):8009-16. |
EXEL-2880 inhibits HMVEC-L tubule formation and migration. Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 15;69(20):8009-16. |
EXEL-2880 inhibits phosphorylation of Met and Flk-1/KDR and reduces tumor burden in an experimental model of lung metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009 Oct 15;69(20):8009-16. |