Gimestat,chlorodihydroxypyridine; CDHP;Gimeracil
| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD): Gimeracil is a selective inhibitor of DPD, the key enzyme for pyrimidine catabolism. In purified human DPD enzyme assays, the IC50 of Gimeracil for DPD activity was 0.12 μM (measured by inhibiting the conversion of [14C]-dihydrouracil to [14C]-β-ureidopropionate) [2]
- Homologous recombination (HR) pathway: Gimeracil inhibits the early step of HR, specifically suppressing Rad51-mediated DNA strand exchange. In HR reporter gene assays (DR-GFP U2OS cells), the EC50 for inhibiting HR efficiency was 3.8 μM; it had no effect on non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) at concentrations up to 10 μM [1][2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
吉美嘧啶降低了新阳性克隆的频率。此外,与 G0/G1 期细胞相比,它还提高了 S 期细胞的敏感性 [1]。 Gimeracil 抑制 HR 介导的 DNA 修复途径,这可能会提高放射治疗的有效性 [1]。虽然用 gigeracil 预处理增加了 Nbs1、Mre11、Rad50 和 FancD2 病灶的数量,但它显着减少了辐射诱导的 Rad51 和 RPA 病灶的发展 [2]。
癌细胞(A549、HCT116、MCF-7)的辐射增敏作用: - 克隆形成存活:吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(1-10 μM)联合X射线照射(2-8 Gy)呈剂量依赖性降低癌细胞的克隆形成存活率。对于A549细胞,4 Gy照射下的存活分数从单独照射组的0.45降至4 μM 吉美拉西(Gimeracil)+4 Gy组的0.18,增敏比(SER)为1.6 [1] - HR效率抑制:在DR-GFP U2OS细胞中,吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(2-8 μM)使HR介导的GFP表达降低40-75%。5 μM时,HR效率为对照组的0.3倍,而NHEJ活性(通过EJ5-GFP报告基因测得)保持不变(>对照组的90%) [1][2] - Rad51焦点形成抑制:免疫荧光染色显示,吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(3-6 μM)使HCT116细胞中电离辐射(IR)诱导的Rad51焦点(HR标志物)减少55-80%。5 μM时,每个细胞的Rad51焦点数从单独照射组的28个降至8个 [2] - DPD活性抑制与嘧啶代谢影响: - DPD酶活抑制:吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(0.05-2 μM)呈剂量依赖性抑制A549细胞裂解液中的DPD活性。0.2 μM时,DPD活性降低65%,导致细胞内尿嘧啶浓度升高2.5倍(HPLC测得) [2] - 对正常细胞无影响:吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(浓度高达10 μM)对正常人肺成纤维细胞(MRC-5)或正常结肠上皮细胞(NCM460)无显著细胞毒性,克隆形成存活率>85%(vs对照组) [1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Gimeracil(口服,2.5–25 mg/kg)可以防止 X 射线造成的肿瘤 DNA 损伤快速愈合 [3]。
人癌裸鼠异种移植模型(A549肺癌、HCT116结直肠癌): - 肿瘤生长抑制(A549模型):小鼠(每组6只)分为4组:溶剂组(0.5% CMC-Na,口服)、吉美拉西(Gimeracil)单药组(20 mg/kg,口服,每日1次)、X射线单独照射组(6 Gy,第7天单次照射)、吉美拉西(Gimeracil)+照射联合组。21天后,联合组肿瘤体积抑制率达78%(vs溶剂组:1200 mm³ vs 264 mm³),肿瘤重量减少72%(1.8 g vs 0.5 g) [3] - 生存获益(HCT116模型):联合组小鼠中位生存期为35天,显著长于单独照射组(22天,P<0.01)和溶剂组(18天,P<0.001)。联合组无小鼠出现转移灶,而单独照射组40%的小鼠出现肝转移 [3] - 肿瘤组织中的机制验证:A549肿瘤组织免疫组化显示,联合组Rad51表达降低(为溶剂组的0.3倍),γ-H2AX焦点增加(为溶剂组的3.2倍),表明HR抑制导致DNA损伤持续存在 [3] |
| 酶活实验 |
DPD活性测定(纯化人DPD):
1. 试剂制备:配制含10 mM MgCl₂、2 mM NADPH和0.1% BSA的50 mM Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH 7.5),准备纯化人DPD(0.5 μg/孔)与[14C]-二氢尿嘧啶(5 μCi/μmol,底物) [2] 2. 反应体系构建:96孔板中加入80 μL缓冲液、10 μL 吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(0.01-5 μM)或溶剂、5 μL DPD,37℃孵育10 min;加入5 μL [14C]-二氢尿嘧啶启动反应,孵育60 min [2] 3. 产物检测:加入100 μL 0.5 M高氯酸终止反应,200 μL乙酸乙酯萃取产物([14C]-β-脲基丙酸),3000×g离心10 min;收集有机相,氮气吹干,50 μL甲醇重悬,液体闪烁计数器测定放射性 [2] 4. 数据计算:DPD活性以每毫克蛋白每小时生成的产物纳摩尔数表示,抑制率=[(对照组活性-处理组活性)/对照组活性]×100%,通过剂量-反应曲线拟合计算IC50 [2] - HR报告基因实验(DR-GFP U2OS细胞): 1. 细胞培养:DR-GFP U2OS细胞(稳定表达HR报告载体)在含10% FBS的DMEM培养基中培养 [1] 2. 转染与处理:细胞(2×10⁵/孔,6孔板)用转染试剂转染I-SceI表达质粒(诱导DNA双链断裂);6 h后加入吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(0.5-10 μM)或溶剂,孵育48 h [1] 3. 流式分析:收集细胞,PBS洗涤2次,流式细胞仪(激发光488 nm,发射光525 nm)检测GFP阳性细胞比例。HR效率=(处理组GFP⁺细胞百分比/对照组GFP⁺细胞百分比)×100% [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型:DLD-1、HeLa 和 LC-11 细胞系。 测试浓度:1 mM。 孵化时间:48小时。 实验结果:抑制辐射引起的 DNA 双链断裂的修复。未照射细胞中 24 小时时未增加 c-H2AX 焦点残留。 克隆形成存活实验: 1. 细胞接种:癌细胞(A549、HCT116)按200-1000细胞/孔(根据照射剂量调整)接种于6孔板,37℃、5% CO₂孵育过夜 [1] 2. 药物与照射处理:加入吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(1-10 μM)或溶剂,孵育2 h后,用X射线发生器照射细胞(2-8 Gy);照射后更换为不含吉美拉西(Gimeracil)的新鲜培养基 [1] 3. 克隆形成与计数:孵育10-14天(直至形成>50个细胞的克隆);4%多聚甲醛固定细胞15 min,0.1%结晶紫染色30 min;流水冲洗,晾干后用克隆计数器计数。存活分数=(处理组克隆数/对照组克隆数)/接种效率 [1] - Rad51焦点免疫荧光实验: 1. 细胞制备:HCT116细胞接种于24孔板的盖玻片上(5×10⁴细胞/孔),孵育过夜 [2] 2. 药物处理与照射:加入吉美拉西(Gimeracil)(3-6 μM)或溶剂,孵育4 h后,用4 Gy X射线照射细胞;继续孵育8 h以促进Rad51焦点形成 [2] 3. 染色:4%多聚甲醛固定细胞15 min,0.2% Triton X-100透化10 min;5% BSA/PBS封闭1 h,4℃下抗Rad51一抗(1:200)孵育过夜;PBS洗涤后,Alexa Fluor 488标记二抗(1:500)室温孵育1 h;DAPI(1 μg/mL)染核5 min [2] 4. 成像与计数:共聚焦显微镜观察细胞,图像分析软件计数每组100个细胞的Rad51焦点数 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Nude mice (Lu-99, LC-11, KB/C3 and PAN-4 tumors were xenografted)[3].
Doses: 2.5-25 mg/kg. Route of Administration: Orally. Experimental Results: demonstrated anti-tumor activity. Human Cancer Xenograft Models (Nude Mice): 1. Animal selection: 6-8 week-old female BALB/c nude mice (n=24 for A549 model, n=24 for HCT116 model) were housed under SPF conditions with a 12 h light/dark cycle, free access to food and water. Acclimate for 1 week before the experiment [3] 2. Tumor induction: Prepare single-cell suspensions of A549 (5×10⁶ cells/mouse) or HCT116 (4×10⁶ cells/mouse) in PBS mixed with Matrigel (1:1, v/v). Inject 0.2 mL of the suspension subcutaneously into the right dorsal flank of each mouse [3] 3. Grouping and treatment: When tumors reach ~100 mm³, randomize mice into 4 groups (n=6/group): - Vehicle group: Oral gavage of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose sodium (CMC-Na) once daily for 21 days. - Gimeracil alone group: Oral gavage of Gimeracil 20 mg/kg once daily for 21 days (dissolved in 0.5% CMC-Na, sonicated to dissolve). - Irradiation alone group: Single X-ray irradiation (6 Gy) on day 7 post-grouping; no drug treatment. - Combined group: Gimeracil (20 mg/kg, p.o., daily) + single X-ray irradiation (6 Gy on day 7) [3] 4. Sample collection and monitoring: - Tumor monitoring: Measure tumor volume (length × width² / 2) and mouse body weight every 3 days. - Survival monitoring (HCT116 model): Record mouse survival daily until all mice in the vehicle group die. - Tissue analysis (A549 model): On day 21, euthanize mice, dissect tumors, weigh them, and fix a portion in 4% paraformaldehyde for immunohistochemistry (Rad51, γ-H2AX staining). Collect liver and kidney tissues for pathological analysis [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Mean 5-FU maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) values were approximately 3-fold higher after Teysuno administration than after administration of tegafur alone, despite a 16-fold lower Teysuno dose (50 mg of tegafur) compared to tegafur alone (800 mg), and are attributed to inhibition of DPD by gimeracil. Maximum plasma uracil concentration was observed at 4 hours, with a return to baseline levels within approximately 48 hours after dosing, indicating the reversibility of the DPD inhibition by gimeracil. After administration of a single dose of 50 mg Teysuno (expressed as tegafur content), median Tmax for Teysuno components tegafur, gimeracil, and oteracil was 0.5, 1.0, and 2.0 hours, respectively. Following a single dose of Teysuno, approximately 3.8% to 4.2% of administered tegafur, 65% to 72% of administered gimeracil, and 3.5% to 3.9% of administered oteracil were excreted unchanged in the urine. Although no intravenous data are available for Teysuno in humans, the volume of distribution could be roughly estimated from the apparent volume of distribution and urinary excretion data as 16 l/m2, 17 l/m2, and 23 l/m2 for tegafur, gimeracil and oteracil, respectively. Biological Half-Life Following a single dose of Teysuno, T1/2 values ranged from 6.7 to 11.3 hours for tegafur, from 3.1 to 4.1 hours for gimeracil, and from 1.8 to 9.5 hours for oteracil. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Protein Binding
Oteracil, gimeracil, 5-FU, and tegafur are 8.4%, 32.2%, 18.4%, and 52.3% protein bound, respectively. In vitro toxicity: - Normal cells: Gimeracil (up to 10 μM) had no significant cytotoxicity on normal human lung fibroblasts (MRC-5) or normal colon epithelial cells (NCM460), with clonogenic survival >85% (vs. control) and no obvious apoptosis (Annexin V⁺ rate <5%) [1] - Cancer cells: Gimeracil alone (≤10 μM) had weak cytotoxicity on A549 and HCT116 cells, with cell viability >75% (MTT assay, 72 h incubation) [1][3] - In vivo toxicity: - General toxicity: Gimeracil (20 mg/kg, p.o., 21 days) caused no significant body weight loss (treatment group: 21.5 ± 1.2 g vs. vehicle group: 22.1 ± 1.0 g) or abnormal behaviors (e.g., lethargy, anorexia) [3] - Organ toxicity: Pathological analysis of liver and kidney tissues from the combined group showed no obvious damage (no hepatocyte necrosis, renal tubular injury, or inflammation). Serum levels of ALT (28 ± 5 U/L vs. vehicle 30 ± 4 U/L), AST (45 ± 6 U/L vs. 48 ± 5 U/L), BUN (14 ± 2 mg/dL vs. 15 ± 2 mg/dL), and creatinine (0.7 ± 0.1 mg/dL vs. 0.8 ± 0.1 mg/dL) were within normal ranges [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Gimeracil is an organic molecular entity.
Gimeracil is an adjunct to antineoplastic therapy, used to increase the concentration and effect of the main active componets within chemotherapy regimens. Approved by the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in March 2011, Gimeracil is available in combination with [DB03209] and [DB09256] within the commercially available product "Teysuno". The main active ingredient in Teysuno is [DB09256], a pro-drug of [DB00544] (5-FU), which is a cytotoxic anti-metabolite drug that acts on rapidly dividing cancer cells. By mimicking a class of compounds called "pyrimidines" that are essential components of RNA and DNA, 5-FU is able to insert itself into strands of DNA and RNA, thereby halting the replication process necessary for continued cancer growth. Gimeracil's main role within Teysuno is to prevent the breakdown of [DB00544] (5-FU), which helps to maintin high enough concentrations for sustained effect against cancer cells. It functions by reversibly and selectively blocking the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), which is involved in the degradation of 5-FU. This allows higher concentrations of 5-FU to be achieved with a lower dose of tegafur, thereby also reducing toxic side effects. Gimeracil is a pyridine derivative with antitumor activity. Gimeracil enhances the antitumor activity of fluoropyrimidines by competitively and reversibly inhibiting the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase causing decreased degradation of the fluoropyrimidines. Drug Indication Gimeracil is used as an adjunct to antineoplastic therapy. When used within the product Teysuno, gimeracil is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced gastric (stomach) cancer when given in combination with cisplatin. Mechanism of Action Gimeracil's main role within Teysuno is to prevent the breakdown of [DB00544] (5-FU), which helps to maintin high enough concentrations for sustained effect against cancer cells. It functions by reversibly blocking the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), which is involved in the degradation of 5-FU. Gimeracil is a key component of the oral chemotherapeutic agent S-1 (a combination of tegafur, Gimeracil, and oteracil potassium), where it inhibits DPD to prevent the rapid catabolism of tegafur (a prodrug of 5-fluorouracil, 5-FU), thereby enhancing 5-FU efficacy [2][3] - Beyond DPD inhibition, Gimeracil exhibits a unique mechanism of inhibiting homologous recombination (HR), which sensitizes cancer cells to radiation and DNA-damaging agents by blocking DNA double-strand break repair. This dual mechanism expands its application in combined radiotherapy [1][2] - In preclinical models, Gimeracil combined with radiotherapy showed significant synergistic antitumor effects in NSCLC and colorectal cancer, with no increased toxicity compared to single-agent treatment. This supports its potential as a radiation sensitizer in clinical oncology [3] - Gimeracil specifically targets HR without affecting NHEJ (a major DNA repair pathway in normal cells), which may explain its low toxicity to normal tissues and high therapeutic index [1] |
| 分子式 |
C5H4CLNO2
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
145.54
|
|
| 精确质量 |
144.993
|
|
| CAS号 |
103766-25-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
54679224
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light brown solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.6±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
524.2±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
274 °C
|
|
| 闪点 |
270.8±28.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.641
|
|
| LogP |
-1.5
|
|
| tPSA |
53.09
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
0
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
9
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
207
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
ZPLQIPFOCGIIHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C5H4ClNO2/c6-3-2-7-5(9)1-4(3)8/h1-2H,(H2,7,8,9)
|
|
| 化学名 |
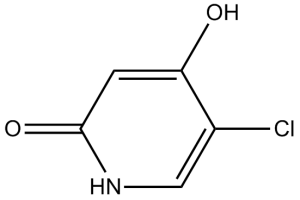
5-chloro-2-hydroxypyridin-4(1H)-one
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (17.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (17.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (17.18 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 6.8710 mL | 34.3548 mL | 68.7096 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.3742 mL | 6.8710 mL | 13.7419 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.6871 mL | 3.4355 mL | 6.8710 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT06255379 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Fuquinitinib+Tegafur Gimeracil Oteracil |
Metastasis Colorectal Cancer Colon Cancer |
Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine |
March 22, 2024 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04310774 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Tegafur, Gimeracil and Oteracil Potassium Capsules (one drug) |
Cervical Cancer Chemotherapy |
Peking Union Medical College Hospital | April 15, 2020 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT03267121 | Completed | Drug: Tegafur Gimeracil Oteracil Potassium Capsules |
Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
Shanghai Ninth People's Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University |
October 1, 2017 | Phase 2 |
| NCT03192735 | Active, not recruiting | Drug: ApatinibMesylateTablets | Apatinib Combined SOX |
Chang-Ming Huang, Prof. | September 1, 2017 | Phase 2 |