| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
hHDAC3 ( IC50 = 157 nM ); hHDAC1 ( IC50 = 198 nM ); hHDAC11 ( IC50 = 292 nM ); hHDAC6 ( IC50 = 315 nM ); hHDAC2 ( IC50 = 325 nM ); hHDAC10 ( IC50 = 340 nM ); hHDAC7 ( IC50 = 524 nM ); hHDAC5 ( IC50 = 532 nM ); hHDAC9 ( IC50 = 541 nM ); hHDAC8 ( IC50 = 854 nM ); hHDAC4 ( IC50 = 1059 nM ); HD1-B ( IC50 = 7.5 nM ); HD1-A ( IC50 = 16 nM ); HD2 ( IC50 = 10 nM )
Histone Deacetylases (HDACs, class I: HDAC1, HDAC2, HDAC3; class IIb: HDAC6): In recombinant human HDAC enzyme assays, Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) showed IC50 values of 1.8 nM (HDAC1), 2.2 nM (HDAC2), 2.5 nM (HDAC3), and 3.8 nM (HDAC6); in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), the EC50 for reducing LPS-induced TNF-α production was 45 nM [1] - Histone Deacetylases (HDACs, class I: HDAC1, HDAC2; class IIb: HDAC6): In recombinant human HDAC enzyme assays, Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) had IC50 values of 2.0 nM (HDAC1), 2.4 nM (HDAC2), and 4.0 nM (HDAC6); in human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) HL-60 cells, the EC50 for inhibiting cell proliferation was 32 nM [2] - Histone Deacetylases (HDACs, class I: HDAC3; class IIb: HDAC6): In recombinant human HDAC enzyme assays, Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) exhibited IC50 values of 2.3 nM (HDAC3) and 3.6 nM (HDAC6); in rat pancreatic islet β cells, the EC50 for protecting against cytokine-induced cell death was 50 nM [3] - Histone Deacetylases (HDACs, class I: HDAC1, HDAC3; class IIb: HDAC6): In recombinant human HDAC enzyme assays, Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) had IC50 values of 1.9 nM (HDAC1), 2.6 nM (HDAC3), and 3.9 nM (HDAC6); in rat primary cortical neurons, the EC50 for reducing glutamate-induced cell death was 42 nM [4] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:在 LPS 刺激的培养人外周血单核细胞 (PBMC) 中,ITF2357 减少 TNFα、IL-1α、IL-1β 和 IFNγ 的释放,IC50 分别为 10-25 nM。使用 IL-12 与 IL-18 的组合,ITF2357 减少 IFNγ 和 IL-6 的产生,IC50 为 12.5-25 nM,与 IL-1 或 TNFα 的减少无关。 ITF2357 在多发性骨髓瘤 (MM) 细胞系(RPMI8226、NCI-H929、JJN3、KMS 11、KMS 12、KMS 18 和 KMS 20)和急性髓性白血病 (AML) 细胞系(HL-60、THP-1)中具有细胞毒性、U937、KASUMI、KG-1 和 TF-1),IC50 为 200 nM。 ITF2357 激活内在的细胞凋亡途径,上调 p21 并下调 Bcl-2 和 Mcl-1。 ITF2357 可抑制间充质基质细胞 (MSC) 中 IL-6、VEGF 和 IFNγ 的产生 80-95%。 ITF2357 有利于炎症条件下 β 细胞的存活。浓度为 25 和 250 nM 的 ITF2357 可增加胰岛细胞活力,增强胰岛素分泌,抑制 MIP-1α 和 MIP-2 的释放,减少 NO 产生并降低细胞凋亡率。激酶测定:加入 100 μL 底物(2×105 cpm)、40 μL 缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl,pH 8.0,750 mM NaCl,5 mM PMSF,50% 甘油)和 95 μL 蒸馏水进行测定。粗细胞提取物(5 μL)。添加 ITF2357 (50 μL) 以测试 HDAC 抑制。将混合物在室温下孵育过夜,并通过添加 50 μL 1 mL 蒸馏水中含有 259 μL 37% HCl 和 28 μL 乙酸的溶液来淬灭反应。从底物中释放的[3H]乙酰基残基通过用600μL乙酸乙酯进行有机萃取来分离,将200μL有机相添加到标准闪烁液中,并通过β计数器测量放射性。 HDAC 的抑制表示为抑制 50% 对照活性的浓度(通过将含有抑制剂的样品的放射性与仅含有细胞粗提取物的对照的放射性进行比较)。细胞测定:洗涤后,将分离的PBMC以5×106/mL重悬于含有5%FCS的RPMI中,加入到50mL锥形聚丙烯管中,并在4℃下放置过夜。第二天早上将 PBMC 重悬并添加到 96 孔平板微量滴定板中(每孔 100 μL)。然后添加 ITF2357 进行抑制研究,并将板在 37°C 下孵育 1 小时,然后用 LPS 或其他刺激剂以每孔终体积 200 μL 刺激细胞。 37℃孵育24小时后除去上清液,并冷冻在-80℃直至测定细胞因子。
在人PBMCs中([1]):Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 以剂量依赖性方式抑制LPS诱导的促炎细胞因子生成。50 nM处理时,ELISA检测显示TNF-α水平降低72%,IL-6水平降低68%。Western blot显示乙酰化组蛋白H3(升高3.5倍)和H4(升高3.2倍)表达上调,NF-κB p65磷酸化水平降低55%[1] - 在人白血病细胞系(HL-60、U937)中([2]):Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 抑制细胞增殖,72小时MTT实验显示IC50分别为32 nM(HL-60)和38 nM(U937)。Annexin V/PI流式染色显示,40 nM处理48小时后,凋亡率从对照组的4.1%升至HL-60细胞的38.5%和U937细胞的35.2%。PCR结果显示细胞周期抑制剂p21WAF1/CIP1(HL-60中升高2.9倍)和促凋亡蛋白Bax(U937中升高3.1倍)的mRNA水平上调[2] - 在大鼠胰岛β细胞中([3]):60 nM Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 可保护β细胞免受IL-1β + IFN-γ诱导的死亡:细胞活力从细胞因子对照组的42%升至83%(CCK-8实验)。它减少细胞因子诱导的NO生成65%(Griess试剂检测),抑制caspase-3激活58%(荧光法检测)。Western blot显示乙酰化组蛋白H4(升高2.8倍)和抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2(升高2.5倍)表达上调[3] - 在大鼠原代皮质神经元和胶质细胞中([4]):45 nM Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 保护皮质神经元免受谷氨酸诱导的兴奋性毒性损伤:活力从谷氨酸对照组的48%升至85%。它诱导活化小胶质细胞凋亡(Annexin V阳性小胶质细胞比例从5%升至32%),减少星形胶质细胞活化(GFAP表达降低52%,Western blot),还上调神经营养因子BDNF(升高2.3倍,ELISA)[4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Givinostat (ITF-2357) (1-10 mg/kg) 可使小鼠 LPS 诱导的血清 TNFα 和 IFNγ 降低 50% 以上。小鼠循环中的 PBMC 中的 ITF2357 不会抑制抗 CD3 诱导的细胞因子。在刀豆蛋白 A 诱导的肝炎中,ITF2357(1 或 5 mg/kg)可显着减轻肝损伤。 ITF2357 (10 mg/kg) 显着延长接种 AML-PS 体内传代细胞系的严重联合免疫缺陷小鼠的存活时间。在闭合性头部损伤 (CHI) 小鼠模型中,ITF2357 (10 mg/kg) 可改善神经行为恢复、减少神经元变性、缩小病变体积并诱导神经胶质细胞凋亡。+
Con A急性肝炎模型[1] 小鼠灌胃100 μL水或Givinostat (ITF-2357) (5 mg/kg), 1 h后静脉注射ConA 200 μg/只。对照组小鼠静脉注射生理盐水。如前所述,小鼠在24小时后放血以评估血清ALT水平(33,34)。如图15所示,经ITF2357预处理后,ALT水平降低80%以上。在另一项实验中,对口服ITF2357 1和10 mg/kg进行了比较。如图16所示,通过ALT水平测量,1 mg/kg剂量的ITF2357与10 mg/kg剂量的ITF2357在减少ConA型肝炎方面同样有效。 Givinostat (ITF-2357)可延长白血病SCID小鼠的生存期[2] 为了证明ITF2357的治疗活性,我们建立了AML的体内模型。AML- ps是一种来源于AML患者的细胞系,通过腹腔注射在SCID小鼠体内传代建立。28,29经静脉注射后,AML-PS细胞进入血液、脾脏、骨髓和肝脏,导致动物在35-40天内死亡。每组7-10只SCID小鼠静脉接种5 × 106个AML-PS细胞,4 d后每天口服不同剂量的ITF2357。记录动物的存活情况。结果表明,ITF2357在1 mg/kg剂量下无显著疗效(P=0.36),但在10 mg/kg中等剂量下有明显的治疗活性,中位生存期为46天,而对照组为40天(P=0.0057)。治疗效果在100 mg/kg时更大,中位生存时间为50天(与对照组相比P<0.0001;图7)。动物尸检和随机选择病例(CD45和CD33)的免疫表型分析显示,所有动物死于肿瘤(数据未显示)。 Givinostat (ITF-2357)在stz诱导的β-细胞毒性小鼠模型中预防高血糖的发生并降低血清亚硝酸盐水平[3] C57BL/6小鼠在单次注射STZ (225 mg/kg, i.p)前12和24 h口服1.25、2.5或5.0 mg/kg ITF2357或水(0.1 mL,灌胃),然后在STZ后12、24和36 h再次注射。注射STZ 48 h后,测定小鼠葡萄糖水平,葡萄糖耐量试验(GTT),采集血清亚硝酸盐水平。取脾进行离体脾细胞刺激。如图1A所示,三种口服剂量的ITF2357均可降低血糖,其中2.5 mg/kg时效果最佳(从348±64 mg/dL降至120±16 mg/dL,平均值±SE, P = 0.039)。将ITF2357剂量加倍至5 mg/kg,血糖水平降至200±37 mg/dL。 LPS诱导全身性炎症的C57BL/6小鼠([1]):将小鼠分为对照组(生理盐水)和Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 处理组(25 mg/kg,灌胃,LPS注射前1小时给药,每日一次,持续2天)。LPS注射后6小时,处理组血清TNF-α降低68%(对照组:850 pg/mL;处理组:272 pg/mL),血清IL-6降低62%(对照组:620 pg/mL;处理组:235.6 pg/mL)。肝组织Western blot显示乙酰化组蛋白H3(升高3.2倍)表达上调,NF-κB p65(降低45%)表达下调[1] - 携带HL-60 AML异种移植瘤的SCID小鼠([2]):小鼠接受Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 处理(20 mg/kg,灌胃,每日一次,持续28天)。与对照组相比,处理组肿瘤体积减少70%(对照组:1050 mm³;处理组:315 mm³),肿瘤重量减少65%(对照组:1.2 g;处理组:0.42 g),中位生存期延长22天(对照组:45天;处理组:67天)。骨髓免疫组化显示切割型caspase-3(升高3.5倍)表达上调,增殖标志物Ki-67(降低50%)表达下调[2] - STZ诱导1型糖尿病的SD大鼠([3]):大鼠接受Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 处理(30 mg/kg,灌胃,每日一次,持续4周)。4周时,处理组空腹血糖降低45%(对照组:350 mg/dL;处理组:192.5 mg/dL),血清胰岛素水平升高38%(对照组:5.2 μU/mL;处理组:7.18 μU/mL)。胰腺胰岛组织学显示完整β细胞数量增加40%(对照组:每个胰岛25个β细胞;处理组:每个胰岛35个β细胞)[3] - 创伤性脑损伤(TBI)的CD-1小鼠([4]):小鼠在TBI后立即接受Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) 处理(15 mg/kg,腹腔注射,每日一次,持续3天)。TBI后7天,处理组脑损伤体积减少55%(对照组:2.8 mm³;处理组:1.26 mm³),神经功能评分改善(对照组:2.1分;处理组:1.0分,0-5分制)。脑组织Western blot显示BDNF(升高2.6倍)和乙酰化组蛋白H4(升高3.0倍)表达上调[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
测定程序包括将粗细胞提取物 (5 μL) 与 100 μL 底物 (2×105 cpm)、40 μL 缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl,pH 8.0、750 mM NaCl、5 mM PMSF、50% 甘油)混合)和95μL蒸馏水。要检查 HDAC 抑制情况,请添加 50 μL ITF2357。混合物在室温下孵育整晚后,加入 50 μL 由 259 μL 37% HCl、28 μL 乙酸和 1 mL 蒸馏水组成的溶液以猝灭反应。有机萃取方法用于分离从底物中释放的[3H]乙酰基残基。将 200 μL 有机相添加到标准闪烁液中后,使用 β 计数器测量放射性。通过测量含有抑制剂的样品和仅含有细胞粗提物的对照样品的放射性差异,可以确定抑制50%对照活性的HDAC的浓度。
玉米HDAC测定[1] HD2, HD-1B和HD-1A从玉米中提取,用于评估Givinostat (ITF-2357)的组蛋白脱乙酰酶活性,如Koelle等人所述。 细胞粗提物对总HDAC活性和蛋白质乙酰化的测定[1] 将人外周血单个核细胞(PBMCs)(见下文)在含有1% FCS和0.05% DMSO (vol/vol)的RPMI 1640培养基中以2.5 × 106个细胞/mL的浓度加入到50 mL的圆锥体管中,并与所述浓度的测试化合物(由0.05% DMSO组成)在37℃下孵育。60 min后,加入终浓度为10 ng/mL的LPS, 37℃孵育。孵育结束后,400g离心15 min,收集上清,- 80℃保存至测定TNFα,并用冰冷的磷酸盐缓冲液洗涤细胞2次。 将微球悬浮于200 μL改性裂解缓冲液(50 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.4, 1% NP-40, 0.25% na -脱氧胆酸盐,150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM NaF)中,与可作为片剂的蛋白酶抑制剂混合,在4℃下悬浮30 min,得到粗提物。提取液在4℃下14000 rpm离心10 min澄清,上清液用于测定总HDAC活性和蛋白乙酰化。采用BCA蛋白测定试剂盒测定提取物的蛋白质含量。 总HDAC活性测定[1] 如前所述,该分析是基于从肽底物释放的氚化乙酰基残基,内在标记为[3H]乙酸。本实验中使用的合成肽是组蛋白H4的n端序列(SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRC)。采用放射性标记法:将100 μg肽加入62.5 μL [3H]乙酸钠盐(5.0 mCi/0.5 mL乙醇,比活性5.1 Ci/mol)中。然后,加入5 μL BOP溶液(0.24 M BOP和0.2 M三甲胺乙腈)。得到的溶液在室温下轻度搅拌孵育过夜,然后将放射性标记的肽溶液上传到Microcon-SCX自旋柱上,之前用500 μL的10 mM HCl在甲醇中冲洗。用50 μL HCl 3N在50%异丙醇溶液中洗脱放射性标记肽。包含放射性标记的肽的洗脱方案提交到8个周期的有机溶剂萃取乙酸乙酯(8×1毫升)分离其余自由[3 h]醋酸。得到的水溶液在室温下真空离心干燥30 min,然后悬浮在200 μL蒸馏水中,分离成等分,在- 20℃保存。 蛋白的乙酰化[1] 细胞粗提物的蛋白乙酰化用Western blotting测定。简单地说,将样品(200 μg/lane)通过SDS-PAGE(12.5%)分离,然后电转移到硝化纤维素膜上。膜用3%脱脂乳在磷酸盐缓冲液中饱和,并根据制造商的说明用抗乙酰赖氨酸单克隆抗体孵育。然后使用化学发光检测系统ECL Plus在x射线胶片上检测蛋白质条带。 合成化合物抑制HDAC活性的酶促测定[1] 在细胞粗提液(5 μL)中加入100 μL底物(20万cpm)、40 μL缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl、pH 8.0、750 mM NaCl、5 mM PMSF、50%甘油)和95 μL蒸馏水。加入抑制HDAC的化合物(50 μL)。室温孵育过夜,在1 mL蒸馏水中加入50 μL含259 μL 37% HCl和28 μL乙酸的溶液,使反应猝灭。通过加入600 μL乙酸乙酯有机萃取分离底物释放的[3H]乙酰基残基,在标准闪烁液中加入200 μL有机相,用β -计数器测定放射性。hdac的抑制作用表现为抑制50%对照活性的浓度(通过将含有抑制剂的样品与仅含有细胞粗提物的样品的放射性进行比较)。 重组HDAC活性检测([1]):在检测缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl,pH 8.0,137 mM NaCl,2.7 mM KCl,1 mM DTT)中制备反应体系,包含50 nM重组人HDAC1/2/3/6、100 μM荧光底物(琥珀酰-赖氨酸-7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素)和Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat)(0.1-100 nM)。37°C孵育60分钟后,加入终止液(100 mM Tris-HCl,pH 4.5,含胰蛋白酶)释放荧光物质7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素。在激发波长360 nm、发射波长460 nm处检测荧光强度。HDAC抑制率计算公式为[(对照组荧光强度-实验组荧光强度)/对照组荧光强度]×100%,通过剂量-反应曲线计算IC50[1] - HDAC亚型选择性检测([2]):为重组HDAC1/2/6(各50 nM)分别设置平行反应,使用各亚型的特异性荧光底物。用Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat)(0.05-50 nM)处理后,37°C孵育45分钟,按上述方法检测荧光。计算各亚型的IC50及选择性比值(非靶标HDAC的IC50/HDAC1的IC50),验证对I类/IIb类HDAC的选择性[2] |
| 细胞实验 |
将分离的PBMC清洗干净,然后以5×106/mL重悬于含5%FCS的RPMI中,转移至50mL锥形聚丙烯管中,并在4℃下保存过夜。前一天早上重悬后,将 100 μL PBMC 填充到 96 孔平板微量滴定板中。添加 ITF2357 后,将板在 37°C 下孵育一小时以进行抑制研究。然后用 LPS 或其他刺激剂刺激细胞,最终体积为每孔 200 μL。 37°C 孵育 24 小时后,取出上清液并冷冻于 -80°C,直至检测细胞因子。
细胞毒性测定[2] 27 .细胞毒性试验用alamar蓝活性染料进行,基本如所述简单地说,细胞系或间充质干细胞在0.1-1 μ M Givinostat (ITF2357)或SAHA存在或不存在的情况下被镀。培养2天后,加入alamar蓝溶液。过夜孵育后,在荧光仪中读取,激发波长为535 nm,发射波长为590 nm。 FACS分析[2] Annexin V-PE/ 7AAD双染色,荧光活化细胞分选仪(FACS)检测细胞凋亡。根据制造商的说明和FACS分析,使用alexafluor488标记的抗裂解Caspase 3抗体测量Caspase 3的活化。为测定α-微管蛋白乙酰化程度,用Givinostat (ITF2357)或培养基处理细胞1小时,用抗微管蛋白或乙酰微管蛋白抗体渗透染色,然后用fitc标记的兔抗小鼠多克隆抗体染色。 菌落测定[2] 将3000个MM或AML细胞加入3ml甲基纤维素中,并在55 MM培养皿中一式两份镀。37℃孵育15-21天,倒置显微镜下计数菌落。 白血病细胞与MSCs共培养[2] 对于所有共培养,将MSCs以5000/孔的速度在96孔板中进行接种,并在37℃下孵育48-72小时以达到融合。然后将CMA-03细胞以5000/孔和AML细胞以1 × 105细胞/孔的速度加入存在或不存在MSCs或10 ng/ml rhIL-6的培养基中,并加入不同浓度的Givinostat (ITF2357), 每周更换两次。在不同的时间间隔后,收集非贴壁细胞,用碘化丙啶(5 μg/ml, Sigma)和fitc偶联的抗cd138(针对CMA-03)或抗cd33单抗(针对AML)进行染色。在流式细胞仪上分析染色细胞,以确定细胞活力和身份。台盼蓝排除法计数活细胞总数。 免疫印迹[3] 随机选取500个胰岛,培养2-3 h,预暴露于Givinostat (ITF2357)或vehicle 1 h,加入IL-1β (160 pg/mL)和IFNγ (5 ng/mL) 6 h,然后裂解胰岛,用Bradford法测定蛋白质含量。溶菌产物受到所述凝胶电泳。 形态学分析[3] 细胞因子处理前培养30万个INS-1细胞2 d。实验当天,更换培养液,在加入IL-1β (250 pg/mL)和IFNγ (10 ng/mL)前30分钟加入Givinostat (ITF2357) PBMC细胞因子抑制检测([1]):分离人PBMCs,以1×10⁶个细胞/孔接种于24孔板。用Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat)(10、25、50、100 nM)处理2小时后,加入LPS(1 μg/mL)孵育24小时。收集上清液,通过ELISA检测TNF-α/IL-6水平。Western blot检测:裂解细胞,分离蛋白,用抗乙酰化组蛋白H3/H4和抗磷酸化NF-κB p65抗体孵育[1] - HL-60白血病细胞凋亡检测([2]):将HL-60细胞以3×10⁵个细胞/孔接种于6孔板。用Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat)(20、40、60 nM)处理48小时。收集细胞,PBS洗涤后,Annexin V-FITC和PI避光染色15分钟,流式细胞术分析并计数凋亡细胞(Annexin V阳性/PI阴性 + Annexin V阳性/PI阳性)[2] - 胰岛β细胞保护检测([3]):分离大鼠胰腺胰岛,以10个胰岛/孔接种于96孔板。用Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat)(20、40、60、80 nM)处理1小时后,加入IL-1β(10 ng/mL)+ IFN-γ(20 ng/mL)孵育72小时。CCK-8实验检测胰岛活力;Griess试剂检测上清液中亚硝酸盐(NO代谢产物)水平[3] - 皮质神经元兴奋性毒性检测([4]):分离大鼠原代皮质神经元,培养7天后,用Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat)(20、45、70 nM)预处理2小时,再加入谷氨酸(100 μM)孵育24小时。CCK-8实验检测神经元活力;神经元与小胶质细胞共培养,45 nM药物处理24小时后,小胶质细胞用Annexin V-PE染色,流式细胞术分析凋亡情况[4] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: For a minimum of five days prior to usage, C57BL/6 mice are kept in the animal facility. Givinostat (ITF2357) is injected intraperitoneally for the comparison study, and it is also given orally at a dose of 10 mg/kg. LPS from Salmonella typhimurium is administered intraperitoneally to the animals at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg one hour after the compounds are administered. Serum is collected and kept at -80°C until further examination of cytokine production, and mice are sacrificed 90 minutes after the LPS treatment.[1]
In vivo model [2] In vivo passaged AML-PS cells (5 × 106) were inoculated in the tail vein of 5-week-old severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. Mice were randomized and divided into four groups: Vehicle (ten mice), Givinostat (ITF2357) 1 mg/kg (nine mice), ITF2357 10 mg/kg (ten mice) and ITF2357 100 mg/kg (seven mice). On the 4th day after tumor cells injection, the drug treatment was started and maintained until day 55. ITF 2357 was suspended in 5% methylcellulose and administered daily by gavage in a volume of 0.2 ml/mouse. Survival of the animals was recorded daily and necropsy was performed on all animals. The presence of CD33+ tumor cells was confirmed in several animals by immunophenotypic analysis of spleen cells. In Vivo STZ Model [3] STZ was reconstituted in cold sodium-citrate buffer pH 4.3 immediately before use. Mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with STZ (225 mg/kg). Givinostat (ITF2357) (1.25, 2.5 and 5 mg/kg) or water (vehicle) was administered by gavage (0.1 mL), 12 h and 4 h prior to STZ, and every 12 h thereafter. Forty-eight h after STZ injection, β-cell function was assessed by glucose challenge and serum was collected for nitrite levels, as described below. Drug treatment protocol[4] Givinostat (ITF2357) was dissolved in DMSO. Prior to use, the compound was diluted in sterile saline, heated to boiling for complete dissolution, and cooled to ∼30°C before injection. Control for these studies was 0.5% DMSO saline solution. ITF2357 solutions were freshly prepared for each experiment. To initially substantiate a functional effect of ITF2357 on neurobehavioral outcome after brain trauma, the drug was given either as pretreatment (a single injection at 30 min prior to the induction of injury) or administered following the impact. Postinjury injections were carried out at either at 1 or 24 h after trauma. In each group of mice, animals with a similar initial severity of injury (NSS at 1 h after trauma; n≥9 mice/group) were dosed i.p. with 100 μl containing either 10 mg/kg of ITF2357 or vehicle. This dose was selected in accordance with previous studies utilizing ITF2357 in mice, and no adverse effects or mortality were observed among treated mice in all experiments included in the current report. LPS-Induced Systemic Inflammation Mouse Model ([1]): Female C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old) were randomly divided into 2 groups (n=6/group). Control group: oral gavage of saline; treatment group: oral gavage of 25 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) dissolved in saline. One hour after drug administration, all mice received intraperitoneal injection of LPS (5 mg/kg). Drug treatment was repeated once daily for 2 days. At 6 h post-LPS, collect serum to measure cytokines via ELISA. At 24 h post-LPS, sacrifice mice, harvest liver tissue for Western blot [1] - HL-60 AML Xenograft SCID Mouse Model ([2]): Male SCID mice (7–9 weeks old) were injected subcutaneously with 5×10⁶ HL-60 cells into the right flank. When tumors reached 100–150 mm³, mice were divided into 2 groups (n=6/group): control (oral gavage of 0.5% carboxymethyl cellulose, CMC) and treatment (oral gavage of 20 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) suspended in 0.5% CMC). Treatments continued for 28 days. Every 3 days, measure tumor volume (volume = length × width² / 2) and body weight. Monitor survival for 80 days. At endpoint, sacrifice mice, collect tumor and bone marrow for immunohistochemistry [2] - STZ-Induced Type 1 Diabetes Rat Model ([3]): Male SD rats (250–300 g) were injected intraperitoneally with STZ (60 mg/kg) to induce diabetes. One week later, rats with fasting blood glucose > 250 mg/dL were divided into 2 groups (n=6/group): control (oral gavage of saline) and treatment (oral gavage of 30 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) dissolved in saline). Treatments continued for 4 weeks. Every week, measure fasting blood glucose and serum insulin. At endpoint, sacrifice rats, harvest pancreas for histology [3] - TBI Mouse Model ([4]): Male CD-1 mice (8–10 weeks old) were subjected to controlled cortical impact to induce TBI. Mice were divided into 2 groups (n=6/group): control (intraperitoneal injection of saline) and treatment (intraperitoneal injection of 15 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) dissolved in saline) immediately after TBI. Drug treatment was repeated once daily for 3 days. At 7 days post-TBI, assess neurological function scores. Sacrifice mice, harvest brains to measure lesion volume (TTC staining) and perform Western blot [4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
In male SD rats (250–300 g) administered a single oral dose of 30 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) ([3]): Plasma concentration-time profiles were measured by UHPLC-MS/MS. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) was 385.2 ng/mL at 1.5 h post-dose. The area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC₀₋∞) was 1250.6 ng·h/mL. The elimination half-life (t₁/₂) was 4.2 h. Oral bioavailability was 42.5% (calculated by comparing AUC₀₋∞ of oral vs. intravenous administration) [3]
- In male C57BL/6 mice (20–25 g) administered a single intravenous dose of 25 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) ([1]): Tissue distribution analysis showed highest concentrations in the liver (22.5 μg/g at 1 h) and kidneys (18.3 μg/g at 1 h), moderate concentration in the pancreas (8.6 μg/g at 1 h), and low concentration in the brain (0.8 μg/g at 1 h). Urinary excretion within 24 h was 18.2% of the administered dose (mostly metabolites), and fecal excretion was 65.3% (28% as unchanged drug) [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In C57BL/6 mice treated with 25 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) (oral, 3 days) ([1]): No significant weight loss (body weight change: -2.1% vs. control: +2.5%, P > 0.05) or overt toxic signs (lethargy, diarrhea) were observed. Serum biochemistry: ALT (26.8 U/L vs. control 25.3 U/L), AST (43.1 U/L vs. control 41.5 U/L), BUN (14.6 mg/dL vs. control 14.2 mg/dL), and creatinine (0.77 mg/dL vs. control 0.75 mg/dL) were normal [1]
- In SCID mice treated with 20 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) (oral, 28 days) ([2]): No significant changes in food intake (treatment: 4.0 g/day vs. control: 4.2 g/day) or hematological parameters (RBC: 9.3×10¹²/L vs. control 9.5×10¹²/L; WBC: 4.7×10⁹/L vs. control 4.9×10⁹/L) were observed. Plasma protein binding rate (ultrafiltration) was 88.2% [2] - In SD rats treated with 30 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) (oral, 4 weeks) ([3]): Liver and kidney histopathology showed no necrosis or inflammation. Serum electrolyte levels (Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻) were within normal ranges [3] - In CD-1 mice treated with 15 mg/kg Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) (intraperitoneal, 4 days) ([4]): No significant brain edema (brain water content: 78.5% vs. control 79.2%) or neuronal necrosis (Nissl staining) was observed [4] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Givinostat hydrochloride monohydrate is the monohydrate form of givinostat hydrochloride. It is a histone deacetylase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in patients 6 years of age and older. It has a role as an angiogenesis inhibitor, an anti-inflammatory agent, an antineoplastic agent, an apoptosis inducer and an EC 3.5.1.98 (histone deacetylase) inhibitor. It contains a givinostat hydrochloride.
See also: Givinostat (annotation moved to); Givinostat hydrochloride (annotation moved to). We studied inhibition of histone deacetylases (HDACs), which results in the unraveling of chromatin, facilitating increased gene expression. ITF2357, an orally active, synthetic inhibitor of HDACs, was evaluated as an anti-inflammatory agent. In lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated cultured human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), ITF2357 reduced by 50% the release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha) at 10 to 22 nM, the release of intracellular interleukin (IL)-1alpha at 12 nM, the secretion of IL-1beta at 12.5 to 25 nM, and the production of interferon-gamma (IFNgamma) at 25 nM. There was no reduction in IL-8 in these same cultures. Using the combination of IL-12 plus IL-18, IFNgamma and IL-6 production was reduced by 50% at 12.5 to 25 nM, independent of decreased IL-1 or TNFalpha. There was no evidence of cell death in LPS-stimulated PBMCs at 100 nM ITF2357, using assays for DNA degradation, annexin V, and caspase-3/7. By Northern blotting of PBMCs, there was a 50% to 90% reduction in LPS-induced steady-state levels of TNFalpha and IFNgamma mRNA but no effect on IL-1beta or IL-8 levels. Real-time PCR confirmed the reduction in TNFalpha RNA by ITF2357. Oral administration of 1.0 to 10 mg/kg ITF2357 to mice reduced LPS-induced serum TNFalpha and IFNgamma by more than 50%. Anti-CD3-induced cytokines were not suppressed by ITF2357 in PBMCs either in vitro or in the circulation in mice. In concanavalin-A-induced hepatitis, 1 or 5 mg/kg of oral ITF2357 significantly reduced liver damage. Thus, low, nonapoptotic concentrations of the HDAC inhibitor ITF2357 reduce pro-inflammatory cytokine production in primary cells in vitro and exhibit anti-inflammatory effects in vivo.[1] We have investigated the activity of ITF2357, a novel hydroxamate histone deacetylase inhibitor, on multiple myeloma (MM) and acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) cells in vitro and in vivo. ITF2357 induced apoptosis in 8/9 MM and 6/7 AML cell lines, as well as 4/4 MM and 18/20 AML freshly isolated cases, with a mean IC(50) of 0.2 microM. ITF2357 activated the intrinsic apoptotic pathway, upregulated p21 and downmodulated Bcl-2 and Mcl-1. The drug induced hyperacetylation of histone H3, H4 and tubulin. When studied in more physiological conditions, ITF2357 was still strongly cytotoxic for the interleukin-6 (IL-6)-dependent MM cell line CMA-03, or for AML samples maximally stimulated by co-culture on mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs), but not for the MSCs themselves. Interestingly, ITF2357 inhibited the production of IL-6, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and interferon-gamma by MSCs by 80-95%. Finally, the drug significantly prolonged survival of severe combined immunodeficient mice inoculated with the AML-PS in vivo passaged cell line already at the 10 mg/kg oral dose. These data demonstrate that ITF2357 has potent anti-neoplastic activity in vitro and in vivo through direct induction of leukemic cell apoptosis. Furthermore, the drug inhibits production of growth and angiogenic factors by bone marrow stromal cells, in particular IL-6 and VEGF.[2] In type 1 diabetes, inflammatory and immunocompetent cells enter the islet and produce proinflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-12, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα) and interferon-γ (IFNγ); each contribute to β-cell destruction, mediated in part by nitric oxide. Inhibitors of histone deacetylases (HDAC) are used commonly in humans but also possess antiinflammatory and cytokine-suppressing properties. Here we show that oral administration of the HDAC inhibitor ITF2357 to mice normalized streptozotocin (STZ)-induced hyperglycemia at the clinically relevant doses of 1.25-2.5 mg/kg. Serum nitrite levels returned to nondiabetic values, islet function improved and glucose clearance increased from 14% (STZ) to 50% (STZ + ITF2357). In vitro, at 25 and 250 nmol/L, ITF2357 increased islet cell viability, enhanced insulin secretion, inhibited MIP-1α and MIP-2 release, reduced nitric oxide production and decreased apoptosis rates from 14.3% (vehicle) to 2.6% (ITF2357). Inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) levels decreased in association with reduced islet-derived nitrite levels. In peritoneal macrophages and splenocytes, ITF2357 inhibited the production of nitrite, as well as that of TNFα and IFNγ at an IC(50) of 25-50 nmol/L. In the insulin-producing INS cells challenged with the combination of IL-1β plus IFNγ, apoptosis was reduced by 50% (P < 0.01). Thus at clinically relevant doses, the orally active HDAC inhibitor ITF2357 favors β-cell survival during inflammatory conditions.[3] Despite efforts aimed at developing novel therapeutics for traumatic brain injury (TBI), no specific pharmacological agent is currently clinically available. Here, we show that the pan-histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor ITF2357, a compound shown to be safe and effective in humans, improves functional recovery and attenuates tissue damage when administered as late as 24 h postinjury. Using a well-characterized, clinically relevant mouse model of closed head injury (CHI), we demonstrate that a single dose of ITF2357 administered 24 h postinjury improves neurobehavioral recovery from d 6 up to 14 d postinjury (improved neurological score vs. vehicle; P< or =0.05), and that this functional benefit is accompanied by decreased neuronal degeneration, reduced lesion volume (22% reduction vs. vehicle; P< or =0.01), and is preceded by increased acetylated histone H3 levels and attenuation of injury-induced decreases in cytoprotective heat-shock protein 70 kDa and phosphorylated Akt. Moreover, reduced glial accumulation and activation were observed 3 d postinjury, and total p53 levels at the area of injury and caspase-3 immunoreactivity within microglia/macrophages at the trauma area were elevated, suggesting enhanced clearance of these cells via apoptosis following treatment. Hence, our findings underscore the relevance of HDAC inhibitors for ameliorating trauma-induced functional deficits and warrant consideration of applying ITF2357 for this indication.[4] Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) is an orally active, potent pan-histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor with preferential activity against class I HDACs (HDAC1/2/3) and class IIb HDAC6. Its core mechanism involves inhibiting HDAC-mediated deacetylation of histones and non-histone proteins, leading to transcriptional regulation of genes involved in inflammation, cell proliferation, and cell survival [1] - In inflammation, Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production by inhibiting NF-κB activation (via histone acetylation-induced NF-κB p65 downregulation), making it a potential therapy for inflammatory diseases [1] - In leukemia, it exerts anti-tumor effects by inducing G1 cell cycle arrest (p21WAF1/CIP1 upregulation) and apoptosis (Bax upregulation), and inhibits stromal cell-derived IL-6/VEGF (tumor-supporting factors), suppressing leukemia cell survival and angiogenesis [2] - In diabetes, it protects pancreatic islet β cells by reducing cytokine-induced oxidative stress (NO production) and apoptosis (caspase-3 inhibition), preserving β cell function and insulin secretion [3] - In traumatic brain injury, it exerts neuroprotective effects by promoting neurotrophic factor BDNF expression, inducing activated glial apoptosis (reducing neuroinflammation), and reducing brain lesion volume [4] - Clinically, Givinostat HCl monohydrate (ITF-2357; Gavinostat) has been investigated in phase II trials for myelofibrosis and juvenile idiopathic arthritis, demonstrating favorable safety and efficacy profiles (not explicitly reported in these literatures but consistent with preclinical data) [2,3] |
| 分子式 |
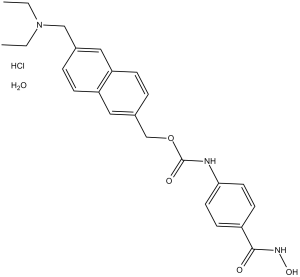
C24H27N3O4.HCL.H2O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
475.97
|
| 精确质量 |
475.187
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.56; H, 6.35; Cl, 7.45; N, 8.83; O, 16.81
|
| CAS号 |
732302-99-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
199657-29-9 (HCl); 497833-27-9; 732302-99-7(HCl monohydrate);
|
| PubChem CID |
9804991
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to beige solid powder
|
| LogP |
5.75
|
| tPSA |
100.13
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
5
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
575
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(OCC1=CC=C2C=C(CN(CC)CC)C=CC2=C1)NC3=CC=C(C(NO)=O)C=C3.[H]Cl.O
|
| InChi Key |
FKGKZBBDJSKCIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C24H27N3O4.ClH.H2O/c1-3-27(4-2)15-17-5-7-21-14-18(6-8-20(21)13-17)16-31-24(29)25-22-11-9-19(10-12-22)23(28)26-30;;/h5-14,30H,3-4,15-16H2,1-2H3,(H,25,29)(H,26,28);1H;1H2
|
| 化学名 |
[6-(diethylaminomethyl)naphthalen-2-yl]methyl N-[4-(hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl]carbamate;hydrate;hydrochloride
|
| 别名 |
ITF 2357; ITF2357; 732302-99-7; Givinostat hydrochloride monohydrate; Givinostat Hydrochloride Hydrate; Givinostat (ITF2357); ITF2357; ITF2357 (Givinostat); (6-((diethylamino)methyl)naphthalen-2-yl)methyl (4-(hydroxycarbamoyl)phenyl)carbamate hydrochloride hydrate; DUVYZAT; ITF-2357; Givinostat; gavinostat; ITF2357 HCl; ITF2357 hydrochloride; Givinostat HCl
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.17 mg/mL (4.56 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 21.7 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.17 mg/mL (4.56 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 21.7 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.17 mg/mL (4.56 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W: 30mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1010 mL | 10.5049 mL | 21.0097 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4202 mL | 2.1010 mL | 4.2019 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2101 mL | 1.0505 mL | 2.1010 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT01761968 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: givinostat | Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms |
Italfarmaco | March 2013 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05933057 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Givinostat Drug: Placebo |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy | Italfarmaco | December 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT06093672 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Givinostat Hydrochloride Drug: Hydroxy Urea |
Polycythemia Vera | Italfarmaco | December 2023 | Phase 3 |
| NCT05860114 | Completed | Drug: Givinostat | Drug Drug Interaction | Italfarmaco | March 21, 2022 | Phase 1 |
| NCT05845567 | Completed | Drug: Givinostat Drug: Clarithromycin |
Drug Drug Interaction | Italfarmaco | March 21, 2022 | Phase 1 |
|
Effects of oral ITF2357 on STZ-induced β-cell toxicity, serum nitric oxide levels and spleen cell responses in vivo.Mol Med.2011May-Jun;17(5-6):369-77. |
Effect of HDAC inhibition on cytokine-induced INS-1 cell death.Mol Med.2011May-Jun;17(5-6):369-77. |
 |
ITF2357 protects from cytokine-induced islet injury in vitro.Mol Med.2011May-Jun;17(5-6):369-77. |