| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
rTRPV4 (IC50 = 2 nM); hTRPV4 (IC50 = 40 nM)[1]
Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) [1] Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GSK2193874 选择性靶向 TRPV1、TRPA1、TRPC3、TRPC6 和 TRPM8 (IC50>25 μM) 并靶向 TRP 通道 [1]。 GSK2193874 是一种口服 TRPV4 阻滞剂,通过抑制天然内皮 TRPV4 电流和重组 TRPV4 通道,充当 Ca2+ 内流的选择性抑制剂。当以 3 nM 及以上的浓度添加到外部溶液中时,GSK2193874 在全细胞膜片钳测试中抑制了重组 TRPV4 电流的激活。然而,当通过细胞内移液器溶液递送到细胞内时,GSK2193874 在浓度高达 10 μM 时无效 [2]。
GSK2193874 是一种强效且选择性的TRPV4阳离子通道阻滞剂,在研发过程中已解决了意外的心血管脱靶毒性问题 [1] - 可抑制重组TRPV4通道的Ca²⁺内流,并抑制原生内皮细胞的TRPV4电流 [2] - 在分离的啮齿动物和犬肺组织中,可阻止与肺静脉压(PVP)升高相关的血管通透性增加及后续肺水肿的发生 [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在评估 GSK2193874 在大鼠和狗体内的药代动力学 (PK) 特性后,发现这些动物的半衰期和口服暴露量适合慢性动物模型中的口服给药(大鼠 PK:iv CL=7.3 mL/min/kg,po t1/2=10小时,%F=31;狗PK:静脉注射CL=6.9mL/min/kg,口服t1/2=31小时,%F=53)。此外,剂量高达 30 mg/kg 时,GSK2193874 对大鼠的心率或血压没有影响。 GSK2193874 是一种口服生物可利用的 TRPV4 抑制剂,是同类首创,已被证明可以增强许多心力衰竭动物的肺功能 [1]。在大鼠中,GSK2193874 表现出良好的口服生物利用度 (31%) 和低清除率 (7.3 mL/min/kg) [2]。
在急性和慢性心力衰竭(HF)模型中,GSK2193874 预处理可抑制肺水肿的形成,并提高动脉血氧合水平 [2] - 能有效缓解小鼠心肌梗死诱导的已形成肺水肿 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
筛查、钙内流和电生理学[2]
在荧光成像板读数器(FLIPR)平台上用hTRPV4转导的HEK细胞进行TRPV4阻断剂筛选,评估用GSK634775激活后抑制TRPV4 Ca2+内流的能力。在HEK293、BHK和HUVEC中进行了电生理学和其他钙内流测定(补充方法)。 选择性[2] TRP选择性测定在FLIPR平台上用钙或膜电位指示剂进行。使用了以下配体:TRPV1、辣椒素;TRPA1,百里酚;TRPC3和TRPC6、卡巴胆碱;TRPM8、西林。hERG和Cav1.2通过全细胞电压钳进行评估。详见补充办法 心脏离子通道选择性测定:[1] hERG和Cav1.2通过PatchXpress 7000A上的全细胞电压钳进行评估。Nav1.5是在IonWorks Quattro上使用群体膜片钳运行的。 |
| 细胞实验 |
内皮细胞完整性[2]
通过Diff-Quik细胞鉴定评估HUVEC分离,并用Sorcerer系统(Optomax)成像。用xCELLigence系统监测HUVEC单层阻抗。 TRPV4 FLIPR检测:[1] 将HEK MSRII细胞解冻并悬浮在15 K细胞/50µL的细胞培养基中(DMEM/F12 1:1,含L-谷氨酰胺、15 mM HEPES@pH 7.3、10%FBS、1%青霉素-链霉素溶液、1%L-谷氨酰胺)。将TRPV4-BacMam病毒以1%的终浓度加入细胞中并轻轻混合。然后以15K细胞/孔的速度接种细胞,在室温下静置1小时,然后在组织培养箱中在37°C和5%CO2的条件下孵育24至72小时。然后移除培养基,用2µM Fura-4、0.5 mM亮黑和2.5µM丙磺舒对细胞进行染色。然后在FLIPR Tetra 384上运行板。在TRPV4激活前10分钟,用EC80浓度的TRPV4激动剂如GSK634775A加入阻断剂。使用Activity Base XE曲线拟合模块对11点阻断剂浓度曲线进行数据分析。 原生内皮细胞TRPV4电流抑制检测:在适宜培养条件下培养肺毛细血管内皮细胞,将细胞暴露于相关浓度的GSK2193874中。采用电生理技术检测药物处理前后TRPV4介导的电流,分析药物对电流幅度的抑制作用 [2] - 重组TRPV4通道Ca²⁺内流抑制评估:将重组TRPV4表达载体转染至细胞中,培养至稳定表达。用Ca²⁺敏感荧光探针负载细胞,先加入GSK2193874处理,再加入TRPV4激活剂,通过监测并定量荧光强度变化,评估药物对Ca²⁺内流的抑制效果 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Hemodynamic Measurement in Anesthetized Mice: [1]
Male TRPV4+/+ and TRPV4-/- mice, 25–30 g and age from 10 to 12 weeks, on a BALB/c AnNCrl background strain, were utilized. Mice were anesthetized and maintained with isoflurane (1.5% in O2). The right common carotid artery and jugular vein were isolated and cannulated with polyethylene 50 tubing for continuous monitoring of blood pressure, HR, and for infusion of test drug. Drug doses were administered at an escalating dose from 3 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and 30 mg/kg with an infusion rate of 20 µL/min. The vehicle was a 1% dimethyl sulfoxide saline. Blood samples were collected at the end of infusion. Hemodynamic Measurement in the Anesthetized Dog: [1] Male Marshall Beagles weighing 8 to 12 kg were fasted for 18 h and then anesthetized with propofol (10 mg/kg i.v.). Femoral arteries and veins were isolated, and an arterial catheter was inserted into the left femoral artery to monitor blood pressure. Catheters were inserted into femoral veins for drug and anesthesia administration. Anesthesia was maintained with alpha chloralose (65 mg/kg i.v. + 0.5 mg/kg/min). Hemodynamic parameters were continuously recorded on CA Recorder computer software. Test compound was administered as an ascending i.v. infusion. The vehicle was a 1% dimethyl sulfoxide in saline. Blood samples were collected at the end of infusion. Osmoregulation[2] Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats (n = 7 to 8 per group) were treated with vehicle (6% Cavitron) or GSK2193874 (30 mg kg−1 day−1) via oral gavage for at least 4 days before osmotic challenges. Rats underwent acute and chronic hyper- and hypo-osmotic challenges, as described in the Supplementary Methods. Rodent radiotelemetry[2] Sprague-Dawley (control, n = 18) and spontaneously hypertensive rats (n = 11) were implanted with Data Sciences International (DSI) radiotelemetry transmitters. Rats were dosed with vehicle (6% Cavitron) or GSK2193874, and data were captured with DSI receivers and analyzed with Microsoft Excel. Diuretic studies[2] Sprague-Dawley rats were administered vehicle (0.9% NaCl, 25 ml/kg), furosemide (30 mg/kg), or hydrochlorothiazide (30 mg/kg) via oral gavage. Urine was then collected over 4 hours followed by blood sampling. Rats recovered for 4 days and then received GSK2193874 (30 mg kg−1 day−1 oral gavage) for 5 days before repeating the diuretic challenge. Rodent in vivo efficacy[2] Sprague-Dawley rats were used for in vivo testing of GSK2193874 in the presence of the TRPV4 activator GSK1016790 and for aortic banding. Mice were used for MI studies. See the Supplementary Methods for details. Isolated rodent/canine lung pulmonary edema prevention experiment: Isolate lungs from rodents or canines and establish an ex vivo perfusion system. Adjust the perfusion pressure to simulate elevated PVP. Administer GSK2193874 into the perfusion system. Continuously monitor vascular permeability and edema formation indicators (e.g., fluid accumulation, protein leakage) to assess the drug's preventive effect [2] - Acute and chronic HF models for pulmonary edema inhibition: Establish acute and chronic HF models in animals via appropriate methods (e.g., surgical or pharmacological induction). Once the models are successfully established, administer GSK2193874 orally at a therapeutic dose. Regularly measure indicators such as pulmonary edema severity (e.g., lung wet/dry weight ratio) and arterial blood oxygenation levels to evaluate the drug's inhibitory effect on edema formation [2] - Myocardial infarction-induced pulmonary edema resolution experiment: Induce myocardial infarction in mice to establish pulmonary edema models. After edema is established, administer GSK2193874 orally. Assess the resolution of pulmonary edema by measuring relevant indicators (e.g., lung edema degree, respiratory function) at specified time points [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
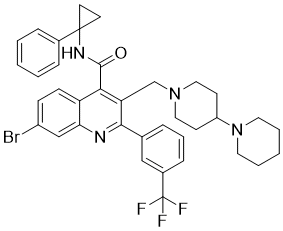
Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) is a member of the Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) superfamily of cation channels. TRPV4 is expressed in the vascular endothelium in the lung and regulates the integrity of the alveolar septal barrier. Increased pulmonary vascular pressure evokes TRPV4-dependent pulmonary edema, and therefore, inhibition of TRPV4 represents a novel approach for the treatment of pulmonary edema associated with conditions such as congestive heart failure. Herein we report the discovery of an orally active, potent, and selective TRPV4 blocker, 3-(1,4'-bipiperidin-1'-ylmethyl)-7-bromo-N-(1-phenylcyclopropyl)-2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-quinolinecarboxamide (GSK2193874, 28) after addressing an unexpected off-target cardiovascular liability observed from in vivo studies. GSK2193874 is a selective tool for elucidating TRPV4 biology both in vitro and in vivo.[1]
Pulmonary edema resulting from high pulmonary venous pressure (PVP) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in heart failure (HF) patients, but current treatment options demonstrate substantial limitations. Recent evidence from rodent lungs suggests that PVP-induced edema is driven by activation of pulmonary capillary endothelial transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channels. To examine the therapeutic potential of this mechanism, we evaluated TRPV4 expression in human congestive HF lungs and developed small-molecule TRPV4 channel blockers for testing in animal models of HF. TRPV4 immunolabeling of human lung sections demonstrated expression of TRPV4 in the pulmonary vasculature that was enhanced in sections from HF patients compared to controls. GSK2193874 was identified as a selective, orally active TRPV4 blocker that inhibits Ca(2+) influx through recombinant TRPV4 channels and native endothelial TRPV4 currents. In isolated rodent and canine lungs, TRPV4 blockade prevented the increased vascular permeability and resultant pulmonary edema associated with elevated PVP. Furthermore, in both acute and chronic HF models, GSK2193874 pretreatment inhibited the formation of pulmonary edema and enhanced arterial oxygenation. Finally, GSK2193874 treatment resolved pulmonary edema already established by myocardial infarction in mice. These findings identify a crucial role for TRPV4 in the formation of HF-induced pulmonary edema and suggest that TRPV4 blockade is a potential therapeutic strategy for HF patients.[2] Chemical name: 3-(1,4'-bipiperidin-1'-ylmethyl)-7-bromo-N-(1-phenylcyclopropyl)-2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-quinolinecarboxamide [1] - Mechanism of action: GSK2193874 selectively blocks TRPV4 channels, which are expressed in pulmonary vascular endothelium and regulate alveolar septal barrier integrity. By inhibiting TRPV4-mediated Ca²⁺ influx, the drug prevents and resolves increased vascular permeability and pulmonary edema caused by elevated PVP in HF [1][2] - Therapeutic potential: Serves as a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of pulmonary edema associated with conditions such as congestive heart failure [1][2] - Expression of TRPV4 in human lungs: TRPV4 is expressed in the pulmonary vasculature of human lungs, and its expression is enhanced in lung sections from HF patients compared to healthy controls [2] |
| 分子式 |
C37H38BRF3N4O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
691.6230
|
| 精确质量 |
690.218
|
| CAS号 |
1336960-13-4
|
| PubChem CID |
53464483
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
| LogP |
8.819
|
| tPSA |
48.47
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
46
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1020
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
UIVOZBSCHXCGPS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C37H38BrF3N4O/c38-28-12-13-30-32(23-28)42-34(25-8-7-11-27(22-25)37(39,40)41)31(24-44-20-14-29(15-21-44)45-18-5-2-6-19-45)33(30)35(46)43-36(16-17-36)26-9-3-1-4-10-26/h1,3-4,7-13,22-23,29H,2,5-6,14-21,24H2,(H,43,46)
|
| 化学名 |
7-bromo-N-(1-phenylcyclopropyl)-3-[(4-piperidin-1-ylpiperidin-1-yl) methyl]-2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]quinoline-4-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
GSK2193874; GSK2193874A; GSK 2193874; GSK 2193874A; GSK-2193874; GSK-2193874A; 7-bromo-N-(1-phenylcyclopropyl)-3-[(4-piperidin-1-ylpiperidin-1-yl) methyl]-2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]quinoline-4-carboxamide; CHEMBL4073922; 3-([1,4'-Bipiperidin]-1'-ylmethyl)-7-bromo-N-(1-phenylcyclopropyl)-2-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4-quinolinecarboxamide; 3-([1,4'-Bipiperidin]-1'-ylmethyl)-7-bromo-N-(1-phenylcyclopropyl)-2-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)quinoline-4-carboxamide;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~144.59 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (3.61 mM) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
*20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.01 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4459 mL | 7.2294 mL | 14.4588 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2892 mL | 1.4459 mL | 2.8918 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1446 mL | 0.7229 mL | 1.4459 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。