| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In a dermal metabolism rat study, dermal application of 20 mg/kg of radio-labeled icaridin resulted in 61-66% of the dose absorbed through the skin. Following topical application of 20 mg/kg on rats, the peak plasma concentrations were measured to be 0.5 μg/mL in male rats and 0.8-1.6 μg/mL in female rats. In a study of human volunteers, less than 6% of the applied doses were absorbed after topical application of 14.7 or 15.0 mg of technical grade icaridin and covering the application site with a protective wrap for eight hours. Following topical administration on rats at doses of 20 mg/kg, urinary excretion was reported to be the primary route of elimination where 73-88% of the parent compound was recovered in the urine. At doses of 200 mg/kg, 33-40% of the administered dose was excreted in the urine or feces. No data were available on the composition of parent compound and metabolites in the urine of either animals or humans. In a rat study, dermal application of icaridin at doses of either 20 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg resulted in plasma concentrations ranging from 0.5 μg/ml for males and 0.8-1.6 μg/ml for females in the 20 mg/kg test group, and 4.48 μg/ml in male rats and 1.70 μg/ml and female rats in the 200 mg/kg test group. Icaridin applied to the arms of human volunteers was not found in blood plasma. There is no available information on the clearance of icaridin. Picaridin and oxybenzone are two active ingredients found in repellent and sunscreen preparations, respectively. We performed a series of in vitro diffusion studies to evaluate the transmembrane permeation of picaridin and oxybenzone across human epidermis and poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) membrane. Permeation of picaridin (PCR) and oxybenzone (OBZ) across human epidermis was suppressed when both active ingredients were used concurrently; increasing concentration of the test compounds further reduced the permeation percentage of picaridin and oxybenzone. While permeation characteristics were correlative between human epidermis and PDMS membrane, permeability of PDMS membrane was significantly larger than that of human epidermis. The findings were different from concurrent use of repellent DEET and sunscreen oxybenzone in which a synergistic permeation enhancement was observed. Further comparative studies are therefore needed to understand permeation mechanisms and interactions between picaridin and oxybenzone. Increased awareness of skin cancer and mosquito-transmitted diseases has increased use of insect repellents and sunscreens. The challenge in setting recommendations for use and reapplication, especially when used concomitantly, lies in finding the balance between applying a durable product effective in withstanding natural and physical factors such as water, sweat, temperature and abrasion, while limiting percutaneous absorption and decreasing risk of potential dermal and systemic toxicity. Inorganic sunscreens show no or little percutaneous absorption or toxic effects in comparison to organic sunscreens, which show varying levels of dermal penetration and cutaneous adverse effects. An alternative to N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET), the traditional gold standard compound in insect repellents, picaridin appears as efficacious, has lower risk of toxicity, and when used simultaneously with sunscreen may decrease percutaneous absorption of both compounds. Conversely, combined use of DEET and sunscreen results in significantly higher absorption of both compounds. It is important to increase consumer awareness of "washing in" of various compounds leading to increased risk of toxicity, as well as differences in reapplication need due to "washing off" caused by water, sweat and abrasion. Although much remains to be studied, to maximize efficacy and decrease toxicity, contemporary research tools, including dermatopharmokinetics, should aid these prospective advances. The skin of 6 male human volunteers/group was exposed to 15.0 or 14.7 mg/person (37 uCi/person) of 14C-KBR 3023 (undiluted) or as a preparation in ethanol (15% (w/w). The subjects were exposed to the test material for 8 hours under a non-occlusive protective wrap. At the end of the treatment period, the treated area was swabbed with isopropyl alcohol and rinsed with the alcohol. The swabs and alcohol were saved for further analysis. Tape stripping in the proximity of the dosing site was performed at 1, 23 and 45 hours post-exposure. Blood samples were drawn at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, 24, 36, 48, 72 and 120 hours post-application from both the ipsilateral and contralateral arms. Urine was collected prior to dosing and in the following intervals: 0 to 4, 4 to 8, 8 to 12, 12 to 24, 24 to 36, 36 to 48, 48 to 60, 60 to 72, 72 to 84, 84 to 96, 96 to 108, 108 to 120, and 120 to 128 hours post-application. Feces were collected throughout the 128 hour collection period. Most of the applied dose was recovered in the rinsate and on the swabs, protective covering and duoderm at the end of the exposure period, 94.16% and 95.23% of the test material in ethanol and the undiluted test material, respectively. Radiolabel was recovered in the urine of the test subjects (mean values: 3.76% (range: 2.20 to 7.00%) and 1.66% (range: 0.70 to 2.29%) of the applied dose for the solution and undiluted material, respectively). Ninety three to 94% of the label was recovered in the 1st 24 hours. Recovery of radiolabelled compound from the plasma was negligible. Absorption of the radiolabelled compound through the skin was quite limited under the conditions of the study. The use of a vehicle (ethanol) seemed to enhance its absorption. ... The skin of a total of 5 rats/sex was treated daily for 2 weeks with 20 mg/kg of unlabeled KBR 3023 technical (purity: 99.1%), followed by exposure to a single dose of 20 mg/kg of the radiolabeled test material for 7 days. /In a second test/ the skin of a total of 5 rats/sex was exposed to a single dose of 200 mg/kg of the radiolabeled test material for 7 days. ... The primary route of excretion was the urine (73 to 88% of the absorbed dose). Pretreatment did not appear to affect the excretion profile. For the 200 mg/kg dermal treatment, the mean percentages of the administered dose which were recovered in the urine and feces ranged between 33 and 40% for the males and females, respectively. The radioactivity recovered in the urine represented 78 and 91% of the total for males and females, respectively. Metabolism / Metabolites There is limited data on the metabolism and resulting metabolites of the drug; however, it is estimated that icaridin undergoes phase I metabolic reactions involving 2-methylpropyl side chain or the piperidine ring being hydroxylated. It is also noted that the hydroxyethyl sidechain was oxidized to produce a carbonyl group. There was very little Phase 2 metabolism of the icaridin. Analysis of the metabolites revealed that the predominant modifications of the parent compound were phase 1 reactions in which the piperidine ring or the 2-methylpropyl sidechain was hydroxylated or the hydroxyethyl sidechain was oxidized to the carbonyl moiety. Phase 2 conjugation reactions with glucuronide, linoleic or oleic acid constituted a very minor fraction of the recovered metabolites. Biological Half-Life The first elimination half-lives of icaridin were determined in a study of five male and female rats treated with a single dose of 20 mg/kg icaridin dermally. The half-lives were 35.7 hours for male and 23.9 hours in female rats. In another study of rats treated daily for 2 weeks with 20 mg/kg of unlabeled icaridin, followed by exposure to a single dose of 20 mg/kg of the radiolabeled icaridin for 7 days, the 1st elimination half-lives were 10.9 and 9.1 hours for the males and females, respectively. The 2nd half-lives were 144 and 105 hours, respectively. Five rats/sex were dosed iv in the femoral vein with a single dose of 20 mg/kg of the test material. The test material was prepared in physiological saline. ... The 1st , 2nd and 3rd elimination half-lives were 0.9, 5.2 and 45.5 hours for the males and 0.7, 2.8 and 73.0 hours for the females. ... The skin of a total of 5 rats/sex was exposed to a single dose of 20 mg/kg of the radiolabeled test material for 7 days. ... Only 1st elimination half-lives were determined for the low dose dermal studies. These half-lives were 35.7 ... hours for the males and 23.9 ... hours for the females. ... The skin of a total of 5 rats/sex was treated daily for 2 weeks with 20 mg/kg of unlabeled KBR 3023 technical (purity: 99.1%), followed by exposure to a single dose of 20 mg/kg of the radiolabeled test material for 7 days. ... For the high dose dermal treatments, the 1st elimination half-lives were 10.9 and 9.1 hours for the males and females, respectively. The 2nd half-lives were 144 and 105 hours, respectively. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Picaridin is a colorless liquid. Picaridin is an insect repellent, for application to human or animal skin. In particular, it is used as mosquito repellent. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Allergic contact dermatitis has been reported in a human following routine application of picaridin and produced erythema and pruritis. It is not clear whether the solvent methyl glucose-dioleate had a causative or additive effect. However, insect repellents containing picaridin may be acceptable alternatives in patients who demonstrate sensitivity to products containing DEET. Primary symptoms across all insect repellent exposures included ocular irritation/pain, vomiting, red eye/conjunctivitis, and oral irritation. Unintentional ingestion of picaridin-containing and other insect repellents was associated only with minor toxicity. ANIMAL STUDIES: The skin of 50 rats/sex/group was treated with 0, 50, 100 or 200 mg/kg/day 5 days per week for 2 years (the two year cohort). Additionally, 20 animals/sex/group were treated with 0 or 200 mg/kg/kg and 10 animals/sex/group were treated with 50 or 100 mg/kg/day of the test material. These animals received the treatment for one year (one year cohort). There was no apparent effect of an increased mortality due to the treatment. There was no treatment-related effect upon mean body weight, food consumption, clinical signs, ophthalmology, hematology, clinical chemistry, urinalysis, absolute or relative organ weights, or histopathology. The skin of 30 rats/sex/group was treated with 0, 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg/day 5 days/week for two generations. The treatment periods included 10 weeks prior to mating, mating, 3 weeks gestation and 3 weeks of lactation. At that time, 30 F1 animals/sex/group were selected as parents and treated for an additional 10 weeks, followed by mating and 3 weeks each for gestation and lactation of the F2 generation. There were no apparent treatment-related clinical signs related to systemic toxicity or effects upon the mean body weights and food consumption of the parental animals in either generation. At the application site, hyperkeratosis and acanthosis, apparent for even some of the control animals, increased in severity in a dose-related manner. There was no effect upon the reproductive parameters or development of the offspring in either generation. Picaridin was tested in S. typhimurium TA98, TA100, TA1535 and TA1537 strains at levels ranging from 8 to 5000 ug/plate (both trials) with or without metabolic activation and incubated for 48 hours at 37 °C. There was no apparent treatment-related increase in the incidence of reverse mutation. There was no treatment-related increase in the number of micronuclei in mouse micronucleus test. Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of icaridin (picaridin) during breastfeeding. However, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency consider icaridin to be safe and effective during breastfeeding when used as directed. It should be used by breastfeeding women to avoid exposure to mosquito-borne viruses.[1] Avoid application directly to the nipple and other areas where the infant might directly ingest the product. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding There is no available information on the protein binding of icaridin. Toxicity Data LC50 (rat) >4,364 mg/m3 Interactions Picaridin and oxybenzone are two active ingredients found in repellent and sunscreen preparations, respectively. We performed a series of in vitro diffusion studies to evaluate the transmembrane permeation of picaridin and oxybenzone across human epidermis and poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) membrane. Permeation of picaridin (PCR) and oxybenzone (OBZ) across human epidermis was suppressed when both active ingredients were used concurrently; increasing concentration of the test compounds further reduced the permeation percentage of picaridin and oxybenzone. While permeation characteristics were correlative between human epidermis and PDMS membrane, permeability of PDMS membrane was significantly larger than that of human epidermis. The findings were different from concurrent use of repellent DEET and sunscreen oxybenzone in which a synergistic permeation enhancement was observed. Further comparative studies are therefore needed to understand permeation mechanisms and interactions between picaridin and oxybenzone. Increased awareness of skin cancer and mosquito-transmitted diseases has increased use of insect repellents and sunscreens. The challenge in setting recommendations for use and reapplication, especially when used concomitantly, lies in finding the balance between applying a durable product effective in withstanding natural and physical factors such as water, sweat, temperature and abrasion, while limiting percutaneous absorption and decreasing risk of potential dermal and systemic toxicity. Inorganic sunscreens show no or little percutaneous absorption or toxic effects in comparison to organic sunscreens, which show varying levels of dermal penetration and cutaneous adverse effects. An alternative to N,N-diethyl-m-toluamide (DEET), the traditional gold standard compound in insect repellents, picaridin appears as efficacious, has lower risk of toxicity, and when used simultaneously with sunscreen may decrease percutaneous absorption of both compounds. Conversely, combined use of DEET and sunscreen results in significantly higher absorption of both compounds. It is important to increase consumer awareness of "washing in" of various compounds leading to increased risk of toxicity, as well as differences in reapplication need due to "washing off" caused by water, sweat and abrasion. Although much remains to be studied, to maximize efficacy and decrease toxicity, contemporary research tools, including dermatopharmokinetics, should aid these prospective advances. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 4743 mg/kg LD50 Rat dermal >2000 mg/kg LC50 Rat (male) inhalation >4364 mg/cu m 4hr |
| 其他信息 |
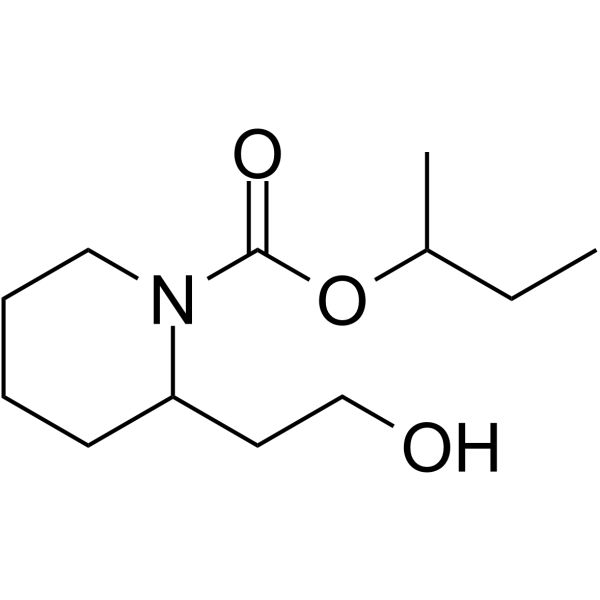
Butan-2-yl 2-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate is a carboxylic acid and a member of piperidines.
Icaridin, also known as Picaridin or hydroxy-ethyl isobutyl piperidine carboxylate, is a cyclic amine and a member of the piperidine chemical family. Piperidines are structural components of [piperine], which is a plant extract from the genus Piper , or pepper. Icaridin has been commonly used as a topically-applied insect repellent in various countries but was officially licensed for use in the United States in 2001 and Canada in 2012. Icaridin was synthesized by Bayer in the 1980s based on molecular modeling. It is considered to be the first choice of repellent by the Public Health Agency of Canada’s Canadian Advisory Committee on Tropical Medicine and Travel for travelers six months to 12 years of age. Icaridin is reported to be less irritating than [Diethyltoluamide], another common insect repellant, and products containing up to 20% of icaridin are considered safe for long-term use in adults. Icaridin, also known as picaridin, KBR 3023, under the INCI name hydroxyethyl isobutyl piperidine carboxylate, and the trade names Bayrepel and Saltidin, is an insect repellent. It has broad efficacy against different insects and is almost colorless and odorless. Drug Indication Icaridin is indicated for use to repel insects, such as mosquitoes, biting flies, ticks, chiggers, and fleas, via topical use or over clothing. Mechanism of Action The exact mechanism and target molecules of icaridin repelling insects are not fully understood; it is presumed that piperine interacts with the olfactory system consisting of odorant receptors (ORs) that need a common co-receptor (ORCO), and of ionotropic receptors (IR), leading to the insect's inability to recognize its host's cues. It is also suggested that icaridin may bind to odorant binding protein 1 (AgamOBP1) at different binding sites. A study demonstrated that icaridin inhibited the odorant-induced responses of AaOR2 and AaOR8 expressed in Xenopus oocytes, leading to altered olfactory inputs by olfactory sensory neurons (OSN). DEET, 2-undecanone (2-U), IR3535 and Picaridin are widely used as insect repellents to prevent interactions between humans and many arthropods including mosquitoes. Their molecular action has only recently been studied, yielding seemingly contradictory theories including odorant-dependent inhibitory and odorant-independent excitatory activities on insect olfactory sensory neurons (OSNs) and odorant receptor proteins (ORs). Here we characterize the action of these repellents on two Aedes aegypti ORs, AaOR2 and AaOR8, individually co-expressed with the common co-receptor AaOR7 in Xenopus oocytes; these ORs are respectively activated by the odors indole (AaOR2) and (R)-(-)-1-octen3-ol (AaOR8), odorants used to locate oviposition sites and host animals. In the absence of odorants, DEET activates AaOR2 but not AaOR8, while 2-U activates AaOR8 but not AaOR2; IR3535 and Picaridin do not activate these ORs. In the presence of odors, DEET strongly inhibits AaOR8 but not AaOR2, while 2-U strongly inhibits AaOR2 but not AaOR8; IR3535 and Picaridin strongly inhibit both ORs. These data demonstrate that repellents can act as olfactory agonists or antagonists, thus modulating OR activity, bringing concordance to conflicting models. Pharmacodynamics Icaridin is a cyclic amine and piperidine compound that is expected to stimulate the sensory hairs on the antennae of insects. |
| 分子式 |
C12H23NO3
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
229.32
|
| 精确质量 |
229.167
|
| CAS号 |
119515-38-7
|
| PubChem CID |
125098
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless liquid
|
| 密度 |
1.0±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
330.9±15.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
below -170ºC
|
| 闪点 |
153.9±20.4 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.478
|
| LogP |
1.56
|
| tPSA |
49.77
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
16
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
220
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O(C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])[H])C(N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])O[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
QLHULAHOXSSASE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H23NO3/c1-3-10(2)16-12(15)13-8-5-4-6-11(13)7-9-14/h10-11,14H,3-9H2,1-2H3
|
| 化学名 |
butan-2-yl 2-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperidine-1-carboxylate
|
| 别名 |
HSDB 7374; EC 423-210-8; Icaridin
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~250 mg/mL (~1090.18 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (9.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (9.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (9.07 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3607 mL | 21.8036 mL | 43.6072 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8721 mL | 4.3607 mL | 8.7214 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4361 mL | 2.1804 mL | 4.3607 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。