| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT) (IC50 = 42±3 nM for human ASBT)
Apical Sodium-Dependent Bile Acid Transporter (ASBT, also known as IBAT) (no definite IC₅₀, Ki, or EC₅₀ data provided; described as a "highly potent" inhibitor) [1] Apical Sodium-Dependent Bile Acid Transporter (ASBT) (used to study its regulatory role in hepatic cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSAD) expression) [2] Apical Sodium-Dependent Bile Acid Transporter (ASBT) (target for treating pruritus in Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)) [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
化合物 56 也称为两性离子、非吸湿性结晶盐形式,在 pH 7.4 下具有良好的溶解度 (>7 mg/mL)、良好的热稳定性,并且不会产生伪影或反应性 [1]。GSK2330672是一种高效、不可吸收的ASBT抑制剂,具有优异的水溶性、选择性和可开发性,可用于安全性研究,最终用于人类。GSK2330672将是一种有价值的临床工具,用于探索非吸收性ASBT抑制剂对2型糖尿病患者的治疗效用。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 2 型糖尿病动物模型中,使用 Linerixibat(GSK2330672;0.05–10 mg/kg;侧壁灌胃;每天两次,持续 14 天;重量分析 ZDF 含量)治疗可降低糖尿病水平 [1]。
GSK2330672在大鼠中导致ASBT的有效抑制和非常低的口服吸收。GSK2330672显示出强大的小鼠和大鼠ASBT活性,并且在GI稳定性测定中是稳定的。GSK2330672在啮齿类动物的胃肠道中是稳定的,并能有效诱导小鼠的粪便胆汁酸排泄,这使我们选择这三种化合物分别用于瘦大鼠和Zucker糖尿病脂肪(ZDF)大鼠的体内机制和疗效研究[1]。 1. 2型糖尿病动物模型的降糖作用:Linerixibat(GSK2330672)作为强效非吸收性ASBT抑制剂,在2型糖尿病动物模型中可显著降低血糖水平,证实其治疗2型糖尿病的潜在价值[1] 2. 小鼠肝脏CSAD表达的调控作用:雄性C57BL/6J小鼠通过灌胃给予Linerixibat(GSK2330672)(2 mg/kg,每日两次),持续1周。小鼠过夜禁食后收集组织,检测显示Linerixibat(GSK2330672)可显著诱导肝脏CSAD的mRNA和蛋白表达,表明ASBT抑制可上调小鼠肝脏CSAD表达[2] 3. PBC患者中的疗效与安全性(IIb期研究):Linerixibat(GSK2330672)正处于IIb期研究阶段,用于治疗PBC患者的瘙痒症状。该研究旨在确定改善瘙痒的最佳剂量和给药频率,并评估其对PBC基础疾病的影响。前期小型研究显示,药物总体耐受性良好,无严重不良事件报告;药物被开发为片剂,通过阻断肠道胆汁酸重吸收,促进致瘙痒化学物质随粪便排出[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
测定人、小鼠和大鼠ASBT抑制作用的方法[1]
在准备测量表达ASBT的细胞对胆汁酸的吸收时,将HEK293细胞在补充有10%FBS的DMEM/F12中培养。在进行实验前24小时,在80–90%的汇合处收获细胞。将细胞以50000个细胞/孔接种在聚d-赖氨酸包被的平板中,并加入ASBT Bacmam病毒,使得每个孔含有3.67×106pfu(73.4pfu/细胞)。用Breathe Easy Seal覆盖每个测定板,并将其放置在培养箱中24小时,以使转运蛋白表达。 在摄取实验当天,将10mM HEPES加入Hank’s Balanced Salt Solution,并用TRIS(HBSSH)将pH调节至7.4。将100pM[3H]-牛磺胆酸盐和10μM冷牛磺胆酸钠加入室温HBSSH中制备测定缓冲液。通过向HBSSH中加入10μM冷牛磺胆酸盐(每个测定板~30mL)制备单独的洗涤缓冲液,并放置在冰上。使用100%DMSO,从200μM开始制备每种测试化合物的8点3倍稀释曲线。类似地,从1.8mM开始,制备对照化合物1的8点剂量-反应曲线。通过将每种浓度的3μL添加到v底96孔板中,然后用177μL的测定缓冲液稀释60倍,形成药物板。将培养皿从培养箱中取出,冷却至25°C。抽吸培养基,并用300μL HBSSH洗涤一次孔。然后,将50μL的每种剂量-反应曲线浓度一式三份逐柱加入到测定板中,保留第10列用于对照(测定缓冲液+1.67%DMSO),第11和12列用于对照化合物。将平板在环境温度下孵育90分钟,然后抽吸平板,然后用300μL洗涤缓冲液洗涤1倍。然后向每个孔中加入220μL Microscint 20,并将板密封。第二天使用微板闪烁计数器对细胞裂解物中[3H]-牛磺胆酸盐的量进行定量。 使用以下公式测定每种药物浓度下的摄取抑制百分比:100×(1-((T1–C2)/(C1–C2));其中T1是试验化合物的平均cpm,C1是在不存在任何添加的抑制剂的情况下观察到的平均cpm,C2是在存在已知引起100%摄取抑制的物质(30μM对照化合物)的情况下观测到的平均cpm。IC50可以使用公式y=(Vmax×xn)/(Kn+xn)生成。 |
| 细胞实验 |
MDCK渗透率的测定方法[1]
使用在与肠道吸收相关的条件下孵育的稳定转染的人多药耐药性1–Madin–Darby犬肾(hMDR1-MDCK)细胞在体外测量被动通透性。简言之,将hMDR1-MDCK细胞以6.6×105个细胞/孔的速度接种到孔径为0.4μm的12孔聚碳酸酯Transwells滤膜上,并在37°C、5%CO2和95%相对湿度的环境中保持在含有10%胎牛血清(DMEM-FBS)的Dulbecco改良Eagle培养基中。三天后,从心尖和基底外侧腔中取出培养基,并用最终浓度为2μM的含有P-gp抑制剂GF120918A的转运缓冲液(含有25mM葡萄糖和25mM HEPES的HBSS)代替。在30分钟的平衡后,从心尖腔中取出运输缓冲液,并用含有3μM测试化合物、2μM GF120918A、25mM葡萄糖和250μM路西法黄CH的禁食状态模拟肠液(FaSSIF)代替。接下来,从基底外侧腔中取出运输缓冲液,用含有1%(w/v)人血清白蛋白和2μM GF 120918A的运输缓冲液代替。 在37°C下孵育60分钟后,从根尖(供体)和基底外侧(受体)室收集样品,并加入乙腈(分别为1:1和1:2(v/v))中。然后对受试者样品进行离心,去除上清液并通过LC-MS/MS进行分析。 所有剂量溶液中的最终DMSO浓度为0.3%(v/v)。每次治疗重复进行。普萘洛尔(一种高渗透性标记化合物)和安非那韦(一种P-gp活性的标记化合物)被包括在单独的孔中作为测定的对照。通过基于荧光的测定法测量路西法黄转运来评估细胞单层完整性。 大鼠灯具内容物稳定性测定[1] 如下制备在磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS,pH 7.4)中的来自大鼠盲肠和结肠的管腔内容物的10%(w/v)匀浆。 将两只雄性SD大鼠禁食过夜,并通过CO2窒息实施安乐死,然后放血。从两只动物身上取下大肠和盲肠,并纵向切开。取出管腔内容物,合并到预先称重的50mL锥形管中,用PBS(10mL/g样品重量)稀释,并通过倒置轻轻混合。将匀浆置于湿冰上直至使用。 将试验化合物(10μM终浓度)加入4 mL玻璃螺旋盖小瓶中,该小瓶含有3 mL大鼠盲肠和结肠管腔内容物的匀浆。加入受试化合物后,立即轻轻混合小瓶,取出3×100μL等分试样(t=0),并将其放入含有400μL停止溶液(80%乙腈/20%甲醇)的96深孔板中。接下来,将玻璃小瓶在温和的氮气流下吹扫约30秒,加盖,并放置在37°C的振荡水浴中。在t=2、4和24小时时,从小瓶中取出3×100μL等分试样,并将其放入含有400μL停止溶液的96深孔板中。小瓶在温和的氮气流下吹扫约30 s,加盖,并在每个时间点后放置在37°C的振荡水浴中。覆盖样品并在−10°C下储存,直到进行LC-MS/MS分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Zucker diabetic fat (ZDF) rat [1]
Doses: 0.05 mg/kg, 0.1 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg twice (two times) daily; Results lasting 14 days: Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) diminished by 1.30-1.64%, non-fasting blood glucose diminished by more than 50% to less than 200 mg/dL, and plasma insulin increased Dramatically. \nRat Oral Absorption Assay[1] \nMale Sprague–Dawley (SD) rats (271–303 g; Charles River Laboratories, Raleigh, NC) were housed with free access to standard chow (PMI 5002 block chow) and water, unless otherwise noted. Animals for intravenous treatment groups were surgically implanted with a jugular and femoral vein cannula. Animals for oral treatment groups were surgically implanted with a jugular and portal vein cannula. Food was withheld from rats overnight prior to dosing and was returned at approximately 4 h postdose.\nOral treatment groups received test compounds formulated as a homogeneous suspension in 0.5% HPMC/0.1% Tween via oral gavage at a dose of 10 mg/kg. Blood samples were collected from both jugular and portal vein cannulae at 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, and 8 h postdose. Plasma samples were prepared and stored at −70 °C until analysis. \n\nRat Fecal Drug Recovery[1] \nFecal Recovery[1] \nMale SD rats (Charles River Laboratories, Raleigh, NC) were administered test compounds formulated as a homogeneous suspension in 0.1% HPMC:0.5% Tween via oral gavage at a dose of 10 mg/kg. Fecal samples were collected across the following intervals: 0–6, 6–12, 12–24, 24–36, 36–48, 48–60, and 60–72 h postdose. After each collection interval, the samples were capped and stored at −70 °C until analysis. Prior to analysis, the samples were diluted with 5 volumes of 20% EtOH:80% H2O, soaked overnight at 10 °C, and then homogenized using a Polytron hand-held homogenizer. The homogenates were extracted with 3 volumes of acetonitrile and then centrifuged for 15 min at 2304g and 4 °C. Aliquots of each acetonitrile supernatant was transferred to clean 96-well plates and diluted with an equal volume of water. Drug concentrations were quantified via LC-MS/MS. \n\n\n\n \n \n\n\nView More\n\nAnimals for Efficacy Studies[1] \n\nFecal Collection in Mice[1] \nMale C57BL/6J mice were dosed with vehicle (0.5% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), 0.1% Tween80) or six doses (0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg) of compounds at 0700 and 1500 for one day, and fecal samples were collected for 24 h (0700–0700). Animals were used for up to five studies with one week washout between studies. \n\nFecal Collection in Rat[1] \nMale ZDF rats arrived at seven weeks of age (±3 days). After a one-week acclimation period, rats were assigned to different treatment groups (n = 6–8/group) based upon baseline glucose/vehicle (0.5% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), 0.1%Tween80); one vehicle group for each compound) and six doses (0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 mg/kg) of compounds 20, 45, and 56. All treatments were given via oral gavage twice a day. Fecal samples were collected for 24 h on day 7 of treatment. \n\nMetabolic Effects in ZDF Rats[1] \nMale ZDF rats arrived at seven weeks of age (±3 days). After a one-week acclimation period, rats were anesthetized with isoflurane (Abbott Laboratories, IL) and tail-vein blood samples were collected at 0900 without fasting. To ensure balanced treatment groups, ZDF rats were assigned to six treatment groups based upon baseline glucose/vehicle (0.5% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), 0.1%Tween80) and selected doses of compounds (0.05, 0.1, 0.5, 1, 5, and 10 mg/kg or 0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, and 10 mg/kg for compounds 20 and 45 or 56, respectively). All treatments were given via oral gavage twice a day, and animals were followed for two weeks with blood samples collected from tail vein on day 14 at 0900 without fasting. Plasma samples were stored at −80 °C for further analyses. \n\nMeasurement of Clinical Chemistry Parameters[1] \nPlasma glucose and bile acids in fecal extraction were measured using the Olympus AU640 clinical chemistry analyzer. Glucose test reagents were manufactured by Beckman Coulter. Bile acids reagents were manufactured by Trinity Biotech. HbA1c was measured by the Primus Affinity Ultra2 HPLC system using Primus Affinity Assay reagents. Insulin, total GLP-1 (tGLP-1), PYY, and GIP were assayed using the Meso Scale Discovery (MSD) assay kits. Total Glp-1 was assayed by the MSD Total Glp-1 assay kit and analyzed on an MSD Sector Imager 6000. \n\nFecal Bile Acid Extraction[1] \nFecal samples were air-dried for five days and extracted in methanol–KOH (300 mM) at 60 °C for 24 h. Fecal extract was then mixed with 150 mM Mg2SO4 (1:1). After centrifugation, the supernatant was saved and submitted for bile acids measurement as described above.\n\n 1. Type 2 diabetes animal model experiment: Specific animal species (e.g., mice, rats) were used to establish a type 2 diabetes model. Linerixibat (GSK2330672) was administered via an appropriate route (likely oral, consistent with its nonabsorbable property and later tablet formulation). The dosing frequency and duration were set to evaluate glucose-lowering effects. Glucose levels were measured at specified time points to assess therapeutic efficacy [1] 2. Mouse hepatic CSAD regulation experiment: Male C57BL/6J mice were used (n=5 per group). Linerixibat (GSK2330672) was dissolved in a suitable vehicle (not specified) and administered via oral gavage at a dose of 2 mg/kg twice a day for 1 week. After the treatment period, mice were fasted overnight, then euthanized, and liver tissues were collected. Liver samples were used for mRNA detection (e.g., RT-PCR) and protein detection (e.g., Western blot) to analyze CSAD expression levels [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Nonabsorbable property: Linerixibat (GSK2330672) is explicitly described as a "nonabsorbable" inhibitor. After oral administration, it is not absorbed into the systemic circulation, remaining primarily in the gastrointestinal tract to exert local inhibitory effects on ASBT, with no systemic distribution [1]
2. Local action in the gastrointestinal tract: Due to its nonabsorbable nature, the drug acts specifically on ASBT located in the apical membrane of intestinal epithelial cells, blocking bile acid reabsorption from the intestinal lumen. It is excreted primarily in feces (inferred from nonabsorbable property) [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Adverse events in clinical studies: In a small prior study of Linerixibat (GSK2330672) in PBC patients, diarrhea was the most frequent adverse event (7 cases in the drug group vs. 1 case in the placebo group), while headache was more common in the placebo group (7 cases in the placebo group vs. 6 cases in the drug group). No serious adverse events were reported [3]
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
GSK2330672 has been investigated for the treatment of Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2.
Drug Indication Treatment of primary biliary cholangitis 1. Therapeutic indications: Linerixibat (GSK2330672) was initially developed for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, targeting ASBT to regulate glucose metabolism [1]; later, it was repurposed for the treatment of pruritus in Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC), addressing the unmet need for effective pruritus treatments in PBC (since ursodeoxycholic acid, the first-line PBC treatment, is ineffective for pruritus) [3] 2. Mechanism of action: Linerixibat (GSK2330672) inhibits ASBT-mediated bile acid reabsorption in the intestinal lumen. For type 2 diabetes, this inhibition modulates hepatic cholesterol metabolism and glucose homeostasis; for PBC-related pruritus, it reduces systemic bile acid accumulation (a key cause of pruritus) by promoting bile acid excretion in stool [1, 3] 3. Drug development status: Linerixibat (GSK2330672) was granted "Orphan Status" by the FDA in September 2019. Orphan status is designated for drugs targeting rare diseases, shortening the development process and accelerating availability for patients. It is being developed as an oral tablet and evaluated in a Phase 2b study to determine optimal dose, dosing frequency, safety, and tolerability in PBC patients with moderate to severe pruritus [3] 4. Clinical study design (Phase 2b): The Phase 2b study of Linerixibat (GSK2330672) includes 7 on-site visits and 1 final telephone follow-up with study doctors/nurses. In Canada, the study is conducted at 5 research centers (Montreal, Winnipeg, Calgary, Edmonton, London). Participants receive reimbursement for travel expenses and compensation for meals/refreshments for 2 visits (duration: 2-5 hours per visit) [3] 5. Role in bile acid metabolism research: Linerixibat (GSK2330672) was used as a tool to study the link between bile acid reabsorption and hepatic taurine production. It induced hepatic CSAD expression in mice, confirming that ASBT inhibition couples bile acid metabolism to taurine synthesis [2] |
| 分子式 |
C28H38N2O7S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
546.675527095795
|
| 精确质量 |
546.24
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 61.52; H, 7.01; N, 5.12; O, 20.49; S, 5.87
|
| CAS号 |
1345982-69-5
|
| PubChem CID |
53492727
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as white to off-white solids at room temperature
|
| LogP |
5.708
|
| tPSA |
150.41
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
| 重原子数目 |
38
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
870
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
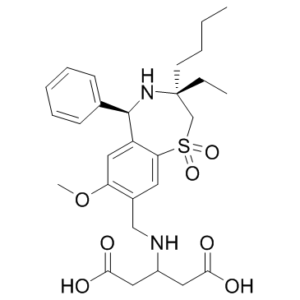
O=C(O)CC(NCC1=C(OC)C=C(C2=C1)[C@@H](C3=CC=CC=C3)N[C@](CC)(CCCC)CS2(=O)=O)CC(O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
CZGVOBIGEBDYTP-VSGBNLITSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C28H38N2O7S/c1-4-6-12-28(5-2)18-38(35,36)24-13-20(17-29-21(14-25(31)32)15-26(33)34)23(37-3)16-22(24)27(30-28)19-10-8-7-9-11-19/h7-11,13,16,21,27,29-30H,4-6,12,14-15,17-18H2,1-3H3,(H,31,32)(H,33,34)/t27-,28-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
3-[[(3R,5R)-3-butyl-3-ethyl-7-methoxy-1,1-dioxo-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-2H-1lambda6,4-benzothiazepin-8-yl]methylamino]pentanedioic acid
|
| 别名 |
1345982-69-5; Linerixibat; GSK2330672; GSK-2330672; Iinerixibat; Linerixibat [USAN]; CHEMBL2387408; Linerixibat (USAN);
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~91.46 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (4.57 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液;超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.57 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.57 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8292 mL | 9.1461 mL | 18.2922 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3658 mL | 1.8292 mL | 3.6584 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1829 mL | 0.9146 mL | 1.8292 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。