| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
结核分枝杆菌的 KatG 细菌过氧化氢酶-过氧化物酶是激活前药异烟肼 (INH) 所必需的 [1]。当 KatG 将异烟酰与 NADH 结合时,会产生异烟酰-NADH 复合物。该复合物可抑制天然烯烃聚酰亚胺-AcpM 底物和植物制造的酶,该复合物与基于烯烃聚酰亚胺的载体化妆品还原酶(称为 InhA)牢固结合。在此过程中,分枝杆菌培养基的细胞壁必须回流。一氧化氮是异烟肼被 KatG 激活时产生的序列之一,也被证明对另一种抗分枝杆菌前药 PA-824 的活性至关重要 [2] [3]。对于分裂速度快的分枝杆菌,异烟肼有杀菌作用;对于生长缓慢的分枝杆菌,具有抑菌作用[4]。
|
|---|---|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Readily absorbed following oral administration; however, may undergo significant first pass metabolism. Absorption and bioavailability are reduced when isoniazid is administered with food. From 50 to 70 percent of a dose of isoniazid is excreted in the urine within 24 hours. ISONIAZID DIFFUSES READILY INTO ALL BODY FLUIDS AND CELLS. THE DRUG IS DETECTABLE IN SIGNIFICANT QUANTITIES IN PLEURAL AND ASCITIC FLUIDS; CONCENTRATIONS IN CEREBROSPINAL FLUID ARE SIMILAR TO THOSE IN THE PLASMA. ISONIAZID PENETRATES WELL INTO CASEOUS MATERIAL. THE CONCENTRATION OF THE AGENT IS INITIALLY HIGHER IN THE PLASMA AND MUSCLE THAN IN THE INFECTED TISSUE, BUT THE LATTER RETAINS THE DRUG FOR A LONG TIME IN QUANTITIES WELL ABOVE THOSE REQUIRED FOR BACTERIOSTASIS. FROM 75 TO 95% OF A DOSE OF ISONIAZID IS EXCRETED IN THE URINE WITHIN 24 HR, MOSTLY AS METABOLITES. Readily absorbed following oral administration; however, may undergo significant first pass metabolism. Absorption and bioavailability were reduced when isoniazid was administered with food. Widely distributed to all fluids and tissues, including cerebrospinal fluid, pleural and ascitic fluids, skin, sputum, saliva, lungs, muscle, and caseous tissue. Crosses the placenta and is excreted in breast milk. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for ISONIAZID (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Primarily hepatic. Isoniazid is acetylated by N -acetyl transferase to N -acetylisoniazid; it is then biotransformed to isonicotinic acid and monoacetylhydrazine. Monoacetylhydrazine is associated with hepatotoxicity via formation of a reactive intermediate metabolite when N-hydroxylated by the cytochrome P450 mixed oxidase system. The rate of acetylation is genetically determined. Slow acetylators are characterized by a relative lack of hepatic N -acetyltransferase. Isoniazid is inactivated in the liver, mainly by acetylation and dehydrazination. Metabolites of the drug include acetylisoniazid, isonicotinic acid, monoacetylhydrazine, diacetylhydrazine, and isonicotinyl glycine. /IN MAN/ ... MOST IMPORTANT METABOLITES OF INH IN URINE /WERE FOUND/ TO BE 1-ACETYL-2-ISONICOTINOYLHYDRAZINE (ACETYL INH), N-ACETYL-N'-ISONICOTINIC ACID, ISONICOTINYLGLYCINE, PYRUVIC ACID ISONICOTINYLHYDRAZONE AND ALPHA-OXOGLUTARIC ACID ISONICOTINYLHYDRAZONE ... . IN VIVO METABOLISM OF INH IN RABBIT ... YIELDS ISONICOTINIC ACID AND AMMONIA, LATTER BEING DERIVED FROM RAPID BREAKDOWN OF HYDRAZINE GROUP ... . Acetylation of acetylisoniazid results in the formation of monoacetylhydrazine which has been shown to be a potent hepatotoxin in animals. Microsomal metabolism of monoacetylhydrazine in animals results in production of a reactive acylating species capable of covalently binding with tissue macromolecules (i.e., liver protein) and subsequently causing hepatic necrosis. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for ISONIAZID (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Isoniazid has known human metabolites that include 3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-[2-(pyridine-4-carbonyl)hydrazinyl]oxane-2-carboxylic acid and isoniazid N-acetyl. Primarily hepatic. Isoniazid is acetylated by N -acetyl transferase to N -acetylisoniazid; it is then biotransformed to isonicotinic acid and monoacetylhydrazine. Monoacetylhydrazine is associated with hepatotoxicity via formation of a reactive intermediate metabolite when N-hydroxylated by the cytochrome P450 mixed oxidase system. The rate of acetylation is genetically determined. Slow acetylators are characterized by a relative lack of hepatic N -acetyltransferase. Route of Elimination: From 50 to 70 percent of a dose of isoniazid is excreted in the urine within 24 hours. Half Life: Fast acetylators: 0.5 to 1.6 hours. Slow acetylators: 2 to 5 hours. Biological Half-Life Fast acetylators: 0.5 to 1.6 hours. Slow acetylators: 2 to 5 hours. Adults (including elderly patients)- Fast acetylators: 0.5 to 1.6 hr. Slow acetylators: 2 to 5 hr. Acute and chronic liver disease: May be prolonged (6.7 hr vs 3.2 hr in controls), Children (age 1.5 to 15 years)-2.3 to 4.9 hours. Neonates-7.8 and 19.8 hours in newborns who received isoniazid transplacentally. The long half-life may be due to the limited acetylation capacity of neonates. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Despite its limited use, isoniazid remains one of the most common causes of serious, idiosyncratic liver injury in the United States. Therapy with isoniazid is associated with transient serum aminotransferase elevations in 10% to 20% of patients, and levels rising above 5 times the upper limit of the normal range (ULN) in 3% to 5%. These enzyme elevations are usually asymptomatic and often resolve even with continuation of therapy without dose adjustment (Case 1 and 2). In addition, isoniazid can also cause clinically apparent acute liver injury with jaundice, which arises in 0.5% to 1% and is fatal in 0.05 to 0.1% of recipients. Rates of hepatic injury vary greatly in the published literature. A major determinant of the variability is probably age. The rates of clinically apparent hepatitis due to isoniazid are estimated at 0.5% in patients 20 to 35 years of age, 1.5% in those 35 to 50 years of age, and 3% or higher in persons above the age of 50 years. Isoniazid hepatotoxicity is rare in children (but still occurs and can be fatal). Other risk factors are preexisting liver disease (hepatitis B or C), concurrent use of rifampin or pyrazinamide, and possibly alcoholism, black race and genetic factors. The typical time to onset of injury ranges from 2 weeks to 6 months, but can be as long as one year and as short as one week. The onset is usuallly insidious and resembles acute viral hepatitis with a prodromal period of nausea, anorexia, abdominal discomfort and fatigue, which is followed by dark urine and jaundice (Case 3 and 4). The pattern of liver enzyme elevations is typically hepatocellular with marked increases in ALT levels (>10 times ULN) and minimal increases in alkaline phosphatase values (usually Likelihood score: A (well established cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Because of the low levels of isoniazid in breastmilk and safe administration directly to infants, it is unlikely to cause adverse reactions in infants, but infants should be monitored for rare instances of jaundice. Giving the maternal once-daily dose before the infant's longest sleep period will decrease the dose the infant receives. The amount of isoniazid in milk is insufficient to treat tuberculosis in the breastfed infant. If breastfed infants are treated with isoniazid, they should also receive pyridoxine 1 mg/kg daily. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other professional organizations state that breastfeeding should not be discouraged in women taking isoniazid. All nursing mothers who are taking isoniazid should take 25 mg of oral pyridoxine daily. A study of nursing African mothers with concurrent HIV and tuberculosis infections found that those receiving isoniazid had an increased risk of niacin deficiency (pellagra). The authors suggested that a multivitamin supplement might be advisable during isoniazid therapy in populations with undernutrition. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants In one uncontrolled study, 6-beta-hydroxycortisol levels were measured in 10 male infants whose mothers had tuberculosis and took ethambutol 1 gram daily plus isoniazid 300 mg daily and the infants of mothers (apparently without tuberculosis) who took no chronic drug therapy. The infants of mothers taking the antituberculars had consistently lower 6-beta-hydroxycortisol levels on 8 occasions at 15-day intervals from 90 to 195 days of age, but these differences were statistically significant on days 120 and 195 only. The authors attributed the lower levels to inhibition of hepatic metabolism of cortisol to 6-beta-hydroxycortisol by the antitubercular drugs in milk. However, ethambutol is not known to inhibit drug metabolism, so if the effect occurs it is more likely caused by isoniazid. One woman taking rifampin 450 mg, isoniazid 300 mg and ethambutol 1200 mg daily during pregnancy and rifampin 450 mg and isoniazid 300 mg for the first 7 months of lactation (extent not stated). The infant was born with mildly elevated serum liver enzymes which persisted for to 1 (alanine transferase) to 2 years (aspartate transaminase), but had no other adverse reactions. Isoniazid was used as part of multi-drug regimens to treat 2 pregnant women with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy and postpartum. Their two infants were breastfed (extent and duration not stated). At age 3.9 and 4.6 years, the children were developing normally except for a mild speech delay in one. Two mothers in Türkiye were diagnosed with tuberculosis at the 30th and 34th weeks of pregnancy. They immediately started isoniazid 300 mg, rifampin 600 mg, pyridoxine 50 mg daily for 6 months, plus pyrazinamide 25 mg/kg and ethambutol 25 mg/kg daily for 2 months. Both mothers breastfed their infants (extent not stated). Their infants were given isoniazid 5 mg/kg daily for 3 months prophylactically. Tuberculin skin tests were negative after 3 months and neither infant had tuberculosis at 1 year of age. No adverse effects of the drugs were mentioned. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Very low (0-10%) |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Isoniazid appears as odorless colorless or white crystals or white crystalline powder. Taste is slightly sweet at first and then bitter. pH (1% aqueous solution) 5.5-6.5. pH (5% aqueous solution) 6-8. (NTP, 1992)
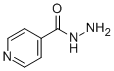
Isoniazide is a carbohydrazide obtained by formal condensation between pyridine-4-carboxylic acid and hydrazine. It has a role as an antitubercular agent and a drug allergen. It is functionally related to an isonicotinic acid. Isoniazid is an antibacterial prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention and treatment of tuberculosis (TB). TB can be an opportunistic infection (OI) of HIV. Antibacterial agent used primarily as a tuberculostatic. It remains the treatment of choice for tuberculosis. Isoniazid is an Antimycobacterial. Isoniazid is the most reliable and most commonly used medication for tuberculosis. Isoniazid therapy is often associated with minor, transient and asymptomatic elevations in serum aminotransferase levels but, more importantly, isoniazid is a well known cause of acute clinically apparent liver injury which can be severe and is sometimes fatal. Isoniazid has been reported in Aspergillus ochraceopetaliformis, Ganoderma colossus, and other organisms with data available. Isoniazid is a synthetic derivative of nicotinic acid with anti-mycobacterial properties. Although its mechanism of action is still unclear, isoniazid appears to block the synthesis of mycolic acids, major components of the mycobacterial cell wall. This agent is only active against actively growing mycobacteria because, as a pro-drug, it requires activation in susceptible mycobacterial species. Isoniazid also interferes with mycobacterial metabolism of vitamin B6. Resistance occurs due to decreased bacterial wall penetration. (NCI04) Antibacterial agent used primarily as a tuberculostatic. It remains the treatment of choice for tuberculosis. Antibacterial agent used primarily as a tuberculostatic. It remains the treatment of choice for tuberculosis. See also: Isoniazid; rifampin (component of); Stevia rebaudiuna Leaf (part of); Isoniazid; pyrazinamide; rifampin (component of). Drug Indication Isoniazid is used for the treatment of all forms of tuberculosis in which organisms are susceptible. It is also used in combination with rifampin and pyrazinamide. For active immunisation of chicks from 1 day of age to reduce clinical signs (diarrhoea), intestinal lesions and oocysts output associated with coccidiosis caused by Eimeria acervulina, Eimeria brunetti, Eimeria maxima, Eimeria necatrix and Eimeria tenella. , Mechanism of Action Isoniazid is a prodrug and must be activated by bacterial catalase. Specficially, activation is associated with reduction of the mycobacterial ferric KatG catalase-peroxidase by hydrazine and reaction with oxygen to form an oxyferrous enzyme complex. Once activated, isoniazid inhibits the synthesis of mycoloic acids, an essential component of the bacterial cell wall. At therapeutic levels isoniazid is bacteriocidal against actively growing intracellular and extracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms. Specifically isoniazid inhibits InhA, the enoyl reductase from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, by forming a covalent adduct with the NAD cofactor. It is the INH-NAD adduct that acts as a slow, tight-binding competitive inhibitor of InhA. Although the mechanism of action of isoniazid is unknown, several hypotheses have been proposed. These include effects on lipids, nucleic acid biosynthesis, and glycolysis. ... /It has been suggested that/ a primary action of isoniazid /is/ to inhibit the biosynthesis of mycolic acids, important constituents of the mycobacterial cell wall. Because mycolic acids are unique to mycobacteria, this action would explain the high degree of selectivity of the antimicrobial activity of isoniazid. Exposure to isoniazid leads to a loss of acid fastness and a decrease in the quantity of methanol-extractable lipid of the microorganisms. Isoniazid is bacteriostatic for "resting" bacilli but is bactericidal for rapidly dividing microorganisms. The minimal tuberculostatic concentration is 0.025 to 0.05 ug/ml. |
| 分子式 |
C6H7N3O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
137.1393
|
| 精确质量 |
137.058
|
| CAS号 |
54-85-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Isoniazid-d4;774596-24-6
|
| PubChem CID |
3767
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 熔点 |
171-173 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
>250°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.584
|
| LogP |
-0.89
|
| tPSA |
68.01
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
1
|
| 重原子数目 |
10
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
120
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
QRXWMOHMRWLFEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H7N3O/c7-9-6(10)5-1-3-8-4-2-5/h1-4H,7H2,(H,9,10)
|
| 化学名 |
pyridine-4-carbohydrazide
|
| 别名 |
Isoniazid HyzydIsovitIsonicotinylhydrazideNydrazidHydra
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~364.59 mM)
H2O : ~33.33 mg/mL (~243.04 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 150 mg/mL (1093.77 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 7.2918 mL | 36.4591 mL | 72.9182 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.4584 mL | 7.2918 mL | 14.5836 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.7292 mL | 3.6459 mL | 7.2918 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT02043314 | COMPLETED | Drug: Isoniazida | Tuberculosis | Oswaldo Cruz Foundation | 2008-10 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00397709 | TERMINATED | Drug: I ( isoniazid), II (isoniazid + rifampin ) | Tuberculosis | Hospital Virgen de la Luz | 1996-03 | Phase 4 |
| NCT00571753 | TERMINATED | Drug: isoniazid Drug: isoniazid |
Pulmonary Tuberculosis | University of Cologne | 2008-06 | Phase 3 |
| NCT00164281 | COMPLETED | Drug: Isoniazid | HIV Infections Tuberculosis |
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention | 2004-11 | Phase 4 |
| NCT02980016 | COMPLETED | Drug: rifapentine + isoniazid Drug: Isoniazid |
HIV Tuberculosis |
The Aurum Institute NPC | 2016-11 | Phase 3 |