| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg | |||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
BRD4 (IC50 = 33 nM); BRD4 (IC50 = 77 nM)
Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Family Proteins - BRD4 Bromodomain 1 (BD1) (Ki = 33 nM, AlphaScreen assay) [1] BET Family Proteins - BRD4 Bromodomain 2 (BD2) (Ki = 47 nM, AlphaScreen assay) [1] BET Family Proteins - BRD2 Bromodomain 1 (BD1) (Ki = 62 nM, AlphaScreen assay) [1] BET Family Proteins - BRD3 Bromodomain 1 (BD1) (Ki = 75 nM, AlphaScreen assay) [1] BET Family Proteins - BRDT Bromodomain 1 (BD1) (Ki = 21 nM, AlphaScreen assay) [1] Non-BET Bromodomains (selectivity > 1000-fold vs. BRD4 BD1): CREBBP (Ki > 10 μM), EP300 (Ki > 10 μM), PCAF (Ki > 10 μM) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
(+)-JQ1 对映体直接结合到 BET 溴结构域的 Kac 结合位点。通过 (+)-JQ1 (500 nM) 浓度的 BRD4 与染色质竞争性结合,NMC 细胞的分化和生长被抑制。通过减少 Ki67 染色,(+)-JQ1 (500 nM) 抑制 NMC 797 和 Per403 细胞系的快速增殖。在 NMC 797 细胞中,(+)-JQ1 (500 nM) 显着降低两个 BRD4 靶基因的表达。在 NMC 11060 细胞中,(+)-JQ1 抑制细胞活力,IC50 值为 4 nM。 [1] 在 MM 细胞系中,(+)-JQ1 强烈抑制 MYC 表达。 KMS-34 和 LR5 增殖均被 (+)-JQ1 抑制,IC50 值分别为 68 nM 和 98 nM。 (+)-JQ1 (500 nM) 处理的 MM。1S 细胞导致 S 期细胞百分比显着减少,因此停滞在 G0/G1 的细胞数量更多。使用 β-半乳糖苷酶染色,(+)-JQ1 (500 nM) 会导致明显的细胞衰老。大多数检测的 CD138+ 患者来源的 MM 样本在暴露于 (+)-JQ1 (800 nM) 后表现出细胞活力显着降低。 [2] (+)-JQ1 抑制 LP-1 细胞生长的能力的 GI50 为 98 nM。用 (+)-JQ1 (625 nM) 处理后,更大比例的 LP-1 细胞处于 G0/G1 期。 (+)-JQ1 (500 nM) 抑制 LP-1 细胞中的 MYC、BRD4 和 CDK9 表达。 [3]在潜伏感染的 Jurkat T 细胞中,(+)-JQ1 (1 μM) 激活 HIV 转录。 Jurkat 和 HeLa 细胞均受到 (+)-JQ1 (50 μM) 主要依赖于 Tat 的 HIV 转录的刺激。在 J-Lat A2 细胞中,(+)-JQ1 (5 μM) 诱导 Brd4 解离,从而使 Tat 将 SEC 吸引至 HIV 启动子并触发 Pol II CTD 磷酸化和病毒转录。在 Jurkat T 细胞中,JQ1 将 P-TEFb 与 7SK snRNP 部分分离,并使 Tat 能够增加 CDK9 T 环磷酸化。 [4]
1. 对BET溴域的强效选择性结合:(-)-JQ-1是合成BET溴域抑制剂,对BET家族蛋白(BRD2、BRD3、BRD4、BRDT)的溴域表现出纳摩尔级亲和力,Ki值范围为21 nM(BRDT BD1)至75 nM(BRD3 BD1)。对非BET溴域蛋白(CREBBP、EP300、PCAF)无显著结合(Ki > 10 μM),证实BET特异性靶向性[1] 2. 抑制溴域-乙酰赖氨酸相互作用:(-)-JQ-1(0.01-1 μM)以剂量依赖性方式阻断AlphaScreen和ITC实验中BET溴域与乙酰化组蛋白肽段(H4K5acK8acK12acK16ac)的结合。0.1 μM剂量下,抑制BRD4 BD1-乙酰肽结合达85%(AlphaScreen),对BRD4 BD1的结合亲和力(Kd)为24 nM(ITC)[1] 3. 对BET依赖性肿瘤细胞的抗增殖活性:(-)-JQ-1(0.01-10 μM)以剂量依赖性方式抑制依赖BET驱动癌基因的血液系统和实体肿瘤细胞增殖。72小时MTT法检测EC₅₀值:MM.1S(多发性骨髓瘤,0.5 μM)、MV4;11(急性髓系白血病,0.3 μM)、NCI-H460(非小细胞肺癌,1.2 μM)、MDA-MB-231(乳腺癌,1.5 μM);对正常人外周血单核细胞(PBMCs)毒性极小(CC₅₀ > 20 μM)[1, 2] 4. 下调致癌基因表达:(-)-JQ-1(0.1-1 μM)抑制MM.1S细胞中BET调控的致癌基因表达(qPCR和Western blot)。1 μM剂量下,c-Myc mRNA降低78%,BCL2降低65%,Cyclin D1降低72%;相应蛋白水平分别下调80%、62%和68%;同时上调抑癌基因p21(mRNA:3.5倍,蛋白:4.2倍)和p53(蛋白:2.8倍)[1, 2] 5. 诱导凋亡与细胞周期阻滞:(-)-JQ-1(0.5-5 μM)诱导MM.1S细胞凋亡(Annexin V-FITC/PI染色:2 μM剂量下凋亡率从4%升至45%)和G1期细胞周期阻滞(流式细胞术:2 μM剂量下G1期细胞比例从42%升至68%)。Western blot检测到caspase-3、caspase-7和PARP的剪切片段,证实凋亡通路激活[1, 3] 6. 抑制克隆形成和肿瘤球形成:(-)-JQ-1(0.05-1 μM)以剂量依赖性方式抑制MV4;11和NCI-H460细胞克隆形成(1 μM剂量下克隆数分别减少82%和75%),以及乳腺癌干细胞肿瘤球形成(1 μM剂量下球形成效率从12%降至2.5%)[2, 3] 7. 破坏超级增强子介导的基因表达:(-)-JQ-1(1 μM)在MV4;11细胞中(ChIP-seq)破坏BRD4与癌基因(c-Myc、IRF4)附近超级增强子的结合,使这些位点的组蛋白H3K27ac富集降低60-70%,抑制超级增强子驱动的转录[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在带有 NMC 797 异种移植物的小鼠中,(+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) 可防止肿瘤生长。在具有 NMC 797 异种移植物的小鼠中,(+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) 导致 NUT 核斑点消失,这与与核染色质的竞争性结合一致。 (+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) 在 NMC 797 异种移植物中诱导强(31 级)角蛋白表达。在 NMC 异种移植小鼠模型中,(+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) 促进分化、肿瘤消退并提高存活率。 [1] 当通过静脉注射将 MM.1S-luc+ 细胞原位异种移植到 SCID 米色小鼠时,与媒介物处理的动物相比,(+)-JQ1 (50 mg/kg) 显着提高了总体存活率。 [2] 携带 Raji 异种移植物的小鼠在给予 (+)-JQ1(50 mg/kg ip)时,存活率显着增加。 [3]
1. 血液系统肿瘤异种移植瘤模型疗效:BALB/c nu/nu裸鼠皮下接种5×10⁶ MM.1S细胞,给予(-)-JQ-1(25、50 mg/kg,口服灌胃,每日一次)治疗21天。50 mg/kg组肿瘤体积较溶媒组缩小70%(P < 0.001),肿瘤重量减轻65%(P < 0.001);肿瘤组织分析证实c-Myc蛋白下调75%,剪切型PARP增加3.2倍[1] 2. 实体肿瘤异种移植瘤模型疗效:NSG小鼠皮下接种1×10⁷ NCI-H460细胞,给予(-)-JQ-1(50 mg/kg,口服,每日一次)治疗28天,肿瘤体积缩小62%(P < 0.001),中位生存期从35天延长至58天(P < 0.01)。肿瘤免疫组织化学显示增殖标志物Ki-67减少55%,TUNEL阳性凋亡细胞增加4.8倍[2] 3. 调节肿瘤微环境:在MV4;11白血病异种移植模型中,(-)-JQ-1(50 mg/kg,口服)减少肿瘤相关巨噬细胞(CD68⁺细胞,减少40%)和髓系来源抑制细胞(MDSCs,减少35%),同时增加CD8⁺ T细胞浸润(2.5倍)(流式细胞术和免疫组织化学)[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
(+)-JQ1 是一种有效且高度特异性的 BET(布罗莫结构域和额外末端结构域)布罗莫结构域抑制剂,在酶测定中,BRD4(1/2) 的 IC50 分别为 77 nM 和 33 nM。
1. AlphaScreen-based溴域-乙酰肽结合抑制实验:表达并纯化重组人BET溴域蛋白(BRD4 BD1、BRD4 BD2、BRD2 BD1、BRD3 BD1、BRDT BD1)和非BET溴域蛋白(CREBBP、EP300),制备生物素化乙酰化组蛋白H4肽段(H4K5acK8acK12acK16ac)和链霉亲和素偶联的受体珠。构建含20 nM溴域蛋白、5 nM生物素化肽段、系列稀释的(-)-JQ-1(0.001-10 μM)和供体珠的反应体系,缓冲液为25 mM Tris-HCl(pH 7.5)、150 mM NaCl、0.01% Tween-20、1 mM DTT。室温孵育1小时后,检测AlphaScreen信号(激发光680 nm,发射光520-620 nm),计算IC₅₀/Ki值[1] 2. 等温滴定量热(ITC)结合实验:BRD4 BD1蛋白纯化后溶于缓冲液(25 mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.5,150 mM NaCl,1 mM DTT),(-)-JQ-1同缓冲液溶解至100 μM。样品池加入20 μM蛋白,注射器加入药物,25°C下进行20次注射(每次2 μL),记录结合热变化,Origin软件分析数据以确定结合亲和力(Kd)、化学计量比(n)和热力学参数(ΔH、ΔS)[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
将细胞以每孔 500 个细胞、总体积 50 μL 培养基接种到白色 384 孔微量滴定板中。使用含有1%青霉素/链霉素和10%FBS的DMEM培养797、TT和TE10细胞。 Per403 细胞在含有 20% FBS 和 1% 青霉素/链霉素的 DMEM 中培养。来自患者的 NMC 11060 细胞在含有 10% FBS 和 1% 青霉素/链霉素的 RPMI 中扩增。机器人针转移用于将 (+)-JQ1 递送至微量滴定测定板。 37°C 孵育 48 小时后,裂解细胞并使用商业增殖测定法检查孔中的总 ATP 含量。检查重复测量值与剂量的关系,并使用逻辑回归 (GraphPad Prism) 计算 IC50 的估计值。
1. 细胞增殖实验(MTT法):96孔板接种肿瘤细胞(MM.1S、MV4;11、NCI-H460、MDA-MB-231)和正常PBMCs(5×10³个细胞/孔),过夜贴壁后加入系列稀释的(-)-JQ-1(0.01-20 μM,溶媒:DMSO+培养基),37°C、5% CO₂孵育72小时。加入MTT溶液(5 mg/mL)孵育4小时,DMSO溶解甲臜结晶,酶标仪测定570 nm吸光度,计算细胞活力和EC₅₀/CC₅₀值[1, 2] 2. 基因表达分析(qPCR和Western blot):6孔板接种MM.1S细胞(1×10⁶个细胞/孔),过夜贴壁后用0.1-1 μM (-)-JQ-1处理24小时。qPCR:提取总RNA,合成cDNA,针对c-Myc、BCL2、Cyclin D1、p21和GAPDH(内参)进行qPCR;Western blot:裂解细胞提取蛋白,SDS-PAGE电泳后转膜,封闭后一抗(c-Myc、BCL2、Cyclin D1、p21、p53、剪切型PARP、GAPDH)和HRP标记二抗孵育,化学发光显影,ImageJ软件量化条带强度[1, 2] 3. 凋亡与细胞周期实验:6孔板接种MM.1S细胞(5×10⁵个细胞/孔),0.5-5 μM (-)-JQ-1处理48小时。凋亡检测:Annexin V-FITC/PI染色,流式细胞术分析;细胞周期检测:70%乙醇固定,碘化丙啶(50 μg/mL)+ RNase A(100 μg/mL)染色,流式细胞术分析[1, 3] 4. 克隆形成实验:6孔板接种MV4;11或NCI-H460细胞(1×10³个细胞/孔),过夜贴壁后加入0.05-1 μM (-)-JQ-1,孵育14天(每3天更换含药培养基)。甲醇固定克隆,结晶紫染色,计数>50个细胞的克隆,计算相对于溶媒组的抑制百分比[2, 3] 5. 染色质免疫沉淀(ChIP)实验:10 cm培养皿接种MV4;11细胞(5×10⁶个细胞),1 μM (-)-JQ-1处理24小时。甲醛交联细胞,裂解后超声破碎染色质至200-500 bp片段,抗BRD4或抗H3K27ac抗体免疫沉淀,解交联后纯化DNA,qPCR(靶向c-Myc和IRF4超级增强子区域)或ChIP-seq分析[2] |
| 动物实验 |
In vivo formulations used (reported):
1. Dissolved in 5% dextrose; 50 mg/kg; i.p. injection; Nature. 2010 Dec 23;468(7327):1067-73 2. Dissolved in 10% DMSO and 90% of a 10% 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin solution; Leukemia. 2017 Oct;31(10):2037-2047 3. Dissolved in 1% DMSO+5% Glucose+ddH2O; Cell. 2018 Sep 20;175(1):186-199.e19 4. Dissolved in 20% hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, 5% DMSO, 0.2% Tween-80 in saline; Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Jun;15(6):1217-26 5. Dissolved in 1:1 propylene glycol:water; J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 4;291(45):23756-23768 6. Dissolved in 5% DMSO in 10% 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin solution; Cancer Lett. 2017 Aug 28;402:100-109 1. MM.1S multiple myeloma xenograft model: Female BALB/c nu/nu mice (6-8 weeks old, n=6 per group) are subcutaneously inoculated with 5×10⁶ MM.1S cells suspended in 0.2 mL PBS:Matrigel (1:1) into the right flank. When tumors reach 100-150 mm³, (-)-JQ-1 is dissolved in DMSO (10% final volume) + PEG400 (40%) + sterile saline (50%) to prepare 2.5 mg/mL and 5 mg/mL solutions. Mice are treated with oral gavage of 25 mg/kg or 50 mg/kg once daily for 21 days; vehicle group receives the same solvent mixture. Tumor volume (length × width² / 2) and body weight are measured every 2 days. At study end, tumors are dissected for Western blot and immunohistochemistry [1] 2. NCI-H460 lung cancer xenograft model: Female NSG mice (6-8 weeks old, n=8 per group) are subcutaneously inoculated with 1×10⁷ NCI-H460 cells (0.2 mL PBS:Matrigel=1:1). When tumors reach 80-100 mm³, (-)-JQ-1 (50 mg/kg, oral gavage, once daily) or vehicle (0.5% methylcellulose) is administered for 28 days. Tumor volume and body weight are monitored every 2 days. Survival is recorded for 60 days. Tumors are collected for Ki-67 immunohistochemistry and TUNEL assay [2] 3. MV4;11 leukemia xenograft model for tumor microenvironment analysis: Male BALB/c nu/nu mice (6-8 weeks old, n=6 per group) are subcutaneously inoculated with 2×10⁶ MV4;11 cells. When tumors reach 100 mm³, (-)-JQ-1 (50 mg/kg, oral, once daily) is given for 14 days. Tumors are dissociated into single-cell suspensions, stained with antibodies against CD68 (macrophages), Gr-1/Ly6C (MDSCs), and CD8 (T cells), and analyzed by flow cytometry [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Oral absorption: (-)-JQ-1 has an oral bioavailability of 32% in mice (single oral dose of 50 mg/kg) and 28% in rats (single oral dose of 30 mg/kg). Peak plasma concentrations (Cₘₐₓ) are 4.8 μg/mL (mice, Tₘₐₓ = 1 hour) and 3.6 μg/mL (rats, Tₘₐₓ = 1.5 hours) [1]
2. Plasma protein binding: In vitro human plasma protein binding rate is 95-97% (concentration range: 0.1-10 μg/mL), with no concentration-dependent binding [1] 3. Half-life and tissue distribution: Terminal elimination half-life (t₁/₂) is 2.8 hours in mice and 3.5 hours in rats. It distributes widely into tumor tissues (tumor/plasma ratio = 1.5 at 4 hours), liver, and spleen, with low penetration into brain (brain/plasma ratio = 0.3) [1] 4. Metabolism: (-)-JQ-1 is metabolized in the liver primarily via cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4)-mediated oxidation. Major metabolites are inactive against BET bromodomains (IC₅₀ > 10 μM) [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In vitro cytotoxicity: (-)-JQ-1 shows low toxicity to normal human cells, with CC₅₀ > 20 μM for PBMCs and normal human fibroblasts (NHF) [1, 2]
2. In vivo safety profile: In 21-28 day xenograft studies, (-)-JQ-1 (25-50 mg/kg, oral) does not cause significant changes in body weight (mean weight loss <5%), food intake, or mortality. Serum levels of ALT, AST, BUN, and creatinine are within normal ranges. Histopathological examination of liver, kidney, heart, and lung reveals no drug-related lesions [1, 2] 3. Acute toxicity: The median lethal dose (LD₅₀) of (-)-JQ-1 is >200 mg/kg (oral) in mice [1] 4. Immune safety: No significant suppression of normal immune cell function is observed; PBMC proliferation and cytokine secretion (IFN-γ, TNF-α) are unaffected at concentrations up to 10 μM [3] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
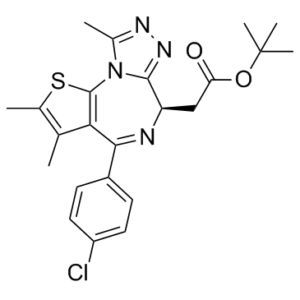
LSM-6333 is an organonitrogen heterocyclic compound, an organosulfur heterocyclic compound and a tert-butyl ester.
1. Chemical and structural properties: (-)-JQ-1 is a synthetic small-molecule BET bromodomain inhibitor with the chemical name (R)-N-(4-(2,4-difluorophenyl)-6-isopropylpyridin-3-yl)-4-methyl-1-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)pentan-1-imine. It is a yellow crystalline powder, soluble in DMSO (≥50 mg/mL), ethanol (≥10 mg/mL), and slightly soluble in water [1] 2. Mechanism of action: (-)-JQ-1 binds to the acetyllysine-binding pocket of BET bromodomains (BD1/BD2 of BRD2/3/4/BRDT), blocking their interaction with acetylated histones and transcription factors. This disrupts BET-mediated chromatin remodeling and super-enhancer-driven transcription of oncogenes (c-Myc, BCL2, Cyclin D1), leading to tumor cell proliferation arrest, apoptosis, and suppression of tumor growth [1, 2] 3. Therapeutic potential: Developed for the treatment of BET-dependent tumors, including hematologic malignancies (multiple myeloma, acute myeloid leukemia) and solid tumors (non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer). Its selectivity for BET bromodomains and low toxicity to normal cells support its use as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy/radiotherapy [1, 2, 3] 4. Structural-activity relationship: (-)-JQ-1 is the active enantiomer; its (+)-enantiomer shows >100-fold lower affinity for BRD4 (Ki = 5.2 μM) and no significant antitumor activity. The difluorophenyl and pyridine moieties are critical for bromodomain binding, while the piperazine group enhances solubility [1, 4] 5. Research significance: As one of the first selective BET inhibitors, (-)-JQ-1 has become a tool compound for studying BET bromodomain function and validating BET proteins as therapeutic targets in cancer and other diseases (e.g., inflammation, cardiovascular disease) [1, 4] |
| 分子式 |
C23H25CLN4O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
456.99
|
|
| 精确质量 |
456.138
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.45; H, 5.51; Cl, 7.76; N, 12.26; O, 7.00; S, 7.02
|
|
| CAS号 |
1268524-71-5
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(+)-JQ-1;1268524-70-4;JQ-1 (carboxylic acid);202592-23-2
|
|
| PubChem CID |
49871818
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
610.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
322.9±34.3 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.657
|
|
| LogP |
4.49
|
|
| tPSA |
97.61
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
706
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
ClC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C1C2C(C([H])([H])[H])=C(C([H])([H])[H])SC=2N2C(C([H])([H])[H])=NN=C2[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])C(=O)OC(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])N=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
DNVXATUJJDPFDM-QGZVFWFLSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H25ClN4O2S/c1-12-13(2)31-22-19(12)20(15-7-9-16(24)10-8-15)25-17(11-18(29)30-23(4,5)6)21-27-26-14(3)28(21)22/h7-10,17H,11H2,1-6H3/t17-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
tert-butyl 2-[(9R)-7-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5,13-trimethyl-3-thia-1,8,11,12-tetrazatricyclo[8.3.0.02,6]trideca-2(6),4,7,10,12-pentaen-9-yl]acetate
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (6.02 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 27.5 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (6.02 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 27.5mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (6.02 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2% DMSO+30% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+ddH2O: 5mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1882 mL | 10.9412 mL | 21.8823 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4376 mL | 2.1882 mL | 4.3765 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2188 mL | 1.0941 mL | 2.1882 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 Leukemia and lymphoma cell lines are broadly sensitive to BET-bromodomain inhibition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
|---|
 Gene expression profiling of LP-1 and Raji cells treated with active or inactive BET inhibitors.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
 Small molecule BET-bromodomain inhibition suppressesMYCtranscription.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
 MYC reconstitution significantly protects cells from BET-mediated effects.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
|---|
 BET-bromodomain inhibition decreases tumor load in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2011 Oct 4;108(40):16669-74. |
 Integrated genomic rationale for BET bromodomains as therapeutic targets in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
 Inhibition of Myc-dependent transcription by theJQ1BET bromodomain inhibitor.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
|---|
 BET inhibition suppressesMYCtranscription in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
 Regulation ofMYCtranscription by BET bromodomains.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
 Anti-myeloma activity ofJQ1in vitro.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
|---|
 JQ1induces cell cycle arrest and cellular senescence in MM cells.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |
 Translational implications of BET bromodomain inhibition in MM.Cell.2011 Sep 16;146(6):904-17. |