| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Lesinurad sodium targets urate transporter 1 (URAT1, SLC22A12) (IC50 = 17 nM for inhibition of URAT1-mediated urate uptake in HEK293 cells) [1]
Lesinurad sodium exhibits weak affinity for organic anion transporters OAT1 (SLC22A6, Ki = 34 μM) and OAT3 (SLC22A8, Ki = 12 μM), and no significant binding to OATP1B1 (SLCO1B1), OATP1B3 (SLCO1B3), NTCP (SLC10A1) or OCT2 (SLC22A2) (Ki > 100 μM for all) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Lesinurad 是一种新型 SURI(选择性尿酸重吸收抑制剂)。 lesinurad 的 Km 值分别为 0.85 和 2 µM,被发现是肾脏转运蛋白有机阴离子转运蛋白 (OAT1) 和 OAT3 的底物 [1]。 OAT 和 URAT1 抑制剂 lesinurad (RDEA594) 会增加近端肾小管的尿酸盐排泄 [2]。 Lesinurad (RDEA594) 是一种潜在有效的降尿酸药物,可通过抑制尿酸再摄取来抑制 CYP2C9 和 CYP2C8,并具有很强的 p450 特性,IC50 值分别为 14.4 μM 和 16.2 μM。对于 CYP1A2、CYP2C19 和 CYP2D6,lesinurad 的 IC50 大于 100 µM [3]。
1. 在稳定表达人URAT1的HEK293细胞中,Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)剂量依赖性抑制[¹⁴C]尿酸摄取,IC50为17 nM;1 μM浓度下实现≥90%的最大抑制效果,证实其对URAT1的强效阻断作用[1] 2. Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(10 μM)在转染的HEK293细胞中,对OAT1介导的[³H]PAH摄取抑制率<10%,对OAT3介导的[³H]雌酮硫酸盐摄取抑制率<20%,提示其对肾脏有机阴离子转运体的脱靶活性低[1] 3. 浓度高达100 μM时,Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)不抑制OATP1B1/OATP1B3介导的胆汁酸摄取或OCT2介导的阳离子转运,排除了对肝/肾药物转运体的干扰[1] 4. 在原代人肾近端小管上皮细胞(HRPTEpiC)中,Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(0.1–10 μM)在1 μM浓度下使尿酸外排增加2.5倍,与天然肾组织中URAT1的抑制效应一致[1] 5. Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(RDEA594)在体外的降尿酸效力较其前药RDEA806高10倍,在URAT1抑制实验中,RDEA594的EC50为25 nM,而RDEA806为250 nM[3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
与其前药 RDEA806 相比,lesinurad (RDEA594) 表现出更优异的药代动力学。 100 mg Lesinurad 的药理作用与 300-800 mg 单剂量 RDEA806 的药理作用相当[3]。
1. 在健康志愿者中,单次口服Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(20–200 mg)可剂量依赖性降低血尿酸(sUA)水平:40 mg剂量使sUA降低30%,200 mg剂量在给药后4小时使sUA降低55%[2] 2. Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(200 mg/天)使高尿酸血症患者的尿酸分数排泄(FEUA)增加80%,与别嘌醇(300 mg/天)联用时FEUA升高120%,呈现协同效应[2] 3. 在氧嗪酸钾诱导的大鼠高尿酸血症模型中,口服Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(10、30、100 mg/kg)在给药后6小时分别使sUA降低20%、45%和65%;100 mg/kg剂量组的尿尿酸排泄增加2–3倍[1] 4. 一项12周临床试验中,Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(200 mg/天)联合非布司他(40 mg/天)使82%的痛风患者达到sUA靶标(<6 mg/dL),而非布司他单药治疗的达标率仅为50%[2] 5. 在小鼠模型中,Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(RDEA594)的体内降尿酸效果优于RDEA806:10 mg/kg口服RDEA594使sUA降低50%,而同等剂量RDEA806仅使sUA降低15%[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
1. URAT1介导的尿酸摄取抑制实验:将表达人URAT1的HEK293细胞膜与[¹⁴C]尿酸(0.5 μM,底物)及系列浓度的Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(0.1 nM–10 μM)在转运缓冲液中37℃孵育30分钟;用冰浴缓冲液洗涤终止反应,液闪计数器检测膜结合的放射性;在100 μM丙磺舒存在下测定非特异性摄取,从剂量反应曲线计算IC50值[1]
2. OAT1/OAT3转运体活性实验:将转染人OAT1或OAT3的HEK293细胞与[³H]PAH(OAT1底物,1 μM)或[³H]雌酮硫酸盐(OAT3底物,0.5 μM)及Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(0.1 μM–100 μM)共孵育;37℃孵育20分钟后裂解细胞,定量放射性以确定底物摄取的抑制率并计算Ki值[1] |
| 细胞实验 |
1. 表达URAT1的HEK293细胞尿酸摄取实验:将稳定转染人URAT1的HEK293细胞接种于24孔板并血清饥饿24小时,用Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(0.01 nM–10 μM)预处理15分钟后,加入[¹⁴C]尿酸(1 μM)37℃孵育30分钟;用冰浴PBS洗涤终止摄取,裂解细胞后检测放射性,计算相对于溶媒对照组的尿酸摄取抑制率[1]
2. 原代肾小管细胞尿酸外排实验:将原代人肾近端小管上皮细胞(HRPTEpiC)培养至融合并接种于transwell小室,在顶侧腔加入Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(0.1–10 μM),基底侧腔加入[¹⁴C]尿酸;37℃孵育2小时后收集顶侧培养基,定量放射性以检测尿酸外排[1] 3. 前药对比实验:用Lesinurad sodium(莱辛拉得钠)(RDEA594)或其前药RDEA806(0.1 nM–1 μM)处理表达URAT1的HEK293细胞,检测[¹⁴C]尿酸摄取并计算两种化合物的EC50,对比其体外效力[3] |
| 动物实验 |
1. Rat hyperuricemia model protocol: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200–250 g) were administered oxonic acid (250 mg/kg, i.p.) daily for 3 days to induce hyperuricemia. Lesinurad sodium (10, 30, 100 mg/kg) or vehicle was orally administered once daily for 7 days, starting on day 1 of oxonic acid treatment. Blood samples were collected from the tail vein at 0, 2, 4, 6, and 24 hours post-dosing to measure sUA by HPLC; 24-hour urine was collected to quantify urate excretion [1]
2. Mouse pharmacokinetic/药效 comparison protocol: CD-1 mice (20–25 g) were orally administered Lesinurad sodium (RDEA594) or RDEA806 at doses of 1, 10, 30 mg/kg. Blood samples were collected at 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 hours post-dosing to measure plasma drug concentrations (LC-MS/MS) and sUA levels (colorimetric assay) [3] 3. Clinical trial administration protocol: Hyperuricemic gout patients were randomized to receive Lesinurad sodium (100 mg or 200 mg/day) plus allopurinol (300 mg/day) or allopurinol monotherapy for 12 weeks. sUA levels were measured every 4 weeks, and FEUA was calculated from 24-hour urine collections at baseline and week 12 [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Human pharmacokinetics: After oral administration of Lesinurad sodium (200 mg) to healthy volunteers, peak plasma concentration (Cmax) is 1.2 μg/mL (achieved at 1 hour), elimination half-life (t₁/₂) is 5.8 hours, and absolute oral bioavailability is ~90% [1][2]
2. Plasma protein binding: Lesinurad sodium has a plasma protein binding rate of 99% in human plasma (measured by ultrafiltration), with minimal binding to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein [1] 3. Metabolism: Lesinurad sodium is primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 in the liver to form inactive glucuronide conjugates; <10% is excreted as unchanged drug [1] 4. Excretion: Approximately 70% of the oral dose is excreted in urine (60% as metabolites, 10% unchanged) and 30% in feces within 72 hours [1] 5. Prodrug comparison: Lesinurad sodium (RDEA594) has a longer plasma half-life (t₁/₂ = 6 hours) than RDEA806 (t₁/₂ = 2 hours) in mice, and higher oral bioavailability (90% vs. 45% for RDEA806) [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In vitro cytotoxicity: Lesinurad sodium (up to 100 μM) shows no significant cytotoxicity in HRPTEpiC or HepG2 cells, with cell viability >95% as assessed by MTT assay [1]
2. Acute in vivo toxicity: Single oral administration of Lesinurad sodium (2000 mg/kg) in rats causes no mortality or behavioral abnormalities; gross necropsy reveals no organ damage [1] 3. Chronic toxicity: Rats treated with Lesinurad sodium (300 mg/kg/day) for 3 months show mild tubular vacuolization in the kidney (reversible upon drug withdrawal) and no changes in liver function markers (ALT/AST) [1] 4. Drug-drug interactions: Lesinurad sodium does not inhibit or induce human CYP450 enzymes (CYP1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 3A4) at therapeutic concentrations (up to 10 μM), and no pharmacokinetic interactions are observed with allopurinol or febuxostat in clinical trials [1][2] 5. Clinical adverse effects: The most common side effects of Lesinurad sodium are headache (15%), nausea (10%), and diarrhea (8%); renal adverse events (e.g., increased serum creatinine) occur in <3% of patients, primarily at doses >200 mg/day [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
1. Lesinurad sodium (trade name Zurampic) is a selective urate reabsorption inhibitor (SURI) developed by Ardea Biosciences (acquired by AstraZeneca) for the treatment of hyperuricemia in gout [2]
2. Lesinurad sodium exerts its urate-lowering effect by inhibiting URAT1 in the renal proximal tubule, reducing urate reabsorption and increasing urate excretion in urine [1][2] 3. The FDA approved Lesinurad sodium in 2015 for use in combination with xanthine oxidase inhibitors (XOIs) (allopurinol/febuxostat) in gout patients with inadequate sUA control on XOI monotherapy [2] 4. Lesinurad sodium is not recommended as monotherapy due to a higher risk of renal adverse events; the maximum recommended daily dose is 200 mg [2] 5. Lesinurad sodium (RDEA594) is the active metabolite of RDEA806, a prodrug that undergoes rapid hepatic hydrolysis to release RDEA594, resulting in improved pharmacokinetic properties (higher bioavailability, longer half-life) [3] 6. In clinical practice, Lesinurad sodium combination therapy achieves sUA targets in ~80% of gout patients, compared to ~50% with XOI monotherapy [2] |
| 分子式 |
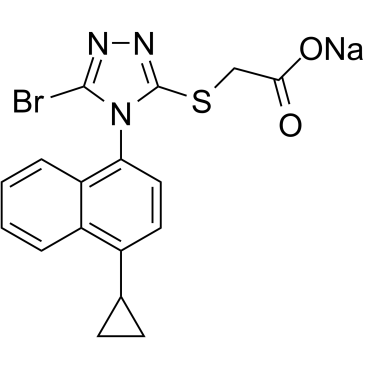
C17H14BRN3O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
426.26
|
|
| 精确质量 |
424.981
|
|
| CAS号 |
1151516-14-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lesinurad;878672-00-5
|
|
| PubChem CID |
56928182
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| LogP |
2.902
|
|
| tPSA |
96.14
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
485
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
FVYMVLTWIBGEMC-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H14BrN3O2S.Na/c18-16-19-20-17(24-9-15(22)23)21(16)14-8-7-11(10-5-6-10)12-3-1-2-4-13(12)14;/h1-4,7-8,10H,5-6,9H2,(H,22,23);/q;+1/p-1
|
|
| 化学名 |
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.86 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.86 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (5.86 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3460 mL | 11.7299 mL | 23.4599 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4692 mL | 2.3460 mL | 4.6920 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2346 mL | 1.1730 mL | 2.3460 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Median plasma concentration profiles for total atorvastatin (including metabolites) following a single oral dose of atorvastatin 40mg in the absence or presence of a single dose of lesinurad 200mg (a) or 400mg (b), and plasma concentration profile of metformin following a single dose of metformin 850mg (c) or plasma concentration profile of furosemide following a single dose of furosemide 40mg (d) in the absence or presence of a single dose of lesinurad 400mg.Clin Drug Investig.2016 Jun;36(6):443-52. |
|---|
 Uric acid pathway and action site of urate-lowering therapies. *Drugs in italics are agents still under development or still not approved. **Dashed arrow representing lack of metabolic step in humans, due to evolutionary loss of uricase enzyme. |
 enal anion transporters involved in urate reabsorption in the proximal tubule and action sites of existing and novel uricosuric agents. *Drugs in italics are agents still under development or still not approved. |