| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Levetiracetam 通过增加 HDAC 转录并在启动子上招募辅阻遏物复合物来抑制 O6-甲基鸟嘌呤-DNA-甲基转移酶 (MGMT) 的活性 [1]。多形性胶质母细胞瘤干细胞 (GSC) 对左乙拉西坦 (40 μg/mL) 的替莫唑胺 (250 μM) 处理更加敏感 [1]。左乙拉西坦 (40 μg/mL) 处理 GCSC 会导致 MGMT 表达下调[1]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
左乙拉西坦(10、25 或 50 mg/kg)可抑制缺氧新生儿的脑电图和行为癫痫活动[2]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型: GCSC 神经球 测试浓度: 40 μg/mL 孵育时间: 48 小时 实验结果:单独使用替莫唑胺 (250 µM) 或左乙拉西坦 (40 μg/mL) 治疗所产生的轻微抗肿瘤作用,当添加替莫唑胺和左乙拉西坦时,会显着增强结合。 蛋白质印迹分析[1] 细胞类型: 多形性胶质母细胞瘤干细胞 (GSC) 测试浓度: 40 μg/ mL 孵育持续时间: 48 小时 实验结果:未处理的 GCSC 中 MGMT 表达水平较高;在单独用替莫唑胺(250 µM)和左乙拉西坦治疗后,该表达略有减少,但在替莫唑胺和左乙拉西坦联合治疗后,该表达显着减少。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Long-Evans rats[2]
Doses: 10, 25, or 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection 60 min before hypoxia. Experimental Results: Treatment resulted in a significant decrease in hypoxic seizure (HS) duration at 25 mg/ kg and at 50 mg/kg. Anticonvulsant activity was maximal at 50 mg/kg, at which HSs were decreased by 63.6%. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Levetiracetam is rapidly and nearly completely absorbed following oral administration, with a reported absolute oral bioavailability of essentially 100%. Tmax is approximately 1.3 hours after dosing, and Cmax is 31 μg/mL following a single 1000mg dose and 43 μg/mL following repeated dosing. Co-administration of levetiracetam with food delays Tmax by approximately 1.5 hours and decreases Cmax by 20%. Approximately 66% of the administered dose of levetiracetam is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug, while only 0.3% of the total dose is excreted via the feces. The primary inactive metabolite of levetiracetam, L057, is also found in the urine as approximately 24% of the administered dose. The volume of distribution of levetiracetam is approximately 0.5 to 0.7 L/kg. The total plasma clearance of levetiracetam is 0.96 mL/min/kg, with renal clearance comprising 0.6 mL/min/kg. The primary inactive metabolite of levetiracetam, L057, has a renal clearance of 4 mL/min/kg. Given the relatively high proportion of drug undergoing renal clearance, overall clearance of levetiracetam is reduced in patients with renal impairment. Absorption of levetiracetam is rapid, with peak plasma concentrations occurring in about an hour following oral administration in fasted subjects. The oral bioavailability of levetiracetam tablets is 100% and the tablets and oral solution are bioequivalent in rate and extent of absorption. Food does not affect the extent of absorption of levetiracetam but it decreases C max by 20% and delays T max by 1.5 hours. The pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam are linear over the dose range of 500-5000 mg. Steady state is achieved after 2 days of multiple twice-daily dosing. Levetiracetam is not significantly protein-bound (<10% bound) and its volume of distribution is close to the volume of intracellular and extracellular water. Levetiracetam C max and AUC were 20% higher in women (N=11) compared to men (N=12). However, clearances adjusted for body weight were comparable. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for LEVETIRACETAM (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Levetiracetam is minimally metabolized within the body - the major metabolic pathway appears to be the enzymatic hydrolysis of its acetamide group which produces an inactive carboxylic acid metabolite, L057, which accounts for approximately 24% of the total administered dose. The specific enzyme(s) responsible for this reaction are unclear, but this pathway is known to be independent of hepatic CYP enzymes and has been proposed to be driven primarily by type B esterases in the blood and other tissues. Two minor metabolites involving modifications to the pyrrolidone ring have been identified, one involving hydroxylation of the ring (constituting 1.6% of the total dose) and the other involving opening of the ring structure (constituting 0.9% of the total dose). Levetiracetam is not extensively metabolized in humans. The major metabolic pathway is the enzymatic hydrolysis of the acetamide group, which produces the carboxylic acid metabolite, ucb L057 (24% of dose) and is not dependent on any liver cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. The major metabolite is inactive in animal seizure models. Two minor metabolites were identified as the product of hydroxylation of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring (2% of dose) and opening of the 2-oxo-pyrrolidine ring in position 5 (1% of dose). There is no enantiomeric interconversion of levetiracetam or its major metabolite. Biological Half-Life The plasma half-life of levetiracetam is 6-8 hours and is not affected by dose or repeat administration. Half-life is increased in the elderly (by about 40%) and those with renal impairment. ... The plasma elimination half-life of the unchanged drug varied between 7.4 hr and 7.9 hr. ... Levetiracetam plasma half-life in adults is 7 +/-1 hour and is unaffected by either dose or repeated administration. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Interactions
No interaction between probenecid and levetiracetam was observed; however, probenecid decreased the renal clearance of ucb L057 (inactive metabolite of levetiracetam) by 60%. /Levetiracetam/ had no effect on the pharmacokinetic disposition of phenytoin in patients with refractory epilepsy. Pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam were also not affected by phenytoin. Levetiracetam did not alter the pharmacokinetics of valproate in healthy volunteers. Valproate 500 mg twice daily did not modify the rate or extent of levetiracetam absorption or its plasma clearance or urinary excretion. There also was no effect on exposure to and the excretion of the primary metabolite, ucb L057. Potential drug interactions between /levetiracetam/ and other Antiepileptic Drugs (AEDs) (carbamazepine, gabapentin, lamotrigine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone and valproate) were also assessed by evaluating the serum concentrations of levetiracetam and these AEDs during placebo-controlled clinical studies. These data indicate that levetiracetam does not influence the plasma concentration of other AEDs and that these AEDs do not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. /Levetiracetam/ did not influence the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (ECG) of digoxin given as a 0.25 mg dose every day. Coadministration of digoxin did not influence the pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. For more Interactions (Complete) data for LEVETIRACETAM (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Levetiracetam is indicated as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of partial onset seizures in adults and children 4 years of age and older with epilepsy. /included in US product labe/ Drug Warnings Adverse neuropsychiatric effects reported during levetiracetam treatment are classified into 3 categories: somnolence and fatigue, coordination difficulties, and behavioral changes. In controlled studies, 14.8% of patients who received levetiracetam experienced somnolence compared with 8.4% of placebo-treated patients, and about 3% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to somnolence. About 14.7% of patients who received levetiracetam experienced asthenia compared with 9.1% of placebo-treated patients, and 0.8% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment due to asthenia. Coordination difficulties were experienced by 3.4% of levetiracetam patients compared with 1.6% of placebo-treated patients. Somnolence, asthenia, and coordination difficulties occurred most frequently within the first 4 weeks of treatment. Psychotic manifestations and hallucinations were reported rarely in patients receiving levetiracetam in clinical studies. Other behavioral symptoms (e.g., agitation, hostility, anxiety, apathy, emotional lability, depersonalization, depression, aggression, anger, irritability) occurred in 13.3% of levetiracetam-treated patients in clinical studies compared with 6.2% of placebo patients, and 1.7% of levetiracetam-treated patients discontinued treatment because of these events. Because of the possibility of increased seizure frequency, anticonvulsant drugs, including levetiracetam, should not be discontinued suddenly. Levetiracetam should be withdrawn gradually by reducing the dosage by 1g daily at 2-week intervals. Adverse effects occurring in 1% or more of patients receiving levetiracetam and more frequently than placebo include somnolence, asthenia, headache, infection, dizziness, pain, pharyngitis, depression, nervousness, rhinitis, anorexia, ataxia, vertigo, amnesia, anxiety, emotional lability, hostility, paresthesia, increased cough, sinusitis, and diplopia and were reported in clinical studies in which levetiracetam was administered in conjunction with other anticonvulsants. Asthenia, somnolence, and dizziness occurred predominantly during the initial 4 weeks of treatment. Minor decreases in total mean erythrocyte count, mean hemoglobin, and mean hematocrit have been reported. Leukopenia, neutropenia, pancytopenia (with myelosuppression in some cases), and thrombocytopenia also have been observed, although a causal relationship to the drug has not been established. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for LEVETIRACETAM (12 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Levetiracetam appears to prevent seizure activity via the selective inhibition of hypersynchronized epileptiform burst firing without affecting normal neuronal transmission, though the exact mechanism through which this occurs is unclear. The therapeutic index of levetiracetam is wide, making it relatively unique amongst other anti-epileptic medications. Anti-epileptic drugs, including levetiracetam, may increase the risk of suicidal ideation or behaviour - patients taking levetiracetam should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depressive symptoms, suicidal ideation, and behavioural abnormalities. |
| 分子式 |
C8H14N2O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
170.21
|
| 精确质量 |
170.105
|
| CAS号 |
102767-28-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Etiracetam;33996-58-6
|
| PubChem CID |
5284583
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
395.9±25.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
118-119°C
|
| 闪点 |
193.2±23.2 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.519
|
| LogP |
-0.67
|
| tPSA |
63.4
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
12
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
203
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
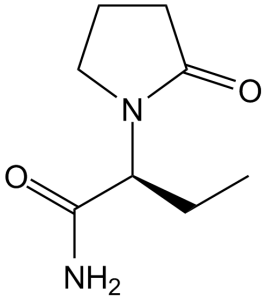
| SMILES |
CC[C@@H](C(=O)N)N1CCCC1=O
|
| InChi Key |
HPHUVLMMVZITSG-LURJTMIESA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C8H14N2O2/c1-2-6(8(9)12)10-5-3-4-7(10)11/h6H,2-5H2,1H3,(H2,9,12)/t6-/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(S)-2-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)butanamide
|
| 别名 |
Levetiracetam, UCBL059, UCB L059, UCB-L059, SIB S1, SIBS1, SIB-S1, Keppra, Etiracetam, UCB6474, UCB-6474,
UCB 6474,
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: Saline: 30 mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (587.51 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.8751 mL | 29.3755 mL | 58.7510 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.1750 mL | 5.8751 mL | 11.7502 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5875 mL | 2.9375 mL | 5.8751 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT06224530 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Levetiracetam Drug: Placebo |
Psychosis | King's College London | February 2024 | Not Applicable |
| NCT04004702 | Not yet recruiting | Drug: Levetiracetam | Alzheimer Disease | Walter Reed National Military Medical Center |
January 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT04317807 | Recruiting | Drug: Levetiracetam Pill Other: Placebo |
Early Psychosis | NYU Langone Health | August 27, 2020 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06067412 | Completed | Drug: Levetiracetam Drug: Phenytoin |
Status Epilepticus | Shaheed Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto Medical University |
August 1, 2022 | Not Applicable |