| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
一种称为脂质肽的口服微粒体甘油三酯转移蛋白 (MTP) 抑制剂用于治疗功能顺势疗法 (HoFH) 患者,这是一种罕见类型的高胆固醇血症,可导致早期动脉粥样硬化性疾病。细胞色素 P-450 (CYP) 同工酶 3A4 负责洛美他派的肝脏代谢。它与 CYP3A4 底物(例如辛伐他汀和阿托伐他汀)有相互作用 [2]。
|
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
单独使用或与其他降脂药物联合使用时,洛美他派可将低密度脂蛋白胆固醇 (LDL-C) 血浆浓度平均降低 50% 以上。显着的胃肠道副作用和肝脂肪水平升高与洛美他派有关。 50 mg 洛美他派的生物利用度为 7.1%。 Lomapide 的平均半衰期为 39.7 小时 [2]。结果表明,0.3 mg/kg 和 1 mg/kg 剂量的洛美他派仅在一次治疗后即可使血清甘油三酯降低 35% 和 47%。多剂量洛美他派治疗后还观察到甘油三酯(71%–87%)、非酯化脂肪酸(33%–40%)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(26–29%)呈剂量依赖性下降[3]。
|
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
In healthy patients, time to maximum lomitapide concentration is about 6 hours with a single dose of 60 mg. Lomitapide has an approximate absolute bioavailability of 7%. About 52.9-59.5% is eliminated by the urine and 33.4-35.1% is eliminated by the feces. The steady state volume of distribution is about 985-1292 L. The mean lomitapide volume of distribution at steady state is 985-1292 liters. Lomitapide is 99.8% plasma-protein bound. Upon oral administration of a single 60-mg dose of Juxtapid, the lomitapide tmax is around 6 hours in healthy volunteers. The absolute bioavailability of lomitapide is approximately 7%. Lomitapide pharmacokinetics is approximately dose-proportional for oral single doses from 10-100 mg. In a mass-balance study, a mean of 59.5% and 33.4% of the dose was excreted in the urine and feces, respectively. In another mass-balance study, a mean of 52.9% and 35.1% of the dose was excreted in the urine and feces, respectively. Lomitapide was not detectable in urine samples. M1 is the major urinary metabolite. Lomitapide is the major component in the feces. It is not known whether lomitapide is excreted in human milk. Metabolism / Metabolites Lomitapide is mainly metabolized by CYP3A4 to it's inactive metabolites, M1 and M3. CYP enzymes that metabolize lomitapide to a minor extent include CYP 1A2,2B6,2C8,2C19. Lomitapide is metabolized extensively by the liver. The metabolic pathways include oxidation, oxidative N-dealkylation, glucuronide conjugation, and piperidine ring opening. Cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 metabolizes lomitapide to its major metabolites, M1 and M3, as detected in plasma. The oxidative N-dealkylation pathway breaks the lomitapide molecule into M1 and M3. M1 is the moiety that retains the piperidine ring, whereas M3 retains the rest of the lomitapide molecule in vitro. CYPs 1A2, 2B6, 2C8, and 2C19 may metabolize lomitapide to a small extent to M1. M1 and M3 do not inhibit activity of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in vitro. Biological Half-Life Lomitapide half-life is about 39.7 hours. The mean lomitapide terminal half-life is 39.7 hours. |
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Lomitapide is a white to off-white powder. Lomitapide is indicated as an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments, including LDL apheresis where available, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), apolipoprotein B (apo B), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Very few data are available on the effects of overdose to lomitapide. The maximum dose administered to human subjects in clinical studies was 200 mg lomitapide, as a single dose, without adverse consequences. Lomitapide should not be used during pregnancy because lomitapide may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Lomitapide may also cause diarrhea and malabsorption in patients with rare hereditary disorders, including galactose intolerance, the Lapp lactase deficiency, and glucose-galactose malabsorption; therefore, use of lomitapide should be avoided in such patients. Lomitapide causes a risk of hepatotoxicity. Lomitapide can cause elevations in transaminases and hepatic steatosis. To what extent lomitapide-associated hepatic steatosis promotes the elevations in transaminases is unknown. Although cases of hepatic dysfunction or hepatic failure have not been reported, there is concern that lomitapide could induce steatohepatitis, which can progress to cirrhosis over several years. Therefore, it should not be administered to patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C) or patients with active liver disease, including unexplained, persistent elevations in serum aminotransferase concentrations. Lomitapide did not exhibit genotoxic potential in a battery of studies, including an in vitro cytogenetics assay using primary human lymphocytes. ANIMAL STUDIES: In a 2-year dietary carcinogenicity study in mice, lomitapide was administered at doses of 0.3, 1.5, 7.5, 15, or 45 mg/kg/day. There were statistically significant increases in the incidences of liver adenomas and carcinomas in males at doses as low as 1.5 mg/kg/day and in females at as low as 7.5 mg/kg/day. Incidences of small intestinal carcinomas in males and combined adenomas and carcinomas in females were significantly increased at doses as low as 15 mg/kg/day. In 2 year studies in rats, there were no statistically significant drug-related increases in tumor incidences. Reproduction studies were conducted in rats, rabbits and ferrets. Oral gavage doses of 0.04, 0.4, or 4 mg/kg/day lomitapide given to pregnant rats from gestation day 6 through organogenesis were associated with fetal malformations at greater than or equal to 2-times human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (60 mg) based on plasma AUC comparisons. Fetal malformations included umbilical hernia, gastroschisis, imperforate anus, alterations in heart shape and size, limb malrotations, skeletal malformations of the tail, and delayed ossification of cranial, vertebral and pelvic bones. Oral gavage doses of 1.6, 4, 10, or 25 mg/kg/day lomitapide given to pregnant ferrets from gestation day 12 through organogenesis were associated with both maternal toxicity and fetal malformations at exposures that ranged from less than the human exposure at the MRHD to 5-times the human exposure at the MRHD. Fetal malformations included umbilical hernia, medially rotated or short limbs, absent or fused digits on paws, cleft palate, open eye lids, low-set ears, and kinked tail. In rabbits, exposures up to 3 times the MRHD based on body surface area (BSA) (MRDH-BSA) from gestational day 6 through organogenesis were not associated with adverse effects. However, exposure equal to or greater than 6 times the MRHD-BSA resulted in embryo-fetal death. Lomitapide had no effect on fertility in rats at doses up to 5 mg/kg/day at systemic exposures estimated to be 4-times (females) and 5-times (males) higher than in humans at 60 mg based on AUC. Lomitapide did not exhibit genotoxic potential in a battery of studies, including the in vitro Bacterial Reverse Mutation (Ames) and an oral micronucleus study in rats. Hepatotoxicity Lomitapide is associated with a moderately high rate of serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy, levels above 3 times the upper limit of normal (ULN) occurring in 34% of patients. Aminotransferase elevations above 10 times ULN have also been reported which can necessitate drug discontinuation. Despite the frequency of ALT elevations, however, increases in serum bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels are rare and there have been no reports of clinically apparent acute liver injury with jaundice. Chronic therapy with lomitapide can be associated with fluctuations in serum aminotransferase levels and accumulation of liver fat. In some instances, the increase in liver fat is from baseline levels of Likelihood score: C (probable cause of clinically significant liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No relevant published information exists with the use of lomitapide during breastfeeding. Because of a concern with disruption of infant lipid metabolism and possible tumorigenicity, lomitapide should not be used during breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Plasma protein binding is about 99.8% Interactions Concomitant use of lomitapide with potent (e.g., boceprevir, clarithromycin, conivaptan, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, lopinavir/ritonavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, posaconazole, ritonavir, saquinavir, telaprevir, telithromycin, tipranavir/ritonavir, voriconazole) or moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., aprepitant, atazanavir, ciprofloxacin, crizotinib, darunavir/ritonavir, diltiazem, erythromycin, fluconazole, fosamprenavir, imatinib, verapamil) is contraindicated. If concomitant use with moderate or potent CYP3A4 inhibitors cannot be avoided, lomitapide therapy should be interrupted during the course of treatment with the CYP3A4 inhibitor. Concomitant use of lomitapide with inhibitors of CYP3A4 may result in increased systemic exposure to lomitapide. When the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor ketoconazole (200 mg twice daily for 9 days) was administered concomitantly with lomitapide (60 mg once daily), peak plasma concentration and area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of lomitapide were increased by 15- and 27-fold, respectively. When the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor clarithromycin was added to lomitapide therapy in at least 1 patient, ALT and AST concentrations were increased to 24 and 13 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), respectively, within days of initiating the potent CYP3A4 inhibitor. Concomitant use of lomitapide with moderate inhibitors of CYP3A4 has not been studied; however, results of pharmacokinetic studies evaluating concomitant use of lomitapide with potent and weak CYP3A4 inhibitors suggest that moderate CYP3A4 inhibitors will likely increase lomitapide exposure. Following concomitant use of lomitapide (10 mg once daily for 7 days) with fenofibrate (single 145-mg dose as micronized formulation), peak plasma concentration and AUC of fenofibric acid were decreased by 29 and 10%, respectively. Dosage adjustment of fenofibrate (as micronized formulation) is not required during concomitant use with lomitapide. Following concomitant use of lomitapide (10 mg once daily for 7 days) with ezetimibe (single 10-mg dose), peak plasma concentration and AUC of ezetimibe were increased by 3 and 6%, respectively. Dosage adjustment of ezetimibe is not required during concomitant use with lomitapide. For more Interactions (Complete) data for Lomitapide (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
|
| 参考文献 |
|
|
| 其他信息 |
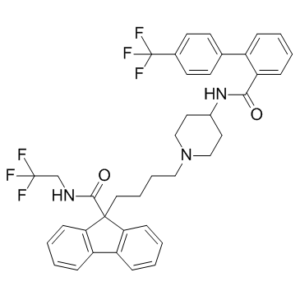
Lomitapide is a member of the class of benzamides obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4'-(trifluoromethyl)biphenyl-2-carboxylic acid with the primary amino group of 9-[4-(4-aminopiperidin-1-yl)butyl]-N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9H-fluorene-9-carboxamide. Used (as its mesylate salt) as a complement to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. It has a role as an anticholesteremic drug and a MTP inhibitor. It is a member of piperidines, a member of fluorenes, a member of benzamides and a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes. It is a conjugate base of a lomitapide(1+).
Lomitapide is a microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP) inhibitor used in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) patients. It is marketed under the name Juxtapid (R). Lomitapide is a Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of lomitapide is as a Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitor, and P-Glycoprotein Inhibitor. Lomitapide is a cholesterol lowering agent that acts by inhibition of the microsomal triglyceride transfer protein and is used to treat the severe lipid abnormalities of familial hypercholesterolemia. Lomitapide is associated with mild, asymptomatic and self-limited serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy that are usually accompanied by an increase in hepatic fat. Long term therapy with lomitapide has been linked to development of steatohepatitis and hepatic fibrosis. Lomitapide is a small molecule inhibitor of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), an enzyme located in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum responsible for absorbing dietary lipids and transferring triglycerides onto apolipoprotein B (apo-B) in the assembly of very-low-density lipoprotein. Inhibition of MTP by lomitapide blocks transfer of lipid to apo-B, and as a result emerging apo-B is destroyed and lipoprotein secretion is inhibited. See also: Lomitapide Mesylate (has salt form). Drug Indication Used in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) patients to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), apolipoprotein B (apo B), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C). FDA Label Lojuxta is indicated as an adjunct to a lowâfat diet and other lipidâlowering medicinal products with or without low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) apheresis in adult patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia (HoFH). , , Genetic confirmation of HoFH should be obtained whenever possible. Other forms of primary hyperlipoproteinaemia and secondary causes of hypercholesterolaemia (e. g. nephrotic syndrome, hypothyroidism) must be excluded. , Treatment of (heterozygous or homozygous) familial hypercholesterolaemia Mechanism of Action Within the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, lomitapide inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), which prevents the formation of apolipoprotein B, and, thus, the formation of VLDL and chylomicrons as well. Altogether, this leads to a reduction of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Juxtapid directly binds and inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), which resides in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby preventing the assembly of apo B-containing lipoproteins in enterocytes and hepatocytes. This inhibits the synthesis of chylomicrons and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL). The inhibition of the synthesis of VLDL leads to reduced levels of plasma low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). Therapeutic Uses Juxtapid is indicated as an adjunct to a low-fat diet and other lipid-lowering treatments, including LDL apheresis where available, to reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), apolipoprotein B (apo B), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH). /Included in US product label/ Because of the risk of hepatotoxicity, lomitapide is available only under a restricted distribution program (Juxtapid Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS)). Healthcare providers and pharmacies must be certified with the Juxtapid REMS program before they can prescribe or dispense lomitapide. Drug Warnings /BOXED WARNING/ WARNING: RISK OF HEPATOTOXICITY. Juxtapid can cause elevations in transaminases. In the Juxtapid clinical trial, 10 (34%) of the 29 patients treated with Juxtapid had at least one elevation in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) or aspartate aminotransferase (AST) > or =3x upper limit of normal (ULN). There were no concomitant clinically meaningful elevations of total bilirubin, international normalized ratio (INR), or alkaline phosphatase. Juxtapid also increases hepatic fat, with or without concomitant increases in transaminases. The median absolute increase in hepatic fat was 6% after both 26 and 78 weeks of treatment, from 1% at baseline, measured by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Hepatic steatosis associated with Juxtapid treatment may be a risk factor for progressive liver disease, including steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. Measure ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin before initiating treatment and then ALT and AST regularly as recommended. During treatment, adjust the dose of Juxtapid if the ALT or AST are > or =3x ULN. Discontinue Juxtapid for clinically significant liver toxicity. Because of the risk of hepatotoxicity, Juxtapid is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the Juxtapid REMS Program. FDA Pregnancy Risk Category: X /CONTRAINDICATED IN PREGNANCY. Studies in animals or humans, or investigational or post-marketing reports, have demonstrated positive evidence of fetal abnormalities or risk which clearly outweights any possible benefit to the patient./ Juxtapid can cause elevations in transaminases and hepatic steatosis, ... . To what extent Juxtapid-associated hepatic steatosis promotes the elevations in transaminases is unknown. Although cases of hepatic dysfunction (elevated transaminases with increase in bilirubin or international normalized ratio (INR)) or hepatic failure have not been reported, there is concern that Juxtapid could induce steatohepatitis, which can progress to cirrhosis over several years. The clinical studies supporting the safety and efficacy of Juxtapid in homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) would have been unlikely to detect this adverse outcome given their size and duration. Consistent with the mechanism of action of Juxtapid (lomitapide), most treated patients exhibited increases in hepatic triglyceride content, with or without concomitant increases in hepatic transaminases. In an open-label Phase 3 study, 18 of 23 patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH) developed hepatic steatosis, i.e., hepatic fat > 5.6%, as measured by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMRS). There was a mean increase in absolute hepatic fat content of 6% after both 26 weeks and 78 weeks of treatment, from a mean of 1% at baseline. Clinical data suggest that hepatic fat accumulation is reversible after stopping treatment with Juxtapid, generally over 4 to 6 weeks, but whether histological sequelae remain is unknown, especially after long-term use. The long term consequences of hepatic steatosis associated with Juxtapid treatment are unknown, including risk of progression to steatohepatitis and cirrhosis. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for Lomitapide (22 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Lomitapide directly inhibits microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP). |
| 分子式 |
C39H37N3O2F6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
693.72038
|
| 精确质量 |
693.278
|
| CAS号 |
182431-12-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lomitapide mesylate;202914-84-9;Lomitapide-d8;2459377-96-7
|
| PubChem CID |
9853053
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
778.2±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
424.4±32.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.7 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.606
|
| LogP |
7.78
|
| tPSA |
68.42
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
50
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1110
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
MBBCVAKAJPKAKM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C39H37F6N3O2/c40-38(41,42)25-46-36(50)37(33-13-5-3-10-30(33)31-11-4-6-14-34(31)37)21-7-8-22-48-23-19-28(20-24-48)47-35(49)32-12-2-1-9-29(32)26-15-17-27(18-16-26)39(43,44)45/h1-6,9-18,28H,7-8,19-25H2,(H,46,50)(H,47,49)
|
| 化学名 |
N-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-9-(4-(4-(4'-(trifluoromethyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2-carboxamido)piperidin-1-yl)butyl)-9H-fluorene-9-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
BMS 201038; AEGR733; BMS-201038; AEGR-733; BMS201038; BMS 201038-01; AEGR 733; Lomitapide mesylate. trade name: Juxtapid; Lojuxta.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~144.15 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.60 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (3.60 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.60 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4415 mL | 7.2075 mL | 14.4150 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2883 mL | 1.4415 mL | 2.8830 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1442 mL | 0.7208 mL | 1.4415 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。