| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
ET-A ( IC50 = 0.5 nM ); ET-B ( IC50 = 0.5 nM )
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Macitentan 可完全抑制 ET-1 对原代人肺平滑肌细胞诱导的细胞内钙增加,IC50 约为 1 nM。 Macitentan 抑制 ET-1 诱导的离体大鼠主动脉环收缩或 S6c 诱导的离体大鼠气管环收缩,pA2 分别为 7.6 和 5.9。细胞测定:在过表达人 ETA 和 ETB 的中国仓鼠卵巢细胞的微粒体膜中,马西腾坦抑制 125I-ET-1 与重组 ETA 受体之间的结合,平均 IC50 值为 0.5 ± 0.2 nM (n= 17)。 ETB 受体的平均 IC50 值为 391±182 nM (n= 17)。马西腾坦完全抑制了ET-1增加非重组细胞内钙的作用。
|
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
对血压正常的大鼠施用马西腾坦可增加血浆 ET-1 浓度,其剂量比波生坦低 10 倍。马西腾坦剂量依赖性地降低高血压 DOCA 盐大鼠的平均动脉血压,剂量为 10 mg/kg 时的最大效果为 -26 mm Hg,ED50 为 1mg/kg。在最大有效剂量下,马西腾坦的血压反应持续时间约为 40 小时。口服马西腾坦可剂量依赖性地预防肺动脉高压的发生和右心室肥大的发生,在野百合碱大鼠肺动脉高压模型中,最大疗效为 30 mg/kg/天。长期口服 30 mg/kg/天的马西替坦可显着改善野百合碱大鼠的 42 天生存率(马西替坦与载体相比,生存率分别为 83% 和 50%;42 天死亡率降低 66%)。在链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠模型中,马西腾坦(30 mg/kg/天)治疗 24 小时可部分阻止肾血管收缩的发生并增加肾血流量。马西腾坦可增加肾小球滤过率并降低滤过分数,并减轻血管和肾小管间质病变以及肾小球损伤。马西腾坦(25 mg/kg/天,口服)可减弱肾脏、心脏和视网膜 ET-1、TGF-β1、VEGF、FN、EDB+FN、胶原α-I(IV) mRNA 表达的增加以及 FN、胶原蛋白的增加db/db 小鼠中 2 型糖尿病诱导的蛋白质和 NF-κB 激活。马西腾坦还可以改善这些糖尿病小鼠的系膜扩张、心脏功能障碍以及 ANP 和 BNP 表达的增加。马西腾坦 (100mg/kg) 联合紫杉醇 (5 mg/kg) 治疗可降低肿瘤发生率(紫杉醇为 5/9 vs 紫杉醇 9/9)并进一步降低肿瘤重量(中位[范围]:0.1 g 与紫杉醇 0.4 g)与单独使用紫杉醇相比,SKOV3ip1 卵巢癌模型中腹水的发生率(紫杉醇为 0/9 vs 4/9)。马西腾坦联合紫杉醇通过降低 pVEGFR2、pAkt 和 pMAPK 的水平来抑制 ETR 的磷酸化并抑制肿瘤细胞的生存途径。马西腾坦增强紫杉醇对肿瘤细胞分裂(Brud+细胞:18.5 vs 紫杉醇 30.8)和细胞凋亡(TUNEL+细胞:195 vs 150 紫杉醇)的作用。
|
|
| 动物实验 |
|
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Macitentan has a median Tmax of 8h although some studies have found up to 30h at higher doses. Although the bioavailability has not been experimentally determined, pharmacokinetic modeling has estimated it at 74%. Food has not been found to have a significant effect on absorption. Eliminated 50% through urine and 24% through feces. Of the 50% excreted through the urine, none of the recovered dose was in the form of the parent drug nor the active metabolite. Macitentan has an apparent volume of distribution of 40-50L. Clearance data was not found. Metabolism / Metabolites Macitentan undergoes oxidative depropylation of the sulfonamide moiety via CYP3A4, 2C8, 2C9, and 2C19 to form the active metabolite M6. The ethylene glycol moiety undergoes oxidative cleavage via CYP2C9 to the alcohol metabolite M4. M4 is oxidized to its corresponding acid, M5, then hydrolyzed to the metabolite termed m/z 324. Oxidative depropylation of a distal carbon atom via CYP2C8, 2C9, and 2C19 forms M7. Hydrolysis of both macitentan and M5 produces M3. Finally M5 may be further metabolized via hydrolysis and hydroxylation to M2 or via glucuronidation to a glucuronide metabolite, M1. Biological Half-Life The half-life of elimination of macitentan is 16 hours. The half-life of elimination of the active metabolite is 40-66h |
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
Macitentan is associated with a low rate of serum aminotransferase elevations (0% to 4%) that, in clinical trials, was similar to the rate among placebo recipients. These elevations were usually mild, transient and not associated with symptoms, but were above 8 times the ULN in 2% of subjects (vs 0.4% of controls) in at least one long term study. For these reasons, the product label recommends that patients have serum enzymes tested before starting therapy and be alerted to the possibility and symptoms of liver injury during therapy. While there have been no published reports of clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice associated with macitentan, it has had limited general use. Other endothelin receptor antagonists (bosentan, sitaxentan) have been linked to several instances of acute liver injury, some of which have been severe. The onset of illness was usually within 1 to 6 months of starting bosentan and the enzyme pattern was typically hepatocellular or mixed. Immunoallergic features were not present and autoantibodies absent or present in low titer. Macitentan and ambrisentan have not been linked to similar cases. Likelihood score: E* (unlikely but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding Macitentan is >99% bound to plasma proteins, primarily to albumin and to a lesser extent α1-acid glycoprotein. |
|
| 参考文献 |
|
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Macitentan acts primarily by reducing vasoconstriction and cell proliferation due to endothelin overexpression. |
| 分子式 |
C19H20BR2N6O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
588.27
|
| 精确质量 |
585.96
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 38.79; H, 3.43; Br, 27.17; N, 14.29; O, 10.88; S, 5.45
|
| CAS号 |
441798-33-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Macitentan-d4; 1258428-05-5; Macitentan (n-butyl analogue); 556797-16-1
|
| PubChem CID |
16004692
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
692.4±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
134-136°C
|
| 闪点 |
372.5±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.2 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.634
|
| LogP |
5.41
|
| tPSA |
159.84
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
11
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
642
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
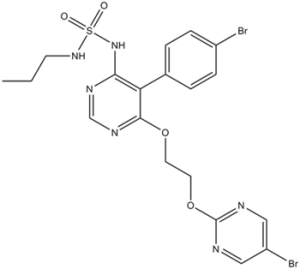
BrC1=CN=C(OCCOC2=C(C3=CC=C(Br)C=C3)C(NS(NCCC)(=O)=O)=NC=N2)N=C1
|
| InChi Key |
JGCMEBMXRHSZKX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C19H20Br2N6O4S/c1-2-7-26-32(28,29)27-17-16(13-3-5-14(20)6-4-13)18(25-12-24-17)30-8-9-31-19-22-10-15(21)11-23-19/h3-6,10-12,26H,2,7-9H2,1H3,(H,24,25,27)
|
| 化学名 |
5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-[2-(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxyethoxy]-N-(propylsulfamoyl)pyrimidin-4-amine
|
| 别名 |
ACT 064992; Macitentan; ACT-064992; ACT064992; trade name: Opsumit
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.25 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.25 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.25 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6999 mL | 8.4995 mL | 16.9990 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3400 mL | 1.6999 mL | 3.3998 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1700 mL | 0.8499 mL | 1.6999 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
A Study to Assess Whether Macitentan Delays Disease Progression in Children With Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH)
CTID: NCT02932410
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Active, not recruiting
Date: 2024-10-09
|
|
|