| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
NLRP3 inflammasomes
NLR family, pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome: MCC950 sodium is a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of NLRP3; it blocks canonical and noncanonical NLRP3 activation at nanomolar concentrations (no specific IC₅₀/Ki values provided) and does not inhibit AIM2, NLRC4, or NLRP1 inflammasomes[1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在纳摩尔剂量下,MCC950 可抑制常规和非经典 NLRP3 激活。 MCC950 选择性阻止 NLRP3 激活,但不阻止 AIM2、NLRC4 或 NLRP1 激活。使用人单核细胞源性巨噬细胞 (HMDM) 和小鼠骨髓源性巨噬细胞 (BMDM),研究了 MCC950 对 NLRP3 炎性体激活的影响。 MCC950 在 HMDM 中表现出 8.1 nM 的抑制能力,而在 BMDM 中的 IC50 约为 7.5 nM。此外,MCC950 剂量依赖性地减少 IL-1β 分泌,但不减少 TNF-α 分泌。 MCC950 在刺激由 caspase-11 引起的非经典途径时选择性抑制 NLRP3 激活和 IL-1β 释放。即使剂量为 10 μM,MCC950 也不能阻止鼠伤寒沙门氏菌刺激 NLRC4 产生 IL-1β 和 TNF-α。当存在鼠伤寒沙门氏菌血清型时,MCC950 不会阻止 caspase-1 激活或 IL-1β 加工。 MCC950处理对细胞裂解物中pro-caspase-1和pro-IL-1β的产生基本上没有影响[1]。
抑制骨髓来源巨噬细胞(BMDM)中NLRP3炎性小体激活:MCC950 sodium(1-1000 nM)可剂量依赖性降低LPS+ATP或LPS+尼日利亚菌素(经典NLRP3刺激剂)刺激的BMDM中IL-1β的产生,对TNF-α产生无显著影响。Western blot证实,MCC950 sodium可抑制LPS+ATP处理的BMDM中caspase-1剪切和IL-1β成熟,而格列本脲(非特异性NLRP3抑制剂)抑制作用较弱。对于非经典NLRP3激活(Pam3CSK4+转染LPS),MCC950 sodium可降低C57BL/6 BMDM中IL-1β产生,但对Nlrp3⁻/⁻或casp11⁻/⁻ BMDM无作用,证实其NLRP3特异性。MCC950 sodium不影响BMDM中LDH释放(细胞死亡标志物),表明无细胞毒性[1] - 对NLRP3炎性小体的选择性:MCC950 sodium对LPS+鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(NLRC4炎性小体激活剂)或LPS+转染Poly(dA:dT)(AIM2炎性小体激活剂)刺激的BMDM中IL-1β产生无抑制作用,而小白菊内酯(非特异性炎性小体抑制剂)和拜耳化合物(AIM2抑制剂)可有效阻断上述模型中IL-1β产生。MCC950 sodium也不抑制TLR信号通路(LPS或Poly(A:U)诱导的TNF-α产生)或NLRP3启动(LPS诱导的BMDM中NLRP3蛋白表达)[1] - NLRP3抑制机制:MCC950 sodium可阻断LPS+尼日利亚菌素刺激的BMDM中NLRP3依赖的ASC寡聚化(交联实验和Western blot检测),并减少尼日利亚菌素、LeuLeu-Ome或致死毒素处理的ASC-cerulean报告细胞中ASC斑点形成(活细胞成像和流式细胞术检测)。该药物不阻断K⁺外流、Ca²⁺内流(FLIPR TETRA检测BMDM中ATP诱导的Ca²⁺流),也不直接抑制NLRP3与ASC的相互作用(HEK-293T细胞中FLAG-NLRP3/HA-NLRP3和ASC的免疫共沉淀实验)[1] - 抑制人外周血单个核细胞(PBMC)中NLRP3激活:MCC950 sodium可降低穆克-威尔士综合征(MWS,E313K NLRP3突变)患者PBMC经LPS刺激后的IL-1β产生,Western blot证实其可减少caspase-1剪切和IL-1β成熟[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
MCC950 减少白细胞介素-1p (IL-1β) 的产生,并减轻多发性硬化症模型实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎 (EAE) 的严重程度。 MCC950预处理降低了血清IL-1β和IL-6水平,但没有显着降低TNF-α水平。使用 MCC950 治疗的小鼠 EAE 发作延迟且严重程度降低。第22天处死的小鼠脑单核细胞进行细胞内细胞因子染色和FACS分析,结果显示MCC950处理的小鼠比PBS处理的小鼠具有更多产生IL-17和IFN-γ的CD3+T细胞。频率略有下降。 CD3+ T 细胞的 CD4+ 和 γδ+ 亚群产生 IFN-γ(尤其是 IL-17)的细胞数量也有所减少 [1]。
改善小鼠实验性自身免疫性脑脊髓炎(EAE):经MCC950 sodium处理的EAE小鼠(多发性硬化模型)临床评分显著低于PBS处理对照组。EAE诱导后22天分离小鼠脑单核细胞,流式细胞术显示MCC950 sodium可降低活IL-17⁺/IFN-γ⁺ CD3⁺ T细胞、CD3⁺CD4⁺ T细胞和CD3⁺γδ TCR⁺细胞比例,提示神经炎症被抑制[1] - 减轻小鼠全身性炎症:预先给予MCC950 sodium的C57BL/6小鼠,腹腔注射LPS后2小时血清IL-1β水平降低(TNF-α和IL-6无变化)(Mann-Whitney检验,P ≤ 0.05,n=3)[1] - 挽救CAPS小鼠模型新生致死性:Nlrp3A³⁵⁰VneoR×LysMCre小鼠(NLRP3功能获得性突变,CAPS模型)从出生后第9天开始给予MCC950 sodium,其体重和存活率(观察至45天,药物于28天停用)显著高于PBS处理的突变小鼠(第9天体重:非配对双尾t检验,P ≤ 0.005;存活率:MCC950组n=5 vs PBS组n=9)。MCC950 sodium处理的突变小鼠第9天血浆IL-18水平(NLRP3炎性小体产物)降低,停药14天后IL-18水平回升。该药物对NLRP1突变(Nlrp1aQ593P)小鼠无作用,证实NLRP3特异性[1] - 改善db/db小鼠糖尿病脑病(DEP):8周龄db/db小鼠(2型糖尿病模型)经MCC950 sodium处理8周后,胰岛素敏感性改善(空腹血糖降低,口服葡萄糖耐量试验[OGTT]和胰岛素耐量试验[ITT]曲线改善,OGTT/ITT中葡萄糖曲线下面积[AUC]降低)。行为学实验显示,MCC950 sodium可逆转db/db小鼠的焦虑样行为(明暗箱实验中亮箱停留时间和穿梭次数增加)、抑郁样行为(强迫游泳实验[FST]和悬尾实验[TST]中不动时间减少)和认知功能障碍(莫里斯水迷宫[MWM]隐藏平台实验中逃避潜伏期缩短,探索实验中穿越目标平台次数和目标象限停留时间增加)。Western blot和caspase-1活性实验证实,MCC950 sodium可降低db/db小鼠海马中NLRP3、ASC、IL-1β蛋白水平,减少caspase-1活性。MCC950 sodium处理的db/db小鼠血浆IL-1β水平降低,胰岛素水平升高;血浆和海马TNF-α水平无显著变化[2] |
| 酶活实验 |
炎症小体活化测定[1]
将BMDM以5×0 105/ml或1×0 6/ml接种,HMDM以5倍10 5/ml接种,PBMC以2×10 6/ml或5×0 6 g/ml接种于96孔板中。第二天,更换过夜培养基,并用来自大肠杆菌血清型EH100(ra)TLRgrade™的10 ng/ml LPS刺激细胞3小时。取出培养基,用含有二甲基亚砜(1:1000)、MCC950(0.001-10µM)、格列本脲(200µM),孤雌内酯(10µM)或拜耳半胱氨酰白三烯受体拮抗剂1-(5-羧基-2{3-[4-(3-环己基丙氧基)苯基]丙氧基}苯甲酰基)哌啶-4-羧酸(40µM)的无血清培养基(SFM)代替。然后用炎症小体激活剂刺激细胞30分钟:5 mM腺苷5’-三磷酸二钠盐水合物(ATP)(1小时)、用Lipofectamine 2000™(Invitrogen)转染的1µg/ml聚脱氧腺苷酸胸苷酸钠盐(Poly dA:dT)(3-4小时)、200µg/ml MSU(过夜)和10µM尼格瑞金(1小时。细胞也用25µg/ml聚腺苷酸-多ridylic acid刺激(4小时)。对于非典型炎症小体激活细胞,用100 ng/ml Pam3CSK4引发4小时,移除培养基并用含有DMSO或MCC950的SFM代替,并使用0.25%FuGENE®转染2µg/ml LPS 16小时。根据制造商的说明,移除上清液并使用ELISA试剂盒分析。使用Cytox96®非放射性细胞毒性测定法测量LDH释放。[1] 飞行时间炎症小体评估(TOFIE)测定[1] 使用Lipofectamine 2000™在24孔板中用以下质粒转染HEK293T细胞(4×105/ml):pEF6人ASC-GFP、pEF6人类C-mCherry或空载体对照。转染后1小时,用DMSO或MCC950(0.1–50µM)处理细胞。将转染后15小时的细胞移除并悬浮在含有1%FCS和2mM EDTA的DPBS中。使用Gallios™流式细胞仪和FlowJo软件对细胞进行分析。在GFP和Cherry表达上对活细胞进行门控(当共转染时)。通过分析GFP脉冲区域的高度和宽度(低宽度:区域和高高度:区域)来确定含有ASC斑点的细胞的百分比。Sester et al。 细胞/组织裂解物中caspase-1活性实验:将细胞裂解物(BMDM、海马组织)或上清与caspase-1特异性底物(含对硝基苯胺)在37℃孵育特定时间(如1-2小时),通过分光光度法(405 nm)检测对硝基苯胺释放量,以蛋白浓度或对照组吸光度为参照计算caspase-1活性。MCC950 sodium处理可降低NLRP3激活的BMDM和db/db小鼠海马中caspase-1活性,反映其对NLRP3炎性小体介导的caspase-1剪切的抑制作用[1, 2] |
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹[1]
通过在50µl 5中直接裂解制备细胞裂解物ィ 莱姆利样品缓冲液。根据制造商的说明,使用StrataClean™树脂浓缩上清液的蛋白质含量。将蛋白质样品在15%SDS-PAGE凝胶上解析,并使用湿转移系统转移到聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上。在室温(RT)下,将膜封闭在TBS-T(50mM Tris/HCL,pH 7.6,150mM NaCl和0.1%(v/v)Tween-20)中的5%(w/v)奶粉中1小时。将膜与稀释在TBS-T中的5%(w/v)奶粉中的一级抗体一起孵育,然后与适当的辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)偶联的二级抗体在TBS-T中稀释在5%(w/v)奶粉中孵育1小时。使用20ィ LumiGLO®化学发光试剂。在重新处理之前,使用Restore™PLUS蛋白质印迹剥离缓冲液剥离膜。[1] 将患有CAPS的个体的PBMC以2×0 106/ml的剂量接种在12孔板中,然后用1µg/ml LPS预处理3小时。用含有MCC950(5–1000 nM)的SFM代替培养基。45分钟后,收集细胞培养上清液和细胞裂解物。使用Novex®Tris-Glycine凝胶系统解析样品。[1] 荧光成像平板阅读器(FLIPR)Ca2+分析[1] 将BMDM(3×104/孔)在37°C下用不洗涤的钙染料(Molecular Devices)在含有0.1%BSA的生理盐水溶液(PSS;成分NaCl 140 mM,葡萄糖11.5 mM,KCl 5.9 mM,MgCl2 1.4 mM,NaH2PO4 1.2 mM,NaHCO3 5 mM,CaCl2 1.8 mM,HEPES 10 mM)中加载30分钟。然后将细胞转移到FLIPRETTRA荧光板读取器上,并使用冷却的CCD相机测量Ca2+响应,激发为470–495 nM,发射为515–575 nM。调节每个板的相机增益和强度,以产生至少1000个任意荧光单位(AFU)的基线荧光。在添加MCC950之前,采集10个基线荧光读数,然后在添加样品后300秒内每秒读取荧光读数,并在添加PSS或ATP(500µM)后再读取300秒。 BMDM培养及NLRP3激活实验:从C57BL/6、Nlrp3⁻/⁻、casp11⁻/⁻小鼠分离骨髓细胞,在含M-CSF的完全培养基中培养7天分化为BMDM。BMDM经LPS(100 ng/mL)预刺激3-4小时后,加入经典NLRP3激动剂(ATP 5 mM、尼日利亚菌素10 μM)或非经典激动剂(Pam3CSK4预刺激24小时后转染LPS 1 μg/mL)刺激。MCC950 sodium(1-1000 nM)在激动剂刺激前30分钟加入。刺激6-24小时后,收集细胞上清用于ELISA(IL-1β、TNF-α、IL-1α)和LDH实验;制备细胞裂解物用于Western blot(NLRP3、ASC、caspase-1、IL-1β、GAPDH)[1] - ASC寡聚化实验:BMDM经LPS预刺激后,在MCC950 sodium或小白菊内酯存在下用尼日利亚菌素刺激。用去垢剂裂解细胞,胞质组分与双琥珀酰亚胺辛二酸酯(DSS)室温交联30分钟,交联蛋白经SDS-PAGE分离后,用抗ASC抗体通过Western blot检测ASC寡聚体[1] - ASC斑点形成实验:将稳定表达ASC-天蓝荧光蛋白融合蛋白的ASC-cerulean报告细胞接种于96孔板,加入MCC950 sodium(0.05-10 μM)预处理30分钟,再用尼日利亚菌素、LeuLeu-Ome或致死毒素刺激2-4小时。采用共聚焦显微镜(×40倍)进行活细胞成像,计数ASC斑点阳性细胞;流式细胞术分析时,收集细胞并定量活细胞中ASC斑点阳性细胞比例[1] - K⁺外流和Ca²⁺内流实验:K⁺外流实验中,Nlrp3⁻/⁻ BMDM经LPS预刺激后,在MCC950 sodium存在下用尼日利亚菌素、ATP或SiO₂刺激,裂解细胞后通过电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法(ICP-OES)检测细胞内K⁺浓度。Ca²⁺内流实验中,LPS预刺激的C57BL/6或Ice⁻/⁻ BMDM负载Fluo-4 AM,加入MCC950 sodium后,采用FLIPR TETRA系统实时检测ATP诱导的Ca²⁺内流(激发光488 nm,发射光525 nm)[1] - HEK-293T细胞转染及免疫共沉淀实验:采用转染试剂将FLAG-NLRP3、HA-NLRP3、ASC或空载体质粒转染至HEK-293T细胞。24小时后,细胞经MCC950 sodium处理4小时,用免疫沉淀缓冲液裂解。用抗FLAG抗体和蛋白G磁珠免疫沉淀FLAG标签蛋白,通过抗ASC抗体Western blot检测共沉淀的ASC。ASC斑点分析实验中,HEK-293T细胞共转染GFP-ASC和NLRP3-mCherry质粒,经MCC950 sodium处理后,流式细胞术检测活细胞中ASC斑点阳性细胞比例[1] - 人PBMC实验:通过密度梯度离心从穆克-威尔士综合征(E313K突变)患者分离PBMC,经LPS(1 μg/mL)预刺激3小时后,加入MCC950 sodium预处理30分钟,继续培养24小时。收集细胞上清和裂解物,Western blot检测caspase-1剪切和IL-1β成熟[1] |
| 动物实验 |
In vivo LPS challenge[1]
C57BL/6 mice were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with 50 mg/kg MCC950 or vehicle control (DMSO/PBS) 1 h h before i.p. injection of 10 mg/kg LPS Escherichia coli 055:B5 or PBS. After for 2 h mice were sacrificed and serum levels of IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 were measured by ELISA.[1] Induction and Assessment of EAE[1] C57BL/6 mice were immunized subcutaneously with 150 µg of MOG peptide 35–55 (GenScript) emulsified in CFA containing 4 mg/ml (0.4.mg/mouse) of heat-killed MTB (Chondrex). Mice were injected i.p. with 500 ng pertussis toxin (PT: kaketsuken) on days 0 and 2. MCC950 was administered i.p. to mice (10 mg/kg) at induction of the disease, day 0, 1 and 2 and every 2 days thereafter. Control mice were administered vehicle (PBS) at the same time points. Mice were observed for clinical signs of disease daily (unblinded). Disease severity was scored as follows: no clinical signs, 0; limp tail, 1; ataxic gait, 2; hind limb weakness, 3; hind limb paralysis, 4; and tetra paralysis, 5., Experiments were performed under license (BI00/2412) from The Irish Medicine Board and with approval from the Trinity College Dublin BioResources Ethics Committee.[1] FACS analysis of EAE[1] On day 22 post immunization mononuclear cells were isolated from whole brains of perfused mice with EAE, following homogenisation and centrifugation on a Percoll gradient. Mononuclear cells (MNC) (2 × 106/ml) were stimulated for 4 h with PMA (10 ng/ml) and ionomycin (1 µg/ml) in the presence of brefeldin A (5 µg/ml). Cells were washed in PBS and re-suspended in 50 µL PBS with 1:1,000 LIVE/DEAD® Fixable Aqua Dead Cell Stain kit for 20 min. Surface stains for CD3 (145-2c11) (0.5 µl/106 cells), CD4 (RM4-5) (0.5 µl/106 cells) and γδ TCR (GL3) (1 µl/106 cells) (eBioscience) were added and cells were incubated for a further 20 mins. Cells were then fixed with 2% paraformaldehyde and washed in PBS twice, before being intracellularly stained for IL-17 or IFN-γ in permeabilization buffer (0.2% saponin in PBS + 1% FBS). Flow cytometric analysis of MNC was performed using a BD LSRFortessa™ and analysed with FlowJo software. MNC were first gated on live CD3+ T cells followed by CD4 expression, γδ TCR expression or cytokine production.[1] NLRP3 and NLRP1 activating mutation mice[1] Mice were backcrossed to C57BL/6 at least ten times. Nlrp3A350VneoR mice were provided by Hal M. Hoffman, The University of California, San Diego, U.S.A. and crossed with LysMCre mice (B6.129P2-Lyz2tm1(cre)Ifo/J. MCC950 was administered i.p. (20 mg/kg) every second day starting at day 4 after birth. Mice with an activating mutation in NLRP1, Nlrp1aQ593P were generated on a C57BL/6 background as described previously and administered MCC950 i.p. (20 mg/kg) every second day for 9 days. Blood was collected at the timepoints indicated for analysis of plasma cytokines by ELISA. IL-18 ELISA was performed as described by Westwell-Roper et al. Experiments were performed under AEC Project 2013.011 and were approved by the Animal Ethics Committee of The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research. EAE induction and treatment in mice: Female C57BL/6 mice (6-8 weeks old) were immunized with MOG₃₅₋₅₅ peptide emulsified in Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA) supplemented with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and pertussis toxin (200 ng) was injected intraperitoneally on day 0 and day 2 post-immunization to induce EAE. MCC950 sodium was dissolved in PBS and administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) at a specific dose (not detailed) once daily starting from the day of immunization. Clinical scores (0-5 scale, based on paralysis severity) were recorded daily for 22 days. On day 22, mice were sacrificed, and brain mononuclear cells were isolated for flow cytometry to detect IL-17/IFN-γ secreting T cells[1] - LPS-induced systemic inflammation in mice: C57BL/6 mice were pre-treated with MCC950 sodium (i.p., dose not detailed) or vehicle (PBS) 1 hour before intraperitoneal injection of LPS (10 mg/kg). Blood samples were collected 2 hours after LPS injection, and serum IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 levels were measured by ELISA (n=3 per group)[1] - CAPS mouse model treatment: Nlrp3A³⁵⁰VneoR × LysMCre mice (NLRP3 gain-of-function mutant) and wild-type (WT) littermates were treated with MCC950 sodium (dissolved in PBS, i.p., dose not detailed) or PBS starting from day 9 after birth. Body weight was measured at day 9, and survival was monitored up to day 45 (MCC950 withdrawn at day 28). Plasma IL-18 levels were measured by ELISA at day 9 and 14 days after drug withdrawal (n=3-6 per group). NLRP1 mutant (Nlrp1aQ593P) mice were used as controls and treated with MCC950 sodium or PBS[1] - Diabetic encephalopathy (DEP) model in db/db mice: Male db/db mice (8 weeks old) and db/m littermates were randomly divided into groups: db/m + vehicle, db/db + vehicle, db/db + MCC950 sodium. MCC950 sodium was dissolved in PBS and administered intraperitoneally at a dose of 10 mg/kg once daily for 8 weeks; vehicle-treated groups received PBS. Body weight and fasting blood glucose were measured weekly. Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT): mice fasted for 12 hours, then received glucose (2 g/kg) by gavage, and blood glucose was measured at 0, 30, 60, 90, 120 minutes. Insulin tolerance test (ITT): mice fasted for 4 hours, then received insulin (0.75 U/kg) i.p., and blood glucose was measured at 0, 15, 30, 60, 90 minutes. Behavioral tests (light/dark box, FST, TST, MWM) were performed after 8 weeks of treatment. After behavioral tests, mice were sacrificed, hippocampal tissue was collected for Western blot (NLRP3, ASC, IL-1β) and caspase-1 activity assay; plasma was collected for ELISA (insulin, IL-1β, TNF-α) (n=3-8 per group)[2] |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
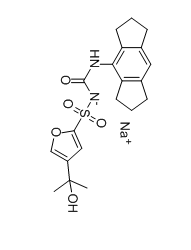
The NOD-like receptor (NLR) family, pyrin domain-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is a component of the inflammatory process, and its aberrant activation is pathogenic in inherited disorders such as cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS) and complex diseases such as multiple sclerosis, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's disease and atherosclerosis. We describe the development of MCC950, a potent, selective, small-molecule inhibitor of NLRP3. MCC950 blocked canonical and noncanonical NLRP3 activation at nanomolar concentrations. MCC950 specifically inhibited activation of NLRP3 but not the AIM2, NLRC4 or NLRP1 inflammasomes. MCC950 reduced interleukin-1β (IL-1β) production in vivo and attenuated the severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a disease model of multiple sclerosis. Furthermore, MCC950 treatment rescued neonatal lethality in a mouse model of CAPS and was active in ex vivo samples from individuals with Muckle-Wells syndrome. MCC950 is thus a potential therapeutic for NLRP3-associated syndromes, including autoinflammatory and autoimmune diseases, and a tool for further study of the NLRP3 inflammasome in human health and disease.[1]
Diabetes is associated with a high risk of developing cognitive dysfunction and neuropsychiatric disabilities, and these disease symptomsare termed diabetic encephalopathy (DEP). Inflammation is involved in the development of DEP. The cleavage and maturation of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-1β is regulated by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Obese and type 2 diabetic db/db mice show anxiety- and depression-like behaviors and cognitive disorders associated with hippocampal inflammation. The purpose of this study was to explore the role of NLRP3 inflammasome in DEP. Results showed that expression levels of inflammasome components including NLRP3, apoptosis-associated speck-like protein (ASC), and caspase-1, as well as IL-1β in the hippocampus of diabetic db/db mice were higher than those of non-diabetic db/m mice. Treatment of db/db mice with NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor MCC950 ameliorated anxiety- and depression-like behaviors as well as cognitive dysfunction, and reversed increased NLRP3, ASC, and IL-1βexpression levels and caspase-1 activity in hippocampus. Moreover, MCC950 treatment significantly improved insulin sensitivity in db/db mice. These results demonstrate that inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation may prove to be a potential therapeutic approach for DEP treatment.[2] MCC950 sodium (chemical name: N-(1,2,3,5,6,7-hexahydro-S-indacen-4-ylcarbamoyl)-4-(2-hydroxy-2-propanyl)-2-furansulfonamide sodium salt) is a potent, selective, small-molecule inhibitor of the NLRP3 inflammasome[1, 2] - The NLRP3 inflammasome is a key mediator of inflammatory responses, and its aberrant activation is associated with cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome (CAPS), multiple sclerosis, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer's disease, and atherosclerosis[1] - MCC950 sodium inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation by blocking ASC oligomerization (a critical step in NLRP3 assembly) without affecting upstream events (K⁺ efflux, Ca²⁺ flux, NLRP3 priming, or TLR signaling)[1] - MCC950 sodium is active in preclinical models of NLRP3-associated diseases: it attenuates EAE (multiple sclerosis model), rescues neonatal lethality in CAPS mice, and ameliorates diabetic encephalopathy in db/db mice by reducing hippocampal NLRP3 activation and neuroinflammation[1, 2] - MCC950 sodium is effective in ex vivo samples from individuals with Muckle-Wells syndrome (a CAPS subtype), indicating potential clinical application in human NLRP3-associated autoinflammatory and autoimmune diseases[1] |
| 分子式 |
C20H23N2O5S.NA
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
426.46
|
| 精确质量 |
426.122
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.33; H, 5.44; N, 6.57; Na, 5.39; O, 18.76; S, 7.52
|
| CAS号 |
256373-96-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
MCC950;210826-40-7
|
| PubChem CID |
91826093
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to yellow solid
|
| LogP |
4.977
|
| tPSA |
119.85
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
690
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
S(C1=C([H])C(=C([H])O1)C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])O[H])([N-]C(N([H])C1=C2C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C2=C([H])C2C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C=21)=O)(=O)=O.[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
LFQQNXFKPNZRFT-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H24N2O5S.Na/c1-20(2,24)14-10-17(27-11-14)28(25,26)22-19(23)21-18-15-7-3-5-12(15)9-13-6-4-8-16(13)18;/h9-11,24H,3-8H2,1-2H3,(H2,21,22,23);/q;+1/p-1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium ((1,2,3,5,6,7-hexahydro-s-indacen-4-yl)carbamoyl)((4-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)furan-2-yl)sulfonyl)amide
|
| 别名 |
CP-45677; CP45677; CP 45677; 256373-96-3; MCC950 sodium; CRID3 sodium salt; CP-456773 sodium; MCC950 (sodium); MCC950 sodium salt; CP-456773 sodium salt; MCC-950 sodium salt; MCC950; MCC 950; MCC-950; CRID-3; CRID3; CRID 3; CP-456773 sodium
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (11.72 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5%DMSO 95%PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。<
配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.86 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.86 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.88 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: 2%DMSO 98%PBS 配方 6 中的溶解度: 6.25 mg/mL (14.66 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3449 mL | 11.7244 mL | 23.4489 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4690 mL | 2.3449 mL | 4.6898 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2345 mL | 1.1724 mL | 2.3449 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。