| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
AR/Androgen-receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
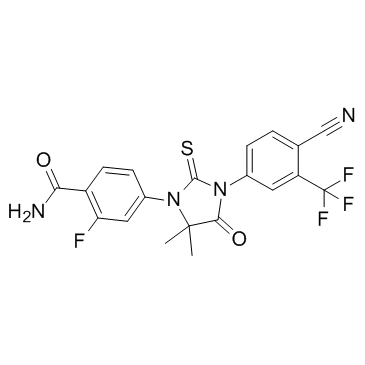
n-去甲基zalutamide是由4-{3-[4-氰基-3-(三氟甲基)苯基]-5,5-二甲基-4-氧-2-硫氧咪唑烷-1-基}-2-氟苯甲酸的羧基与氨缩合而成的一种苯酰胺。它具有抗肿瘤剂和雄激素拮抗剂的作用。它是苯酰胺、咪唑烷酮、腈、硫羰基化合物、(三氟甲基)苯和单氟苯的成员。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
由于 N-去亚甲基杂鲁胺比恩杂鲁胺更有效,并且显示出相似的主要功效和次要药效,因此 N-去亚甲基杂鲁胺是一种活性佐剂,可能在恩杂鲁胺的临床效果中发挥作用。恩杂鲁胺的葡萄糖胺代谢物具有药理学惰性,其循环浓度比恩杂鲁胺低约 25% [1]。
吉非罗齐联合给药使恩杂鲁胺与活性代谢物从零到无穷时血浆浓度-时间曲线下的复合面积(AUC∞)增加2.2倍,伊曲康唑联合给药使复合AUC∞增加1.3倍。恩杂鲁胺对口服吡格列酮暴露没有影响。恩杂鲁胺使口服s -华法林、奥美拉唑和咪达唑仑的AUC∞分别降低56%、70%和86%;因此,恩杂鲁胺是CYP2C9和CYP2C19的中度诱导剂,是CYP3A4的强诱导剂。 结论:如果患者需要与恩杂鲁胺同时使用强CYP2C8抑制剂,那么恩杂鲁胺的剂量应减少至80mg /天。建议避免enzalutamide与CYP2C9、CYP2C19或CYP3A4代谢的窄治疗指数药物同时使用,因为enzalutamide可能会减少它们的暴露。[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
以CYP2C8、CYP2C9、CYP2C19和CYP3A4为底物的研究。恩杂鲁胺及其主要代谢物的药代动力学参数(表4)证实,本研究中的血浆暴露与其他研究中观察到的结果相似,在其他研究中,恩杂鲁胺以160 mg每日一次的剂量给药至稳定状态[4]。对enzalutamide、n -去甲基enzalutamide、羧酸代谢物以及enzalutamide + n -去甲基enzalutamide的和的平均through值分别为12.0、10.6、6.32和23.0 μg/mL。[1]
|
| 动物实验 |
A parallel-treatment design (n = 41) was used to evaluate the effects of a strong cytochrome P450 (CYP) 2C8 inhibitor (oral gemfibrozil 600 mg twice daily) or strong CYP3A4 inhibitor (oral itraconazole 200 mg once daily) on the pharmacokinetics of enzalutamide and its active metabolite N-desmethyl enzalutamide after a single dose of enzalutamide (160 mg). A single-sequence crossover design (n = 14) was used to determine the effects of enzalutamide 160 mg/day on the pharmacokinetics of a single oral dose of sensitive substrates for CYP2C8 (pioglitazone 30 mg), CYP2C9 (warfarin 10 mg), CYP2C19 (omeprazole 20 mg), or CYP3A4 (midazolam 2 mg).[1]
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Study with Strong CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 Inhibitors As evidenced in Fig. 2, gemfibrozil decreased the rates of elimination of enzalutamide and formation of N-desmethyl enzalutamide while increasing the rate of formation of the carboxylic acid metabolite; these rates changed suddenly when gemfibrozil was discontinued on day 22. Given the apparent changes in pharmacokinetics of N-desmethyl enzalutamide after discontinuation of gemfibrozil, extrapolation of the observed concentration–time data in the terminal phase could not be used to estimate the magnitude of the effect of gemfibrozil on AUC∞. To address this issue, pharmacokinetic models were used to simulate concentration–time profiles for enzalutamide and metabolites for enzalutamide administered alone and enzalutamide coadministered with continuous gemfibrozil (i.e., no discontinuation on day 22) (Electronic Supplementary Material 1). Simulated concentration–time data for each of the 41 subjects in the study were then analyzed by NCA methods to estimate AUC∞ values. As AUC18 d and Cmax were defined by plasma concentration–time data prior to gemfibrozil discontinuation on day 22, these parameters were estimated by NCA analysis of observed data. [1]
As indicated by the geometric mean ratios (GMRs; Table 3), gemfibrozil had the following effects on enzalutamide and the active metabolite: for enzalutamide, AUC18 d and AUC∞ increased by 2.53-fold and 4.26-fold, respectively, while Cmax decreased by 18 %; for N-desmethyl enzalutamide, AUC18 d, AUC∞, and Cmax decreased by 67, 25, and 44 %, respectively; and for the composite sum of enzalutamide plus N-desmethyl enzalutamide, AUC18 d and AUC∞ increased by 1.39-fold and 2.17-fold, respectively, while Cmax decreased by 16 %. Notably, the estimated magnitude of the effect of gemfibrozil on the sum of exposure to active moieties (enzalutamide plus N-desmethyl enzalutamide) was smaller for the AUC term based on observed data (AUC18 d) than for the AUC term based on modeling and simulation (AUC∞).[1] Itraconazole appeared to have only a small impact on the elimination of enzalutamide and the rates of formation of N-desmethyl enzalutamide and the carboxylic acid metabolite (Fig. 2); therefore, all pharmacokinetic parameters for assessing the itraconazole drug interaction were based on observed data. As indicated by the GMR values (Table 3), itraconazole had the following effects on enzalutamide and the active metabolite: for enzalutamide, AUC18 d and AUC∞ increased 1.34-fold and 1.41-fold, respectively, while Cmax decreased by 2 %; for N-desmethyl enzalutamide, AUC18 d decreased by 4 %, AUC∞ increased 1.21-fold, and Cmax decreased by 14 %; and for the sum of enzalutamide plus N-desmethyl enzalutamide, AUC18 d and AUC∞ increased 1.14-fold and 1.28-fold, respectively, while Cmax decreased by 3 %.[1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
No deaths, serious adverse events, or adverse events resulting in discontinuation occurred during the healthy subject study with CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 inhibitors. Thirteen subjects (three in arm 1, six in arm 2, and four in arm 3) experienced at least one treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE). All events were categorized as National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI-CTCAE) grade 1, with the exception of grade 2 flatulence in one subject (arm 2) that was attributed to a possible relationship to gemfibrozil. Four additional subjects experienced at least one TEAE that was attributed a possible relationship to the study drug. All TEAEs resolved by the end of the study.
In the patient study with CYP substrates, the most frequent TEAEs (i.e., in at least three of 14 patients, ≥21.4 %) were nausea, constipation, dizziness, arthropod bite, fatigue, and hot flush. The majority of reported TEAEs were NCI-CTCAE grade 1 or 2. One patient experienced a single and transient episode of generalized tonic–clonic seizure that was assessed as probably related to enzalutamide and led to discontinuation of study treatment with enzalutamide. No clinically significant changes were noted for safety laboratory tests or electrocardiograms.[1]
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
N-desmethylenzalutamide is a benzamide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-{3-[4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-thioxoimidazolidin-1-yl}-2-fluorobenzoic acid with ammonia. It has a role as an antineoplastic agent and an androgen antagonist. It is a member of benzamides, an imidazolidinone, a nitrile, a thiocarbonyl compound, a member of (trifluoromethyl)benzenes and a member of monofluorobenzenes.
|
| 分子式 |
C₂₀H₁₄F₄N₄O₂S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
450.41
|
| 精确质量 |
450.077
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.33; H, 3.13; F, 16.87; N, 12.44; O, 7.10; S, 7.12
|
| CAS号 |
1242137-16-1
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Enzalutamide;915087-33-1;N-desmethyl Enzalutamide-d6;Enzalutamide carboxylic acid;1242137-15-0
|
| PubChem CID |
70678916
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.562
|
| tPSA |
122.52
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
824
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
JSFOGZGIBIQRPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H14F4N4O2S/c1-19(2)17(30)27(11-4-3-10(9-25)14(7-11)20(22,23)24)18(31)28(19)12-5-6-13(16(26)29)15(21)8-12/h3-8H,1-2H3,(H2,26,29)
|
| 化学名 |
4-[3-[4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-sulfanylideneimidazolidin-1-yl]-2-fluorobenzamide
|
| 别名 |
N-desmethyl MDV 3100; N-desmethyl MDV-3100; N-desmethyl enzalutamide; 1242137-16-1; N-desmethylenzalutamide; 4-(3-(4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-thioxoimidazolidin-1-yl)-2-fluorobenzamide; CHEMBL5171907; N-desmethyl MDV3100
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~222.02 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.55 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2202 mL | 11.1010 mL | 22.2020 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4440 mL | 2.2202 mL | 4.4404 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2220 mL | 1.1101 mL | 2.2202 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。