| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Two female goats weighing 43 kg (#1) and 34 kg (#2) (1.4 and 1.8 mg/kg bodyweight respectively), were dosed daily for 3 consecutive days in feed rations treated with (pyrimidine2-(14)C)nicosulfuron, sp. act., 62.2 uCi/mg, radiochemical purity, >95%, isotopic purity, 97%, and (pyridine-2-(14)C)nicosulfuron, sp. act., 62.9 uCi/mg, radiochemical purity, >95%, isotopic purity, >99%, respectively. Dosing capsules were prepared with the (14)C-labeled materials, 13C-enriched isomers (C2 position of each respective ring), and nonradioactive nicosulfuron. The capsules were analyzed prior to dosing by LSC for total (14)C-activity and by HPLC for chemical analysis. These capsules were imbedded in a larger gelatin capsule containing 6 g of goat chow. Goat #1 was housed for a 9-day acclimation period, while goat #2 was kept for 11 days. Both goats showed good health and milk production before and during dosing. The dosage represents a daily feeding level of approximately 60 ppm based on the average feed and hay consumption of 1 kg/day. Samples of milk, bile, urine, and feces were collected daily and analyzed by combustion/liquid scintillation counting. A control goat was not used in the study. Milk, bile, urine, and feces were collected at least one day prior to dosing for use as control samples. ... The administered 14C-dosage was excreted in the urine at 46% and 17%, and in the feces at 62% and 32%, respectively for the pyridinyl- and pyrimidinyl-labeled nicosulfuron. Uptake of residues was low for all tissues and organs for either label. The highest level, 0.1 ppm (0.04% of total dose) was in the liver from the goat treated with the pyridinyl label. All other tissues had total readioactive residue (TRR) of approximately 0.07 ppm or less (nicosulfuron equivalents). Radioactivity in the collected bile comprised 0.1% and 0.7% of the total dose, respectively for the pyridinyl- and pyrimidinyl labeled nicosulfuron. ... The ... /absorption and elimination/ of /nicosulfuron/ (2-(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl) aminocarbonylaminosulfonyl-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridinecarboxamide) was studied in male and female Sprague-Dawley Crl:CDBR rats. Pyridine-2-(14)C nicosulfuron was administered orally at 10 mg/kg or 1000 mg/kg, at 10 mg/kg following oral administration of unlabeled nicosulfuron at 10 mg/kg/day for 14 days, and intravenously at 10 mg/kg. Pyrimidine-2-(14)C labeled nicosulfuron was also administered orally at 1000 mg/kg. Total recovery of administered radioactivity 4 days postdosing accounted for 98-109% of the dose. Most of the radioactivity was excreted unchanged within 24 hours post dosing. With oral dosing, there were no apparent differences between sexes or dose groups, although a slightly greater percentage of the administered radioactivity was detected in feces of animals receiving the high dose than in animals receiving the low dose. Following oral dosing, elimination in the feces accounted for 80 to 95% of the dose, and elimination in the urine accounted for 9 to 20%. Elimination of (14)C-CO2 was negligible (<0.01 of the administered dose). ... Following intravenous administration, approximately 76 to 80% of the dose was eliminated in the urine and 27 to 30% in the feces. Residues in tissues accounted for 0.05 to 0.5% of the dose. The major excretion product in urine and feces was unchanged parent compound. In addition, pyridinesulfonamide (N,N-dimethyl-2-sulfonamide pyridine-3-carboxamide) was detected in the urine and accounted for 1.1 to 5.7% of the dose. Pyridine acid sulfonamide (2-sulfonamidepyridine-3-carboxylic acid) was tentatively identified as a minor metabolite in the feces of orally dosed rats and urine of intravenously dosed rats. ... Metabolism / Metabolites Two female goats weighing 43 kg (#1) and 34 kg (#2) (1.4 and 1.8 mg/kg bodyweight respectively), were dosed daily for 3 consecutive days in feed rations treated with (pyrimidine2-(14)C)nicosulfuron, sp. act., 62.2 uCi/mg, radiochemical purity, >95%, isotopic purity, 97%, and (pyridine-2-(14)C)nicosulfuron, sp. act., 62.9 uCi/mg, radiochemical purity, >95%, isotopic purity, >99%, respectively. Dosing capsules were prepared with the (14)C-labeled materials, 13C-enriched isomers (C2 position of each respective ring), and nonradioactive nicosulfuron. The capsules were analyzed prior to dosing by LSC for total (14)C-activity and by HPLC for chemical analysis. These capsules were imbedded in a larger gelatin capsule containing 6 g of goat chow. Goat #1 was housed for a 9-day acclimation period, while goat #2 was kept for 11 days. Both goats showed good health and milk production before and during dosing. The dosage represents a daily feeding level of approximately 60 ppm based on the average feed and hay consumption of 1 kg/day. Samples of milk, bile, urine, and feces were collected daily and analyzed by combustion/liquid scintillation counting. A control goat was not used in the study. Milk, bile, urine, and feces were collected at least one day prior to dosing for use as control samples. ... The proposed metabolic pathway for nicosulfuron in the goat showed primarily three mechanisms: 1) hydrolysis of the sulfonylurea bridge to yield pyridine sulfonamide and pyrimidine amine (both of which undergo additional metabolism); 2) N-demethylation and subsequent loss of sulfur dioxide leading to the cyclized compound N2; and 3) oxidation and conjugation at the 5-position of the pyrimidine ring. The metabolism of /nicosulfuron/ (2-(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl) aminocarbonylaminosulfonyl-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridinecarboxamide (Accent)) was studied in male and female Sprague-Dawley Crl:CDBR rats. Pyridine-2-(14)C Accent was administered orally at 10 mg/kg or 1000 mg/kg, at 10 mg/kg following oral administration of unlabeled Accent at 10 mg/kg/day for 14 days, and intravenously at 10 mg/kg. Pyrimidine-2-(14)C labeled Accent was also administered orally at 1000 mg/kg. ... Metabolites; / pyridinesulfonamide (N,N-dimethyl-2-sulfonamide pyridine-3-carboxamide) and Pyridine acid sulfonamide (2-sulfonamidepyridine-3-carboxylic acid)/ represent hydrolytic cleavage/oxidation of the parent molecule. Biological Half-Life The ... /absorption and elimination/ of /nicosulfuron/ (2-(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl) aminocarbonylaminosulfonyl-N,N-dimethyl-3-pyridinecarboxamide) was studied in male and female Sprague-Dawley Crl:CDBR rats. Pyridine-2-(14)C nicosulfuron was administered orally at 10 mg/kg or 1000 mg/kg, at 10 mg/kg following oral administration of unlabeled nicosulfuron at 10 mg/kg/day for 14 days, and intravenously at 10 mg/kg. Pyrimidine-2-(14)C labeled nicosulfuron was also administered orally at 1000 mg/kg. ... The average total cumulative excretion indicated half-lives between 12 and 24 hours. |
|---|---|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Non-Human Toxicity Values
LC50 Rat inhalation 5.47 mg/L/4 hr LD50 Rat dermal >2000 mg/kg LD50 Mouse oral >5000 mg/kg LD50 Rat oral >5000 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
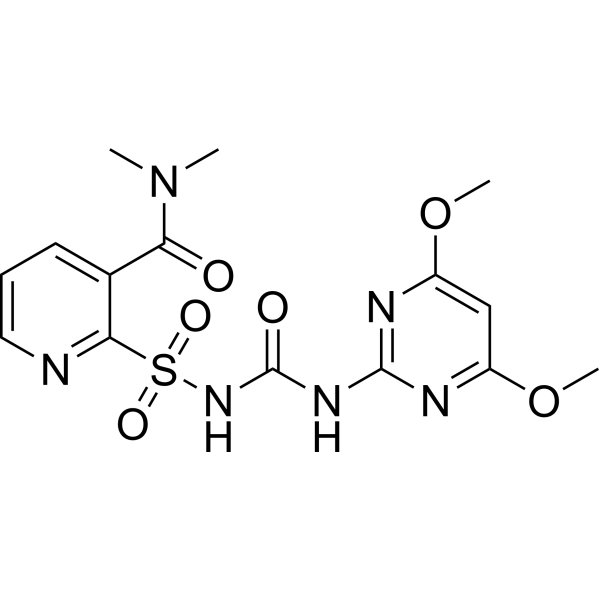
Nicosulfuron is a N-sulfonylurea that is 2-(carbamoylsulfamoyl)-N,N-dimethylpyridine-3-carboxamide substituted by a 4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl group at the amino nitrogen. It has a role as an environmental contaminant, a xenobiotic and a herbicide. It is a member of pyridines, a N-sulfonylurea and a member of pyrimidines.
|
| 分子式 |
C15H18N6O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
410.41
|
| 精确质量 |
410.1
|
| CAS号 |
111991-09-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Nicosulfuron-d6;1189419-41-7
|
| PubChem CID |
73281
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
719.1±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
141-144°C
|
| 闪点 |
388.7±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.640
|
| LogP |
-2.09
|
| tPSA |
161.09
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
9
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
642
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
RTCOGUMHFFWOJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H18N6O6S/c1-21(2)13(22)9-6-5-7-16-12(9)28(24,25)20-15(23)19-14-17-10(26-3)8-11(18-14)27-4/h5-8H,1-4H3,(H2,17,18,19,20,23)
|
| 化学名 |
2-[(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)carbamoylsulfamoyl]-N,N-dimethylpyridine-3-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
Milagro; Accent; Nicosulfuron
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~33.33 mg/mL (~81.21 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.09 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.09 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4366 mL | 12.1829 mL | 24.3659 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4873 mL | 2.4366 mL | 4.8732 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2437 mL | 1.2183 mL | 2.4366 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。