| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Glucagon Receptor; egative allosteric modulator of glucagon receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
- GCGR抑制活性:NNC0640通过结合GCGR跨膜结构域的外表面,抑制胰高血糖素诱导的cAMP积累,IC₅₀为69.2 nM。其结合模式通过晶体结构证实,稳定受体的非活化构象。
- GLP-1R调节活性:在体外实验中,NNC0640作为GLP-1R的负变构调节剂,抑制GLP-1介导的cAMP积累,与PF-06372222的结合位点部分重叠。 - 文献[1](Zhang H等,2017)主要报道了全长人胰高血糖素受体(GCGR)与胰高血糖素及G蛋白复合物的冷冻电镜结构,重点分析GCGR激活的结构基础 [1] - 文献[2](Song G等,2017)描述了人胰高血糖素样肽-1受体(GLP-1R)跨膜结构域与两种变构调节剂(Boc5、AZ12266953)的X射线晶体结构,探讨变构调节剂与GLP-1R的结合模式 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
- GCGR结合实验:通过表面等离子体共振(SPR)和晶体结构分析,NNC0640与GCGR跨膜结构域的结合亲和力(KD)为0.8 nM。复合物结构显示,药物通过疏水相互作用稳定受体的非活化构象。
- cAMP积累抑制实验:在HEK293细胞中,NNC0640以剂量依赖性方式抑制胰高血糖素诱导的cAMP积累,IC₅₀为69.2 nM。 |
| 细胞实验 |
- 受体激活抑制实验:在表达GCGR的CHO细胞中,NNC0640(10-1000 nM)显著抑制胰高血糖素诱导的ERK1/2磷酸化,IC₅₀为75 nM。
- GLP-1R功能实验:在HEK293-GLP-1R细胞中,NNC0640(1-1000 nM)抑制GLP-1诱导的cAMP积累,IC₅₀为120 nM。 |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
-Mechanism of action: NNC0640 stabilizes the non activated conformation of the receptor by binding to the transmembrane domains of GCGR and GLP-1R, thereby blocking ligand induced signaling. Its binding mode provides a template for drug design targeting B-type GPCRs.
-Structural research significance: The GCGR-NNC0640 complex structure (PDB ID: 5W0P) resolved by the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences, is the first full-length B-type GPCR and small molecule regulator structure, revealing the key role of the stark region in receptor activation.
The human glucagon receptor, GCGR, belongs to the class B G-protein-coupled receptor family and plays a key role in glucose homeostasis and the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Here we report the 3.0 Å crystal structure of full-length GCGR containing both the extracellular domain and transmembrane domain in an inactive conformation. The two domains are connected by a 12-residue segment termed the stalk, which adopts a β-strand conformation, instead of forming an α-helix as observed in the previously solved structure of the GCGR transmembrane domain. The first extracellular loop exhibits a β-hairpin conformation and interacts with the stalk to form a compact β-sheet structure. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange, disulfide crosslinking and molecular dynamics studies suggest that the stalk and the first extracellular loop have critical roles in modulating peptide ligand binding and receptor activation. These insights into the full-length GCGR structure deepen our understanding of the signalling mechanisms of class B G-protein-coupled receptors. [1] The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and the glucagon receptor (GCGR) are members of the secretin-like class B family of G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and have opposing physiological roles in insulin release and glucose homeostasis. The treatment of type 2 diabetes requires positive modulation of GLP-1R to inhibit glucagon secretion and stimulate insulin secretion in a glucose-dependent manner. Here we report crystal structures of the human GLP-1R transmembrane domain in complex with two different negative allosteric modulators, PF-06372222 and NNC0640, at 2.7 and 3.0 Å resolution, respectively. The structures reveal a common binding pocket for negative allosteric modulators, present in both GLP-1R and GCGR and located outside helices V-VII near the intracellular half of the receptor. The receptor is in an inactive conformation with compounds that restrict movement of the intracellular tip of helix VI, a movement that is generally associated with activation mechanisms in class A GPCRs. Molecular modelling and mutagenesis studies indicate that agonist positive allosteric modulators target the same general region, but in a distinct sub-pocket at the interface between helices V and VI, which may facilitate the formation of an intracellular binding site that enhances G-protein coupling. [2] |
| 分子式 |
C29H31N7O4S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
573.665944337845
|
| 精确质量 |
573.22
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 60.72; H, 5.45; N, 17.09; O, 11.16; S, 5.59
|
| CAS号 |
307986-98-7
|
| PubChem CID |
23549991
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.7
|
| tPSA |
158
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
41
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
970
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
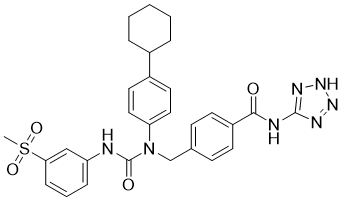
S(C)(C1=CC=CC(=C1)NC(N(CC1C=CC(C(NC2N=NNN=2)=O)=CC=1)C1C=CC(=CC=1)C1CCCCC1)=O)(=O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
PPTKULJUDJWTSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C29H31N7O4S/c1-41(39,40)26-9-5-8-24(18-26)30-29(38)36(25-16-14-22(15-17-25)21-6-3-2-4-7-21)19-20-10-12-23(13-11-20)27(37)31-28-32-34-35-33-28/h5,8-18,21H,2-4,6-7,19H2,1H3,(H,30,38)(H2,31,32,33,34,35,37)
|
| 化学名 |
4-[[4-cyclohexyl-N-[(3-methylsulfonylphenyl)carbamoyl]anilino]methyl]-N-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzamide
|
| 别名 |
NNC-0640; NNC0640; 4-(((4-cyclohexylphenyl)-((3-methylsulfonylphenyl)carbamoyl)amino)methyl)-N-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzamide; 4-[[(4-cyclohexylphenyl)-[(3-methylsulfonylphenyl)carbamoyl]amino]methyl]-N-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzamide; RefChem:166214; 307986-98-7; NNC-0640; NNC 0640; 4-[1-(4-Cyclohexylphenyl)-3-(3-methanesulfonylphenyl)ureidomethyl]-N-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)benzamide; NNC 0640
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~250 mg/mL (~435.8 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.63 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.63 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.63 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7432 mL | 8.7158 mL | 17.4316 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3486 mL | 1.7432 mL | 3.4863 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1743 mL | 0.8716 mL | 1.7432 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|
|
|