| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
JAK1 (IC50 = 10 nM); JAK2 (IC50 = 18 nM); Tyk2 (IC50 = 84 nM); JAK3 (IC50 = 99 nM)
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
使用分离的酶系统和体外人类或犬细胞模型评估 Oclacitinib 对 JAK 家族成员和导致细胞中 JAK 激活的细胞因子的功效和选择性。在分离的酶系统中,确定了 oclacitinib 对 JAK 家族成员的抑制作用。 Oclacitinib 在剂量(IC50)分别为 10、18、99 和 84 nM 时,JAK1、JAK2、JAK3 和 TYK2 均被抑制 50%。 oclacitinib 对 JAK1 的选择性是 JAK2 的 1.8 倍,对 JAK1 的选择性是 JAK3 的 9.9 倍,因此对 JAK1 酶表现出最高的效力。 Oclacitinib 不抑制 38 种非 JAK 激酶(IC50 > 1000 nM),但在 10 至 99 nM 的剂量(IC50)下,它可抑制 JAK 家族成员 50%。 oclacitinib 的 IC50 值范围为 36 至 249 nM,还降低与过敏、炎症和瘙痒相关的 JAK1 依赖性细胞因子(IL-2、IL-4、IL-6 和 IL-13)的活性。 Oclacitinib 对不激活细胞中 JAK1 酶的细胞因子(促红细胞生成素、粒细胞/巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、IL-12、IL-23;IC50 > 1000 nM)的影响可以忽略不计[1]。与用媒介物处理的耳朵相比,用托法替尼 (0.1%) 和奥拉替尼 (0.1%) 局部治疗显着减少了小鼠耳外植体的细胞迁移(所有 P < 0.05)。与用 JAK 抑制剂处理的每个表皮相比,用媒介物处理的表皮中 MHC II 类阳性细胞或朗格汉斯细胞的数量显着较低(所有 P<0.01)[2]。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Oclacitinib 组中高剂量的抓挠次数明显少于仅使用媒介物的组 (P<0.01)[2]。包括经主人评估患有中度至重度瘙痒且推定诊断为过敏性皮炎的客户自养狗 (n=436)。狗被随机接受 0.4-0.6 mg/kg 口服 Oclacitinib,每天两次,或接受赋形剂匹配的安慰剂。使用改进的 10 厘米视觉模拟量表 (VAS) 来评估第 0 天至第 7 天的瘙痒强度,并评估第 0 天和第 7 天皮炎的严重程度。狗可以继续研究 28 天。奥拉替尼在 24 小时内快速起效[3]。
与仅使用载体组相比,高剂量 Oclacitinib 组的抓挠次数明显减少 (P<0.01)。登记的客户拥有的狗(n = 436)可能被诊断为过敏性皮炎,并且主人评估患有中度至重度瘙痒。狗被随机接受赋形剂匹配的安慰剂或奥拉替尼,剂量为 0.4-0.6 mg/kg,每天口服两次。在第0天和第7天测量皮炎的强度,并使用改进的10cm视觉模拟量表(VAS)从第0天到第7天测量瘙痒程度。狗可以接受长达 28 天的试验。 Oclacitinib 24 小时快速起效[3]。 结果:两个治疗组的预处理所有者和兽医VAS评分相似Oclacitini在24小时内迅速起效。在每个评估日,平均Oclacitinib所有者Pruritus VAS评分明显优于安慰剂评分(P<0.0001)。经oclacitinib治疗后,瘙痒评分从7.58 cm降至2.59 cm。第7天的平均oclacitinib兽医皮炎VAS评分也明显优于安慰剂评分(P<0.0001)。两组报告的腹泻和呕吐频率相似。 结论和临床重要性:在这项研究中,奥拉西替尼对与过敏性皮炎相关的瘙痒提供了快速、有效和安全的控制,业主和兽医注意到瘙痒和皮炎VAS评分有了显著改善[3]。 |
||
| 酶活实验 |
Janus激酶活性测定和激酶选择性面板[1]
如前所述(Meyer等人,2010),使用Caliper微流体技术在分离的酶测定中使用JAK1(氨基酸852-1142;NP_002218)、JAK2(氨基酸808-1132;NP_004963)、JAK3(氨基酸781-1124;NP_000206)和TYK2(氨基酸870-1187;NP_003322)的重组人活性激酶结构域,以确定Oclacitinib对JAK家族成员的效力。与犬JAK酶中类似序列的序列同源性分别为98、98、100和90%(图S1)。使用SelectScreen™激酶分析服务进行Invitrogen激酶面板测试,以确定奥拉西替尼对38种不同非JAK激酶的效力奥拉西替尼的浓度为1μm。激酶特异性测定条件和数据分析在他们的网站上进行了描述http://www.lifetechnologies.com/us/en/home/products-and-services/services/custom-services/screening-and-profiling-services/selectscreen-profiling-service/selectscreen-kinase-profiling-service.html.该服务利用Z'-Lyte技术进行所有激酶筛查。所有测试都进行了两次。 |
||
| 细胞实验 |
白细胞介素-6细胞因子功能[1]
使用Invitrogen的CellSensor®STAT3-bla-HEK293T人上皮细胞系。将细胞在含有5%FBS的DMEM高糖培养基中以每孔1.875×105个细胞的密度铺入384孔、黑壁、透明底部的测定板中,并在37°C、5%CO2下孵育Oclacitinib(0.0000954-25μm)或载体对照加入细胞1小时。然后将每毫升20纳克hIL-6加入细胞培养物5小时。通过用LiveBLAzer™-FRET B/G底物(CCF-4 AM)检测β-内酰胺酶活性来确定IL-6对STAT3β-内酰酶报告基因的激活。使用荧光板读数器获得460和530nm处的荧光发射值。460/530 nm比值表示为对照百分比,剂量反应数据使用4参数逻辑斯谛方程进行分析。 白细胞介素-13细胞因子功能[1] 使用美国典型培养物保藏中心的HT-29人结肠上皮细胞系。细胞在含有10%FBS、50 U/mL青霉素、50μg/mL链霉素和2 mm l-谷氨酰胺的McCoy 5A培养基中增殖。从培养瓶中胰蛋白酶消化细胞,在新鲜培养基中洗涤,并以每孔3×105个细胞的密度重新悬浮在96孔的测定板上Oclacitini(0.0015-30μm))或载体对照加入细胞中,同时在冰上放置30分钟。然后加入每毫升1纳克hIL-13。细胞在37°C水浴中孵育30分钟,然后在1.75%甲醛的PBS中固定,在含有0.5%BSA的PBS中洗涤,并在-20°C的无水甲醇中孵育过夜。固定细胞用PE标记的人pSTAT6抗体染色。使用配备板式自动取样器的FACSCalibur对样品进行分析,并使用FlowJo软件7.6.1版进行分析。数据表示为平均荧光,然后表示为对照百分比。然后使用4参数逻辑斯谛方程分析剂量反应数据。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
The objective of this study was to determine the pharmacokinetic parameters of oclacitinib maleate as a top dress given to adult horses. Six adult horses with a mean weight of 528 kg were administered a single dose of 0.5 mg/kg oclacitinib maleate. Blood was collected prior to drug administration and at 15 min, 30 min, 45 min, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h after treatment. Oclacitinib maleate plasma concentrations were measured by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Pharmacokinetic parameters were found best to fit a one-compartment model. Mean Cmax was 486 ng/ml (range 423-549 ng/ml), and Tmax was estimated to be 1.7 h (range 0.3-3.1 h). The estimated T1/2 was 7.5-8 h. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35098559/
Background: Oclacitinib is a Janus kinase (JK)1 inhibitor that has been shown to be effective and safe for the treatment of allergic dermatitis in dogs. Its use in cats has been limited by the absence of pharmacokinetic data. Objective: To determine the pharmacokinetic parameters of oclacitinib in cats after oral and intravenous administration. Animals: Six adult domestic short hair cats. Methods and materials: A two period, two treatment design was used in which cats received oclacitinib maleate i.v. and p.o., at a dose of 0.5 mg/kg and 1 mg/kg, respectively. There was a one-week interval of washout between the two treatments. Cats received each treatment only once. The plasma concentration of oclacitinib was determined by high-performance liquid chromatography at 0 min, 5 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 4 h, 6 h, 10 h and 24 h after intravenous.v administration, at 0 min, 15 min, 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, 10 h and 24 h after p.o. administration. Results: After p.o. administration, oclacitinib was absorbed rapidly and almost completely, as shown by an absolute bioavailability of 87% and a Tmax of 35 min. The elimination of the drug also was very rapid as shown by a half-life of 2.3 h and a clearance calculated as 4.45 mL/min/kg (after i.v. administration). Conclusions and clinical importance: The pharmacokinetic parameters of oclacitinib in the cat are similar to those described for the dog, although absorption and elimination are somewhat faster and variability between individuals is somewhat greater. Larger doses and/or shorter dosing intervals would be recommended in cats to achieve similar blood concentrations to those in dogs. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31769185/ The pharmacokinetics of oclacitinib maleate was evaluated in four separate studies. The absolute bioavailability study used a crossover design with 10 dogs. The effect of food on bioavailability was investigated in a crossover study with 18 dogs. The breed effect on pharmacokinetics was assessed in a crossover study in beagles and mongrels dogs. Dose proportionality and multiple dose pharmacokinetics were evaluated in a parallel design study with eight dogs per group. In all four studies, serial blood samples for plasma were collected. Oclacitinib maleate was rapidly and well absorbed following oral administration, with a time to peak plasma concentration of <1 h and an absolute bioavailability of 89%. The prandial state of dogs did not significantly affect the rate or extent of absorption of oclacitinib maleate when dosed orally, as demonstrated by the lack of significant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters between the oral fasted and oral fed treatment groups. The pharmacokinetics of oclacitinib in laboratory populations of beagles and mixed breed dogs also appeared similar. Following oral administration, the exposure of oclacitinib maleate increased dose proportionally from 0.6 to 3.0 mg/kg. Additionally, across the pharmacokinetic studies, there were no apparent differences in oclacitinib pharmacokinetics attributable to sex. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24330031/ |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Janus kinase (JAK) enzymes are involved in cell signaling pathways activated by various cytokines dysregulated in allergy. The objective of this study was to determine whether the novel JAK inhibitor oclacitinib could reduce the activity of cytokines implicated in canine allergic skin disease. Using isolated enzyme systems and in vitro human or canine cell models, potency and selectivity of oclacitinib was determined against JAK family members and cytokines that trigger JAK activation in cells. Oclacitinib inhibited JAK family members by 50% at concentrations (IC50 's) ranging from 10 to 99 nm and did not inhibit a panel of 38 non-JAK kinases (IC50 's > 1000 nM). Oclacitinib was most potent at inhibiting JAK1 (IC50 = 10 nM). Oclacitinib also inhibited the function of JAK1-dependent cytokines involved in allergy and inflammation (IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, and IL-13) as well as pruritus (IL-31) at IC50 's ranging from 36 to 249 nM. Oclacitinib had minimal effects on cytokines that did not activate the JAK1 enzyme in cells (erythropoietin, granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor, IL-12, IL-23; IC50 's > 1000 nM). These results demonstrate that oclacitinib is a targeted therapy that selectively inhibits JAK1-dependent cytokines involved in allergy, inflammation, and pruritus and suggests these are the mechanisms by which oclacitinib effectively controls clinical signs associated with allergic skin disease in dogs. [1]
The prevalence of allergic skin disorders has increased rapidly, and development of therapeutic agents to alleviate the symptoms are still needed. In this study, we orally or topically administered the Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, tofacitinib and oclacitinib, in a mouse model of dermatitis, and compared the efficacy to reduce the itch and inflammatory response. In vitro effects of JAK inhibitors on bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDCs) were analyzed. For the allergic dermatitis model, female BALB/c mice were sensitized and challenged with toluene-2,4-diisocyanate (TDI). Each JAK inhibitor was orally or topically applied 30 minutes before and 4 hours after TDI challenge. After scratching bouts and ear thickness were measured, cytokines were determined in challenged skin and the cells of the draining lymph node were analyzed by means of flow cytometry. In vitro, both JAK inhibitors significantly inhibited cytokine production, migration, and maturation of BMDCs. Mice treated orally with JAK inhibitors showed a significant decrease in scratching behavior; however, ear thickness was not significantly reduced. In contrast, both scratching behavior and ear thickness in the topical treatment group were significantly reduced compared with the vehicle treatment group. However, cytokine production was differentially regulated by the JAK inhibitors, with some cytokines being significantly decreased and some being significantly increased. In conclusion, oral treatment with JAK inhibitors reduced itch behavior dramatically but had only little effect on the inflammatory response, whereas topical treatment improved both itch and inflammatory response. Although the JAK-inhibitory profile differs between both JAK inhibitors in vitro as well as in vivo, the effects have been comparable.[2] Background: Oclacitinib (Apoquel(®) ) inhibits the function of a variety of pro-inflammatory, pro-allergic and pruritogenic cytokines that are dependent on Janus kinase enzyme activity. Oclacitinib selectively inhibits Janus kinase 1. Hypothesis/objectives: We aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of oclacitinib for the control of pruritus associated with allergic dermatitis in a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial. Methods: Client-owned dogs (n = 436) with moderate to severe owner-assessed pruritus and a presumptive diagnosis of allergic dermatitis were enrolled. Dogs were randomized to either oclacitinib at 0.4-0.6 mg/kg orally twice daily or an excipient-matched placebo. An enhanced 10 cm visual analog scale (VAS) was used by the owners to assess the severity of pruritus from day 0 to 7 and by veterinarians to assess the severity of dermatitis on days 0 and 7. Dogs could remain on the study for 28 days. Results: Pretreatment owner and veterinary VAS scores were similar for the two treatment groups. Oclacitinib produced a rapid onset of efficacy within 24 h. Mean oclacitinib Owner Pruritus VAS scores were significantly better than placebo scores (P < 0.0001) on each assessment day. Pruritus scores decreased from 7.58 to 2.59 cm following oclacitinib treatment. The day 7 mean oclacitinib Veterinarian Dermatitis VAS scores were also significantly better (P < 0.0001) than placebo scores. Diarrhoea and vomiting were reported with similar frequency in both groups. Conclusions and clinical importance: In this study, oclacitinib provided rapid, effective and safe control of pruritus associated with allergic dermatitis, with owners and veterinarians noting substantial improvements in pruritus and dermatitis VAS scores.[3] |
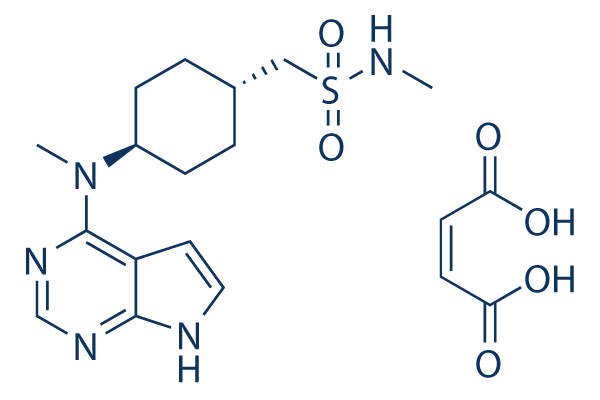
| 分子式 |
C19H27N5O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
453.512583017349
|
| 精确质量 |
453.168
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 50.32; H, 6.00; N, 15.44; O, 21.17; S, 7.07
|
| CAS号 |
1640292-55-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Oclacitinib;1208319-26-9; 1208319-27-0; 1640292-55-2
|
| PubChem CID |
44631937
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| tPSA |
174
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
31
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
606
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
S(C([H])([H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C1C2C([H])=C([H])N([H])C=2N=C([H])N=1)(N([H])C([H])([H])[H])(=O)=O.O([H])C(/C(/[H])=C(/[H])\C(=O)O[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
VQIGDTLRBSNOBV-BTJKTKAUSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C15H23N5O2S.C4H4O4/c1-16-23(21,22)9-11-3-5-12(6-4-11)20(2)15-13-7-8-17-14(13)18-10-19-15;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h7-8,10-12,16H,3-6,9H2,1-2H3,(H,17,18,19);1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/b;2-1-
|
| 化学名 |
N-methyl-1-((1r,4r)-4-(methyl(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)amino)cyclohexyl)methanesulfonamide maleate
|
| 别名 |
PF 03394197 maleate; Apoquel; OCLACITINIB MALEATE; 1208319-27-0; 1640292-55-2; Oclacitinib (maleate); Apoquel; PF-03394197 maleate; PF03394197 maleate;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.59 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2050 mL | 11.0251 mL | 22.0502 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4410 mL | 2.2050 mL | 4.4100 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2205 mL | 1.1025 mL | 2.2050 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|
|
|