| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
recombinant PFKFB3 (IC50 = 110 nM); PFKFB3 activity in cancer cells (IC50 = 20 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:PFK15 对一系列癌细胞产生有效的生长抑制作用。在 Jurkat T 细胞白血病细胞和 H522 肺腺癌细胞中,PFK15 还可降低 F26BP、葡萄糖摄取和细胞内 ATP 水平。激酶测定:通过将 13 ng 重组人 PFKFB3 蛋白在含有 10 μmol/L ATP、10 μmol/L F6P 和二甲基亚砜 (DMSO) 载体对照、3PO 或 PFK15 的反应混合物中孵育 1 小时来进行激酶反应在室温下。激酶活性按照制造商的细胞测定法使用 Adapta 通用激酶测定法进行测量:使用台盼蓝排除法测定活力。将细胞在 20% 台盼蓝中孵育 5 分钟。使用标准血细胞计数器对不包括台盼蓝的细胞进行计数,以确定活细胞的总数。实验一式三份进行。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在体内,PFK15 具有足够的药代动力学特性。 PFK15 (25 mg/kg ip) 抑制同基因小鼠中 LLC 肿瘤的生长、转移扩散和葡萄糖代谢。在无胸腺小鼠的三种人类异种移植癌症模型中,PFK15 还产生与批准的化疗药物相当的抗肿瘤作用。
PFK15抑制Lewis肺癌(LLC)异种移植物的生长[1] 根据血液、尿液和组织学分析,每三天腹腔注射25mg/kg PFK15可导致体重减轻<10%,且无终末器官毒性。尽管PFK15的溶解度有限,但25mg/kg的PFK15很容易以小体积给药,因此选择这种无毒剂量和时间表进行异种移植物和同基因肿瘤模型的疗效测试。我们首先研究了每天腹腔注射PFK15对体内已建立的LLC肿瘤生长的相对影响。尽管我们没有观察到PFK15给药后肿瘤消退,但我们确实观察到LLC肿瘤生长在统计学上显著减少(图4A),对体重没有重大影响(图4B)。重要的是,尽管LLC细胞已经很好地从皮下肿瘤转移到肺部,但在用PFK15治疗的LLC携带小鼠中没有发现肺部转移(图4C)。然后,我们在开始PFKFB3抑制剂给药四天后检查了一部分肿瘤的F26BP和凋亡细胞(n=4)。我们发现PFK15降低了肿瘤相关的F26BP(图4D),并通过免疫组织化学导致切割胱天蛋白酶3阳性的细胞数量显著增加(图4E和F)。综上所述,这些结果表明,PFK15可以在体内减少肿瘤生长并诱导细胞凋亡,在体重方面具有良好的耐受性,并且具有意想不到的预防转移起始或生长的能力。 PFK15抑制Lewis肺癌(LLC)异种移植物对18F-FDG的摄取[1] 我们假设PFK15会在体内急性减弱异种移植物肿瘤的葡萄糖摄取。我们对携带LLC的C57Bl/6小鼠进行了18F-FDG-PET基线成像,24小时后注射PFK15,然后在45分钟后重新植入携带LLC的小鼠。我们观察到,在PFK15给药后,18F-FDG摄取减少了约50%,与小脑中的FDG摄取正常化(神经元不表达PFKFB3蛋白;图4G和H)。这些数据表明,PFK15在体内选择性抑制肿瘤对葡萄糖的摄取,并表明FDG摄取扫描可能是PFKFB3抑制剂在临床试验中的一个有用的药效学终点。 PFK15显示出与常用化疗药物相似的抗肿瘤活性[1] 最后,我们直接比较了PFK15与FDA批准用于治疗人类癌症的三种化疗药物的抗肿瘤作用。我们发现PFK15分别与伊立替康(图5A)和吉西他滨(图5C)类似地抑制了结肠和胰腺腺癌的生长。然而,PFK15对胶质母细胞瘤生长的抑制活性低于替莫唑胺观察到的活性(图5B)。这些临床前研究提出了PFK15和封闭合成衍生物可能在临床试验中对人类癌症具有细胞毒性活性的前景。 |
| 酶活实验 |
对于激酶反应,将 13 ng 重组人 PFKFB3 蛋白在含有 10 μmol/L ATP、10 μmol/L F6P 和二甲基亚砜 (DMSO) 载体对照、3PO 或PFK15。据制造商介绍,激酶活性是使用 Adapta 通用激酶测定法测定的。
重组PFKFB3检测[1] 激酶反应是通过在室温下将13ng重组人PFKFB3蛋白在含有10μM ATP、10μM F6P和DMSO载体对照、3PO或PFK15的反应混合物中孵育一小时来进行的。根据制造商的说明,使用Adapta通用激酶测定法测量激酶活性,并在Tecan Safire2平板读数器上测量荧光和FRET信号。使用SigmaPlot软件生成图表,使用三参数Hill方程计算IC50值。KINOMEscanEDGE的96种激酶列表可以在以下网址访问http://www.kinomescan.com. |
| 细胞实验 |
2-[1-14C]-脱氧-D-葡萄糖摄取[1]
将Jurkat或H522细胞接种在补充了10%FCS和50μg/ml庆大霉素的RPMI 1640培养基中,浓度为100000/ml,并立即用DMSO载体对照、3PO或PFK-15处理三小时。用预热的无葡萄糖RPMI培养基洗涤细胞两次,并在PFKFB3抑制剂存在下孵育30分钟。细胞用25μl 14C-脱氧葡萄糖(0.1μCi/μl)处理一小时,用冰冷的无葡萄糖RPMI洗涤一次,用冰冷PBS洗涤两次。细胞在500μl 0.5%SDS中裂解。将400μl裂解液加入5ml Microscint 40闪烁液中,在Tri-Carb 2910液体闪烁分析仪上测量计数。根据制造商的说明,用BCA测定法对剩余的裂解物进行定量,并在Powerwave XS平板读数器上测量蛋白质水平。计数标准化为蛋白质浓度。 ATP测定[1] 用冷PBS×1洗涤细胞(同时仍粘附),用直接添加到板中的被动裂解缓冲液(1X)裂解,并立即通过刮擦收获。将裂解物快速冷冻(至-80°C)并解冻(至37°C)一次以完成完全裂解,然后离心(在4°C下)30秒以清除裂解物。使用重组萤火虫荧光素酶及其底物D-荧光素的生物发光测定法测定细胞内ATP水平。在TD-20/20光度计中在560 nm处读取发光。使用ATP标准曲线计算ATP值。使用BCA测定法估算裂解物的蛋白质浓度,ATP表示为nmol/mg蛋白质。 流式细胞术[1] Jurkat细胞被置于RPMI 1640培养基中,该培养基补充了10%FCS和50μg/ml庆大霉素,浓度为100000个细胞/ml,并立即与DMSO载体对照、3PO、PFK-15或依托泊苷一起孵育5小时。用PBS洗涤细胞,用膜联蛋白V和碘化丙啶染色。使用FACSCalibur测量荧光,并使用FloJo进行分析。Annexin V+/PI+(晚期凋亡)和Annexin V+/PI-(早期凋亡)细胞通过荧光标记细胞的频率进行定量,并通过双样本T检验(自变量)评估统计学意义。 台盼蓝排除法用于测定活力。将细胞在 20% 台盼蓝中孵育五分钟。使用标准血细胞计数器对所有活细胞进行计数,不包括台盼蓝细胞。每个实验重复三份。 |
| 动物实验 |
C57Bl/6 mice bearing LLC xenografts, Balb/C athymic mice bearing CT26, U-87 MG, or BxPC-3 xenografts.
25 mg/kg every 3 days i.p. Pharmacokinetic Studies [1] The PK profile was determined in female C57Bl/6 mice following IV administration of the PFKFB3 inhibitors. Using only female mice lowered the number of animals required for meaningful results without the issues of potential gender differences in exposure. Eight time points and three animals per time point were used to determine the PK parameters calculated using WinNonLin v5.0 (Tmax, Cmax, volume of distribution, half-life, clearance, AUCs and MRT). Plasma samples were extracted using acetonitrile and analyzed by LC/MS-MS using a PhenomexSynergi Polar-RP 4micron 50×2.0 mm column eluted with a biphasic mobile phase (0.5% formic acid in acetonitrile and water). FDG-PET Imaging [1] Tumor-bearing mice were anesthetized with isoflurane and 200 μCi of FDG was administered intravenously via the tail veins. The baseline micro-PET imaging of FDG in the mice was acquired by the ordered subsets expectation maximization (OSEM), using 6 subsets/4 iterations for 15-minute static scans 45 minutes after IV injection of the tracer using a Concorde Microsystems 4-ring micro-PET system. Regions of interest in the tumor and cerebellum were quantified in quadruplicate and, 24 hours later (18F half-life, 109.8 min), PFK-15 (25 mg/kg) was administered i.p. and the micro-PET scan was repeated 45 minutes later. Xenograft Studies [1] LLC, CT26, U-87 or BxPC-3 cells were collected from exponential growth phase culture in DMEM supplemented with 10% FCS. Cells were washed twice and re-suspended in PBS (1×107 cells/ml). Groups of C57Bl6 (for LLC cells) or Balb/C athymic mice(for CT26, U-87 MG or BxPC-3 cells) (20 gm) were injected s.c. with 0.1 ml of the cell suspension (1 ×106 cells). Tumor masses were determined in a blinded fashion with Vernier calipers according to the following formula: mass(mg)=(width, mm)2×(length, mm)/2 (19)and then monitored daily with microcalipers. Mice bearing xenografts (150–200 mg) were then randomized to DMSO, PFK-15 (25 mg/kg i.p. every 3 days × 4), irinotecan (70 mg/kg i.v. every 3 days × 4), temozolomide (30 mg/kg p.o. 3 days on 3 days off), or gemcitabine (100 mg/kg every 3 days × 4) and microcaliper measurements were conducted daily. All data are expressed as the mean±SD of two experiments (n = 8 per group). Statistical significance was assessed by the unpaired two tail T-test. In a separate series of experiments, LLC-tumor bearing mice were euthanized after only four days of treatment and the tumors were excised, fixed in formalin, embedded in paraffin and stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin or with anti-cleaved caspase 3 using standard immunohistochemical methodologies. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
In human cancers, loss of PTEN, stabilization of hypoxia inducible factor-1α, and activation of Ras and AKT converge to increase the activity of a key regulator of glycolysis, 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase (PFKFB3). This enzyme synthesizes fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (F26BP), which is an activator of 6-phosphofructo-1-kinase, a key step of glycolysis. Previously, a weak competitive inhibitor of PFKFB3, 3-(3-pyridinyl)-1-(4-pyridinyl)-2-propen-1-one (3PO), was found to reduce the glucose metabolism and proliferation of cancer cells. We have synthesized 73 derivatives of 3PO and screened each compound for activity against recombinant PFKFB3. One small molecule, 1-(4-pyridinyl)-3-(2-quinolinyl)-2-propen-1-one (PFK15), was selected for further preclinical evaluation of its pharmacokinetic, antimetabolic, and antineoplastic properties in vitro and in vivo. We found that PFK15 causes a rapid induction of apoptosis in transformed cells, has adequate pharmacokinetic properties, suppresses the glucose uptake and growth of Lewis lung carcinomas in syngeneic mice, and yields antitumor effects in three human xenograft models of cancer in athymic mice that are comparable to U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved chemotherapeutic agents. As a result of this study, a synthetic derivative and formulation of PFK15 has undergone investigational new drug (IND)-enabling toxicology and safety studies. A phase I clinical trial of its efficacy in advanced cancer patients will initiate in 2013 and we anticipate that this new class of antimetabolic agents will yield acceptable therapeutic indices and prove to be synergistic with agents that disrupt neoplastic signaling.[1]
Metabolic inhibition via PFKFB3 inhibition has demonstrated considerable tumor inhibitory effects in various studies; however, PFKFB3 inhibition did not show satisfactory tumor inhibition when used in clinical trials. PFKFB3 is a crucial metabolic enzyme that is highly upregulated in cancer cells and directly affects tumor glycolysis. Here, we showed that PFKFB3 inhibition suppresses tumors in vitro and in vivo in immune-deficient xenografts. However, this inhibition induces the upregulation of PD-L1 levels, which inactivated cocultured T-cells in vitro, compromises anti-tumor immunity in vivo, and reduced anti-tumor efficacy in an immune-competent mouse model. Functionally, PD-1 mAb treatment enhances the efficacy of PFKFB3 inhibition in immunocompetent and hu-PBMC NOG mouse models. Mechanistically, PFKFB3 inhibition increases phosphorylation of PFKFB3 at residue Ser461, which increases interaction with HIF-1α, and their colocalization into the nucleus, where HIF-1α transcriptionally upregulate PD-L1 expression and causes subsequent tumor immune evasion. Higher phos-PFKFB3 correlated with higher PD-L1 expression, lower CD8 and GRZMB levels, and shorter survival time in ESCC patients.Oncoimmunology. 2022 May 25;11(1):2079182. |
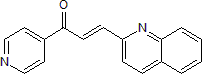
| 分子式 |
C17H12N2O
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
260.29
|
|
| 精确质量 |
260.094
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 78.44; H, 4.65; N, 10.76; O, 6.15
|
|
| CAS号 |
4382-63-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
25142799
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
464.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
233.5±35.1 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.698
|
|
| LogP |
2.62
|
|
| tPSA |
42.85
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
20
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
360
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
O=C(/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C1C([H])=C([H])C2=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C2N=1)C1C([H])=C([H])N=C([H])C=1[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
UJJUKZPBUMCSJZ-BQYQJAHWSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H12N2O/c20-17(14-9-11-18-12-10-14)8-7-15-6-5-13-3-1-2-4-16(13)19-15/h1-12H/b8-7+
|
|
| 化学名 |
(E)-1-pyridin-4-yl-3-quinolin-2-ylprop-2-en-1-one
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (7.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2 mg/mL (7.68 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2 mg/mL (7.68 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 5% DMSO +45% PEG 300 +1% Tween 80 +ddH2O: 5mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.8419 mL | 19.2093 mL | 38.4187 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7684 mL | 3.8419 mL | 7.6837 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3842 mL | 1.9209 mL | 3.8419 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
|
|---|
|
|