| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
p110α (IC50 = 3 nM); p110β (IC50 = 33 nM); p110δ (IC50 = 3 nM); p110γ (IC50 = 75 nM); p110α-H1047R (IC50 = 3 nM); p110α-E545K (IC50 = 3 nM); DNA-PK (IC50 = 1.23 μM); mTOR (Ki = 0.58 μM); Autophagy
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
与单药治疗相比,Pictilisib (GDC-0941) 和 RP-56976 可将乳腺癌细胞系中的肿瘤细胞活力降低 80% 或更多。在肿瘤模型 Hs578T1.2(PI3K 野生型)、MCF7-neo/HER2(PI3K 突变型)和 MX-1(PTEN 缺失)中,GDC-0941 抑制 Akt 磷酸化以及 Akt 信号转导的下游靶标,例如如 pPRAS40 和 pS6。 pictilisib (GDC-0941) 可缩短 RP-56976 诱导的细胞凋亡前有丝分裂停滞的持续时间[1]。 Pictilisib (GDC-0941) 在两种 ZD1839 耐药性非小细胞肺癌 (NSCLC) 细胞系 A549 和 H460 中显示出高效的抗肿瘤活性。 Pictilisib (GDC-0941) 与 U0126 联合使用可非常有效地抑制细胞生长、G0-G1 停滞和细胞凋亡。 Pictilisib (GDC-0941) 对具有野生型 PIK3CA 的 A549 细胞的毒性相对高于对具有 PIK3CA 激活突变的 H460 细胞的毒性[3]。 pAK 下降证明,pictilisib (GDC-0941) 会降低两种细胞系中 PI3K 通路的活性。缺氧/缺氧暴露后,pictilisib (GDC-0941) 显着降低所有细胞培养基中分泌的 VEGF 量[4]。
GDC-0941和多烯紫杉醇的联合用药降低了体外乳腺肿瘤细胞系的细胞活力,但在不同程度上存在药物协同作用。与未转化的MCF10A细胞相比,两种药物的添加在癌症亚型未预测的肿瘤细胞系亚群中产生了更强的协同作用。[1] 肺癌是一种预后不佳的恶性疾病,这促使人们寻找新的治疗方法。PI3K/Akt/mTOR和Ras/raf/Erk通路是肿瘤生长和存活的关键调节因子。本研究采用MTT法、流式细胞术和Western印迹法对其在肺癌细胞中的作用进行了评价。我们发现GDC-0941在两种吉非替尼耐药的非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)细胞系A549和H460中显示出高效的抗肿瘤活性。此外,携带PIK3CA激活突变的H460细胞对GDC-0941的敏感性相对高于携带野生型PIK3CA的A549细胞。此外,GDC-0941与U0126联合使用在诱导细胞生长抑制、G0-G1期阻滞和细胞凋亡方面非常有效。联合治疗的这些抗肿瘤活性可能归因于同时阻断PI3K/Akt/mTOR和Ras/raf/Erk通路诱导的G0-G1期调节因子、凋亡相关蛋白和真核翻译起始因子4B(eIF4B)的改变。总之,这项研究表明,多靶点干预是治疗肿瘤最有效的方法。此外,GDC-0941和MEK抑制剂阻断PI3K、mTOR和Erk显示出治疗吉非替尼耐药NSCLC的希望[3]。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Pictilisib (GDC-0941)(150 mg/kg,口服)可在携带 MCF7-neo/HER2 的动物模型中导致肿瘤停滞。 Pictilisib (GDC-0941) 和 RP-56976 在治疗期间导致肿瘤消退,从而增强抗肿瘤反应[1]。当 Pictilisib (GDC-0941) 治疗停止时,测试组小鼠的肿瘤再次生长[2]。 Pictilisib (GDC-0941) 治疗的小鼠中的肿瘤表现出显着的非线性收缩。 Pictilisib (GDC-0941)(25 或 50 mg/kg)可降低 eGFP-FTC133 荷瘤小鼠的肿瘤生长以及 PI3K 和 HIF-1 通路活性[4]。
GDC-0941和多西他赛联合使用可增强体内抗肿瘤疗效和细胞凋亡[1] 为了证实我们的体外观察结果,即GDC-0941与多西他赛的组合导致肿瘤生长抑制增加,我们评估了PI3Kα突变体(MCF7-neo/HER2)、PTEN缺失(MX-1)或PI3Kα野生型(MAXF1162)的肿瘤异种移植物模型。用7.5 mg/kg多烯紫杉醇或150 mg/kg GDC-0941治疗携带MCF7-neo/HER2乳腺癌症异种移植物的动物,分别导致肿瘤生长延迟和肿瘤停滞(图4A)。相比之下,GDC-0941和多西他赛的组合在治疗期间导致肿瘤消退,从而增强抗肿瘤反应(图4A)。基于动物体重的最小变化,单药和联合治疗达到最大耐受剂量(图4B)。与MCF7-neo/HER2异种移植物模型类似,我们观察到,在MX-1异种移植物模式中,当GDC-0941与多西他赛联合给药时,其效果大于加性效应,导致治疗期间肿瘤消退增加(图4C)。由于Hs578T1.2肿瘤细胞系在体内是非肿瘤原性的,我们评估了MAXF1162患者来源的乳腺肿瘤异种移植物模型,该模型为HER2+/ER+/PR+、PI3Kα野生型和PTEN阳性(Oncotest Inc;个人通讯)。以15mg/kg多西他赛作为单一药物在体内治疗MAXF1162原发性乳腺肿瘤异种移植物导致肿瘤生长延迟(图4D)。然而,100 mg/kg GDC-0941和多西他赛的组合在给药结束后持续的治疗期间导致肿瘤停滞(图4D)。GDC-0941和多西他赛以最大耐受剂量给药,当两种药物联合使用时,没有发现动物体重的额外变化(数据未显示)。 GDC-0941与多西他赛联合体内给药方案[1] 鉴于PI3K活性已被描述为细胞周期G1、S-和G2期进展所必需,我们确定了GDC-0941和多西他赛的联合作用是否取决于药物治疗的顺序。与单独使用多西他赛或GDC-0941相比,在GDC-0491前1至4小时服用多西他赛时,检测到凋亡增加(图5A)。同样,当在GDC-0941前4小时给药多西他赛时,亚G1细胞群的增加表明细胞死亡增加(补充图S4)。然而,当GDC-0941在多西他赛前4小时给药时,与单独使用多西他赛相比,没有观察到凋亡增加(图5A)。 在大鼠、狗和人类分别以30mg/kg、5mg/kg和60mg的目标剂量单次口服[14C]匹替利西伯后,对匹替利西伯的吸收、代谢和排泄进行了表征,匹替利昔布是一种1A类磷酸肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)的选择性小分子抑制剂。Pictilisib在物种间迅速吸收,Tmax不到2小时。在体循环中,皮克西比在所有物种中占主导地位,总放射性大于86.6%。从大鼠、狗和人类的尿液和粪便中分别回收了98%、80%和95%的总苦替尼和相关放射性物质,其中不到2%通过尿液排泄,其余通过粪便排泄。在大鼠和狗中,超过40%的药物相关放射性物质排泄到胆汁中,表明胆汁排泄是主要的排泄途径。未改变的西替尼是大鼠和狗胆汁中的次要成分。胆汁中的主要代谢产物是大鼠吲唑部分氧化的O-葡萄糖醛酸(M20,剂量的21%)和狗的氧化哌嗪基开环代谢产物M7(剂量的10.8%)。氧化型谷胱甘肽(GSH)偶联物(M18、M19)是在大鼠胆汁中检测到的新型代谢产物,表明苦提西布可能产生反应性中间体。NMR进一步证实M18的结构是吲唑环部分上的N-羟基化和GSH共轭代谢产物。Xenobiotica. 2021 Jul;51(7):796-810. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33938357/ |
| 酶活实验 |
重组人 PI3Kα、PI3Kβ 和 PI3Kδ 在 Sf9 杆状病毒系统中与 p85α 调节亚基共表达,并使用谷胱甘肽-琼脂糖上的亲和层析纯化为 GST 融合蛋白。单体 GST 融合体用于重组人 PI3Kγ 的表达和纯化。将 GDC-0941 溶解在 DMSO 中,并添加到含有 200 μg 硅酸钇 (Ysi) 聚赖氨酸 SPA 珠、4 mM MgCl2、1 mM 二硫苏糖醇 (DTT)、1 μM ATP、0.125 μCi [γ 的 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5) 中。 -33P]-ATP 和 4% (v/v) DMSO,总体积为 50 μL。通过添加 PI3Kα (5 ng)、PI3Kβ (5 ng)、PI3Kδ (5 ng) 或 PI3Kγ (5 ng) 的重组 GST 融合体,在测定混合物中启动激酶反应。室温孵育一小时后,用 150 μL PBS 终止激酶反应。然后以 2000 rpm 离心 2 分钟后使用 Wallac Microbeta 计数器读取。 MDL Assay Explorer 中的 S 形剂量反应曲线拟合用于确定报告的 IC50 值。
|
| 细胞实验 |
GDC-0941 以不同浓度应用于细胞 48 和 72 小时。 CellTiter-Glo 发光细胞活力测定用于鉴定细胞活力和增殖。通过使用蛋白质印迹,可以检查 pAkt (Ser473)、裂解的 caspase-3 和裂解的 PARP。分别使用细胞死亡检测 ELISAplus 测定法和 Caspase-Glo 3/7 测定法检测细胞凋亡和 caspase 3/7 活性。
细胞活力测定[1] 在4天的潜伏期内,对所有药物治疗进行了四次测试,并使用CellTiter Glo估算活细胞的相对数量。在Wallac多标签阅读器上测量总发光。细胞同时用多西他赛(剂量范围=0.0003-0.020μmol/L)或GDC-0941(剂量范围=0.083-5μmol/L)以8×10的浓度矩阵进行处理,以包含临床相关剂量。使用Prism软件测定产生50%最大有效浓度(EC50)的药物浓度。通过Bliss独立性分析确定GDC-0941和多西他赛的联合协同作用。联合反应(C)的Bliss预期通过以下方程式计算:C=(A+B)-(A×B),其中A和B是给定剂量下药物A和B的生长抑制分数。药物A和B在相同剂量下的组合的Bliss预期和观察到的生长抑制之间的差异是“Delta。Bliss。”Delta。将剂量矩阵中的Bliss评分相加,得到Bliss总和。Bliss sum=0表示联合治疗是加性的(正如独立途径效应所预期的那样);Bliss sum>0表示活性大于加性(协同作用);Bliss和<0表示组合小于加性(拮抗)。通过Student t检验对每个细胞系的Bliss总和进行统计分析。 蛋白质印迹[1] 细胞在GDC-0941、多西他赛或两者的EC50浓度下处理4或24小时,并在补充有蛋白酶抑制剂和磷酸酶抑制剂混合物1和2的1×细胞提取缓冲液中裂解。使用Pierce BCA蛋白检测试剂盒测定蛋白质浓度。对于免疫印迹,通过NuPAGE-Bis-Tris 10%梯度凝胶电泳分离等量的蛋白质,使用Criterion系统转移到聚偏二氟乙烯膜上,并用单特异性一抗进行检测。使用LI-COR成像系统用IRDye 680或IRDye 800红外二抗检测特异性抗原-抗体相互作用。 FACS分析[1] 对于细胞周期分析,用EC50浓度的GDC-0941和/或多西他赛处理细胞24小时,在100%冰冷的乙醇中固定,在碘化丙啶(PI)溶液中孵育30分钟,并用FACScan流式细胞仪进行分析。对于细胞死亡分析,将细胞与GDC-0941、多西他赛或两种药物一起孵育48小时,根据制造商的说明用Annexin V-FITC和PI溶液染色,并用FACScan流式细胞仪进行分析。 延时显微镜成像[1] 将细胞接种到玻璃底24孔板上,24小时后,用含药物的培养基孵育。细胞用EC50浓度的GDC-0941和/或多西他赛处理,每种条件选择多个场,并在AxioObserver倒置显微镜上每15分钟用10倍物镜记录荧光和相差图像,持续72小时,该显微镜配备有环境室、MS2000 XY载物台和CoolSNAP CCD相机。如前所述,对有丝分裂事件和细胞死亡进行评分。细胞还与胱天蛋白酶抑制剂Z-VAD-FMK以2μmol/L的终浓度共同处理。通过Student t检验进行统计分析。 |
| 动物实验 |
Female nu/nu mice are inoculated subcutaneously with MCF7-neo/HER2 or MX-1 breast cancer cells. Animals are distributed into groups of 10 animals each when tumors reach a mean volume of 200 to 250 mm3. Group sizes are determined by size matching. Once a week, intravenous RP-56976, a formulation of 3% EtOH and 97% saline, is given. Pictilisib (GDC-0941), a daily oral dose of MCT (0.5% methylcellulose, 0.2% Tween-80), is administered. By directly implanting tumors from patients under the skin of NMRI nu/nu mice, the MAXF1162 HER2+/ER+/PR+ patient-derived breast cancer tumor xenograft model was created. Volume of the tumor is calculated. Throughout a study, tumor size measurements are taken twice a week.
In vivo xenograft models [1] Female nu/nu mice were inoculated subcutaneously with MCF7-neo/HER2 or MX-1 breast cancer cells. When tumors reached a mean volume of 200 to 250 mm3, animals were size-matched and distributed into groups consisting of 10 animals per group. Docetaxel formulated in 3% EtOH, 97% saline was administered intravenously once weekly. GDC-0941, formulated in MCT (0.5% methylcellulose, 0.2% Tween-80) was dosed orally and daily. MAXF1162 is an HER2+/ER+/PR+ patient-derived breast cancer tumor xenograft model established at Oncotest, Inc., by directly implanting tumors subcutaneously from patient to NMRI nu/nu mice. Tumor volume was calculated as follows: tumor size (mm3) = (longer measurement × shorter measurement2) × 0.5. Tumor sizes were recorded twice weekly over the course of a study. Following data analysis, P values were determined using the Dunnett t test. For pharmacodynamic studies, tumor samples (n = 4) were immediately frozen or fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin. Tumors were dissociated in cell extraction buffer, and lysates were analyzed by Western blotting as described above. Immunohistochemistry was conducted using 5-μm paraffin sections of formalin-fixed tissue on a Ventana Benchmark XT instrument (VMSI) by deparaffinization, treatment with antigen retrieval buffer (VMSI), and incubation with anti-cleaved caspase-3 primary antibody (Cell Signaling Technology) at 37°C. Bound antibody was detected using DABMap technology (VMSI), and sections were counterstained with hematoxylin. Ten Pten+/−Lkb1+/hypo mice bearing tumours, ranging in age from 7 to 9.5 months and weights from 25 to 30 g, were divided into two groups: the test group (n=6) were given PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 (GDC-0941 bismesylate at 75 mg/kg), whilst the control group (n=4) were given saline vehicle solution only. The experimental protocol is depicted in Figure 1A, where ΔV is change in tumour volume and R is tumour growth rate. It includes a pre-treatment phase where tumour growth rates were measured; two treatment stages (treatment 1 and 2) where the efficacy of anticancer agents were determined; and two periods with no treatment (off-treatment 1 and 2) where tumour re-growth was quantified. Day 1 was assigned as the first day the mice were imaged and the mice were imaged three times during the 21-day pre-treatment period, and at intervals between 8 to 15 days thereafter. The mice were treated daily by oral gavage during two 28-day treatment sessions. The first treatment session (treatment 1) ran from day 23 to 50, followed by a 21-day period without any treatment (off-treatment 1). The second 28 day treatment session (treatment 2) was from day 72 to 99, followed by a period without any treatment (off-treatment 2), ending on day 119. At the end of the study, the mice were sacrificed and tumours were extracted and fixed in 10% formalin. [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Pharmacokinetics[10]
Pharmacokinetic parameters of pictilisib were estimated for all dose cohorts and are summarized in Table 3 and Supplementary Table 1. Under fasting conditions, pictilisib was rapidly absorbed after oral administration (median Tmax of 2 hours [range 0.5-8]); this was independent of dose and was unchanged after multiple doses. Terminal plasma elimination half-life (T1/2) on day 1 ranged between 13.1 and 24.1 hours. Dose-proportional increases in exposure (Cmax and AUC0-24) was observed across the dose levels studied (Figure 1). Similar pharmacokinetic characteristics were seen on day 15. The accumulation index (AUCDay15/AUCDay1) ranged from 1.2 to 2.2, suggesting modest accumulation following multiple doses. The absorption, metabolism and excretion of pictilisib, a selective small molecule inhibitor of class 1 A phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), was characterized following a single oral administration of [14C]pictilisib in rats, dogs and humans at the target doses of 30 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg and 60 mg, respectively.Pictilisib was rapidly absorbed with Tmax less than 2 h across species. In systemic circulation, pictilisib represented the predominant total radioactivity greater than 86.6% in all species.Total pictilisib and related radioactivity was recovered from urine and faeces in rats, dogs, and human at 98%, 80% and 95%, respectively, with less than 2% excreted in urine and the rest excreted into faeces.In rat and dog, more than 40% of drug-related radioactivity was excreted into the bile suggesting biliary excretion was the major route of excretion. Unchanged pictilisib was a minor component in rat and dog bile. The major metabolite in bile was O-glucuronide of oxidation on indazole moiety (M20, 21% of the dose) in rats and an oxidative piperazinyl ring-opened metabolite M7 (10.8% of the dose) in dogs.Oxidative glutathione (GSH) conjugates (M18, M19) were novel metabolites detected in rat bile, suggesting the potential generation of reactive intermediates from pictilisib. The structure of M18 was further confirmed by NMR to be a N-hydroxylated and GSH conjugated metabolite on the moiety of the indazole ring. Xenobiotica . 2021 Jul;51(7):796-810. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33938357/ |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Safety and tolerability [10]
Pictilisib was well-tolerated up to 330mg (21/28 schedule); most adverse events were mild to moderate in severity with no treatment-related deaths (Table 2). At the assessed dose levels, there did not appear to be a significant difference in the toxicity profile between the 21/28 and 28/28 schedules. Treatment-related adverse events that occurred in ≥10% of patients included: nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, fatigue, dysgeusia, decreased appetite and rash. In addition to the 2 DLTs of grade 3 rash at the 450mg dose level, the third patient at this dose level experienced grade 2 rash; nonetheless, this patient received 8 months of pictilisib with concomitant use of oral antihistamines and skin emollients. Of 10 patients treated with 330mg once-daily(28/28 schedule), grade 1 or 2 rash was observed in 2 patients, and grade 3 rash (occurring after the DLT-defining window) in 2 patients; these similarly resolved with the introduction of drug holidays and supportive medications including emollients and corticosteroids. Other clinically-relevant drug-related adverse events ≥grade 3 were grade 4 hyperglycemia (n=1, 130mg) and grade 3 pneumonitis (n=1, 340mg). The grade 4 hyperglycemia was transient, unaccompanied by clinically significant symptoms, signs or acidosis, and occurred in a patient with cholangiocarcinoma and previous pancreatico-duodenectomy who started the use of low-dose prednisolone 2 days prior to the event. Grade 3 pneumonitis was observed at the end of cycle 1 in a breast cancer patient previously treated with chest radiotherapy who developed grade 1 dyspnea, reduced DLCO and a ground glass appearance on HRCT; these resolved following 2 weeks of drug interruption and concomitant use of prednisolone. When pictilisib was reintroduced at 240mg, the dyspnea and HRCT changes recurred; these subsequently resolved following permanent discontinuation of pictilisib due to disease progression. DLTs and MTD [10] The MTD was exceeded at 450mg once-daily (21/28 schedule) with a DLT of grade 3 rash in 2 patients. This was a maculopapular rash covering 70-80% of the body surface area that presented approximately 2 weeks after commencement of daily pictilisib dosing and resolved spontaneously 2 weeks after treatment discontinuation. At 330mg once-daily (21/28 schedule), the grade 3 maculopapular rash observed in 1 of 7 patients had a similar temporal pattern of onset and resolution; this was also declared as a DLT. On the 28/28 schedule, no DLT was observed. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
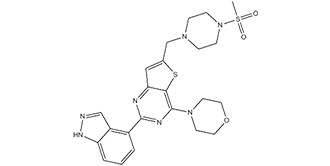
Pictrelisib is a sulfonamide composed of indazole, morpholine, and methylsulfonyl-substituted piperazine rings bound to a thienopyrimidine ring. It has a role as an EC 2.7.1.137 (phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase) inhibitor. It is a sulfonamide, a member of piperazines, a member of morpholines, a member of indazoles and a thienopyrimidine.
Pictilisib has been used in trials studying the treatment of Solid Cancers, Breast Cancer, Advanced Solid Tumours, Metastatic Breast Cancer, and Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma, Solid Cancers, among others. Pictilisib is a small molecule inhibitor of class I phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K), with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon administration, pictilisib selectively binds to PI3K in an ATP-competitive manner, inhibiting the production of the secondary messenger phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3) and activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. This may result in inhibition of tumor cell growth, motility and survival in susceptible tumor cell populations. Activation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway is frequently associated with tumorigenesis; dysregulated PI3K/Akt signaling may contribute to tumor resistance to a variety of antineoplastic agents. Purpose: Docetaxel is a front-line standard-of-care chemotherapeutic drug for the treatment of breast cancer. Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K) are lipid kinases that regulate breast tumor cell growth, migration, and survival. The current study was intended to determine whether GDC-0941, an orally bioavailable class I selective PI3K inhibitor, enhances the antitumor activity of docetaxel in human breast cancer models in vitro and in vivo. Experimental design: A panel of 25 breast tumor cell lines representing HER2+, luminal, and basal subtypes were treated with GDC-0941, docetaxel, or the combination of both drugs and assayed for cellular viability, modulation of PI3K pathway markers, and apoptosis induction. Drug combination effects on cellular viability were also assessed in nontransformed MCF10A human mammary epithelial cells. Human xenografts of breast cancer cell lines and patient-derived tumors were used to assess efficacy of GDC-0941 and docetaxel in vivo. Results: Combination of GDC-0941 and docetaxel decreased the cellular viability of breast tumor cell lines in vitro but to variable degrees of drug synergy. Compared with nontransformed MCF10A cells, the addition of both drugs resulted in stronger synergistic effects in a subset of tumor cell lines that were not predicted by breast cancer subtype. In xenograft models, GDC-0941 enhanced the antitumor activity of docetaxel with maximum combination efficacy observed within 1 hour of administering both drugs. GDC-0941 increased the rate of apoptosis in cells arrested in mitosis upon cotreatment with docetaxel. Conclusion: GDC-0941 augments the efficacy of docetaxel by increasing drug-induced apoptosis in breast cancer models.[1] Aim: To assess the efficacy of multiple treatment of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor on autochthonous tumours in phosphatase and tensin homologue (Pten)-deficient genetically engineered mouse cancer models using a longitudinal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) protocol. Materials and methods: Using 3D MRI, B-cell follicular lymphoma growth was quantified in a Pten(+/-)Lkb1(+/hypo) mouse line, before, during and after repeated treatments with a PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 (75 mg/kg). Results: Mean pre-treatment linear tumour growth rate was 16.5±12.8 mm(3)/week. Repeated 28-day GDC-0941 administration, with 21 days 'off-treatment', induced average tumour regression of 41±7%. Upon cessation of the second treatment (which was not permanently cytocidal), tumours re-grew with an average linear growth rate of 40.1±15.5 mm(3)/week. There was no evidence of chemoresistance. Conclusion: This protocol can accommodate complex dosing schedules, as well as combine different cancer therapies. It reduces biological variability problems and resulted in a 10-fold reduction in mouse numbers compared with terminal assessment methods. It is ideal for preclinical efficacy studies and for phenotyping molecularly characterized mouse models when investigating gene function.[2] Lung cancer is a malignant disease with poor outcome, which has led to a search for new therapeutics. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/raf/Erk pathways are key regulators of tumor growth and survival. In the present study, their roles were evaluated by MTT assay, flow cytometry and Western blotting in lung cancer cells. We found that a high efficacy of antitumor activity was shown with GDC-0941 treatment in two gefitinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines, A549 and H460. In addition, H460 cells with activating mutations of PIK3CA were relatively more sensitive to GDC-0941 than A549 cells with wild-type PIK3CA. Furthermore, GDC-0941 was highly efficacious in combination with U0126 in inducing cell growth inhibition, G0-G1 arrest and cell apoptosis. These antitumor activities of combined treatment may be attributed to the alterations of G0-G1 phase regulators, apoptosis-related proteins and eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4B (eIF4B), induced by concomitant blockade of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and Ras/raf/Erk pathways. In conclusion, this study suggests that multi‑targeted intervention is the most effective treatment for tumors. Additionally, the blockade of PI3K, mTOR and Erk with GDC-0941 and MEK inhibitors shows promise for treating gefitinib-resistant NSCLC.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C23H27N7O3S2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
513.6356
|
| 精确质量 |
513.161
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.78; H, 5.30; N, 19.09; O, 9.34; S, 12.49
|
| CAS号 |
957054-30-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Pictilisib dimethanesulfonate;957054-33-0
|
| PubChem CID |
17755052
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
687.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
369.7±34.3 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.753
|
| LogP |
2.04
|
| tPSA |
144.17
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
35
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
832
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=S(C)(N1CCN(CC2=CC3N=C(C4C5=C(NN=C5)C=CC=4)N=C(C=3S2)N2CCOCC2)CC1)=O
|
| InChi Key |
LHNIIDJUOCFXAP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H27N7O3S2/c1-35(31,32)30-7-5-28(6-8-30)15-16-13-20-21(34-16)23(29-9-11-33-12-10-29)26-22(25-20)17-3-2-4-19-18(17)14-24-27-19/h2-4,13-14H,5-12,15H2,1H3,(H,24,27)
|
| 化学名 |
4-(2-(1H-indazol-4-yl)-6-((4-(methylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)methyl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine
|
| 别名 |
Pictrelisib; Pictilisib; RG7321; 957054-30-7; GDC-0941; PICTILISIB; Pictrelisib; 4-(2-(1H-Indazol-4-yl)-6-((4-(methylsulfonyl)piperazin-1-yl)methyl)thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)morpholine; GDC 0941; 2-(1H-Indazol-4-yl)-6-(4-methanesulfonylpiperazin-1-ylmethyl)-4-morpholin-4-yl-thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine; RG-7321; RG 7321; GDC-0941; GDC 0941; GDC0941; GNE0941; GNE-0941; GNE 0941
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~44 mg/mL (85.66 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL (slightly soluble or insoluble) Ethanol: <1 mg/mL (slightly soluble or insoluble) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.87 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (4.87 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (4.87 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 2%DMSO+30%PEG 300+5%Tween 80+ddH2O: 5mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (9.73 mM) in 0.5% MC 0.5% Tween-80 (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浮液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9469 mL | 9.7344 mL | 19.4689 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3894 mL | 1.9469 mL | 3.8938 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1947 mL | 0.9734 mL | 1.9469 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Status | Interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00960960 | Completed | Drug: Bevacizumab Drug: Pictilisib |
Breast Cancer | Genentech, Inc. | August 2009 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01493843 | Completed | Drug: pictilisib Drug: Placebo |
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Genentech, Inc. | January 20, 2012 | Phase 2 |
|
 |
 |