| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MEK1 31 nM (DC50, in HT29 cells) MEK2 17 nM (DC50, in HT29 cells) MEK1 31 nM (DC50, in SK-MEL-28 cells) MEK2 9.3 nM (DC50, in SK-MEL-28 cells)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
化合物 23 或 MS432 能够显着降低 COLO 205 细胞(DC50 (MEK1) = 18±7 nM,DC50 (MEK2) = 11±2 nM)和 UACC257 细胞(DC50 (DC50 ( MEK1) = 56±25 nM,DC50 (MEK2) = 27±19 nM)。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
MS432(化合物23)在小鼠体内具有生物可利用性,可用于体内疗效研究。[1]
在评估的癌细胞系中,MS432(化合物 23)表现出良好的血浆暴露能力,GI50 值比化合物 23 大约高 3 至 20 倍[1]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
激酶抑制试验[1]
使用热点激酶测定法测定化合物对MEK1和MEK2激酶的抑制效力。该测定测量ERK磷酸化上的MEK激酶活性。简而言之,化合物与MEK和ERK蛋白的激酶反应混合物在室温下孵育20分钟后,将33P-ATP(比活10μCi/μL)注入反应混合物中,引发反应,在室温下温育2小时。然后通过滤膜结合法检测放射性。激酶活性数据表示为与DMSO反应相比,样品中剩余激酶活性的百分比。在反应中使用纯化的激酶蛋白,100 nM的MEK1、150 nM的MEB2(PV3615,赛默飞世尔科技公司)和5μM的ERK激酶死亡突变体K52R。在两个独立实验中,以DMSO为对照点,使用10浓度3倍连续稀释法测定IC50值(PD0325901、化合物23(MS432)和化合物24的最高浓度分别为3、30和30μM)。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[1]
细胞类型:(HT-29、SK-MEL-28、COLO 205 和 UACC 257 细胞系。测试 测试浓度: 0-1 μM。 孵育时间:72 小时。 实验结果:有效抑制这些 CRC 和黑色素瘤细胞的增殖浓度依赖性方式,GI50 值范围为 30 至 200 nM。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Swiss Albino mice[1].
Doses: 50 mg/kg (pharmacokinetic/PK Analysis). Route of Administration: IP Experimental Results: Displays good plasma exposure with the maximum plasma concentration of 1,400 nM detected at 0.5 hour post dosing and plasma concentration of 710 nM at 8 hrs (hours) post dosing. Mouse PK Study[1] A standard in vivo PK study was conducted for compound 23 (MS432) using three male Swiss Albino mice. The mice were administered intraperitoneally with solution formulation of compound 23 (MS432) at a 50 mg/kg dose. Sixty microliters of blood samples was collected from each mouse at 0.5, 2, and 8 h. Plasma was harvested by centrifugation of blood and stored at −70 ± 10 °C until analysis. Pharmacokinetic analysis was performed using the NCA module of Phoenix WinNonlin (Version 7.0). Plasma samples were quantified by fit-for-purpose LC–MS/MS method (LLOQ: 5.02 ng/mL for plasma). The formulation of compound 23 (MS432) was 5% NMP, 5% Solutol HS-15, and 90% normal saline. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
MEK1 and MEK2 (also known as MAP2K1 and MAP2K2) are the "gatekeepers" of the ERK signaling output with redundant roles in controlling ERK activity. Numerous inhibitors targeting MEK1/2 have been developed including three FDA-approved drugs. However, acquired resistance to MEK1/2 inhibitors has been observed in patients, and new therapeutic strategies are needed to overcome the resistance. Here, we report a first-in-class degrader of MEK1/2, MS432 (23), which potently and selectively degraded MEK1 and MEK2 in a VHL E3 ligase- and proteasome-dependent manner and suppressed ERK phosphorylation in cells. It inhibited colorectal cancer and melanoma cell proliferation much more effectively than its negative control MS432N (24), and its effect was phenocopied by MEK1/2 knockdown. Compound 23 was highly selective for MEK1/2 in global proteomic profiling studies. It was also bioavailable in mice and can be used for in vivo efficacy studies. We provide two well-characterized chemical tools to the biomedical community.[1]
In this study, researchers discovered compound 23 (MS432) as a first-in-class degrader of MEK1 and MEK2, the gatekeepers of ERK signaling. Compound 23 is a PD0325901-based VHL-recruiting small-molecule degrader of MEK1 and MEK2 with high potency and selectivity. We also developed compound 24 as a degrader negative control for compound 23. Compound 24 is a diastereoisomer of compound 23, thus sharing very high structural similarity with compound 23. We show compounds 23 and 24 inhibited the catalytic activity of MEK1 and MEK2 in vitro with similar potencies. In cellular experiments, compound 23 potently induced the degradation of MEK1 and MEK2 in a concentration- and time-dependent manner with durable effect. In contrast, the negative control compound 24 did not decrease MEK1/2 protein levels in cells. Our rescue experiment results indicate that MEK1/2 degradation induced by compound 23 is mediated through recruiting VHL E3 ligase for MEK1/2 polyubiquitination and proteasome-dependent proteolysis. Our quantitative global proteomic profiling analyses revealed that compound 23 is a highly selective degrader of MEK1 and MEK2. Furthermore, we found that compound 23, but not compound 24, effectively inhibited CRC and melanoma cell proliferation, and knockdown of MEK1/2 via shRNAs phenocopied the antiproliferative effect of compound 23 in BRAFV600E cancer cells. Moreover, compound 23 exhibited good plasma exposure in mice; thus it is suitable for in vivo efficacy studies. Overall, compounds 23 and 24 are a pair of well-characterized chemical tools for the research community to investigate the therapeutic potential of targeting MEK1 and MEK2. Further optimization of compound 23 into drug candidates may lead to novel, effective therapeutics for the treatment of CRC, melanoma, and other cancers.[1] |
| 分子式 |
C50H65F3IN7O6S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
1076.06
|
| 精确质量 |
1075.371
|
| CAS号 |
2672512-44-4
|
| 相关CAS号 |
PD0325901-O-C2-dioxolane;2581116-22-3
|
| PubChem CID |
145712394
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
10.4
|
| tPSA |
202Ų
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
6
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
13
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
26
|
| 重原子数目 |
68
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1570
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
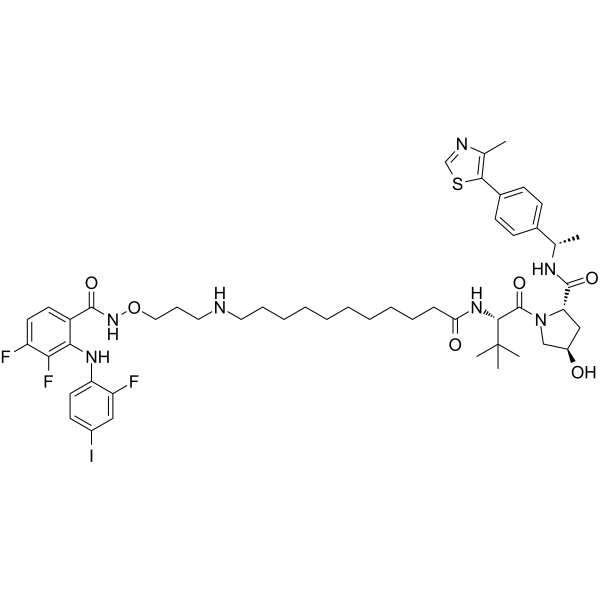
C(N1C[C@@H](C[C@H]1C(=O)N[C@H](C1C=CC(C2=C(N=CS2)C)=CC=1)C)O)(=O)[C@H](C(C)(C)C)NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCNCCCONC(C1C=CC(=C(C=1NC1C=CC(=CC=1F)I)F)F)=O
|
| InChi Key |
KCBAMQOKOLXLOX-BSZYMOERSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C50H65F3IN7O6S/c1-31(33-16-18-34(19-17-33)45-32(2)56-30-68-45)57-48(65)41-28-36(62)29-61(41)49(66)46(50(3,4)5)59-42(63)15-12-10-8-6-7-9-11-13-24-55-25-14-26-67-60-47(64)37-21-22-38(51)43(53)44(37)58-40-23-20-35(54)27-39(40)52/h16-23,27,30-31,36,41,46,55,58,62H,6-15,24-26,28-29H2,1-5H3,(H,57,65)(H,59,63)(H,60,64)/t31-,36+,41-,46+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
(2S,4R)-1-[(2S)-2-[11-[3-[[3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)benzoyl]amino]oxypropylamino]undecanoylamino]-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]-4-hydroxy-N-[(1S)-1-[4-(4-methyl-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)phenyl]ethyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxamide
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: (1). 本产品在运输和储存过程中需避光。 (2). 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: 100 mg/mL (92.93 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液添加到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.9293 mL | 4.6466 mL | 9.2932 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1859 mL | 0.9293 mL | 1.8586 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0929 mL | 0.4647 mL | 0.9293 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。