| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在 U-937 细胞中,丙硫氧嘧啶(5.5-330 μg/mL;24 小时)以剂量依赖性方式引起细胞毒性和生长迟缓 [2]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
通过给予补充有 0.15% Propythouracil 的缺碘饮食,Propythouracil 会诱导 C57BL/6J 小鼠和野生 WSB/EiJ 麋鹿的甲状腺功能减退症 [1]。
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞活力测定[2]
细胞类型: U-937 细胞 测试浓度: 5.5 μg/mL、11 μg/mL、110 μg/mL ,220 μg/mL,330 μg/mL 孵育持续时间:24 小时 实验结果:剂量依赖性诱导方式细胞毒性。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Adult C57BL/6J and wild-type WSB/EiJ male mice (8 weeks old) [1]
Doses: 1.5 g/kg Dietary Route of Administration: Iodine-deficient diet; continued for 7 weeks Experimental Results: In adult C57BL/6J and wild-type WSB/EiJ induces hypothyroidism in male mice. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Well absorbed following oral administration. Propylthiouracil is readily absorbed and is extensively metabolized. Approximately 35% of the drug is excreted in the urine, in intact and conjugated forms, within 24 hours. Elimination: Less than 1% is excreted in the urine unchanged. Total body clearance is approximately 7 L/hr. In dialysis: Elimination and pharmacokinetics are not significantly altered in hemodialysis. In one patient undergoing hemodialysis, 5% of a 200 mg oral dose was removed by 3 hours of hemodialysis; elimination rate was not significantly altered. Peak serum concentration was decreased (from 7.9 to 4.9 ug/mL), although it remained within an approximate therapeutic range. Although distribution of propylthiouracil into human body tissues and fluids has not been fully characterized, the drug appears to be concentrated in the thyroid gland. Propylthiouracil readily crosses the placenta. Propylthiouracil is distributed into milk; however, some studies indicate that the extent of distribution is only about 0.007-0.077% of a single dose. Propylthiouracil is rapidly and readily absorbed from the GI tract following oral administration with peak plasma concentrations of about 6-9 mcg/mL occurring within 1-1.5 hours after a single dose of 200-400 mg. In one study in which the drug was administered orally and IV, about 75% of the oral dose was absorbed. Plasma concentrations of the drug do not appear to correlate with the therapeutic effects. Time to peak effect: 17 weeks (average) to normalize serum T3 and T4 concentrations with use of 300 mg/day. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for PROPYL THIOURACIL (19 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Propylthiouracil was concentrated by thyroid gland, and four sulfur-35 compounds were demonstrated by TLC in both rat and man: unchanged propylthiouracil, (35)-sulfate, unknown propylthiouracil metabolite and protein-bound sulfur-35... Biotransformation: Primarily undergoes glucuronidation. Approximately 33% of an orally administered dose is metabolized by a first-pass effect. Presence of more than one glucuronide conjugate of propylthiouracil ought to be expected, as it has four functional groups, each capable of conjugation with glucuronic acid ... Although the exact metabolic fate of propylthiouracil has not been fully established, the drug is rapidly metabolized to its glucuronide conjugate and other minor metabolites and requires frequent administration to maintain its antithyroid effect. The drug and its metabolites are excreted in urine, with about 35% of a dose excreted within 24 hours. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for PROPYL THIOURACIL (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Route of Elimination: Propylthiouracil is readily absorbed and is extensively metabolized. Approximately 35% of the drug is excreted in the urine, in intact and conjugated forms, within 24 hours. Half Life: 2 hours Biological Half-Life 2 hours The elimination half-life of propylthiouracil has generally been reported to be about 1-2 hours. The plasma half-life of propylthiouracil .../is/ 1 to 2 hours. /After GI absorption/ plasma half-lives of 2.5 hr (human) and 4.8 hr (rat) have been reported ... . The half-life of propylthiouracil in plasma is about 75 min ... Propylthiouracil is rapidly absorbed from /orally/ dosed tablets in man, yielding max plasma levels at 60-120 min, and biological t/2 of about 60 min in euthyroid subjects. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Propylthiouracil binds to thyroid peroxidase and thereby inhibits the conversion of iodide to iodine. Thyroid peroxidase normally converts iodide to iodine (via hydrogen peroxide as a cofactor) and also catalyzes the incorporation of the resulting iodide molecule onto both the 3 and/or 5 positions of the phenol rings of tyrosines found in thyroglobulin. Thyroglobulin is degraded to produce thyroxine (T4) and tri-iodothyronine (T3), which are the main hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Therefore propylthiouracil effectively inhibits the production of new thyroid hormones. Toxicity Data Oral, rat: LD50 = 1250 mg/kg. Interactions In addition to blocking hormone synthesis, propylthiouracil inhibits the peripheral deiodination of thyroxine to triiodothyronine. Methimazole dose not have this effect and can antagonize the inhibitory effect of propylthiouracil. We have investigated immunohistochemically the effect of dl-alpha-tocopherol (vitamin E) on thyroid gland with 6-n-propyl-2-thiouracil (PTU)-induced hypothyroidism in rats. The animals were divided into four groups. Rats in group I were designated as control, rats in group II were treated with injections of PTU (10 mg/kg) for 15 days, rats in group III were treated with injections of PTU+vitamin E (10 mg/100 g) for 15 days. Rats in group IV were treated with injections PTU for 15 days and kept for 15 next days after cessation of PTU treatment. At the end of experiment, the animals were killed by decapitation, blood samples were obtained, thyroid tissues were collected and processed for quantitative evaluation of immunohistochemical PCNA (marker of cell proliferation), Bax (pro-apoptotic marker) and Bcl-2 (anti-apoptotic marker) staining. There was an increase in the number of PCNA-immunopositive cells in follicular epithelial cells of group II rats compared with other groups (p<0.05). After vitamin E treatment, the number of PCNA-immunopositive cells decreased (p<0.05) while the number of Bax-immunopositive cells increased (p<0.05). The number of Bcl-2-positive follicular epithelial cells of group IV rats was higher than in those of other groups (p<0.05). The results of this study indicate that hypothyroidism induces cell proliferation in the thyroid gland and vitamin E may promote involution of the gland. Female Sprague-Dawley rats, 50-60 days of age, were given 7,12-dimethylbenz[ a]anthracene (DMBA) in sesame oil by oral gavage at a dose of 6.5, 10, 13.5 or 15 mg per animal. Propylthiouracil was given in the drinking-water at concentrations between 0.5 and 4.0 mg/100 mL for various times before and after the DMBA treatment, ranging from 17 days before DMBA up to the end of the study at 4 months. Severe hypothyroidism produced by administration of propylthiouracil at the higher dose from 7 days before DMBA up to study termination reduced the mammary tumor incidence from 68/108 in rats given DMBA only to 3/45 in those given DMBA plus propylthiouracil. Two groups of 21 male inbred Wistar rats, 6 weeks of age, were fed basal diet containing propylthiouracil [purity not specified] at a concentration of 0.15% either alone or in combination with a single intraperitoneal injection of N-nitrosobis(2- hydroxypropyl)amine (NBHPA) at the start of the study at a dose of 2.8 g/kg bw. Two additional groups received the initiating dose of NBHPA alone or basal diet alone (control group). The animals were maintained for 20 weeks, at which time the survival rate was 100%. Thyroid follicular-cell tumors occurred in 21/21 rats given NBHPA plus propylthiouracil, 4/21 given NBHPA only (p<0.05) and 0/21 given propylthiouracil only or no treatment. Of the rats given NBHPA plus propylthiouracil, seven of those bearing thyroid tumors had thyroid carcinomas. For more Interactions (Complete) data for PROPYL THIOURACIL (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 1980 mg/kg |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Mesh Heading: Antimetabolites, Antithyroid Agents ... Propylthiouracil /is/ indicated in the treatment of hyperthyroidism, including prior to surgery or radiotherapy, and as adjuncts in the treatment of thyrotoxicosis or thyroid storm. Propylthiouracil may be preferred over methimazole for use in thyroid storm, since propylthiouracil inhibits peripheral conversion of thyroxine (T4) to triiodothyronine (T3). EXPTL USE: Paradoxically propylthiouracil has been shown to reverse histological changes of alcoholic hepatitis in rat and has been proposed as possible treatment for this condition in man. EXPTL USE: Twelve-day pretreatment with PTU prevented the tylenol-induced increase in transaminase activities. Increase in hepatic reduced glutathione levels and prevention of inflammatory response to necrotic liver tissue appeared to be mechanism in protective action of hypothyroidism. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for PROPYL THIOURACIL (14 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Although reported much less frequently, severe adverse effects, including inhibition of myelopoiesis with resultant agranulocytosis, granulocytopenia, and thrombocytopenia; aplastic anemia; drug fever; lupus-like syndrome (including splenomegaly); severe hepatic reactions (including encephalopathy, fulminant hepatic necrosis, and death); periarteritis; and hypoprothrombinemia and bleeding, have been reported to occur in some patients receiving propylthiouracil. Nephritis and interstitial pneumonitis have also been reported. Cutaneous vasculitis, which may manifest as purpuric and/or bullous hemorrhagic lesions or erythema nodosum, and possibly may progress to necrotic ulcerations, and polymyositis also have occurred. Agranulocytosis is potentially the most serious adverse effect of propylthiouracil, and most cases of agranulocytosis appear to occur within the first 2 months of therapy, but rarely may occur after 4 months of therapy. The risk of propylthiouracil-induced agranulocytosis appears to be substantially increased in patients older than 40 years of age compared with younger patients, but, unlike methimazole, an association with dosage has not been established. Although the mechanism(s) of propylthiouracil-induced agranulocytosis has not been determined, antigranulocyte antibodies have been reported in some patients with thioamide-induced agranulocytosis; a direct toxic effect of these drugs on bone marrow has not been excluded as an additional possible cause. Propylthiouracil crosses the placenta and may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women; the drug can induce goiter and hypothyroidism (cretinism) in the developing fetus. If the drug is used during pregnancy for the management of hyperthyroidism, the manufacturer states that careful dosage adjustment, using a sufficient but not excessive dosage of propylthiouracil, is necessary. The manufacturer states that because thyroid dysfunction diminishes in many women as pregnancy proceeds, a reduction in dosage may be possible, and, in some patients, propylthiouracil can be discontinued 2 or 3 weeks before delivery. If propylthiouracil is used during pregnancy, or if a woman becomes pregnant while receiving the drug, she should be advised of the potential hazard to the fetus. ... Disagreement about therapy of thyrotoxicosis during pregnancy. Antithyroid drugs cross placenta and can cause fetal hypothyroidism and goiter. ... There are 3 choices of therapy, each with its advocates: minimal doses of antithyroid drugs, full doses ... with thyroid hormone supplementation, or surgery. /Antithyroid drugs/ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for PROPYL THIOURACIL (20 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Propylthiouracil is a thiourea antithyroid agent. Grave's disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is an autoimmune disease where an individual's own antibodies attach to thyroid stimulating hormone receptors within cells of the thyroid gland and then trigger overproduction of thyroid hormone. The two thyroid hormones manufactured by the thyroid gland, thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), are formed by combining iodine and a protein called thyroglobulin with the assistance of an enzyme called peroxidase. PTU inhibits iodine and peroxidase from their normal interactions with thyroglobulin to form T4 and T3. This action decreases thyroid hormone production. PTU also interferes with the conversion of T4 to T3, and, since T3 is more potent than T4, this also reduces the activity of thyroid hormones. The actions and use of propylthiouracil are similar to those of methimazole. |
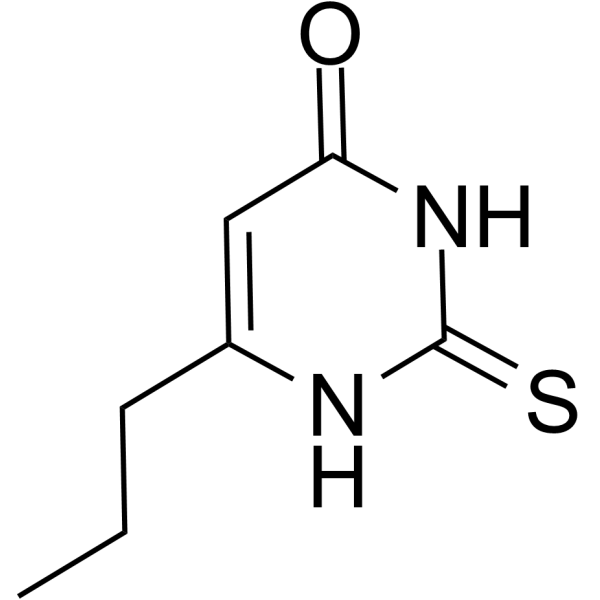
| 分子式 |
C7H5D5N2OS
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
175.26
|
| 精确质量 |
170.051
|
| CAS号 |
51-52-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Propylthiouracil-d5;1189423-94-6
|
| PubChem CID |
657298
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
355.2±34.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
218-220 °C(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
168.6±25.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.601
|
| LogP |
-0.32
|
| tPSA |
80.74
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
11
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
223
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
KNAHARQHSZJURB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C7H10N2OS/c1-2-3-5-4-6(10)9-7(11)8-5/h4H,2-3H2,1H3,(H2,8,9,10,11)
|
| 化学名 |
6-propyl-2-sulfanylidene-1H-pyrimidin-4-one
|
| 别名 |
Procasil-d5; Propylthiouracil-d5; Propylthiouracil
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~587.44 mM)
H2O : ~0.67 mg/mL (~3.94 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (14.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.7058 mL | 28.5290 mL | 57.0581 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.1412 mL | 5.7058 mL | 11.4116 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5706 mL | 2.8529 mL | 5.7058 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。