| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MDM2 (Kd = 11 nM)
The target of RG-7112 (RO-5045337) is MDM2 (murine double minute 2). - In the HTRF (Homogeneous Time-Resolved Fluorescence) MDM2-p53 binding assay, the IC₅₀ value of RG-7112 (RO-5045337) for MDM2 was 11 nM [1] - In the fluorescence polarization (FP) assay measuring MDM2-p53 interaction, the Ki value of RG-7112 (RO-5045337) for MDM2 was 6 nM; no significant binding to MDMX (a homologous protein of MDM2) was observed, with IC₅₀ > 10 μM [1] - In cell-based assays, RG-7112 (RO-5045337) activated p53 signaling, and the EC₅₀ values for inducing p21 (a p53 downstream target) expression were 160 nM in HCT116 (colon cancer cells) and 30 nM in SJSA-1 (osteosarcoma cells) [2] - In MDM2-amplified and TP53 wild-type glioblastoma cell lines (e.g., U87MG, U251MG, LN229), the IC₅₀ values of RG-7112 (RO-5045337) for inhibiting cell growth ranged from 0.1 to 1.0 μM [3] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
RG7112 是 MDM2 拮抗剂 nutlin 家族的有效且选择性成员,目前正处于 I 期临床研究中。在体外,MDM2 与 p53 的相互作用被 RG7112 与 MDM2 的高度特异性结合(KD 为 10.7 nM)所阻断。 RG7112-MDM2 复合物已结晶,表明该小分子通过与 MDM2 的 p53 口袋结合来模拟关键 p53 氨基酸残基的相互作用。通过激活 p53 通路,RG7112 导致表达野生型 p53 的癌细胞发生细胞周期停滞和凋亡。一组实体瘤细胞系对 RG7112 的抗肿瘤作用敏感。然而,这种药物的凋亡活性差异很大,具有MDM2基因扩增的骨肉瘤细胞表现出最好的反应。 [1]
RG7112是p53-MDM2结合的强效抑制剂[2]。 RG7112在癌症细胞中稳定野生型p53并诱导p53信号传导[2]。 RG7112有效激活癌症细胞中的p53功能[2]。 半胱天冬酶抑制不影响RG7112诱导的细胞死亡的开始[2]。 1. 对癌细胞的抗增殖活性:RG-7112 (RO-5045337) 对TP53野生型癌细胞具有强效抗增殖作用,对TP53突变型癌细胞活性极低。TP53野生型细胞的GI₅₀值:HCT116结肠癌细胞(120 nM)、SJSA-1骨肉瘤细胞(25 nM)、A549肺癌细胞(280 nM)、MCF-7乳腺癌细胞(320 nM);TP53突变型细胞的GI₅₀值:SW480结肠癌细胞(>10 μM)、SK-OV-3卵巢癌细胞(>10 μM) [1] 2. p53信号通路的激活:用RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(100–1000 nM)处理HCT116细胞24小时,western blot检测显示p53蛋白水平呈剂量依赖性升高;同时,p53下游靶蛋白(p21、MDM2)的蛋白水平(western blot)和mRNA水平(RT-PCR)也均呈剂量依赖性上调 [2] 3. 诱导SJSA-1细胞凋亡:RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(50–200 nM)处理SJSA-1细胞48小时,可剂量依赖性诱导细胞凋亡。流式细胞术(Annexin V-FITC/PI染色)显示,凋亡细胞比例从对照组的5%升至200 nM处理组的35%;western blot检测到凋亡标志物caspase-3和PARP的切割片段 [2] 4. 抑制胶质母细胞瘤细胞生长:在MDM2扩增且TP53野生型的胶质母细胞瘤细胞(U87MG、U251MG、LN229)中,RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(0.1–5 μM)可剂量依赖性抑制细胞增殖。1 μM浓度下,细胞增殖较对照组降低40–60%;western blot显示p53、p21、MDM2蛋白水平升高,且出现cleaved caspase-3 [3] 5. 抑制HCT116细胞克隆形成:RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(10–100 nM)可显著减少HCT116细胞的克隆形成数量。100 nM浓度下,克隆形成率较对照组降低80% [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在体内,RG7112 导致肿瘤细胞凋亡并激活 p53 通路。在无毒剂量下,对携带人类异种移植物的小鼠口服 RG7112 会导致增殖/凋亡生物标志物以及肿瘤抑制和消退发生剂量依赖性变化。值得注意的是,雄激素剥夺和 RG7112 在 LNCaP 异种移植肿瘤中具有强大的协同作用。 [1]
以无毒浓度对携带人类异种移植物的小鼠口服RG7112,会引起增殖/凋亡生物标志物以及肿瘤抑制和消退的剂量依赖性变化。值得注意的是,RG7112与LNCaP异种移植物肿瘤中的雄激素剥夺具有高度协同作用。我们的研究结果提供了一个临床前的概念证明,即RG7112在治疗表达野生型p53的实体瘤方面是有效的。[2] RG7112处理的PDCL颅内异种移植物的PK分析表明,该化合物显著穿过血脑和血肿瘤屏障。最重要的是,MDM2扩增/TP53野生型PDCL衍生模型(皮下和原位)的治疗减少了肿瘤生长,具有细胞毒性,并显著提高了生存率。 结论:这些数据有力地支持了MDM2抑制剂的开发,用于MDM2扩增的GBM患者的临床试验。此外,在非MDM2扩增模型的一个子集中具有显著疗效,这表明必须确定对MDM2抑制剂反应的其他标志物。[3] 1. SJSA-1异种移植瘤的消退:对携带SJSA-1骨肉瘤异种移植瘤的裸鼠,口服给予RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(100/200/300 mg/kg,每日1次,连续21天)。300 mg/kg组所有小鼠均实现肿瘤完全消退(体积减少>95%);200 mg/kg组肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)为80%。在TP53突变型SW480异种移植模型中,即使300 mg/kg剂量也无肿瘤生长抑制作用 [2] 2. 对U87MG胶质母细胞瘤异种移植瘤的疗效:对携带U87MG(MDM2扩增、TP53野生型)胶质母细胞瘤异种移植瘤的裸鼠,口服给予RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(150 mg/kg,每日2次,连续28天)。TGI为70%,治疗组肿瘤平均重量显著低于对照组(p < 0.01);肿瘤组织免疫组化(IHC)显示,p53和p21的染色强度较对照组升高 [3] 3. SJSA-1异种移植瘤中的药效动力学效应:对携带SJSA-1异种移植瘤的小鼠单次口服RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(200 mg/kg),在给药后2/6/12/24小时收集肿瘤组织。western blot显示,p53和p21蛋白水平在2小时开始升高,6小时达峰值,24小时恢复至基线 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
均匀时间分辨荧光(HTRF)测定测量两种成分在接近时产生的信号。p53-MDM2结合测定使用来源于p53的MDM2结合结构域的生物素化肽和含有p53结合结构域重组人GST标记的MDM2蛋白的截短N端部分。使用编码lacIq阻遏物和稀有tRNAArg[AGA/AGG]的辅助质粒pUBS 520在大肠杆菌BL21菌株中表达用于晶体结构研究的蛋白质。为了结晶,将冷冻的蛋白质解冻,并使用Centricon浓缩器(3000 MW截止)浓缩至9.8mg/mL。然后通过将蛋白质与稍摩尔过量的抑制剂(DMSO中的储备溶液为100 mmol/L)结合形成复合物,并将该溶液在4°C下静置4小时。在布鲁克海文国家实验室的国家同步辐射光源处,使用低温保存的晶体收集光束线X8C的衍射数据[2]。
1. HTRF MDM2-p53结合实验:在384孔板中进行,使用实验缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5、150 mM NaCl、0.01% Tween-20、1 mM DTT)配制含MDM2蛋白(20 nM)、生物素化p53肽(5 nM)和系列浓度RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(0.1–1000 nM)的混合液。室温孵育1小时后,加入链霉亲和素偶联的Eu³⁺穴状化合物和抗小鼠IgG-XL665,继续孵育1小时。用酶标仪检测620 nm和665 nm处的FRET信号,根据665 nm/620 nm信号比计算IC₅₀ [1] 2. MDM2荧光偏振(FP)实验:使用实验缓冲液(20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4、150 mM NaCl、0.1% BSA、1 mM DTT),在384孔板中混合荧光标记p53肽(5 nM)、MDM2蛋白(10 nM)和RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(0.1–100 nM)。25°C孵育30分钟后,检测FP信号(激发波长485 nm,发射波长535 nm),采用竞争性结合模型计算Ki [1] 3. MDMX-p53结合实验(选择性检测):实验流程与HTRF MDM2-p53实验一致,仅用MDMX蛋白(20 nM)替代MDM2。RG-7112 (RO-5045337)浓度范围为0.1–10000 nM,通过测定对MDMX的IC₅₀评估化合物的选择性 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
通过四唑蓝(MTT)法评估细胞增殖/存活率。使用IncuCyte活细胞成像系统测量细胞生长动力学。对于细胞周期分析,将细胞在T75烧瓶中用适当的生长培养基(10 mL中106个细胞/条件)培养,并在37°C下孵育过夜。它们与测试化合物一起孵育,并如前所述进行处理。使用GuavaNexin凋亡检测试剂盒通过Annexin V测定法测定细胞凋亡,并按照制造商的方案使用Guava个人细胞分析仪测定细胞凋亡百分比[2]。
抗增殖试验[3] 对于队列#1细胞系的药物敏感性测定,在37°C下用10μg/mL层粘连蛋白涂覆96孔板1小时。然后将三千个细胞/孔进行电镀RG7112作为10mM DMSO储备溶液重新悬浮,并在镀覆后24小时加入。添加药物72小时后,根据制造商的说明添加WST-1试剂。WST-1盐在活细胞中通过NAD(P)H依赖性反应裂解为可溶性甲氮染料。将板温育3小时,并在450nm波长下通过分光光度法读取。对于队列#2细胞系,细胞以384孔格式铺板,并使用针转移机器人将化合物溶液转移到每个孔中,每种条件有3个重复。通过CellTiter-Glo发光测定法在连续药物暴露72小时后测量细胞存活率。使用GraphPad®Prism 6通过最小二乘曲线拟合确定IC75、IC99和IC100(分别导致细胞存活率降低75%、99%和100%的浓度)。[3] 1. 抗增殖实验(GI₅₀测定):将癌细胞接种于96孔板(1000–3000个细胞/孔),过夜孵育后加入系列浓度的RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(0.01–100 μM),继续孵育72小时。使用MTT或CellTiter-Glo试剂检测细胞活力,通过酶标仪读取吸光度或发光值,GI₅₀定义为抑制细胞生长50%的药物浓度 [1, 2] 2. p53及下游靶蛋白western blot实验:将细胞接种于6孔板,培养至70–80%汇合度,加入RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(0.1–5 μM)孵育24–48小时。用含蛋白酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解细胞,裂解液经SDS-PAGE分离后转移至PVDF膜。膜用5%脱脂牛奶封闭,4°C下与一抗(p53、p21、MDM2、caspase-3、PARP、β-actin)孵育过夜,再与HRP偶联的二抗孵育,最后通过ECL发光法显示蛋白条带 [2, 3] 3. p53靶基因mRNA RT-PCR实验:用RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(0.5–2 μM)处理细胞12–24小时,提取总RNA,通过逆转录酶和随机引物合成cDNA。使用p21、MDM2和内参基因GAPDH的特异性引物进行PCR扩增,扩增产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳分离后,定量条带强度以计算相对mRNA水平 [2] 4. 流式细胞术凋亡检测:用RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(50–200 nM)处理SJSA-1细胞48小时,收集细胞并用PBS洗涤,加入Annexin V-FITC和PI染色。通过流式细胞术分析染色细胞,定量凋亡细胞(Annexin V阳性/PI阴性或阳性)比例 [2] 5. 克隆形成实验:将HCT116细胞接种于6孔板(100–500个细胞/孔),过夜贴壁后加入RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(10–100 nM),孵育14天(每3–4天换液一次)。用甲醇固定克隆,结晶紫染色后,计数含>50个细胞的克隆,计算克隆形成率(相对于对照组) [2] 6. 胶质母细胞瘤细胞增殖实验:将MDM2扩增且TP53野生型的胶质母细胞瘤细胞接种于96孔板(2000个细胞/孔),过夜孵育后加入RG-7112 (RO-5045337)(0.01–10 μM),孵育72小时。通过WST-1实验检测细胞活力,计算IC₅₀ [3] |
| 动物实验 |
1% Klucel LF/0.1% Tween 80; 200 mg/kg; oral taken SJSA-1, SJSA-1luc2, and MHM xenografted Balb/c nude mice \n\nFor SJSA-1, SJSA-1luc2, and MHM xenograft studies, female Balb/c nude mice were implanted subcutaneously in the right flank with 5 × 106 cells suspended in a 0.2 mL volume of a 1:1 mixture of Matrigel:PBS. For studies with hormone-dependent LNCaP xenografts, castrated male Balb/c nude were implanted with 12.5 mg sustained-release testosterone pellets 5 days before subcutaneous inoculation with 1 × 107 cells suspended in 0.2 mL of Matrigel:PBS. Mice were randomized into treatment groups (n = 10 per group) when mean tumor volume reached approximately 150 to 400 mm3. In all studies, mice received either vehicle (1% Klucel LF/0.1% Tween 80) or RG7112, administered as an oral suspension at the dose indicated (25–200 mg/kg). For assessment of androgen ablation treatment in combination with RG7112 in LNCaP xenograft-bearing mice, testosterone pellets were removed under ketamine/xylazine anesthesia. Tumor volume was monitored by caliper measurement and body weights were recorded 2 to 3 times weekly. Tumor volume (in mm3) was calculated as described previously [2].
\n\nFor Western blot analysis, mice bearing established SJSA-1 subcutaneous xenografts received a single oral dose of vehicle or 50, 100, or 200 mg/kg RG7112, and tumors were harvested at 4 and 8 hours after dosing. Protein was extracted from tumor tissue with 1× radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer containing protease inhibitors by homogenization. Equal amounts of total protein were resolved on 4% to 12% NuPAGE gradient gel and blotted with antibody dilutions as recommended by manufacturer. The chemiluminescent signal was generated with enhanced chemiluminescence Plus and detected with Fujifilm LAS-3000 imager. The densitometric quantitation of specific bands was determined using Multi Gauge Software. The complete methods can be found in the online Supplementary Information.[2] \n\nFor the heterotopic (subcutaneous) model, 2x106 cells were resuspended in Hank’s Buffered Salt Solution, mixed with an equal volume of Matrigel and injected into both flanks of eight-week-old NU/NU mice. Animals were randomly assigned to treatment or vehicle arm when tumors measured a volume of 200 mm3. For both orthotopic and heterotopic models, animals were treated by gavage with 100 mg/kg of RG7112formulation (100 mg/mL RG7112, 2% hydroxypropylcellulose, 0.1% Tween 80, 0.09% methylparaben and 0.01% propylparaben in water) or vehicle once per day, 5 days/week for 3 weeks. For the evaluation of GBM blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity only, 1.2 mg of Hoechst 33342 diluted in PBS was injected intravenously (iv) prior to termination. Mice were terminated by asphyxiation when they showed signs of tumor-associated illness or before reaching maximum subcutaneous tumor burden.[3] \n\nPharmacokinetics studies[3] \nGBM cells were inoculated in the brain of Athymic Nude mice as described below and animals were assigned to different pharmacokinetics time points when bioluminescence signal reached 1.108 photon/second. This threshold was selected to ensure that tumor volumes were as significant as possible without causing symptoms of pain or illness. The dose treatment solution of RG7112 (100 mg/mL RG7112) was prepared in a vehicle composed of 2% hydroxypropylcellulose, 0.1% Tween 80, 0.09% methylparaben and 0.01% propylparaben in water . Mice were sacrificed at 0, 1h, 2h, 4h, 8h, 24h and 48h post-gavage (3 mice per time point). Blood was collected via live cardiac puncture in polyethylene tubes using a heparinized syringe. Samples were immediately centrifuged at 5000 rpm for 15 min and plasma was removed and stored at −80°C until analysis. Whole brains were collected, rinsed with 0.9% sodium chloride. The right and left brain hemispheres were harvested separately and labeled as tumor hemisphere and counter hemisphere, respectively, and were frozen at −80°C. RG7112 levels in mice plasma, and brains were measured using validated liquid chromatography coupled with mass tandem spectrometry methods. [3] 1. SJSA-1 osteosarcoma xenograft model: Female athymic nude mice (6–8 weeks old) were subcutaneously injected with 5×10⁶ SJSA-1 cells (0.2 mL PBS/matrigel, 1:1) into the right flank. When tumors reached 100–150 mm³, mice were randomized into 4 groups (n=6/group): control (vehicle), 100/200/300 mg/kg RG-7112 (RO-5045337). The drug was formulated in 0.5% methylcellulose + 0.2% Tween-80 in water and administered orally once daily for 21 days. Tumor volume (V = length×width²/2) and body weight were measured twice weekly [2] 2. SW480 colon cancer xenograft model (TP53-mutant): The protocol was similar to the SJSA-1 model. Mice were injected with 5×10⁶ SW480 cells, and when tumors reached 100–150 mm³, mice were treated with RG-7112 (RO-5045337) (300 mg/kg, oral, once daily for 21 days). Tumor volume and body weight were monitored [2] 3. U87MG glioblastoma xenograft model: Male athymic nude mice (6–8 weeks old) were subcutaneously injected with 1×10⁷ U87MG cells (0.2 mL PBS/matrigel, 1:1) into the right flank. When tumors reached 150–200 mm³, mice were randomized into 2 groups (n=8/group): control (vehicle) and 150 mg/kg RG-7112 (RO-5045337) (formulated as above, oral, twice daily for 28 days). Tumor volume and body weight were measured twice weekly. At study end, mice were euthanized, and tumor tissues were collected for IHC [3] 4. Pharmacodynamic study in SJSA-1 xenografts: SJSA-1 xenograft-bearing mice (tumor volume 200–250 mm³) received a single oral dose of RG-7112 (RO-5045337) (200 mg/kg, formulated as above). Mice were euthanized at 2/6/12/24 hours (n=3/time point), and tumor tissues were frozen in liquid nitrogen. Western blot was performed on tumor lysates to detect p53 and p21 [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. In vitro metabolism in liver microsomes: RG-7112 (RO-5045337) was incubated with human liver microsomes (HLMs) or mouse liver microsomes (MLMs) in the presence of NADPH. In HLMs: t₁/₂ = 45 minutes, intrinsic clearance (CLint) = 35 μL/min/mg protein; in MLMs: t₁/₂ = 60 minutes, CLint = 28 μL/min/mg protein. LC-MS/MS identified monohydroxylated derivatives as major metabolites [1]
2. Oral bioavailability in mice: Mice received RG-7112 (RO-5045337) via oral gavage (100 mg/kg) or intravenous injection (10 mg/kg). Plasma concentrations were measured by LC-MS/MS. Oral bioavailability (F) = 35%; oral Cmax = 2.8 μM, Tmax = 1 hour, terminal t₁/₂ = 3.5 hours [1] 3. Plasma protein binding: Equilibrium dialysis was used to measure protein binding. RG-7112 (RO-5045337) showed high binding to human plasma proteins (>95%) and mouse plasma proteins (>90%) [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. In vivo toxicity in xenograft models: In SJSA-1 and U87MG xenograft studies, RG-7112 (RO-5045337) (up to 300 mg/kg oral) did not cause significant body weight loss (maximal 5% transient loss in 300 mg/kg SJSA-1 group, recovered within 3 days). Serum levels of ALT, AST (liver function markers) and BUN (kidney function marker) were not significantly different from control [2, 3]
2. CYP enzyme inhibition: RG-7112 (RO-5045337) was tested for inhibition of human CYP enzymes (1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 3A4) in vitro. IC₅₀ > 10 μM for all enzymes, indicating no significant drug-drug interaction risk via CYP inhibition [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
RO-5045337 is under investigation in clinical trial NCT01164033 (A Study of RO5045337 in Patients With Solid Tumors).
MDM2 Antagonist RO5045337 is an MDM2 (human homolog of double minutes-2; HDM2) antagonist with potential antineoplastic activity. RO5045337 binds to MDM2, thereby preventing the binding of the MDM2 protein to the transcriptional activation domain of the tumor suppressor protein p53. By preventing this MDM2-p53 interaction, the proteasome-mediated enzymatic degradation of p53 is inhibited and the transcriptional activity of p53 is restored, which may result in the restoration of p53 signaling and thus the p53-mediated induction of tumor cell apoptosis. MDM2, a zinc finger protein, is a negative regulator of the p53 pathway; often overexpressed in cancer cells, it has been implicated in cancer cell proliferation and survival. 1. Background: RG-7112 (RO-5045337) is a small-molecule MDM2 inhibitor in clinical development. It was designed to target the MDM2-p53 interaction, as MDM2 overexpression (common in cancers) inhibits p53 tumor suppressor activity [1] 2. Mechanism of action: RG-7112 (RO-5045337) binds to MDM2 with high affinity, blocking MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination and degradation. This stabilizes p53, activates downstream target genes (e.g., p21, Bax), and induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in TP53 wild-type cancer cells [2] 3. Indication potential: Preclinical data support RG-7112 (RO-5045337) as a candidate for treating MDM2-amplified and TP53 wild-type cancers, including osteosarcoma and glioblastoma [2, 3] |
| 分子式 |
C38H48CL2N4O4S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
727.78
|
|
| 精确质量 |
726.277
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 62.71; H, 6.65; Cl, 9.74; N, 7.70; O, 8.79; S, 4.41
|
|
| CAS号 |
939981-39-2
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
57406853
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
790.4±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
431.8±35.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.8 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.598
|
|
| LogP |
6.67
|
|
| tPSA |
90.9
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
49
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1260
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
|
| SMILES |
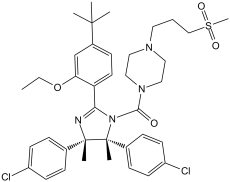
C[C@]1([C@@](C2C=CC(Cl)=CC=2)(C)N=C(C2C=CC(C(C)(C)C)=CC=2OCC)N1C(N1CCN(CCCS(=O)(=O)C)CC1)=O)C1C=CC(Cl)=CC=1
|
|
| InChi Key |
QBGKPEROWUKSBK-QPPIDDCLSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C38H48Cl2N4O4S/c1-8-48-33-26-29(36(2,3)4)14-19-32(33)34-41-37(5,27-10-15-30(39)16-11-27)38(6,28-12-17-31(40)18-13-28)44(34)35(45)43-23-21-42(22-24-43)20-9-25-49(7,46)47/h10-19,26H,8-9,20-25H2,1-7H3/t37-,38+/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
[(4S,5R)-2-(4-tert-butyl-2-ethoxyphenyl)-4,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dimethylimidazol-1-yl]-[4-(3-methylsulfonylpropyl)piperazin-1-yl]methanone
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 10 mg/mL (13.74 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 100.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 10 mg/mL (13.74 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 100.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 5 mg/mL (6.87 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.44 mM) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: 1% CMC Na : 14mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3740 mL | 6.8702 mL | 13.7404 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2748 mL | 1.3740 mL | 2.7481 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1374 mL | 0.6870 mL | 1.3740 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00623870 | Completed | Drug: RO5045337 | Hematologic Neoplasms | Hoffmann-La Roche | May 2008 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00559533 | Completed | Drug: RO5045337 | Neoplasms | Hoffmann-La Roche | December 2007 | Phase 1 |