| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
CDK4 (IC50 = 10 nM); CDK6 (IC50 = 39 nM)
The target of Ribociclib (LEE011) is cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (CDK4) and cyclin-dependent kinase 6 (CDK6). It inhibits CDK4 with an IC50 of 10 nM and CDK6 with an IC50 of 39 nM [1] [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:LEE011 作为 CDK4/CDK6 双重抑制剂,显着抑制 17 种神经母细胞瘤细胞系中 12 种的生长,平均 IC50 为 307 nM。神经母细胞瘤细胞系的生长抑制主要是细胞抑制作用,由 G1 细胞周期停滞和细胞衰老介导。激酶测定:Ribociclib(以前也称为 LEE011、NVP-LEE011;商品名:Kisqali)是一种有效的、口服的、高度特异性的 CDK4/6(细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶)抑制剂,IC50 分别为 10 nM 和 39 nM 。截至2017年3月,Ribociclib被FDA批准用于治疗患有一种晚期乳腺癌的绝经后妇女。 Ribociclib 通过减少磷酸化 RB 和 FOXM1 发挥作用。当用 17 种人类神经母细胞瘤细胞系进行测试时,其中 12 种对 Ribociclib 治疗敏感,平均 IC50=306±68 NM。 Ribociclib 治疗可以通过阻止细胞周期 G0-G1 来显着降低细胞生长。在 17 种人类神经母细胞瘤衍生细胞系中的 12 种中,LEE011 治疗可显着减少细胞增殖。细胞测定:根据先前的基质贴壁生长演示选择一组神经母细胞瘤细胞系,将其一式三份铺板在 Xcelligence 实时细胞电子传感系统上,并在 24 小时后用四对数剂量范围的抑制剂或二甲基亚砜 (DMSO) 对照。连续监测细胞指数约 100 小时,IC50 值确定如下:通过将细胞指数绘制为时间函数来生成生长曲线,并将其归一化为治疗时的细胞指数,基线细胞指数为1. 然后使用基线面积 1(治疗时的细胞指数)计算从治疗时到治疗后 96 小时的标准化生长曲线下的面积。将面积标准化为 DMSO 对照,并使用非线性对数抑制剂与标准化响应函数来分析所得数据。所有实验至少重复一次。
瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011)在具有完整视网膜母细胞瘤(Rb)蛋白的癌细胞中诱导G1期细胞周期阻滞。在表达功能性Rb的神经母细胞瘤细胞系中,用0.1-1 μM的瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011)处理后,通过流式细胞术检测显示G1期细胞比例显著增加。western blot和qPCR分析表明,这伴随着Rb磷酸化(pRb)水平降低和E2F靶基因表达减少 [2] 在神经母细胞瘤细胞中,用瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011)(0.5 μM)长期处理7天可诱导细胞衰老,表现为衰老相关β-半乳糖苷酶(SA-β-gal)活性增加和衰老标志物(如p16INK4a)上调 [2] 该化合物具有选择性抗增殖活性,对Rb阳性细胞的 efficacy 更强,而对Rb阴性细胞的IC50显著更高(> 10 μM) [1] [2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
LEE011(每日 200 mg/kg,口服)显着导致携带 BE2C 或 1643 异种移植物的小鼠肿瘤生长延迟,且没有体重减轻或其他毒性迹象。
Ribociclib (LEE011)对CDK4/6的抑制导致体内肿瘤生长延迟[2] 鉴于观察到神经母细胞瘤细胞系对CDK4/6抑制的不同敏感性,我们使用神经母细胞癌细胞系衍生的异种移植物来检测体内疗效,这些异种移植物代表了体外敏感性的极端。携带BE2C、NB-1643(MYCN扩增,体外敏感)或EBC1(非扩增,体外耐药)异种移植物的CB17免疫缺陷小鼠每天用Ribociclib(LEE011)或载体对照治疗21天。这种给药策略具有良好的耐受性,因为在任何异种移植物模型中都没有观察到体重减轻或其他毒性迹象。如图5A和S6所示,在含有BE2C或1643异种移植物的小鼠中,肿瘤生长在整个21天的治疗过程中明显延迟(两者都有,p<0.0001),尽管治疗后生长恢复(数据未显示)。相比之下,正如体外数据所预期的那样,EBC1异种移植物模型中的肿瘤生长抑制效果较差(p=0.51)。通过免疫组织化学对Ki67增殖标志物的评估证实,仅在BE2C和1643异种移植物模型中增殖受损,因为从单独的BE2C或1643异种移植小鼠队列中切除的肿瘤在用Ribociclib(LEE011)治疗7天后显示出比载体对照相对较弱的染色,而在EBC1异种移植物中没有观察到Ki67染色差异(图5B)。在BE2C和1643异种移植物中,RB的磷酸化也显著减少,而在EBC1模型中仅检测到最小的减少(图5B和5C)[2]。 在神经母细胞瘤(Rb阳性)异种移植小鼠模型中,每日口服瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011) 150 mg/kg,持续21天,可显著抑制肿瘤生长,与溶媒处理对照组相比,肿瘤体积减少60-70%。处理组小鼠的肿瘤样本中pRb水平降低且SA-β-gal活性增加,证实了体内G1期阻滞和衰老诱导 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
Ribociclib 是一种强效、口服、高选择性的 CDK4/6(细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶)抑制剂,IC50 分别为 10 nM 和 39 nM,之前称为 LEE011、NVP-LEE011;商品名:Kisqali。 2017 年 3 月,FDA 批准 Ribociclib 用于治疗患有晚期乳腺癌的绝经后妇女。 Ribociclib 通过降低磷酸化 FOXM1 和 RB 的水平发挥作用。在测试的 17 个人类神经母细胞瘤细胞系中,有 12 个显示出对 ribofacilb 治疗的敏感性(平均 IC50=306±68 NM)。通过停止 G0-G1 细胞周期,ribociclib 治疗可能会显着降低细胞增殖率。 LEE011 治疗可显着抑制 17 种人类神经母细胞瘤来源细胞系中 12 种的细胞增殖。
为测量CDK4/6抑制活性,将重组CDK4/细胞周期蛋白D1和CDK6/细胞周期蛋白D3复合物与荧光肽底物及不同浓度的瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011)共同孵育。通过测量底物的磷酸化水平评估激酶活性,IC50定义为使激酶活性降低50%所需的浓度 [1] [2] |
| 细胞实验 |
在 35 mm 平板中,细胞生长 24 小时,然后用 500 nM Ribociclib 处理 6 天。然后固定细胞,并进行过夜染色。然后,使用 Axio Observer D.1 相差显微镜对细胞进行 SA-β-gal 成像。通过计数三个不同显微镜框架中的阳性细胞数并归一化至对照,可以计算出 SA-β-gal 阳性细胞的百分比。为了评估细胞凋亡活性,用 Ribociclib 处理细胞,一式三份铺板于 96 孔板中,然后 16 小时后,在 Caspase-Glo 3/7 处理后 16 小时测量 caspase 3/7 活化。使用 SN-38 处理的细胞作为阳性对照[2]。
为进行细胞周期分析,用瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011)(0.1-1 μM)处理神经母细胞瘤细胞24-72小时。用碘化丙啶染色细胞,通过流式细胞术分析细胞周期分布,以量化G1、S和G2/M期的细胞比例 [2] 为评估衰老,用瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011)(0.5 μM)处理细胞7天,然后用比色法染色SA-β-gal活性,在显微镜下计数阳性细胞。通过western blot检测衰老标志物(如p16INK4a)的变化 [2] 为进行抗增殖实验,用0.01-10 μM的瑞博西尼(Ribociclib, LEE011)处理细胞5天。通过比色法测量细胞活力并确定IC50值 [1] [2] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: The xenografts derived from BE2C, NB-1643, or EBC1 cell lines are subcutaneously implanted into the right flank of CB17 SCID-/-mice. Then, for a total of 21 days, animals with engrafted tumors measuring 200–600 mm3 are randomly assigned to receive oral treatment with 200 mg/kg Ribociclib in 0.5% methylcellulose (n = 10) or vehicle (n = 10). Throughout the course of treatment, the tumor burden is calculated on a regular basis using the formula (π/6)×d2, where d is the mean tumor diameter measured with a caliper.
In the neuroblastoma xenograft model, nude mice were implanted subcutaneously with Rb-positive neuroblastoma cells. Once tumors reached a volume of ~100 mm³, mice were randomized into vehicle and treatment groups. Ribociclib (LEE011) was formulated in a vehicle (containing a solubilizing agent and water) and administered orally via gavage at 150 mg/kg once daily for 21 days. Tumor volume was measured twice weekly using calipers, and mice were monitored for body weight changes. At the end of the study, tumors were harvested for histopathological and molecular analyses [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Ribociclib is orally bioavailable, highly selective inhibitor of CDK4/6 kinases with inhibitory IC50 concentrations in the low nanomolar range. Following oral dosing, ribociclib was rapidly absorbed with median Tmax ranging from 1 to 5 hours. Plasma concentrations increased approximately 2- to 3-fold from Cycle 1 Day 1 to Cycle 1 Day 18/21 due to accumulation, with steady state reached by approximately Day 8 on the basis of trough concentrations after repeated daily dosing. Dose-proportionality analyses demonstrated that exposure to ribociclib increased with dose, with both Cmax and area under the curve (AUC) increasing slightly more than proportional to dose, over the dose range 50–1,200 mg/day Biological Half-Life 32.6 hours |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In the large clinical trials, adverse events were common and led to dose reductions in 45% of patients and discontinuation in 7%. In preregistration clinical trials, ALT elevations occurred in 46% of ribociclib vs 36% of control subjects and elevations above 5 times the ULN in 10% vs 1%. In one study, 1% of recipients developed clinically apparent liver injury with jaundice, but all recovered. The liver injury arose after 3 to 5 cycles and presented with asymptomatic elevations in serum ALT followed by symptoms and jaundice. Immunoallergic and autoimmune features were not present, although liver histology sometimes showed autoimmune hepatitis-like features. Recovery was slow (3 to 5 months), but ultimately complete. Restarting ribociclib resulted in more rapid and severe recurrence. Thus, experience with ribociclib is limited, but it appears to be capable of causing significant liver injury. Likelihood score: C (probable cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of ribociclib during breastfeeding. Because protein binding of ribociclib is 70%, clinically important amounts of the drug might pass into breastmilk. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during ribociclib therapy and for at least 3 weeks after the final dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
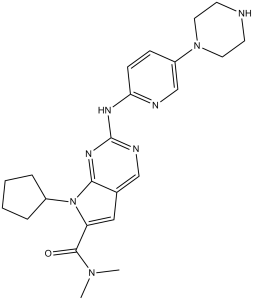
Ribociclib is a member of piperazines and a member of pyridines.
Ribociclib is a selective cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, a class of drugs that help slow the progression of cancer by inhibiting two proteins called cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6). These proteins, when over-activated, can enable cancer cells to grow and divide too quickly. Targeting CDK4/6 with enhanced precision may play a role in ensuring that cancer cells do not continue to replicate uncontrollably. Ribociclib was approved by the U.S. FDA in March, 2017 as Kisqali. Ribociclib is a Kinase Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of ribociclib is as a Kinase Inhibitor, and Cytochrome P450 3A Inhibitor. Ribociclib is a unique cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor that is used in combination with aromatase inhibitors in the treatment of postmenopausal women with metastatic breast cancer. Ribociclib is associated with a moderate rate of serum aminotransferase elevations during therapy, and to clinically apparent liver injury in a proportion of these. Ribociclib is an orally available cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitor targets at cyclin D1/CDK4 and cyclin D3/CDK6 cell cycle pathway, with potential antineoplastic activity. Ribociclib specifically inhibits CDK4 and 6, thereby inhibiting retinoblastoma (Rb) protein phosphorylation. Inhibition of Rb phosphorylation prevents CDK-mediated G1-S phase transition, thereby arresting the cell cycle in the G1 phase, suppressing DNA synthesis and inhibiting cancer cell growth. Overexpression of CDK4/6, as seen in certain types of cancer, causes cell cycle deregulation. See also: Ribociclib Succinate (active moiety of). Drug Indication Kisqali (ribociclib) is a selective cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, a class of drugs that help slow the progression of cancer by inhibiting two proteins called cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6). These proteins, when over-activated, can enable cancer cells to grow and divide too quickly. Targeting CDK4/6 with enhanced precision may play a role in ensuring that cancer cells do not continue to replicate uncontrollably. Kisqali is indicated for the treatment of women with hormone receptor (HR)âpositive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)ânegative locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer in combination with an aromatase inhibitor or fulvestrant as initial endocrine-based therapy, or in women who have received prior endocrine therapy. In preâ or perimenopausal women, the endocrine therapy should be combined with a luteinising hormoneâreleasing hormone (LHRH) agonist. Treatment of neuroblastoma Mechanism of Action Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) may provide protection against oncogenic processes in specific tissue types. For example, CDK4 is not required for normal mammary tissue development based on knockout mouse studies, but it is needed for growth of Ras-induced mammary tumors, suggesting a potential therapeutic window for treatment with lower toxicity. Ribociclib was reported to be a most selective CDK4/6 inhibitor and to have dose dependent antitumor activity in a number of preclinical models. It inhibited growth of tumor cells by arresting the cells at the G1 checkpoint, which prevents the tumor cells from proliferating. Ribociclib (LEE011) is a selective CDK4/6 inhibitor that blocks the cyclin D-CDK4/6-Rb pathway, a key regulator of cell-cycle progression from G1 to S phase. Its activity is dependent on functional Rb protein, making it effective in cancers with intact Rb signaling (e.g., breast cancer, neuroblastoma). It is designed to induce cell-cycle arrest and senescence, thereby inhibiting cancer cell proliferation [1] [2] |
| 分子式 |
C23H30N8O
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
434.54
|
| 精确质量 |
434.254
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 63.57; H, 6.96; N, 25.79; O, 3.68
|
| CAS号 |
1211441-98-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Ribociclib hydrochloride;1211443-80-9;Ribociclib-d6 hydrochloride;Ribociclib succinate;1374639-75-4;Ribociclib succinate hydrate;1374639-79-8;Ribociclib-d6;1328934-40-2;Ribociclib-d8;2167898-24-8
|
| PubChem CID |
44631912
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.4±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
730.8±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
395.8±35.7 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.723
|
| LogP |
-0.74
|
| tPSA |
91.21
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
636
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
N1(CCNCC1)C1C=NC(NC2N=C3N(C(C(N(C)C)=O)=CC3=CN=2)C2CCCC2)=CC=1
|
| InChi Key |
RHXHGRAEPCAFML-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H30N8O/c1-29(2)22(32)19-13-16-14-26-23(28-21(16)31(19)17-5-3-4-6-17)27-20-8-7-18(15-25-20)30-11-9-24-10-12-30/h7-8,13-15,17,24H,3-6,9-12H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26,27,28)
|
| 化学名 |
7-cyclopentyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-[(5-piperazin-1-ylpyridin-2-yl)amino]pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide
|
| 别名 |
LEE 011; Ribociclib; LEE011; LEE-011; trade name: Kisqali; Ribociclib (LEE011); LEE 011; 7-cyclopentyl-N,N-dimethyl-2-((5-(piperazin-1-yl)pyridin-2-yl)amino)-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine-6-carboxamide;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.30 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.30 mM) (饱和度未知) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.89 mg/mL (2.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.89 mg/mL (2.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 8.9 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入 900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 5 中的溶解度: ≥ 0.89 mg/mL (2.05 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 8.9 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入900 μL 玉米油中,混合均匀。 配方 6 中的溶解度: 5% DMSO+40% PEG 300+5%Tween80+ 50%ddH2O: 1.1mg/ml 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3013 mL | 11.5064 mL | 23.0128 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4603 mL | 2.3013 mL | 4.6026 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2301 mL | 1.1506 mL | 2.3013 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
First-in-Human Study of STX-478 as Monotherapy and in Combination With Other Antineoplastic Agents in Participants With Advanced Solid Tumors
CTID: NCT05768139
Phase: Phase 1/Phase 2 Status: Recruiting
Date: 2024-11-25
 Pharmacologic inhibition of CDK4/6 suppresses neuroblastoma growthin vitro.(A)The growth of 12 of 17 neuroblastoma cell lines was significantly impaired in response to CDK4/6 inhibition with LEE011 (mean IC50= 306 ± 68 nM, sensitive lines only). Data are plotted (and tabulated) as the best fit IC50per log(inhibitor) vs. normalized response analysis (GraphPad); upper and lower bars represent 95 % confidence levels.(B)Dose-dependent decreases in pRBS780accompany growth suppression in sensitive lines and are indicative of on- target activity.Clin Cancer Res.2013 Nov 15;19(22):6173-82. |
|---|
 Growth suppression via CDK4/6 inhibition is mediated by cell cycle arrest and senescence. Neuroblastoma cell lines with demonstrated sensitivity or resistance to LEE011 were analyzed for cell cycle arrest and senescence associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity.(A)A significant G1arrest accompanied by reductions in the fraction of cells in S phase and G2/M was observed in sensitive lines only.(B)Representative cell cycle histograms of a sensitive and resistant cell line.(C)Down-regulation of FOXM1 mRNA and(D)protein was observed in sensitive lines and was associated with(E)the induction of a senescent phenotype.Clin Cancer Res.2013 Nov 15;19(22):6173-82. |
 Inhibition of CDK4/6 suppresses neuroblastoma growthin vivo.(A)Mice with subcutaneously implanted xenografts were treated daily with 200 mg/kg LEE011 or with a vehicle for 21 days. In two of three neuroblastoma xenograft models, treatment with LEE011 significantly reduced tumor burden in comparison to vehicle, as determined by linear mixed effects analysis (BE2C, p<0.0001; 1643, p <0.0001; EBC1 p = 0.51).(B)The reduction in tumor proliferation observed in sensitive lines was confirmed by Ki67 staining of resected xenografts, and inhibition of CDK4/6 activity was confirmed by(C)immunohistochemical staining and western blot for pRBS780.Clin Cancer Res.2013 Nov 15;19(22):6173-82. |