| 规格 | 价格 | |
|---|---|---|
| 500mg | ||
| 1g | ||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Pyruvate kinase isoform M2 (PKM2)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
PKM2 是基于 SAICAR 积累的核定位。 PKM2-SAICAR 通过磷酸化和激活 Erk1/2 增加 PKM2 对 SAICAR 结合的敏感性。此外,为了引起丝裂原诱导的细胞增殖和持续的 Erk1/2 激活,需要 PKM2-SAICAR。诱导 H3 T11 和 Erk1/2 磷酸化需要并通过 SAICAR-PKM2 相互作用来满足[2]。当细胞缺乏葡萄糖时,细胞内的 SAICAR 含量会振荡上升,进而导致癌细胞激活 PKM2。此外,在葡萄糖限制条件下,SAICAR-PKM2 连接可提高癌细胞的存活率。 Adsl-kd 细胞和过表达 PAICS 的细胞在葡萄糖限制下表现更好,但 paics-kd 细胞比对照-kd 细胞死亡得更快。在葡萄糖限制环境下,SAICAR 可以提高癌细胞的存活率。
丙酮酸激酶亚型M2(PKM2)在应激条件下癌症细胞的生长和代谢重编程中起着重要作用。在这里,我们报告了SAICAR(琥珀酰氨基咪唑羧酰胺核糖-5′-磷酸,从头嘌呤核苷酸合成途径的中间体)特异性刺激PKM2。葡萄糖饥饿时,细胞SAICAR浓度以振荡方式增加,并刺激癌症细胞中的PKM2活性。癌症细胞SAICAR水平的变化改变了细胞能量水平、葡萄糖摄取和乳酸的产生。SAICAR-PKM2相互作用也促进癌症细胞在葡萄糖限制条件下的存活。无论葡萄糖条件如何,在正常成人上皮细胞或肺成纤维细胞中都没有观察到SAICAR的积累。这种变构调节可以解释癌症细胞如何协调不同的代谢途径,以优化其在肿瘤微环境中常见的营养限制条件下的生长。[1] 代谢异常和持续增殖是癌症的特征。丙酮酸激酶M2(PKM2)是一种代谢酶,在这两个过程中都起着重要作用。最近,PKM2被证明具有磷酸化组蛋白H3和促进癌症细胞增殖的蛋白激酶活性。然而,这种蛋白激酶在癌症细胞中的作用机制和范围尚不清楚。在这里,我们报告了琥珀酰-5-氨基咪唑-4-甲酰胺-1-核糖-5'-磷酸(SAICAR)的结合,一种在增殖细胞中丰富的代谢产物,在体外和细胞内诱导PKM2的蛋白激酶活性。蛋白质微阵列实验表明,100多种人类蛋白质,主要是蛋白激酶,被PKM2-SAICAR磷酸化。特别是,PKM2-SAICAR磷酸化并激活Erk1/2,进而通过磷酸化使PKM2对SAICAR结合敏感。此外,PKM2-SAICAR对于诱导持续的Erk1/2激活和丝裂原诱导的细胞增殖是必要的。因此,配体诱导的PKM2蛋白激酶活性是一种直接将细胞增殖与细胞内代谢状态偶联的机制[2]。 |
| 酶活实验 |
蛋白激酶测定[2]
将反应溶液[0.1-10 nM PKM2、0-4μM组蛋白(NEB,通常为1μM H3单体浓度)、150μM PEP、50 mM HEPES、pH 7.4、100 mM氯化钾、6.2 mM乙酸镁和5%甘油]在25°C下孵育1-120分钟(通常为5分钟)。反应后,将溶液与等体积的SDS凝胶加载缓冲液(375 mM Tris-HCl,pH 8,10%SDS,50%甘油,1 mM DTT,0.1%溴酚蓝)混合,并在95°C下孵育10分钟。除非另有特别说明,否则所有其他蛋白激酶测定均按所述进行,使用固定浓度的PKM2(10nM)30分钟。溶液经过SDS-PAGE、ProQ-Diamond 染色或蛋白质印迹分析。为了测定催化效率(kcat),用更高浓度的PKM2(10nM)进行反应1小时,并假设所得信号代表完成的反应。 蛋白质微阵列实验[2] 在存在和不存在SAICAR的情况下,使用Invitrogen人蛋白微阵列、重组PKM2和PEP进行蛋白质微阵列实验。使用ProQ-Diamond染色 检测磷酸化蛋白。补充信息中提供了对该实验的详细描述。 PKM2的磷酸化[2] 重组PKM2(1μM)和重组GST-Erk1(10 nM)在含有1 mM ATP、50 mM Tris-HCl、pH 7.0、150 mM NaCl、1 mM DTT、1 mM MgCl2的缓冲液中在25°C下一起孵育30分钟。将反应溶液通过谷胱甘肽琼脂糖树脂以耗尽GST-Erk1。用50 mM Tris、pH 8.0、150 mM NaCl、1 mM DTT、1 mM MgCl2缓冲液洗脱未结合的蛋白质。然后对组分进行SDS-PAGE和考马斯亮色或Pro-Q钻石染色。使用Pro-Q钻石染色鉴定含有磷酸化PKM2的组分。通过计算消光系数(28910 M−1 cm−1)在变性条件下测量A280来确定磷酸化PKM2的浓度(Edelhoch,1969)。 Erk1/2活性测定[2] 在室温下孵育10μL反应(25 nM rPKM2、1μM rErk1、150μM PEP、50 mM HEPES pH 7.4、100 mM氯化钾、10%甘油、6.2 mM氯化镁和1 mM DTT)30分钟。用水连续稀释Erk1反应,并将8μL稀释溶液加入到黑色透明底部96孔板中的32μL Omnia激酶测定溶液(10μM Omnia肽17、1 mM ATP、0.2 mM DTT和供应商的专有缓冲液成分)中。使用帝肯Infinity M2荧光微孔板读数器在30°C下每分钟记录一次485 nm的发射(360 nm的激发),持续60分钟。 |
| 细胞实验 |
蛋白质印迹[2]
按照AbCam的描述进行蛋白质印迹(http://www.abcam.com/ps/pdf/protocols/WB-beginner.pdf).简而言之,在补充有1mM苯甲基磺酰氟和1mM氟化钠的冰冷RIPA缓冲液(20mM Tris-HCl,pH 7.5,150mM NaCl,1mM EDTA,1mM EGTA,1%NP-40,1%脱氧胆酸钠)中裂解细胞,并使用Pierce 660试剂以牛血清白蛋白为标准测量总蛋白量。蛋白质通过SDS-PAGE分离,并转移到硝化纤维膜上。用补充了5%牛血清白蛋白的磷酸盐缓冲盐水(PBS)封闭膜,并在4°C下用适当的一抗探测过夜。一抗孵育后,用辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)偶联的山羊抗兔IgG或山羊抗小鼠IgG二抗(Bio-Rad)探测膜。然后使用商业化学发光底物检测HRP偶联的二抗。使用FluorChem M FM0455成像仪采集化学发光图像。 |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
SAICAR is a 1-(phosphoribosyl)imidazolecarboxamide resulting from the formal condesation of the darboxy group of 5-amino-1-(5-O-phosphono-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-1H-imidazole-4-carboxylic acid with the amino group of L-aspartic acid. It has a role as an Escherichia coli metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is functionally related to a succinic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a SAICAR(4-).
SAICAR is a metabolite found in or produced by Escherichia coli (strain K12, MG1655). Saicar has been reported in Homo sapiens, Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and Apis cerana with data available. SAICAR (or (S)-2-[5-Amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamido]succinate) is a substrate for the multifunctional protein ADE2. SAICAR is an intermediate in purine metabolism. (S)-2-[5-Amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole-4-carboxamido]succinate is converted from 5-Amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl) imidazole-4-carboxylate via phosphoribosylaminoimidazole-succinocarboxamide synthase [EC: 6.3.2.6] or SAICAR synthase. This enzyme catalyses the seventh step out of ten in the biosynthesis of purine nucleotides. The appearance of succinylaminoimidazolecarboxamide riboside (SAICAriboside) and succinyladenosine (S-Ado) in cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and to a lesser extent in plasma is characteristic of a heritable deficiency Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency. . SAICAR is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Based on these results, we conclude that at least some aspects of PKM2’s role in tumor biology can be explained by SAICAR-mediated allosteric stimulation. This feature of PKM2 may allow cells to adjust their energy generation in response to nutritional and metabolic demands. When sufficient levels of glucose are provided, diverting glycolytic intermediates to biosynthetic processes like the pentose phosphate pathway can promote cell growth. However, in energy-depleting conditions such as nutrient-limitation, continued diversion of glycolytic intermediates to biosynthetic processes can hamper cells by depleting cellular energy below the minimal level required. The SAICAR-PKM2 interaction described here can be a molecular mechanism for this delicate balance. Ribose-5-phosphate, the starting material of nucleotide biosynthesis, is produced from the pentose phosphate pathway, which diverts glycolytic intermediates away from energy production. Connecting PKM2’s PK activity with an intermediate of the de novo purine nucleotide biosynthesis pathway could give cells fine-tuned control of their metabolism in demanding conditions. SAICAR is produced from L-aspartate, a byproduct of glutaminolysis, which is known to be important in cancer cell metabolism, and the cleavage of SAICAR yields fumarate, which contributes to the citric acid cycle in mitochondria. SAICAR is therefore positioned to convey cellular metabolic demands to PKM2.[1] In addition to previously known histone H3 (Yang et al., 2012a), we also identified many human proteins as potential substrates for PKM2-SAICAR, with the vast majority of proteins involved in the regulation of cell proliferation. Further investigation on how PKM2-SAICAR recognizes its substrates may reveal a previously unrecognized feature common to these proteins involved in cell cycle regulation. Previous work on PKM2 has revealed an interaction between MAPK activity and PKM2, showing that Erk1/2 phosphorylates PKM2 (Yang et al., 2012b). In our work, the reciprocal reaction – phosphorylation of MAPK protein kinases by PKM2 – also occurs in vitro and in cells upon the binding of SAICAR to PKM2. Our result challenges the view that PKM2 is a passive recipient of MAPK protein kinase signaling and suggests that PKM2 is a more active component that is necessary for the MAPK protein kinase signaling. Intricately related to MAPK activity is cell cycle control and proliferation. As has been well documented, malignant tumor cells frequently display sustained proliferation. Many different mechanisms such as mutations in genes encoding MAPK signaling contribute to the sustained proliferation of cancer cells. However, many types of cancer cells show sustained proliferation without showing any mutations in these genes. The altered metabolism associated with most cancer cells, including upregulation of PKM2, may thus be a mechanism to sustain cell proliferation in those cells.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C13H19N4O12P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
454.28336
|
| 精确质量 |
454.074
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 34.37; H, 4.22; N, 12.33; O, 42.26; P, 6.82
|
| CAS号 |
3031-95-6
|
| 相关CAS号 |
3031-95-6
|
| PubChem CID |
160666
|
| 外观&性状 |
Purple to purplish red solid powder
|
| LogP |
-4.3
|
| tPSA |
277.29
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
8
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
14
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
9
|
| 重原子数目 |
30
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
718
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
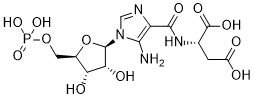
OC(C[C@H](NC(C1N=CN([C@@H]2O[C@H](COP(=O)(O)O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)C=1N)=O)C(=O)O)=O
|
| InChi Key |
NAQGHJTUZRHGAC-ZZZDFHIKSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C13H19N4O12P/c14-10-7(11(22)16-4(13(23)24)1-6(18)19)15-3-17(10)12-9(21)8(20)5(29-12)2-28-30(25,26)27/h3-5,8-9,12,20-21H,1-2,14H2,(H,16,22)(H,18,19)(H,23,24)(H2,25,26,27)/t4-,5+,8+,9+,12+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
N-((5-Amino-1-(5-O-phosphono-beta-D-ribofuranosyl)-1H-imidazol-4-yl)carbonyl)-L-aspartic acid
|
| 别名 |
SAICAR; SAICAR; Succino-AICAR; SAICAriboside; UNII-K1PVR64RIF; K1PVR64RIF; SAICA riboside; 5-Amino-4-imidazole-N-succinocarboxamide ribonucleotide; ...; 3031-95-6; Succino-AICAR.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~220 mg/mL (~484.28 mM)
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~220.13 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 5.5 mg/mL (12.11 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 55.0 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 5.5 mg/mL (12.11 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 55.0mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到900μL 20%SBE-β-CD生理盐水中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 5.5 mg/mL (12.11 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2013 mL | 11.0064 mL | 22.0129 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4403 mL | 2.2013 mL | 4.4026 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2201 mL | 1.1006 mL | 2.2013 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。