| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg | |||
| 250mg | |||
| 500mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
D2 Receptor ( Ki = 0.06 nM ); D1 Receptor ( Ki ~350 nM ); D3 Receptor ( Ki = 0.6 nM ); D4 Receptor ( Ki = 0.08 nM ); D5 Receptor ( Ki ~ 3500 nM ); 5-HT2A Receptor ( Ki = 1 nM ); 5-HT1A Receptor ( Ki = 49 nM ); α1B-adrenoceptor; Calcium-activated chloride channel
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Spiperone 是一种有效的细胞内 Ca2+ 增强剂 (EC50=9.3 μM),通过蛋白酪氨酸激酶偶联的磷脂酶 C 依赖性途径刺激细胞内 Ca2+,从而导致 Calu-3 和 CFBE41o- 细胞单层中 Cl- 的分泌增加[2] 。 Spiperone 显着降低脂多糖刺激的 BV-2 小胶质细胞、原代小胶质细胞和原代星形胶质细胞培养物中一氧化氮的产生。 Spiperone 还显着抑制 ATP 刺激的原代小胶质细胞培养物中一氧化氮的产生。 Spiperone 显着降低 BV-2 小胶质细胞中 TNF-α 的产生。 Spiperone 可减弱 BV-2 小胶质细胞中 mRNA 水平的诱导型一氧化氮合酶和促炎细胞因子(例如 IL-1β 和 TNF-α)的表达[3]。
Spiperone(1)是一种广泛使用的药理学工具,作为一种有效的多巴胺D2、5-HT1A和5-HT2A拮抗剂。尽管spiperone也与5-HT2C受体结合,但它是为数不多的对5-HT2A与5-HT2C受体表现出一定(约1000倍)结合选择性的药物之一,因此,如果已知其各种取代基对结合的影响,它可能作为开发新型5-HT2A拮抗剂的有用模板。在本研究中,我们重点研究了spiperone的1,3,8 -三氮唑斯匹罗[4.5]decanone部分,发现用甲基取代n1 -苯基只会略微降低克隆大鼠5-HT2A受体的亲和力。然而,n1 -甲基衍生物对5-HT1A、5-HT2C和多巴胺D2受体的亲和力显著降低。几个代表性的例子被证明是5-HT2拮抗剂。因此,spiperone的n1 -烷基类似物可以进入一系列新的5- ht2a选择性拮抗剂 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Spiperone(1.5 mg/kg;腹腔注射;第 1、3、6、7 和 13-21 天;C57Bl/6 小鼠)治疗可减少炎症细胞对肺泡间质和肺泡管的浸润,并防止结缔组织的生长博莱霉素肺实质组织[6]。动物模型:C57Bl/6小鼠(7-8周龄)博莱霉素诱导肺纤维化[6] 剂量:1.5 mg/kg 给药方式:腹腔注射;第 1、3、6、7 和 13-21 天结果:炎症细胞对肺泡间质和肺泡管的浸润减少,并阻止博莱霉素肺实质中结缔组织的生长。
|
| 酶活实验 |
囊性纤维化(CF)是由产生囊性纤维化跨膜传导调节因子(CFTR)的基因突变引起的。CFTR起Cl(-)通道的作用。它的功能障碍限制了Cl(-)的分泌,增强了Na+的吸收,导致气道粘液粘稠。Ca2+激活的Cl(-)通道(CaCCs)在气道表面上皮中与CFTR共表达。胞质Ca(2+)的增加激活了上皮细胞的CaCCs,这在CF中提供了另一种Cl(-)分泌途径。我们开发了一种筛选试验,并筛选了一个化合物库,这些化合物可以增强细胞质Ca2+,激活CaCC,增加Cl(-)分泌。我们发现spiperone,一种已知的抗精神病药物,是一种有效的细胞内Ca2+增强剂,并证明它刺激细胞内Ca2+,不是通过其众所周知的5-羟色胺5-HT2或多巴胺D2受体拮抗剂的作用,而是通过蛋白酪氨酸激酶偶联磷脂酶c依赖途径。Spiperone激活CaCCs,在体外和体内cftr敲除小鼠的极化人非CF和CF气道上皮细胞单层中刺激Cl(-)分泌。总之,我们已经确定了spiperone作为一种新的治疗平台,通过独立于CFTR的途径纠正CF中有缺陷的Cl(-)分泌。[2]
详细研究了酮色胺(1)和spiperone(2)的结构,以确定不同取代基对5-HT(2A)受体亲和力和选择性的作用。发现喹唑啉环的存在降低了酮色胺的选择性,而各种开环类似物显示出与酮色胺类似的亲和力,选择性提高了30倍。spiperone的三嗪吡喃癸酮部分是其5-HT亲和力和选择性的主要决定因素。环施加的构象刚性以及N(1)取代基的性质是控制5-HT(2A)、5-HT(2C)、5-HT(1A)和多巴胺D2受体结合的重要因素。甲基取代spiperone的N(1)-苯基环(KML-010)48)得到的化合物与5-HT(2A)受体结合的亲和力略低于spiperone,但对5-HT(2C)和5-HT(1A)受体缺乏亲和力(Ki >10,000 nM),与D2受体结合的亲和力降低了400倍。[4] |
| 细胞实验 |
Spiperone 是一种有效的细胞内 Ca2+ 增强剂 (EC50=9.3 μM),通过蛋白酪氨酸激酶偶联的磷脂酶 C 依赖性途径刺激细胞内 Ca2+,从而导致 Calu-3 和 CFBE41o- 细胞单层中 Cl- 的分泌增加[2] 。 Spiperone 显着降低脂多糖刺激的 BV-2 小胶质细胞、原代小胶质细胞和原代星形胶质细胞培养物中一氧化氮的产生。 Spiperone 还显着抑制 ATP 刺激的原代小胶质细胞培养物中一氧化氮的产生。 Spiperone 显着降低 BV-2 小胶质细胞中 TNF-α 的产生。 Spiperone 可减弱 BV-2 小胶质细胞中 mRNA 水平的诱导型一氧化氮合酶和促炎细胞因子(例如 IL-1β 和 TNF-α)的表达[3]。
|
| 动物实验 |
C57Bl/6 mice (7-8-week-old) induced pulmonary fibrosis by Bleomycin
1.5 mg/kg Intraperitoneal injection; on days 1, 3, 6, 7, and 13-21 |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
rat LD50 oral >1 gm/kg Drugs in Japan, 6(380), 1982
rat LD50 intraperitoneal >500 mg/kg Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics., 3(390), 1969 rat LD50 subcutaneous >50 mg/kg Oyo Yakuri. Pharmacometrics., 3(390), 1969 rat LD50 intravenous 14 mg/kg Psychotropic Drugs and Related Compounds, 2nd ed., Usdin, E., and D.H. Efron, Washington, DC, 1972, -(193), 1972 rat LD50 intramuscular 168 mg/kg Drugs in Japan, 6(380), 1982 |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
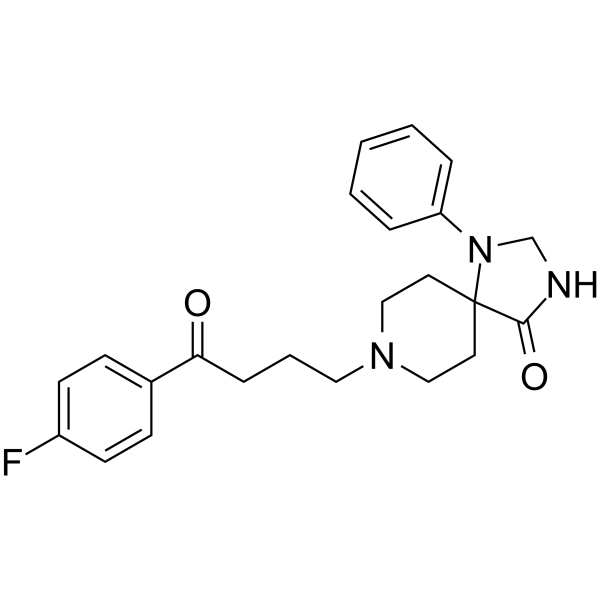
Spiperone is an azaspiro compound that is 1,3,8-triazaspiro[4.5]decane which is substituted at positions 1, 4, and 8 by phenyl, oxo, and 4-(p-fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutyl groups, respectively. It has a role as a dopaminergic antagonist, a serotonergic antagonist, an alpha-adrenergic antagonist, an antipsychotic agent and a psychotropic drug. It is an organofluorine compound, an azaspiro compound, a member of piperidines, a tertiary amino compound and an aromatic ketone.
Spiperone is a dopamine antagonist that binds dopamine and serotonin receptors. A spiro butyrophenone analog similar to HALOPERIDOL and other related compounds. It has been recommended in the treatment of SCHIZOPHRENIA. Objective: Our purpose was to determine the presence of alpha(1)-adrenoceptor messenger RNA subtypes and extend the pharmacologic characterization of alpha(1)-adrenoceptors involved in human umbilical vein (HUV) contraction. Study design: Cords (n=124) from healthy patients after term vaginal or cesarean deliveries were used. The vein was carefully dissected out of cords and used for reverse transcription combined with polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to amplify alpha(1)-adrenoceptor transcripts. In isolated organ baths, HUV rings were mounted and cumulative concentration-response curves were constructed either for epinephrine or the selective alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor agonist, A-61603. In other series of experiments, the effects of the selective alpha(1A)- and alpha(1B)-adrenoceptor antagonists (RS-100329 or B8805-033 or spiperone, AH11110A and cyclazosin, respectively) were evaluated to estimate its blocking potencies on epinephrine concentration-response curves. Results: By means of RT-PCR technique alpha(1a)- and alpha(1b)-adrenoceptor transcripts were detected in the HUV. The blocking potency values of RS-100329 or B8805-033 against responses mediated by epinephrine were not consistent with the activation of an alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor population. Moreover, the low potency of the agonist A-61603 was not in accordance with an alpha(1A)-adrenoceptor interaction. On the other hand, the antagonist potencies of spiperone, AH11110A and cyclazosin were in agreement with an interaction on alpha(1B)-adrenoceptor subtype. Conclusion: Although alpha(1a)- and alpha(1b)-adrenoceptor messenger RNAs are detected in the HUV, only alpha(1B)-adrenoceptors are involved in epinephrine vasoconstrictor action. [5] The antifibrotic properties of spiperone and its effect on stem and progenitor cells were studied on the model of reversible bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in C57Bl/6 mice. Spiperone reduced infiltration of the alveolar interstitium and alveolar ducts with inflammatory cells and prevented the growth of the connective tissue in the parenchyma of bleomycin lungs. Apart from anti-inflammatory effect, spiperone suppressed bone marrow hemopoietic cells (CD3, CD45R (B220), Ly6C, Ly6G (Gr1), CD11b (Mac1), TER-119)-, Sca-1+, c-Kit+, CD34- and progenitor hemopoietic cells (granulocyte-erythroid-macrophage-megakaryocytic and granulocyte CFU). Spiperone-induced disturbances of fi brogenesis were paralleled by restoration of endothelial cells in the lung parenchyma, reduction of the number of circulating bone marrow cells and lung mesenchymopoietic cells (mesenchymal multipotent stromal cells (CD31-, CD34-, CD45-, CD44+, CD73+, CD90+, CD106+) and progenitor fi broblast cells), and suppression of multilineage differentiation of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (including fi broblast-lineage cells). [6] |
| 分子式 |
C23H26FN3O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
395.47
|
| 精确质量 |
395.201
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 69.85; H, 6.63; F, 4.80; N, 10.63; O, 8.09
|
| CAS号 |
749-02-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Spiperone hydrochloride; 2022-29-9
|
| PubChem CID |
5265
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light yellow solid powder
|
| 沸点 |
630.6ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
190-193.6ºC
|
| 闪点 |
335.2ºC
|
| LogP |
3.548
|
| tPSA |
52.65
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
6
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
577
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C1=CC=C(F)C=C1)CCCN2CCC3(CC2)N(CNC3=O)C4=CC=CC=C4
|
| InChi Key |
DKGZKTPJOSAWFA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H26FN3O2/c24-19-10-8-18(9-11-19)21(28)7-4-14-26-15-12-23(13-16-26)22(29)25-17-27(23)20-5-2-1-3-6-20/h1-3,5-6,8-11H,4,7,12-17H2,(H,25,29)
|
| 化学名 |
8-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxobutyl]-1-phenyl-1,3,8-triazaspiro[4.5]decan-4-one
|
| 别名 |
E 525; R-5147; spiperone; 749-02-0; Spiropitan; Spiroperidol; Espiperona; Spiperonum; R 5147; [3H]spiperone; NSC-170983; Spiperone; E525; R 5147; NSC170983; E-525; R5147; NSC 170983
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.03.00
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~33.3 mg/mL (~84.3 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 4.55 mg/mL (11.51 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 45.5 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.32 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5286 mL | 12.6432 mL | 25.2864 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5057 mL | 2.5286 mL | 5.0573 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2529 mL | 1.2643 mL | 2.5286 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。