| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
PGF2α
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
Tafluprost (3 μM, 48 h) 在 RGC-5 细胞中减少细胞数量[1]。 Tafluprost (0.1-100 μM, 48 h) 在 RGC-5 细胞中以剂量依赖性的方式增强细胞活力[2]。细胞活力测定[2]细胞系:RGC浓度:0.1,1,3,10,100μM孵育时间:48小时结果:以剂量依赖性方式增强这些细胞的活力,最佳浓度为3μM。 。增加相对荧光强度 (RFI)。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
Tafluprost (0.0015% AFP168 滴眼液,连用14天) 在化妆品 Sprague-Dawley 中可降低视神经挤压 (ONC) 眼压,提高 RGC 细胞活力,减少神经细胞凋亡[2]。 动物模型: 男性Sprague 大鼠模型[2] 剂量:0.0015% 给药方式:通过滴眼剂 结果:RGC 数量增加,TUNEL 阳性细胞数量减少。动物模型:前列腺素受体缺失C57BL/6小鼠模型[3] 剂量:3 μL(0.0015%他氟前列素) 给药方式:滴注;单剂量结果:WT、EP1KO、EP2KO、EP3KO和FPKO小鼠眼压降低,平均眼压降低率分别为25.8(2.1)%、26.3(0.8)%、24.2(1.4)%、16.5(1.7)%和20.9分别为 (1.5)%。 (EP3KO和FPKO小鼠眼压下降幅度小于WT小鼠。)
|
| 细胞实验 |
细胞系:RGC
浓度:0.1、1、3、10、100 μM 孵育时间:48 小时 结果:以剂量依赖性方式增强这些细胞的活力,最佳浓度为3μM。增加相对荧光强度 (RFI)。 |
| 动物实验 |
Male Sprague rat model
0.0015% Via eye drops C57BL/6J, and EP1, EP2, EP3 and postaglandin F (FP) receptor-deficient wild-type (WT), EP1KO, EP2KO, EP3KO and FPKO, respectively mice were bred and acclimatised under a 12-h (6:00-18:00) light-dark cycle. To evaluate effects of tafluprost (0.002%) on IOP at night, a single 3 microl drop of tafluprost solution was applied topically at 18:00 once into one eye in each mouse. IOP was measured 3 h after the application with a microneedle method. To clarify whether endogenous prostaglandin is concerned with the tafluprost-induced IOP reduction, we applied 0.1% diclofenac Na, a cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor or PBS 30 min before the application of tafluprost in WT and EP3KO mice and measured IOP 3 h after the tafluprost application. We also determined whether animals responded predictably to 0.1% bunazosin HCl, a drug known to increase uveoscleral outflow. Results: 3 h after the application of 0.0015% tafluprost, mean (SEM) IOP reductions were 25.8 (2.1)% 26.3 (0.8)% 24.2 (1.4)% 16.5 (1.7)% and -0.9 (1.5)% in WT, EP1KO, EP2KO, EP3KO and FPKO mice, respectively. IOP reductions in EP3KO and FPKO mice were significantly smaller than in WT mice. Pretreatment with diclofenac Na significantly attenuated the IOP lowering effect of tafluprost in WT mice but not in EP3KO mice. Bunazosin HCl lowered IOP significantly in all genotypes by the same amount.[3] This clinical study included 28 glaucoma patients (28 eyes) with a treatment history of latanoprost ophthalmic solution (Xalatan(®)) or travoprost ophthalmic solution (Travatan Z(®)), who presented with corneal epithelial disorders. The subjects were switched to BAK-reduced tafluprost, and its effect on the ocular surface was examined after 1 and 2 months of treatment [using fluorescein staining score, hyperemia, tear film breakup time, and intraocular pressure (IOP) lowering]. Results: In all analyzed subjects (N=27), the fluorescein staining score was significantly improved after switching to BAK-reduced tafluprost (P<0.0001). Conversely, the IOP-lowering effect was not notably changed. The subjects switched from latanoprost (n=10) showed significant improvement in fluorescein staining score (P<0.05) as well as in IOP lowering (P<0.01). The subjects switched from travoprost (n=17) also showed significant improvement in fluorescein staining score (P<0.001), but without a significant change in IOP lowering. Conclusions: Tafluprost with reduced BAK has potential as a superior antiglaucoma drug, not only for its IOP-lowering effect, but also for its good corneal safety profile.[4] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following instillation, tafluprost is absorbed through the cornea and is hydrolyzed to the biologically active acid metabolite, tafluprost acid. Tafluprost is an ester which makes the drug lipophillic enough to be quickly absorbed through. When administered to the eye, the peak plasma concentration (Cmax) and time to peak plasma concentration (Tmax) of tafluprost acid in healthy subjects was 26 pg/mL and 10 minutes respectively. a AUC, tafluprost acid = 394 pg*min/mL - 432 pg*min/mL. Mean plasma tafluprost acid concentrations were below the limit of quantification of the bioanalytical assay (10 pg/mL) at 30 minutes following topical ocular administration of tafluprost 0.0015% ophthalmic solution. In male rats, it was observed that tafluprost was excreted into the feces. The highest concentration of tafluprost acid was found in the cornea and conjunctiva. Metabolism / Metabolites Tafluprost is an ester prodrug which is rapidly hydrolyzed by corneal esterases to form its biologically active acid metabolite. Tafluprost acid is further metabolized via fatty acid β-oxidation and phase II conjugation into 1,2,3,4-tetranor acid. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of tafluprost during breastfeeding. Because of the extremely low levels in plasma after application to the eye, it is not likely to reach the breastmilk or bloodstream of the infant or to cause any adverse effects in breastfed infants. Professional guidelines consider prostaglandin eye drops acceptable during breastfeeding. To further diminish the amount of drug that reaches the breastmilk after using eye drops, place pressure over the tear duct by the corner of the eye for 1 minute or more, then remove the excess solution with an absorbent tissue. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
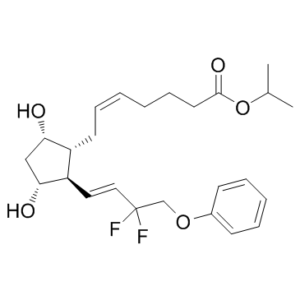
Tafluprost is a prostaglandin Falpha that is prostaglandin F2alpha in which the carboxylic acid function has been converted to the corresponding isopropyl ester and the 3-hydroxy-1-octenyl side-chain is substituted by 3,3-difluoro-4-phenoxybut-1-enyl. Used for treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. It has a role as a prostaglandin receptor agonist. It is a prostaglandins Falpha, an organofluorine compound and an isopropyl ester. It is functionally related to a prostaglandin F2alpha.
A prostaglandin analogue ester prodrug used topically (as eye drops) to control the progression of glaucoma and in the management of ocular hypertension. Chemically, tafluprost is a fluorinated analog of prostaglandin F2-alpha. Tafluprost was approved for use in the U.S. on February 10, 2012. Tafluprost is a Prostaglandin Analog. The mechanism of action of tafluprost is as a Prostaglandin Receptor Agonist. The physiologic effect of tafluprost is by means of Increased Prostaglandin Activity. Drug Indication Tafluprost is indicated for reducing elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. FDA Label Treatment of glaucoma Mechanism of Action Tafluprost acid is a prostanoid selective FP receptor agonist that is believed to reduce the intraocular pressure (IOP) by increasing the outflow of aqueous humor. Studies in animals and humans suggest that the main mechanism of action is increased uveoscleral outflow. This study investigated the intraocular pressure (IOP)-lowering effects and safety of tafluprost ophthalmic solution 0.0015% in actual clinical practice. Methods: We started a mandatory prospective 2-year observational study, which collected IOP, conjunctival hyperemia score, corneal staining score, and adverse event data from glaucoma and ocular hypertension (OH) patients not previously treated with tafluprost at 2, 12, and 24 months. This report analyzes the 2-month findings. Results: Of the 4,180 patients from 553 medical institutions in Japan, most patients had primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG, 38.1%) or normal-tension glaucoma (NTG, 44.2%). After 2 months of tafluprost administration, IOP was significantly reduced by 4.3 ± 5.2 mmHg in POAG, 2.4 ± 2.5 mmHg in NTG, 3.6 ± 5.3 mmHg in primary angle-closure glaucoma, 5.6 ± 7.1 mmHg in other types of glaucoma, and 5.3 ± 4.8 mmHg in OH. IOP was significantly reduced by 4.3 ± 4.0 mmHg in the naïve monotherapy group, 1.9 ± 3.5 mmHg in switching from prior treatment, and 3.7 ± 4.1 mmHg in the add-on therapy group. Among patients switched, the prostaglandin analog (PGA) latanoprost was the previous predominant drug (57.4%), followed by travoprost (13.8%). Significant IOP reductions were observed by 1.5 ± 3.4 mmHg in switching from latanoprost and 1.3 ± 3.7 mmHg in switching from travoprost. The conjunctival hyperemia score peaked at 1 month in the naïve monotherapy and add-on therapy groups, whereas it was significantly decreased in patients switched from another PGA. The corneal staining score showed no particular changes. Incidence of adverse drug reaction (ADR) was 7.70 % (322/4,180 patients), and all major ADRs involved the eyes or skin around the eyes. Conclusion: Tafluprost showed significant IOP-lowering effects without any safety concerns in patients with various types of glaucoma and OH in daily clinical practice and tafluprost is highly effective in any therapeutic patterns.[1] Background: To investigate whether tafluprost, which is a prostaglandin-related compound and an anti-glaucoma drug, has a direct anti-apoptotic effect in cultured retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) and rat RGCs in retinas with optic nerve crush (ONC). Methods: RGC-5 cells were induced to undergo apoptosis by a serum deprivation and by exogenous glutamate. The level of cell death with or without tafluprost was monitored by an XTT assay and by immunocytochemistry with activated caspase-3. Changes in intracellular calcium ([Ca(2+)]i) levels were measured with fluo-4 fluorescence. Rat RGCs were degenerated by ONC. After topical instillation of tafluprost for 7 and 14 days, the numbers of retrograde-labeled RGCs were counted. Retinal flatmounts were subjected to terminal dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining to detect apoptotic cells. Results: Tafluprost dose-dependently promoted RGC-5 cell viability with an optimum concentration of 3 microM (p = 0.006). Tafluprost significantly reduced caspase-3-positive cells and suppressed [Ca(+2)]i evoked by exogenous glutamate. The cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibitor and KT-5823 partially blocked the rescue effect of tafluprost (p = 0.002). The survival rate of RGCs significantly increased in eyes treated with tafluprost (p = 0.01), and the prevalence of TUNEL-positive cells was significantly decreased 14 days after ONC (p < 0.001). Conclusions: These data suggest that tafluprost has an anti-apoptotic effect in RGCs.[2] |
| 分子式 |
C25H34F2O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
452.5313
|
| 精确质量 |
452.237
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 66.35; H, 7.57; F, 8.40; O, 17.68
|
| CAS号 |
209860-87-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
209860-88-8 (Tafluprost acid); 157283-68-6 (Travoprost)
|
| PubChem CID |
9868491
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow liquid
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
552.9±50.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
288.2±30.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.549
|
| LogP |
4.23
|
| tPSA |
75.99
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
7
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
13
|
| 重原子数目 |
32
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
614
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
FC(C([H])([H])OC1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])(/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/[C@@]1([H])[C@@]([H])(C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])([C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C(=O)OC([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])O[H])F
|
| InChi Key |
WSNODXPBBALQOF-VEJSHDCNSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C25H34F2O5/c1-18(2)32-24(30)13-9-4-3-8-12-20-21(23(29)16-22(20)28)14-15-25(26,27)17-31-19-10-6-5-7-11-19/h3,5-8,10-11,14-15,18,20-23,28-29H,4,9,12-13,16-17H2,1-2H3/b8-3-,15-14+/t20-,21-,22+,23-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
propan-2-yl (Z)-7-[(1R,2R,3R,5S)-2-[(E)-3,3-difluoro-4-phenoxybut-1-enyl]-3,5-dihydroxycyclopentyl]hept-5-enoate
|
| 别名 |
AFP-168; MK2452; AFP-168; MK-2452; Tafluprost; 209860-87-7; Saflutan; 1O6WQ6T7G3; AFP-168; MK 2452; Saflutan; Taflotan; Tapros; Zioptan
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ≥ 270 mg/mL (~596.7 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.25 mg/mL (4.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 22.5 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.25 mg/mL (4.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 22.5 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.25 mg/mL (4.97 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2098 mL | 11.0490 mL | 22.0980 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4420 mL | 2.2098 mL | 4.4196 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2210 mL | 1.1049 mL | 2.2098 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05299593 | Recruiting | Drug: tafluprost/timolol | Glaucoma, Open-Angle Ocular Hypertension |
Fondazione G.B. Bietti, IRCCS | June 4, 2020 | Phase 4 |
| NCT04737928 | Completed | Drug: Latanoprost Drug: tafluprost |
Glaucoma, Primary Open Angle | Santen Pharmaceutical (Taiwan) Co., LTD |
April 2, 2018 | Not Applicable |
| NCT01369771 | Completed | Drug: Tafluprost 0.0015% | Ocular Hypertension Open-Angle Glaucoma |
FinnMedi Oy | August 2010 | Phase 4 |
| NCT03204487 | Completed | Drug: Tafluprost 15µg/ml | Glaucoma, Open-Angle Ocular Hypertension |
Ordination Dr. Hommer | May 10, 2016 | Phase 4 |
| NCT00918346 | Completed | Drug: Tafluprost 0.0015% | Open-Angle Glaucoma Ocular Hypertension |
Santen Oy | September 2005 | Phase 3 |
|
|