| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g | |||
| Other Sizes |

| 靶点 |
K/potassium channel; CYP2C9
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:甲苯磺丁脲属于一类称为磺酰脲类的药物。甲苯磺丁脲通过使胰腺产生胰岛素(一种分解体内糖所需的天然物质)并帮助身体有效利用胰岛素来降低血糖。这种药物只能帮助身体自然产生胰岛素的人降低血糖。甲苯磺丁脲不用于治疗 1 型糖尿病(身体不产生胰岛素,因此无法控制血液中的糖含量)或糖尿病酮症酸中毒(如果不治疗高血糖,可能会出现的严重病症) )。 Tolbutamide 抑制基础和环 AMP 刺激的蛋白激酶活性,Tolbutamide 的 IC50 为 4 mM。对于由激素(去甲肾上腺素和 ACTH)或二丁酰环 AMP 加茶碱诱导的体外脂肪分解的半最大抑制,需要类似的甲苯磺丁脲浓度。甲苯磺丁脲还抑制犬心脏的可溶性和膜结合蛋白激酶。甲苯磺丁脲对脂肪组织环 AMP 依赖性蛋白激酶的抑制是该药物抗脂肪分解作用的一种可能解释。 Tolbutamide 通过增加 Cx43 抑制 C6 神经胶质瘤细胞增殖,这与 Cdk 抑制剂 p21 和 p27 上调导致的 pRb 磷酸化减少相关。胞质核苷酸通过对抑制性和刺激性受体的联合作用,增强小鼠胰腺 B 细胞中 ATP 依赖性 K+ 通道对甲苯磺丁脲的敏感性。激酶测定:断头后获得喂养的 Wistar 大鼠(175-225 gm)的切块附睾脂肪垫,并在含有 1.27 mM CaCl2 的 Krebs-碳酸氢盐缓冲液中于 37°C 孵育两小时。添加后,甲苯磺丁脲仅在孵育期间存在。孵育后,在冷的克雷布斯碳酸氢盐缓冲液中冲洗脂肪垫并进行超声处理。在 4 °C 下以 50,000 × g 离心 30 分钟所得的水性上清液每毫升含有 0.75 至 1.25 毫克蛋白质,并测定了环 AMP 刺激的蛋白激酶活性。该测定在 0.2 mL 中进行,添加了 10 μmol 甘油磷酸钠 pH 7.0、2 μmol 氟化钠、0.4 μmol 茶碱、0.1 μmol 乙二醇双(β-氨基乙基醚)-N, N-四乙酸、3 μmol 氯化镁、0.3 mg 混合组蛋白、2 nmole (γ- 32P) ATP、1 nmole 环 AMP(指定时)和 0.05 ml 上清液。细胞测定:每次实验前,将 C6 神经胶质瘤细胞在无血清 DMEM 中于 37°C 孵育至少 24 小时。甲苯磺丁脲 (400 μM) 在无血清培养基中孵育 24 小时。孵化在 37 °C、95% 空气/5% CO2、90–95% 湿度的气氛中进行。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
450 mg Tolbutamide/kg/天,连续 7 天显着增加胰岛素与分离脂肪细胞的结合。结合曲线反映了受体位点数量的增加而不是亲和力的增加。这种效应与脂肪组织对胰岛素的反应增强有关,因为与对照组相比,用甲苯磺丁脲处理的动物的脂肪细胞在胰岛素存在下将更多的葡萄糖转化为脂质。然而,只有在大剂量甲苯磺丁脲时才能观察到胰岛素结合位点的增加,这降低了胰腺胰岛素含量、离体胰腺的分泌反应和血清胰岛素水平。较小的剂量足以通过刺激胰岛素分泌产生代谢作用,但不会提供额外的胰岛素结合位点
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
激酶测定:从喂食Wistar大鼠(175-225gm)中获得切碎的附睾脂肪垫,并在含有1.27mM CaCl2的Krebs碳酸氢盐缓冲液中在37°C下孵育两小时。添加时,甲磺丁脲仅在培养过程中存在。孵育后,将脂肪垫在冷的克雷布斯碳酸氢盐缓冲液中冲洗和超声处理。在4°C下以50000×g离心30分钟得到的含水上清液每毫升含有0.75至1.25 mg蛋白质,并检测环AMP刺激的蛋白激酶活性。在0.2 mL中加入10μmol pH 7.0的甘油磷酸钠、2μmol氟化钠、0.4μmol茶碱、0.1μmol乙二醇双(β-氨基乙基醚)-N,N-四乙酸、3μmol氯化镁、0.3 mg混合组蛋白、2 nmoles(γ-32P)ATP、1 nmoles环AMP(如有指示)和0.05 mL上清液进行测定。
|
||
| 细胞实验 |
在目前的研究中,研究人员表明,甲磺丁脲和dbcAMP增加了肿瘤抑制蛋白Cx43的合成,并降低了Ki-67的水平,Ki-67是细胞增殖时表达的一种蛋白质。这些效应伴随着pRb磷酸化的减少,主要是在Ser-795上,Ser-795是控制细胞增殖的关键残基。pRb磷酸化的减少不太可能是由D型细胞周期蛋白水平的降低介导的,因为用甲磺丁脲或dbcAMP治疗后,D1和D3的表达略有增加,而不是减少细胞周期蛋白的表达。然而,经甲磺丁脲和dbcAMP处理后,Cdk抑制剂p21和p27上调,表明它们可能参与了pRb磷酸化的减少。当Cx43被siRNA沉默时,根据Ki-67表达判断,甲磺丁脲和dbcAMP都不能上调p21,从而减少胶质瘤细胞增殖。总之,甲磺丁脲和dbcAMP通过增加Cx43抑制C6胶质瘤细胞增殖,这与Cdk抑制剂p21和p27上调导致的pRb磷酸化减少有关[2]。
|
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Readily absorbed following oral administration. Tolbutamide is detectable in plasma 30-60 minutes following oral administration of a single dose with peak plasma concentrations occurring within 3-5 hours. Absorption is unaltered if taken with food but is increased with high pH. Unchanged drug and metabolites are eliminated in the urine and feces. Approximately 75-85% of a single orally administered dose is excreted in the urine principally as the 1-butyl-3-p-carboxyphenylsulfonylurea within 24 hours. AFTER ORAL ADMIN, SULFONYLUREAS ARE RAPIDLY ABSORBED. /SULFONYLUREAS/ TOLBUTAMIDE CAN BE DETECTED IN BLOOD WITHIN 30 MIN AFTER ORAL ADMIN; PEAK CONCN ARE REACHED WITHIN 3 TO 5 HR. .../IT/ IS BOUND TO PLASMA PROTEINS. ... HALF-LIFE OF TOLBUTAMIDE IS ABOUT 5 HR. IN CONTRAST TO STUDIES REPORTED IN ANIMALS, METABOLIC CLEARANCE OF...TOLBUTAMIDE IN MAN HAS BEEN SHOWN TO BE UNALTERED BY FASTING. Excreted (percentage)...100 /from table/ Metabolism / Metabolites Metabolized in the liver principally via oxidation of the p-methyl group producing the carboxyl metabolite, 1-butyl-3-p-carboxyphenylsulfonylurea. May also be metabolized to hydroxytolbutamide. Tolbutamide does not undergo acetylation like antibacterial sulfonamides as it does not have a p-amino group. ...MAJOR TOLBUTAMIDE METAB IN MAN HAS BEEN IDENTIFIED AS 1-BUTYL-3-P-CARBOXYPHENYLSULFONYLUREA... 1-BUTYL-3-P-HYDROXYMETHYLPHENYLSULFONYLUREA IS ALSO FORMED IN SMALL AMT. IN RAT, MAJOR URINARY METAB, 1-BUTYL-3-P-HYDROXYMETHYLPHENYLSULFONYLUREA COMPRISED 75% OF DOSE, BUT SMALL AMT OF 1-BUTYL-3-P-CARBOXYPHENYLSULFONYLUREA & P-TOLYLSULFONYLUREA, COMPRISING 5% OF DOSE, WERE ALSO PRESENT. ALTHOUGH 1-BUTYL-3-P-HYDROXYMETHYLPHENYLSULFONYLUREA HAS BEEN REPORTED AS PRINCIPAL METAB IN CAT.../IT IS CLAIMED/ THAT CAT METABOLIZES TOLBUTAMIDE IN SAME WAY AS DOG. .../IT HAS BEEN SHOWN/ THAT TOLBUTAMIDE IS TRANSFORMED INTO 1-BUTYL-3-P-CARBOXYPHENYLSULFONYLUREA IN GUINEA PIGS & RABBITS. IN CONTRAST TO RATS, RABBITS & MAN, DOGS METABOLIZE TOLBUTAMIDE...INTO P-TOLYLSULFONYLUREA & P-TOLYLSULFONAMIDE BY MECHANISM INVOLVING HYDROLYSIS. For more Metabolism/Metabolites (Complete) data for TOLBUTAMIDE (7 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Tolbutamide has known human metabolites that include 4-Hydroxytolbutamide. Biological Half-Life Approximately 7 hours with interindividual variations ranging from 4-25 hours. Tolbutamide has the shortest duration of action, 6-12 hours, of the antidiabetic sulfonylureas. Half-life...3-25 /hours/ /from table/ |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Tolbutamide is no longer marketed in the United States. It is excreted into breastmilk in small amounts that should cause no harm to the breastfed infant. Monitor breastfed infants for signs of hypoglycemia such as jitteriness, excessive sleepiness, poor feeding, seizures cyanosis, apnea, or hypothermia. If there is concern, monitoring of the breastfed infant's blood glucose is advisable during maternal therapy with hypoglycemic agents. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Approximately 95% bound to plasma proteins. Interactions SULFAPHENAZOLE ENHANCES ACTION OF TOLBUTAMIDE & MAY CAUSE SYMPTOMS OF SEVERE HYPOGLYCEMIA IN DIABETIC PT. IT IS UNCLEAR WHETHER THIS INTERACTION ALSO OCCURS WITH OTHER SULFONAMIDES OR SULFONYLUREA COMPD. HYPOGLYCEMIC ACTIVITY OF TOLBUTAMIDE MAY BE ENHANCED BY CONCURRENT ADMIN OF PHENYLBUTAZONE, & DOWNWARD ADJUSTMENT OF TOLBUTAMIDE DOSAGE MAY BE INDICATED. ... ALTHOUGH NOT DOCUMENTED, OXYPHENBUTAZONE & POSSIBLY SULFINPYRAZONE CAN BE EXPECTED TO INTERACT SIMILARLY TO PHENYLBUTAZONE. SINCE MAO INHIBITORS MAY ENHANCE HYPOGLYCEMIC ACTION OF INSULIN IN ANIMALS & IN HUMAN DIABETIC PT, CONCURRENT ADMIN OF MAO INHIBITORS & INSULIN TO DIABETIC SUBJECTS MAY BE POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS. .../TOLBUTAMIDE HAS/ BEEN REPORTED TO INTERACT WITH MAO INHIBITORS. DICUMAROL INCR SERUM HALF-LIFE OF TOLBUTAMIDE & MAY CAUSE SYMPTOMS OF HYPOGLYCEMIA. THIS EFFECT USUALLY OCCURS 3-4 DAYS AFTER INITIATING DICUMAROL THERAPY. ...PHENPROCOUMON INTERACTS WITH TOLBUTAMIDE IN ANIMALS. ...TOLBUTAMIDE DISPLACES WARFARIN FROM PROTEIN BINDING SITES IN VITRO. For more Interactions (Complete) data for TOLBUTAMIDE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
||
| 参考文献 |
[1]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.1973 Jul 2;53(1):291-4;
[2]. Glia.2006 Aug 1;54(2):125-34. [3]. Diabetologia, 1993, 36: 487-492. [4]. Teratology, 1976, 13(1): 65-70. |
||
| 其他信息 |
Tolbutamide appears as white crystals. (NTP, 1992)
Tolbutamide is an N-sulfonylurea that consists of 1-butylurea having a tosyl group attached at the 3-position. It has a role as a hypoglycemic agent, a potassium channel blocker, a human metabolite and an insulin secretagogue. Tolbutamide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It is structurally similar to acetohexamide, chlorpropamide and tolazamide and belongs to the sulfonylurea class of insulin secretagogues, which act by stimulating β cells of the pancreas to release insulin. Sulfonylureas increase both basal insulin secretion and meal-stimulated insulin release. Medications in this class differ in their dose, rate of absorption, duration of action, route of elimination and binding site on their target pancreatic β cell receptor. Sulfonylureas also increase peripheral glucose utilization, decrease hepatic gluconeogenesis and may increase the number and sensitivity of insulin receptors. Sulfonylureas are associated with weight gain, though less so than insulin. Due to their mechanism of action, sulfonylureas may cause hypoglycemia and require consistent food intake to decrease this risk. The risk of hypoglycemia is increased in elderly, debilitated and malnourished individuals. Tolbutamide appears to be metabolized in the liver. Tolbutamide and its metabolites are excreted in urine (75-85%) and feces. Tolbutamide is a Sulfonylurea. Tolbutamide has been reported in Homo sapiens with data available. Tolbutamide is a short-acting, first-generation sulfonylurea with hypoglycemic activity. Compared to second-generation sulfonylureas, tolbutamide is more likely to cause adverse effects, such as jaundice. This agent is rapidly metabolized by CYPC29. A sulphonylurea hypoglycemic agent with actions and uses similar to those of CHLORPROPAMIDE. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p290) See also: Tolbutamide Sodium (has salt form). Drug Indication For treatment of NIDDM (non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus) in conjunction with diet and exercise. Mechanism of Action Sulfonylureas lower blood glucose in patients with NIDDM by directly stimulating the acute release of insulin from functioning beta cells of pancreatic islet tissue by an unknown process that involves a sulfonylurea receptor (receptor 1) on the beta cell. Sulfonylureas inhibit the ATP-potassium channels on the beta cell membrane and potassium efflux, which results in depolarization and calcium influx, calcium-calmodulin binding, kinase activation, and release of insulin-containing granules by exocytosis, an effect similar to that of glucose. SULFONYLUREAS STIMULATE ISLET TISSUE TO SECRETE INSULIN. ... SULFONYLUREAS CAUSE DEGRANULATION OF BETA CELLS, A PHENOMENON ASSOC WITH INCR RATE OF SECRETION OF INSULIN. /SULFONYLUREAS/ ALTHOUGH MOLECULAR MECHANISM...NOT UNDERSTOOD, SEVERAL PERTINENT OBSERVATIONS HAVE BEEN MADE. ...TOLBUTAMIDE IS RESTRICTED IN ITS ACTION TO EXTRACELLULAR SPACE & DOES NOT NEED TO ENTER BETA CELL. INVOKED RELEASE OF INSULIN IS IMMEDIATE & INTIMATELY RELATED TO ACTION OF GLUCOSE...MAY SENSITIZE CELL TO NORMAL SECRETAGOGUE. Sulfonylureas are now...thought to act by a number of different mechanisms. 1. ...produce a depolarization of the pancreatic islet beta cell membrane potassium ion permeability. This results in a release of preformed insulin into the circulation and occurs mostly in non-insulin dependent diabetics. 2. ...reduce basal glucose output from the liver... 3. increase insulin receptor binding... 4. ...increasing intracellular levels of AMP... 5. increase insulin secretion by suppressing the release of glucagon and somatostatin from alpha and delta pancreatic cells. /Sulfonylureas/ Therapeutic Uses Hypoglycemic Agents IT IS USEFUL IN TREATMENT OF SELECTED CASES OF DIABETES MELLITUS, NAMELY MILD UNCOMPLICATED, STABLE DIABETES OF ADULT ONSET & WHICH CANNOT BE CONTROLLED BY DIET ALONE. ... IN DIABETIC PT PEAK EFFECT IS REACHED IN 5 TO 8 HR. DURATION OF ACTION IS USUALLY LESS THAN 24 HR... THERE IS NO FIXED DOSAGE OF SULFONYLUREA TO BE USED IN DIABETES MELLITUS. TREATMENT IS GUIDED BY INDIVIDUAL PATIENT'S RESPONSE... /SULFONYLUREAS/ ...REPORTS HAVE APPEARED OF SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT OF REACTIVE HYPOGLYCEMIAS DUE TO A VARIETY OF CAUSES WITH SULFONYLUREAS. /SULFONYLUREAS/ VET: OCCASIONAL, AS AN ORAL HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENT FOR DOGS. Drug Warnings TOXIC EFFECTS OF TOLBUTAMIDE INCL GI UPSET, WEAKNESS, HEADACHE, TINNITUS, PARESTHESIAS, ALLERGIC REACTIONS (PRURITUS, ERYTHEMA MULTIFORME, MACULOPAPULAR RASH, ALL USUALLY TRANSIENT)...CHOLESTATIC JAUNDICE MAY OCCUR (RARELY)... RARE LEUKOPENIA, THROMBOCYTOPENIA, PANCYTOPENIA & AGRANULOCYTOSIS OCCUR. Despite this relative lack of teratogenicity, tolbutamide should be avoided in pregnancy since the drug will not provide good control in patients who cannot be controlled by diet alone. SULFONYLUREAS SHOULD NOT BE USED IN PT WITH HEPATIC OR RENAL INSUFFICIENCY BECAUSE OF IMPORTANT ROLE OF LIVER IN THEIR METAB & OF KIDNEY IN EXCRETION OF DRUG & THEIR METABOLITES. ... THESE AGENTS ARE ALSO NOT RECOMMENDED FOR USE IN PREGNANCY... /SULFONYLUREAS/ Maternal Medication Usually Compatible with Breast-Feeding: Tolbutamide: Possible jaundice. /from Table 6/ For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for TOLBUTAMIDE (16 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Tolbutamide, a first-generation sulfonylurea antidiabetic agent, is used with diet to lower blood glucose levels in patients with diabetes mellitus type II. Tolbutamide is twice as potent as the related second-generation agent glipizide. Tolbutamide lowers blood sugar by stimulating the pancreas to secrete insulin and helping the body use insulin efficiently. The pancreas must be able to produce insulin for this drug to work. |
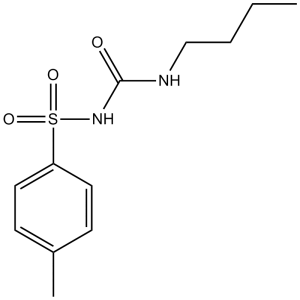
| 分子式 |
C12H18N2O3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
270.35
|
| 精确质量 |
270.103
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.31; H, 6.71; N, 10.36; O, 17.75; S, 11.86
|
| CAS号 |
64-77-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Tolbutamide-d9;1219794-57-6;Tolbutamide sodium;473-41-6;Tolbutamide-13C
|
| PubChem CID |
5505
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
430.0±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
128-130°C
|
| 闪点 |
213.9±26.8 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.557
|
| LogP |
2.93
|
| tPSA |
83.65
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
18
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
354
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| InChi Key |
JLRGJRBPOGGCBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H18N2O3S/c1-3-4-9-13-12(15)14-18(16,17)11-7-5-10(2)6-8-11/h5-8H,3-4,9H2,1-2H3,(H2,13,14,15)
|
| 化学名 |
1-butyl-3-(4-methylphenyl)sulfonylurea
|
| 别名 |
olbutamide, Orinase; Arkozal; Willbutamide; Butamide; Diabetamid; Ipoglicone; trade names: Artosin, Diabetol, Orinase, HLS 831, HLS831, HLS-831
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.69 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.6989 mL | 18.4945 mL | 36.9891 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7398 mL | 3.6989 mL | 7.3978 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3699 mL | 1.8495 mL | 3.6989 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05097716 | Completed Has Results |
Drug: Ritlecitinib Drug: Tolbutamide |
Healthy Volunteers | Pfizer | November 2, 2021 | Phase 1 |
| NCT01185548 | Terminated Has Results |
Drug: Tolbutamide Drug: Tasisulam |
Lymphoma Advanced Cancer |
Eli Lilly and Company | July 2010 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03291288 | Completed Has Results |
Drug: Tolbutamide Drug: Midazolam |
Drug Interaction Potential | Daiichi Sankyo | February 26, 2018 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03716427 | Completed | Drug: CT1812 Drug: tolbutamide |
Healthy Volunteers | Cognition Therapeutics | November 10, 2016 | Phase 1 |