| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
MEK1 (IC50 = 0.92 nM); MEK2 (IC50 = 1.8 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
GSK1120212 的 IC50 范围为 0.92 nM 至 3.4 nM,无论 Raf 和 MEK 的同种型如何,都会抑制 MBP 的磷酸化。 c-Raf、B-Raf、ERK1 和 ERK2 不受 GSK1120212 激酶活性的抑制。此外,GSK1120212 并未显着抑制其他 98 种激酶。 GSK1120212 能有效抑制人结直肠癌细胞系。对 GSK1120212 敏感性最高的细胞的 IC50 值分别为 0.48 nM 和 0.52 nM,并且已知在 HT-29 和 COLO205 中具有组成型活性 B-Raf 突变体。具有 K-Ras 突变的细胞系的 IC50 范围为 2.2–174 nM,对 GSK1120212 表现出广泛的敏感性。 B-Raf 和 K-Ras 中的野生型基因均存在于 COLO320 DM 细胞中,即使在 10 μM 浓度下,该细胞也能抵抗 GSK1120212。所有敏感细胞系在用 GSK1120212 处理 24 小时后都会经历细胞周期停滞在 G1 期。在大多数结直肠癌细胞系中,GSK1120212 治疗后 p15INK4b 和/或 p27KIP1 持续上调。 GSK1120212 的 ERK 磷酸化在所有易感细胞系中均受到抑制。 HT-29 和 COLO205 细胞均经历 GSK1120212 诱导细胞凋亡;然而,COLO205 细胞比 HT-29 细胞更容易受到这种诱导。 [1] 外周血单核细胞 (PBMC) 不能产生肿瘤坏死因子或白细胞介素 6,因为 GSK1120212 抑制此过程。 [2]
曲美替尼/JTP-74057可抑制LPS诱导的ERK1/2磷酸化和促炎细胞因子的产生[2] JTP-74057是一种强效的MEK1/2抑制剂,特异性抑制MEK1/2,IC50值约为2nM。众所周知,LPS通过COT/Tpl2-MEK1/2途径诱导单核细胞中ERK1/2磷酸化,因此我们检测了JTP-74057对LPS刺激的人、小鼠或大鼠PBMC中ERK1/2磷酸化的抑制活性。ERK1/2磷酸化在LPS刺激后30分钟内迅速磷酸化,在所有物种中,10 nM的JTP-74057完全抑制了ERK1/2的磷酸化,表明该化合物的抑制活性没有物种差异(图1)。使用来自不同供体的人PBMCs以及在小鼠和大鼠PBMCs的重复实验中获得了相同的结果(数据未显示)。由于在RA患者的滑膜组织中已经报道了MEK-ERK通路的激活,并且这种激活导致TNF-α和IL-6等促炎细胞因子的产生,我们接下来研究了MEK1/2抑制剂对LPS刺激的hPBMCs产生细胞因子的影响。如图2所示,与MEK1/2的抑制活性一致,10 nM的JTP-74057抑制TNF-α的产生约为对照的10%。IL-6的产生也受到抑制;然而,即使在100nM的化合物下,最大抑制作用也约为对照的50%,这意味着除了MEK-ERK途径外,可能还有其他途径可以激活IL-6的产生。 曲美替尼/JTP-74057和来氟米特对抗CII抗体产生和CII反应性T细胞再激活的差异作用[2] 为了研究MEK1/2抑制是否影响自身抗体的产生,在第35天通过ELISA测定血清中的抗CII IgG。来氟米特以剂量依赖的方式抑制抗CII IgG的升高。另一方面,即使在最高剂量下,JTP-74057也不影响抗CII IgG的产生(图6a),这表明MEK1/2在自身抗体的产生中不起作用。接下来,我们研究了MEK1/2抑制剂对CIA小鼠抗原特异性记忆T细胞再激活的影响。在第二次CII免疫接种后5天,从用CIA进行非药物治疗的小鼠中收集淋巴结细胞,然后在有或没有试验药物的情况下,用热降解的II型胶原在体外重新刺激。两天后,通过[3H]胸苷掺入评估LN细胞的增殖。JTP-74057在CII刺激下抑制了LN细胞的增殖(图6b),这意味着MEK1/2抑制剂对CIA发育的抑制作用至少部分是由于阻断了抗原特异性记忆T细胞的再激活。来氟米特的活性代谢产物A77 1726对LN细胞的增殖影响很小(图6b)。这些结果清楚地表明,MEK抑制剂与来氟米特具有不同的疾病改善活性。 |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
当每天口服一次 0.3 mg/kg 或 1 mg/kg 剂量的 GSK1120212,连续 14 天时,可以有效阻止 HT-29 异种移植物的生长。剂量为 1 mg/kg 时,肿瘤生长几乎完全停止。单次口服剂量1 mg/kg GSK1120212完全抑制已形成肿瘤组织中ERK1/2的磷酸化,治疗14天后,蛋白p15INK4b和p27KIP1的水平均升高。即使剂量为 0.3 mg/kg,COLO205 异种移植模型中也可以看到肿瘤消退。接受 1 mg/kg 剂量的六只小鼠中,有四只经历了完全消退,其中肿瘤已消退到不再可检测到其体积的程度。 [1] Lewis 大鼠或 DBA1/J 小鼠的佐剂诱导性关节炎 (AIA) 和 II 型胶原诱导性关节炎 (CIA) 在给予 0.1 mg/kg 的 GSK1120212 后几乎完全被抑制。 [2]
JTP-74057/曲美替尼对大鼠佐剂性关节炎模型的影响[2] 为了证实MEK1/2抑制剂对炎性关节炎发展的药理作用,我们首先采用了大鼠佐剂诱导性关节炎(AIA)模型,该模型被广泛用作RA的模型。在第0天,雄性Lewis大鼠在尾部底部皮内注射含有佐剂的结核分枝杆菌,然后监测后爪的体积。在第21天,对后爪的关节破坏进行了放射学评估。从第0天开始每天口服一次JTP-74057。来氟米特被用作参考药物。如图3所示,曲美替尼/JTP-74057以剂量依赖的方式显著阻断了后爪肿胀,0.1 mg/kg的JTP-74057显示出与10 mg/kg的来氟米特相当的疗效。AIA大鼠在关节炎发展过程中体重减轻,而JTP-74057和来氟米特都抑制了这种体重减轻(数据未显示)。在肉眼观察中,0.1 mg/kg的JTP-74057或10 mg/kg的来氟米特均未发现不良事件的迹象;特别是用0.1mg/kg JTP-74057治疗的大鼠的肝损伤标志物(AST、ALT)或肾损伤标志物的肌酐没有显著变化(数据未显示)。大鼠JTP-74057的最大耐受剂量(MTD)被确认为0.3mg/kg(数据未显示)。在后爪的放射学评估中,在第21天,在受AIA影响的大鼠中检测到骨侵蚀和破坏,尤其是跗骨和踝骨(图4b)。JTP-74057防止了后爪的骨侵蚀和破坏(图4c),表明MEK抑制剂对AIA大鼠既有抗炎作用,也有骨保护作用。 JTP-74057/曲美替尼给药可改善小鼠胶原诱导性关节炎模型中的足肿胀[2] 为了进一步比较曲美替尼/JTP-74057与来氟米特的药理作用,我们在另一种广泛使用的RA模型——小鼠胶原诱导的关节炎模型中测试了这些化合物。在第0天和第21天,将用弗氏完全佐剂乳化的CII皮内注射到DBA1/J小鼠的尾基。在第二次免疫接种后,定期对爪子肿胀进行评分。从第21天至第35天,每天口服一次JTP-74057或来氟米特。如图5a所示,JTP-74057以剂量依赖的方式抑制关节炎的发展,0.3 mg/kg的JTP-74057完全抑制了临床评分的恶化。来氟米特也抑制了关节炎的发展,但即使在10mg/kg的剂量下也没有完全抑制它(图5b)。据报道,JTP-74057在小鼠体内的MTD为3mg/kg。与此一致,在接受0.3mg/kg JTP-74057治疗的组中,没有出现AST升高或体重减轻等不良反应的迹象(数据未显示)。 |
| 酶活实验 |
B-Raf/c-Raf、非磷酸化 MEK1/MEK2 和 EERRK2 以及非磷酸化髓磷脂碱性蛋白 (MBP) 的活性形式在存在以下物质的情况下与含有 12.5 mM MgCl2 和 10 μM ATP 的 MOPS 缓冲液混合不同浓度的 GSK1120212。抗磷酸化MBP抗体可以识别已磷酸化的MBP。
|
| 细胞实验 |
在 96 孔组织培养板中,将指数生长的细胞预培养 24 小时,然后暴露于 GSK1120212。基于磺胺罗丹明 B 的体外毒理学检测试剂盒可测量细胞生长。收集贴壁细胞和漂浮细胞用于细胞凋亡测定并用 70% 乙醇固定。然后用 PBS 洗涤细胞,悬浮在 100 μg/mL RNase 和 25 μg/mL 碘化丙啶 (PI) 中,并在黑暗中加热至 37°C 30 分钟。 Cytomics FC500 或 Guava EasyCyte plus 流式细胞仪用于测量每个细胞的 DNA 含量。
PBMC在添加了10%热灭活胎牛血清(HI-FBS)的RPMI1640中培养,然后在有或没有不同浓度的曲美替尼/JTP-74057的情况下用LPS(人,1μg/ml;小鼠和大鼠,10μg/ml)激活。对于蛋白质印迹分析,在刺激后30分钟裂解细胞,并如前所述通过蛋白质印迹分析ERK1/2的磷酸化。为了分析细胞因子的产生,在刺激过夜后收集细胞上清液,并通过ELISA测定TNF-α和IL-6的浓度。[2] Affymetrix表达分析[3] 在单独用GSK2118436和曲美替尼/GSK1120212复合处理24小时后,选择16R6-4与A375进行比较。数据分析按照补充方法中的描述进行。微阵列数据保存在NCBI的基因表达综合数据库(GEO,http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/)可通过GEO系列登录号GSE35230访问。 细胞生长试验[4] 将细胞(2.5 E4)铺在96孔板中,并在第二天用浓度递增的药物或等摩尔二甲亚砜(DMSO)处理三次。72小时后,根据制造商的说明,通过荧光光度法,使用Cell Titer Blue Assay测定每种处理相对于单独DMSO处理的氧化还原染料转化率。等摩尔浓度的DMSO载体对所有细胞系的细胞活力没有显著影响。 流式细胞术[4] 对于细胞周期分析,收集培养上清液,并与通过短暂胰蛋白酶处理去除的培养细胞合并。用PBS洗涤细胞两次,并用70%乙醇固定。细胞在-20°C下储存过夜。然后用PBS洗涤细胞两次,在RNA酶A 100ug/mL和20ug/mL碘化丙啶中复溶,并在分析前储存在4°C下。对于凋亡测量,类似地收集细胞,用膜联蛋白V对洗涤后的细胞进行染色,洗涤一次,然后重新悬浮在20 ug/mL碘化丙啶中。在FACs Canto上分析细胞,并使用FlowJo分析数据。细胞指数被确定为S/G2/M期细胞的百分比,与未处理的基线培养物标准化。使用Graphpad Prism将三次重复实验的平均值与重复测量的单因素方差分析和Bonferroni多重比较检验进行比较。显著性表示在95%的置信区间内,p值小于0.05。 |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: The mice used are BALB/c-nu/nu females. HT-29 cells or COLO205 cells suspended in ice-cold HBSS (-) are subcutaneously injected into the right flank of the mice on day 0 at a density of 5×106 cells/100 µL/site or 1×106 cells per 100 µL, respectively. When the mean tumor volume reaches 100 mm3, the acetic acid-solvated form of Trametinib (JTP-74057, 0.3 mg/kg, or 1 mg/kg) is dissolved in 10% Cremophor EL-10% PEG400 and given orally once daily for 14 days. Two weeks after the start of dosing, the tumor's length [L(mm)] and width [W(mm)] are measured using a microgauge, and the tumor's volume is calculated using the formula tumor volume (mm3)=L×W×W/2.
Rat adjuvant-induced arthritis [2] Arthritis was induced by intradermal injection of 0.5 mg of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in 100 μl of paraffin oil into the tail base of male Lewis rats aged 6 weeks (day 0). Normal, untreated rats were used as a control group. Trametinib DMSO solvate and leflunomide were ground and suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose to a volume of 5 ml/kg. On day 0, rats were randomized into 6 groups (6 rats per group) based on body weight. Test drugs were given orally once daily from day 0 to day 21. After arthritis induction, hind paw volume was measured on days 6, 13, 16, and 21 by a water displacement method, using a plethysmometer for rats. Radiographs of both hindlimbs were taken using an X-ray unit on day 21. Collagen-induced arthritis [2] Bovine type II collagen (CII) was dissolved in 0.01 M acetic acid at a concentration of 2 mg/ml and then emulsified in an equal volume of Freund’s complete adjuvant H37Ra. Six-week-old male DBA/1J mice were immunized with 100 μl of the CII emulsion by intradermal injection at the tail base. After 21 days, the mice were randomized into 7 groups (16 mice per group) based on body weight. The mice received the same amount of the CII emulsion to induce arthritis. Trametinib acetic acid solvate was dissolved in 10% Cremophor EL/10% polyethylene glycol 400 solution to a volume of 10 ml/kg. Leflunomide was ground and suspended in 0.5% MC to a volume of 10 ml/kg. Test drug or vehicle was given orally once daily from day 21 to day 35. The clinical score of arthritis was obtained by summing the visual severity grade of each limb, in which swelling of digit and entire paw was scored as follows (maximum score for each limb was 4): for the swelling of digits (0, no swelling; 1, one swollen digit; 2, two or more swollen digits), for the swelling of entire paw (0, no swelling; 1, mild swelling; 2, severe swelling of the entire paw). The score was obtained in a blind manner. Arthritis scores of individual mice were represented as an average score of 4 limbs. CII-specific antibody in sera was measured by a sandwich ELISA method on day 35. Five hundred nanograms of CII were dissolved in 100 μl of PBS, added into 96-well EIA plates, and incubated at 4°C overnight. After washing the excess CII, the plates were blocked with Block Ace for 1 h. Serum from the CIA mice was diluted and added into the plates. After 2 h incubation at RT, the plates were washed, and then the CII-specific antibodies were detected with peroxidase-labeled anti-mouse immunoglobulin (Ig) G antibody. Proliferation of lymph node cells from CIA mice [2] Inguinal lymph node (LN) cells were collected from non-drug-treated CIA mice at 5 days after the second immunization and cultured in a 96-well culture plate at a concentration of 5 × 105 cells/well in RPMI1640 medium containing penicillin–streptomycin, 2-mercaptoethanol, and 10% HI-FBS. CII solution was added to the cells at a final concentration of 10 μg/ml in the presence or absence of test compound, Trametinib or A77 1726. After incubation at 37°C, 5% CO2 for 42 h, 0.5 μCi of [3H]thymidine was added to each well and cultured for 6 h. Incorporated radioactivity was measured using a TopCount microplate scintillation counter. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following oral administration, trametinib is rapidly and readily absorbed. The absorption was examined in patients with solid tumours and BRAF V600 mutation-positive metastatic melanoma. Following the administration of trametinib tablets 0.125 mg (0.0625 times the approved recommended adult dosage) to 4 mg (2 times the approved recommended adult dosage) daily, both Cmax and AUC increased dose-proportionally. Intersubject variability in AUC and Cmax at steady state is 22% and 28%, respectively. Trametinib accumulates with daily repeat dosing with a mean accumulation ratio of 6.0 at 2 mg once daily dose. Steady-state was achieved by Day 15. The mean absolute bioavailability of trametinib is 72% for oral tablets and 81% for oral solution. The Tmax is 1.5 hours. A high-fat, high-calorie meal (approximately 1000 calories) decreased trametinib AUC by 24% and Cmax by 70%, and delayed Tmax by approximately four hours as compared with fasted conditions. Following oral administration of [14C]-trametinib, greater than 80% of excreted radioactivity was recovered in the feces while less than 20% of excreted radioactivity was recovered in the urine with less than 0.1% of the excreted dose as the parent molecule. The apparent volume of distribution (Vc/F) is 214 L. The apparent clearance is 4.9 L/h. Metabolism / Metabolites Trametinib predominantly undergoes deacetylation mediated by carboxylesterases (i.e., carboxylesterase 1b/c and 2) and other hydrolytic enzymes. The deacetylated metabolite may further be glucuronidated. _In vitro_ findings suggest that deacetylation may also be accompanied by mono-oxygenation, hydroxylation, and glucuronidation. CYP3A4-mediated oxidation is a minor pathway. Four metabolites (M1/2/3/4) have been characterized in patients with advanced cancers. _In vitro_, the M1 and M3 metabolites demonstrated approximately equal or 10-fold less potent phospho-MEK1-inhibiting activity than the parent compound. Following a single dose of [14C]-trametinib, approximately 50% of circulating radioactivity represented the parent compound. According to findings from metabolite profiling after repeat dosing of trametinib, unchanged parent drug accounted for greater than or equal to 75% of drug-related material in plasma. Biological Half-Life The estimated elimination half-life is 3.9 to 4.8 days. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In large clinical trials, abnormalities in routine liver tests were common with serum aminotransferase elevations occurring in 39% to 60% and alkaline phosphatase in 24% to 67% of patients treated with trametinib. However, elevations in ALT above 5 times the ULN were uncommon, occurring in 0% to 5% of patients and generally resolving rapidly with temporary discontinuation or dose adjustment. In the prelicensure controlled trials of trametinib with or without dabrafenib, no cases of clinically apparent acute liver injury or hepatic failure were reported. There have yet to be published cases of clinically apparent hepatotoxicity attributed to trametinib. However, it has been used for a short time only. Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of trametinib during breastfeeding. Because trametinib is 97% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is 3.9 to 4.8 days and it might accumulate in the infant. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during trametinib therapy and for 4 months after the last dose. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Trametinib is 97.4% bound to human plasma proteins. |
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Trametinib inhibits cell growth of various BRAF V600 mutation-positive tumours _in vitro_ and _in vivo_. Trametinib is often used in combination with dabrafenib, a BRAF inhibitor. In BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer, induction of EGFR-mediated MAPK pathway re-activation has been identified as a mechanism of intrinsic resistance to BRAF inhibitors. The MAPK pathway is one of the most important pathways for novel anticancer drug development. We performed high-throughput screening for compounds that induce expression of p15INK4b, and identified JTP-74057 (GSK1120212), which is being evaluated in ongoing phase I, II and III clinical trials. We characterized its antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo. JTP-74057 strongly inhibited MEK1/2 kinase activities, but did not inhibit another 98 kinase activities. Treatment by JTP-74057 resulted in growth inhibition accompanied with upregulation of p15INK4b and/or p27KIP1 in most of the colorectal cancer cell lines tested. Daily oral administration of JTP-74057 for 14 days suppressed tumor growth of HT-29 and COLO205 xenografts in nude mice. Notably, tumor regression was observed only in COLO205 xenografts, and COLO205 was much more sensitive to JTP-74057-induced apoptosis than HT-29 in vitro. Treatment with an Akt inhibitor enhanced the JTP-74057-induced apoptosis in HT-29 cells. Finally, JTP-74057 exhibited an additive or a synergistic effect in combination with the standard-of-care agents, 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin or SN-38. JTP-74057, a highly specific and potent MEK1/2 inhibitor, exerts favorable antitumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Sensitivity to JTP-74057-induced apoptosis may be an important factor for the estimation of in vivo efficacy, and sensitivity was enhanced by an Akt inhibitor. These results suggest the usefulness of JTP-74057 in therapeutic applications for colorectal cancer patients.[1] Objective and design: To examine the effects of a mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase 1/2-inhibitor, JTP-74057, on inflammatory arthritis development, and compare its anti-arthritic effect with leflunomide. Materials: Human, mouse, and rat peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were used. Lewis rats and DBA/1J mice were used for animal models. Treatment: JTP-74057 was tested between 0.1-100 nM in in-vitro studies. JTP-74057 (0.01-0.3 mg/kg) and leflunomide (2-10 mg/kg) were administered orally in vivo. Methods: PBMCs were stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. Adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA) and type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) was induced in Lewis rats or DBA1/J mice, respectively. Results: JTP-74057 blocked tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6 production from PBMCs. AIA and CIA development were suppressed almost completely by 0.1 mg/kg of JTP-74057 or 10 mg/kg of leflunomide. In the CIA, JTP-74057, but not leflunomide, suppressed collagen-reactive T-cell proliferation ex vivo, whereas leflunomide, but not JTP-74057, suppressed anti-collagen antibody production. Conclusions: JTP-74057 exerts potent anti-arthritic effects with a different profile from leflunomide, suggesting that JTP-74057 may be useful as a new therapeutic reagent in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.[2] Recent results from clinical trials with the BRAF inhibitors GSK2118436 (dabrafenib) and PLX4032 (vemurafenib) have shown encouraging response rates; however, the duration of response has been limited. To identify determinants of acquired resistance to GSK2118436 and strategies to overcome the resistance, we isolated GSK2118436 drug-resistant clones from the A375 BRAF(V600E) and the YUSIT1 BRAF(V600K) melanoma cell lines. These clones also showed reduced sensitivity to the allosteric mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MEK) inhibitor GSK1120212 (trametinib). Genetic characterization of these clones identified an in-frame deletion in MEK1 (MEK1(K59del)) or NRAS mutation (NRAS(Q61K) and/or NRAS(A146T)) with and without MEK1(P387S) in the BRAF(V600E) background and NRAS(Q61K) in the BRAF(V600K) background. Stable knockdown of NRAS with short hairpin RNA partially restored GSK2118436 sensitivity in mutant NRAS clones, whereas expression of NRAS(Q61K) or NRAS(A146T) in the A375 parental cells decreased sensitivity to GSK2118436. Similarly, expression of MEK1(K59del), but not MEK1(P387S), decreased sensitivity of A375 cells to GSK2118436. The combination of GSK2118436 and GSK1120212 effectively inhibited cell growth, decreased ERK phosphorylation, decreased cyclin D1 protein, and increased p27(kip1) protein in the resistant clones. Moreover, the combination of GSK2118436 or GSK1120212 with the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/mTOR inhibitor GSK2126458 enhanced cell growth inhibition and decreased S6 ribosomal protein phosphorylation in these clones. Our results show that NRAS and/or MEK mutations contribute to BRAF inhibitor resistance in vitro, and the combination of GSK2118436 and GSK1120212 overcomes this resistance. In addition, these resistant clones respond to the combination of GSK2126458 with GSK2118436 or GSK1120212. Clinical trials are ongoing or planned to test these combinations.[3] |
| 分子式 |
C26H23FIN5O4
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
615.39
|
| 精确质量 |
615.077
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 50.74; H, 3.77; F, 3.09; I, 20.62; N, 11.38; O, 10.40
|
| CAS号 |
871700-17-3
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Trametinib (DMSO solvate);1187431-43-1;Trametinib-d4;Trametinib-13C6;Trametinib-13C,d3;2712126-59-3
|
| PubChem CID |
11707110
|
| 外观&性状 |
white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.7±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.734
|
| LogP |
2.68
|
| tPSA |
110.62
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
| 重原子数目 |
37
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1090
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O=C(C)NC1C=C(N2C3C(=C(N(C)C(C=3C)=O)NC3C(F)=CC(I)=CC=3)C(=O)N(C3CC3)C2=O)C=CC=1
|
| InChi Key |
LIRYPHYGHXZJBZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C26H23FIN5O4/c1-13-22-21(23(31(3)24(13)35)30-20-10-7-15(28)11-19(20)27)25(36)33(17-8-9-17)26(37)32(22)18-6-4-5-16(12-18)29-14(2)34/h4-7,10-12,17,30H,8-9H2,1-3H3,(H,29,34)
|
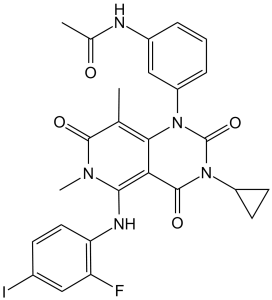
| 化学名 |
N-[3-[3-cyclopropyl-5-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)-6,8-dimethyl-2,4,7-trioxopyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-1-yl]phenyl]acetamide
|
| 别名 |
JTP-74057; GSK 1120212; GSK1120212; GSK-1120212; JTP74057; Trametinib. Trade name: Mekinist
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.06 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.06 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液添加到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 4% DMSO+corn oil: 3mg/mL 配方 4 中的溶解度: 6.67 mg/mL (10.84 mM) in 0.5%HPMC 1%Tween80 (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.6250 mL | 8.1249 mL | 16.2499 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3250 mL | 1.6250 mL | 3.2500 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1625 mL | 0.8125 mL | 1.6250 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Platform Study of JDQ443 in Combinations in Patients With Advanced Solid Tumors Harboring the KRAS G12C Mutation
CTID: NCT05358249
Phase: Phase 1/Phase 2 Status: Active, not recruiting
Date: 2024-11-15
|
|
|
|