| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 2mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg | |||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
IP Receptor ( EC50 = 1.9 nM ); TP Receptor ( EC50 = 919 nM ); IP Receptor ( Ki = 32.1 nM ); IP Receptor ( Ki = 4680 nM );
DP/DP1 Receptor:0.6 nM (EC50); IP Receptor:1.9 nM (EC50); EP2 Receptor:6.2 nM (EC50) ; EP3 Receptor:68.9 nM (EC50) ; EP4 Receptor:181 nM (EC50) ; EP1 Receptor:285 nM (EC50) ; TP Receptor:919 nM (EC50) ; EP2 Receptor:3.6 nM (Ki) ; EP1 Receptor:212 nM (Ki); EP4 Receptor:826 nM (Ki); EP3 Receptor:2505 nM (Ki); DP/DP1 Receptor:4.4 nM (Ki) ; IP Receptor:32.1 nM (Ki) ; FP Receptor:4680 nM (Ki) - Prostacyclin receptor (IP):Treprostinil acts as a potent agonist with a Ki value of 0.3 nM. [1] - Prostaglandin DP1 receptor (DP1):Treprostinil exhibits high agonist activity with a Ki value of 0.14 nM. [1] - Prostaglandin EP2 receptor (EP2):Treprostinil is a potent agonist with a Ki value of 0.7 nM. [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
曲前列环素对 DP1、EP2 和 IP 受体具有高亲和力(Ki 分别为 4.4、3.6 和 32 nM),对 EP1 和 EP4 受体亲和力低,对 EP3、FP 和 TP 受体亲和力更低。与曲前列环素一样,IP、DP1 和 EP2 受体的激活均可导致人肺动脉血管舒张[1]。曲前列环素抑制培养的内皮集落形成细胞的活力。来自曲前列环素预处理的间充质干细胞的条件培养基刺激内皮集落形成细胞增殖[5]。
- 受体结合与激活: - 曲前列尼尔对IP、DP1和EP2受体具有纳摩尔级亲和力,其中对DP1的亲和力最高(Ki = 0.14 nM)。它通过激活这些受体诱导cAMP生成,从而发挥血管舒张和抗增殖作用。[1] - 间充质干细胞(MSCs)中VEGF-A的诱导: - 曲前列尼尔(10–100 nM)通过激活IP和DP1受体显著增加MSCs中VEGF-A的分泌。该效应可被特异性拮抗剂阻断,证实为受体介导的信号通路。[2] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
吸入曲前列环素钠是一种前列环素类似物,是最新获得 FDA 批准用于治疗致命孤儿疾病:肺动脉高压 (PAH) 的药物[2]。与安慰剂相比,曲前列环素可保留窦内皮细胞内层并减少移植后早期血小板沉积。安慰剂组肝组织血流明显受损,而曲前列环素则维持与正常水平相似的血流[3]。曲前列环素治疗显着增加裸鼠基质胶中内皮集落形成细胞联合间充质干细胞的血管形成能力。沉默间充质干细胞中的 VEGF-A 基因也会阻断曲前列环素的促血管生成作用[4]。曲前列环素在提高小鼠和人类造血干细胞和祖细胞的细胞内 cAMP 水平方面最有效[5]。与常氧小鼠相比,曲前列环素治疗显着减少了细胞的募集。曲前列环素还可降低右心室收缩压并略微减少血管重塑,但无法逆转右心室肥厚[6]。
- 肺动脉高压(PAH)治疗: - 在PAH动物模型(如慢性低氧诱导的大鼠)中,曲前列尼尔通过吸入或皮下输注给药可降低肺血管阻力并改善右心室功能。其治疗作用归因于IP和DP1受体的双重激活,导致血管舒张和抑制纤维细胞募集。[3][6] - 缺血再灌注损伤保护: - 在大鼠原位肝移植模型中,曲前列尼尔(10–50 ng/kg/min,静脉注射)通过抑制氧化应激和中性粒细胞浸润减轻肝损伤。该效应与内皮型一氧化氮合酶(eNOS)活性增加和促炎细胞因子释放减少相关。[5] - 增强造血祖细胞移植: - 在小鼠模型中,曲前列尼尔(0.1–1 mg/kg,腹腔注射)通过促进造血干细胞向骨髓迁移改善移植植入。这一过程由祖细胞表面CXCR4趋化因子受体表达上调介导。[4] |
| 酶活实验 |
- 前列腺素受体结合实验:
1. 将转染人IP、DP1或EP2受体的HEK293细胞膜制剂与放射性标记配体(如用于IP的[³H]-伊洛前列素)在不同浓度的曲前列尼尔(0.01–100 nM)存在下孵育。
2. 通过过滤分离结合和游离配体,测量放射性以确定Ki值。曲前列尼尔以高效力置换[³H]-伊洛前列素,IP(Ki = 0.3 nM)和DP1(Ki = 0.14 nM)。[1]
|
| 细胞实验 |
将来自人类或小鼠的造血干细胞和祖细胞在 37°C 下在载体存在下或与 10 μM 曲前列环素和 30 μM 毛喉素联合培养一小时和二十四小时。细胞凋亡试剂盒用于在 4°C 下用磷酸盐缓冲盐水洗涤细胞后对细胞进行外化磷脂酰丝氨酸染色 [5]。
- MSCs中VEGF-A分泌实验: 1. 将MSCs在无血清培养基中用曲前列尼尔(10–100 nM)处理24小时。 2. 收集条件培养基,通过ELISA定量VEGF-A水平。曲前列尼尔以浓度依赖方式增加VEGF-A分泌(EC50 ≈ 50 nM)。[2] - 内皮集落形成细胞(ECFC)血管生成实验: 1. 将ECFCs与曲前列尼尔处理的MSCs在Matrigel中共培养。 2. 12小时后评估管形成。曲前列尼尔使ECFC血管生成芽数比对照组增加2–3倍,依赖于MSCs分泌的VEGF-A。[2] |
| 动物实验 |
Rats: For the study, male Lewis rats weighing between 200 and 300 g are employed. 24 hours prior to hepatectomy, donor animals are given treprostinil or a placebo, and the corresponding recipient animal receives the same care until the moment of sacrifice. Treatment is invisible to the surgeon. To study what happens right after IRI, recipients are sacrificed 1, 3, 6, 24 and 48 hours after transplantation. Using an Alzet implantable osmotic pump, subcutaneous administration of treprostinil (100 ng/kg/min) or placebo is performed. This dosage is chosen to produce a plasma concentration that is steady-state and falls between 5 and 20 ng/mL[3].
Mice: Mice that have had bone marrow transplantation (BMT) are split up into five groups, each with six to ten mice. In a normobaric chamber, one group of mice is exposed to hypoxia (10% inspired oxygen fraction), while the other group of mice (control BMT) spends 28 days in a normoxic chamber with a normal oxygen environment (21% inspired O2 fraction). While the two other groups of mice receive four weeks of hypoxic exposure and receive Treprostinil infusions at varying dose levels (14 ng/kg and 70 ng/kg per minute), the sham group mice receive saline treatment. Comparatively, infusion rates for humans in PAH therapy range from 10 to 60 ng/kg per minute[6]. - Chronic hypoxic PAH model: 1. Rats are exposed to hypoxia (10% O₂) for 4 weeks to induce PAH. 2. Treprostinil is administered via subcutaneous osmotic pumps (10–50 ng/kg/min) or inhaled aerosol (1–5 μg/kg) daily for 2 weeks. 3. Pulmonary hemodynamics are measured via right heart catheterization, and lung tissues are analyzed for fibrocyte infiltration (CD45⁺/collagen I⁺ cells). [6] - Liver transplantation model: 1. Rats undergo orthotopic liver transplantation with 60-minute warm ischemia. 2. Treprostinil (10–50 ng/kg/min) is infused intravenously starting 30 minutes before reperfusion and continuing for 6 hours postoperatively. 3. Liver function is assessed by serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels, and histological damage is evaluated by hematoxylin-eosin staining. [5] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
After subcutaneous infusion, treprostinil is completely absorbed, with a bioavailability of about 100%, and it reaches steady-state concentrations in approximately 10 hours. The pharmacokinetics of treprostinil follow a two-compartment model and are linear between 2.5 and 125 ng/kg/min. Subcutaneous and intravenous doses of treprostinil are bioequivalent at 10 ng/kg/min. Compared to healthy subjects, patients with mild and moderate hepatic insufficiency had a corresponding Cmax 2- and 4-times higher and an AUC0-∞ 3- and 5-times higher when given a subcutaneous treprostinil dose of 10 ng/kg/min for 150 min. When given orally at doses between 0.5 and 15 mg twice a day, treprostinil follows a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile. The oral bioavailability of treprostinil is 17%, and drug concentration reaches its highest level between 4 and 6 hours after oral administration. The oral absorption of treprostinil is affected by food. The AUC and Cmax of oral treprostinil increase 49% and 13%, respectively, when this drug is administered with a high-fat, high-calorie meal. The AUC and Cmax of inhaled treprostinil were proportional to the doses administered (18 to 90 μg). The bioavailability of inhaled treprostinil was 64% in patients receiving 2 doses of 18 μg, and 72% in patients receiving two doses of 36 μg. Two separate studies that evaluated the pharmacokinetics of inhaled treprostinil at a maintenance dose of 54 μg found that the mean Cmax was 0.91 and 1.32 ng/mL, respectively, with a corresponding Tmax of 0.25 and 0.12 hr and a mean AUC of 0.81 and 0.97 hr⋅ng/mL. Treprostinil metabolites are excreted through urine (79%) and feces (13%) over 10 days. Only a small proportion of treprostinil is excreted unchanged. When administered orally, 1.13% and 0.19% of unchanged treprostinil diolamine are found in urine and feces, respectively. When administered subcutaneously, intravenously or by inhalation, 4% of unchanged treprostinil is found in urine. The volume of distribution of treprostinil is 14 L/70 kg. The clearance of treprostinil is 30 L/hr in a 70 kg person. In patients with mild to moderate hepatic insufficiency, clearance is reduced up to 80%. Metabolism / Metabolites Treprostinil is mostly metabolized by the liver, mainly by CYP2C8, and by CYP2C9 to a lesser extent. Treprostinil does not have a single major metabolite. The five metabolites detected in urine (HU1 through HU5) accounted for 13.8, 14.3, 15.5, 10.6 and 10.2% of the dose, respectively. One of the metabolites (HU5) is the glucuronide conjugate of treprostinil. HU1, HU2, HU3 and HU4 are formed through the oxidation of the 3-hydroxyloctyl side chain. None of the metabolites of treprostinil appear to be active. _In vitro_ studies suggest that treprostinil does not inhibit or induce any major CYP enzymes. Biological Half-Life The terminal elimination half-life of treprostinil is approximately 4 hours, following a two-compartment model. - Subcutaneous/intravenous administration: - Treprostinil is rapidly absorbed with a bioavailability of ~90%. Plasma protein binding is ~90%, primarily to albumin. The terminal half-life is 3–4 hours, and elimination occurs via hepatic metabolism (CYP3A4-mediated oxidation) and renal excretion. [3] - Inhaled administration: - Inhaled Treprostinil achieves peak plasma concentrations within 10–15 minutes, with a bioavailability of ~20–30%. The inhaled route reduces systemic exposure compared to parenteral administration, minimizing off-target effects. [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation One patient taking treprostinil breastfed her infant for one year without any complications. However, until more data are available, treprostinil should only be used with careful monitoring during breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants A woman developed pulmonary artery hypertension and was treated with intravenous treprostinil beginning at 32 weeks of gestation and titrated up to 26 ng/kg/min. The dose was nearly doubled postpartum because of worsening symptoms. She breastfed (extent not stated) her infant for one year with no apparent drug-related problems, although there was concern for obesity at 6 months of age. The infant was healthy and developing normally at 2 years of age. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding At _in vitro_ concentrations ranging from 330 to 10,000 μg/L, the human plasma protein binding of treprostinil is approximately 91%. This concentration is above what is considered to be clinically relevant. - Side effects: - Common adverse effects include headache, flushing, and jaw pain, attributed to vasodilation. At higher doses, Treprostinil may cause hypotension, nausea, and diarrhea. [3] - Plasma protein binding: - Treprostinil is highly bound to plasma proteins (~90%), which may increase drug-drug interactions with other highly protein-bound compounds (e.g., warfarin). [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Treprostinil is a carboxylic acid and a carbotricyclic compound. It has a role as a platelet aggregation inhibitor, a vasodilator agent, an antihypertensive agent, a cardiovascular drug, a vitamin K antagonist and a human blood serum metabolite.
Treprostinil is a stable tricyclic analogue of prostacyclin that promotes the vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic arterial vascular beds and the inhibition of platelet aggregation. It reduces symptoms in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease. The first agent approved for the treatment of PAH was [epoprostenol], a synthetic prostacyclin that significantly increases patients' quality of life. However, the use of epoprostenol is limited due to its short half-life (3-5 min) and instability at room temperature. The use of more stable alternatives such as treprostinil provides patients with PAH with more treatment options. Treprostinil was approved by the FDA in 2002 for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. It is available in the following routes of administration: subcutaneous, intravenous, inhaled and oral. The first generic form of treprostinil became available in 2019. Treprostinil is a Prostacycline Vasodilator. The physiologic effect of treprostinil is by means of Vasodilation. See also: Treprostinil Sodium (has salt form); Treprostinil Diolamine (is active moiety of); Treprostinil Palmitil (is active moiety of). Drug Indication The FDA has indicated treprostinil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension and pulmonary hypertension associated with interstitial lung disease to improve exercise ability. It is also used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension in patients requiring transition from epoprostenol. The Health Canada label specifies that treprostinil is indicated for the long-term treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension in NYHA Class III and IV patients who did not respond adequately to conventional therapy. L24244 Treatment of adult patients with WHO Functional Class (FC) III or IV and: inoperable chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH), orpersistent or recurrent CTEPH after surgical treatmentto improve exercise capacity. Treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension Mechanism of Action Treprostinil is a stable analogue of prostacyclin, a prostaglandin that acts as an anti-thrombotic agent and a potent vasodilator. Prostacyclin analogues are useful in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), a disease characterized by abnormally high blood pressure in the arteries between the heart and lungs. PAH leads to right heart failure due to the remodelling of pulmonary arteries, and patients with this condition have a poor prognosis. Treprostinil binds and activates the prostacyclin receptor, the prostaglandin D2 receptor 1, and the prostaglandin E2 receptor 2. The activation of these receptors leads to the elevation of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels, which consequently promotes the opening of calcium-activated potassium channels that lead to cell hyperpolarization. This mechanism promotes the direct vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic arterial vascular beds and the inhibition of platelet aggregation. In addition to its direct vasodilatory effects, treprostinil inhibits inflammatory pathways. Pharmacodynamics As an analogue of prostacyclin, treprostinil promotes the vasodilation of pulmonary and systemic arterial vascular beds and the inhibition of platelet aggregation. In animals, the vasodilatory effects of treprostinil lead to a reduction of right and left ventricular afterload and an increase in cardiac output and stroke volume. Treprostinil also causes a dose-related negative inotropic and lusitropic effect, and no major effects on cardiac conduction have been detected. Short-lasting effects on QTc were detected in healthy volunteers (n=240) given inhaled single doses of 54 and 84 μg of treprostinil. These effects dissipated rapidly as treprostinil concentrations lowered. When given subcutaneously or intravenously, treprostinil has the potential to reach higher concentrations. The effect of oral treprostinil on QTc has not been evaluated. Due to its ability to inhibit platelet aggregation, treprostinil can increase the risk of bleeding, and patients with low systemic arterial pressure taking treprostinil may experience symptomatic hypotension. The abrupt withdrawal of treprostinil or drastic changes in dose may worsen the symptoms of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). The inhalation of treprostinil can also cause bronchospasms in patients with asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), or bronchial hyperreactivity. When given intravenously, treprostinil can lead to infusion complications and increase the risk of bloodstream infections. - Mechanism of action: - Treprostinil exerts its therapeutic effects through dual activation of IP and DP1 receptors, leading to vasodilation, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and suppression of vascular remodeling. Its activation of EP2 receptors may also contribute to anti-inflammatory effects. [1][6] - Clinical use: - Approved for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH). Available in multiple formulations: subcutaneous/intravenous solution, inhaled aerosol, and oral tablets. [3] - FDA-approved indications: - Treprostinil is indicated for improving exercise capacity and delaying clinical worsening in patients with PAH. The inhaled formulation is specifically approved for patients with severe symptoms (WHO functional class III/IV). [3] |
| 分子式 |
C23H34O5
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
412.49500
|
| 精确质量 |
390.24
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 70.74; H, 8.78; O, 20.48
|
| CAS号 |
81846-19-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Treprostinil sodium; 289480-64-4; Treprostinil-13C2,d; Treprostinil-d9; 2747918-14-3; Treprostinil diethanolamine; 830354-48-8
|
| PubChem CID |
6918140
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to yellow oily liquid or solid
|
| 密度 |
1.158g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
587.1ºC at 760mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
121-123°
|
| 闪点 |
199.3ºC
|
| 折射率 |
1.553
|
| LogP |
2.248
|
| tPSA |
89.82
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
10
|
| 重原子数目 |
28
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
495
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
5
|
| SMILES |
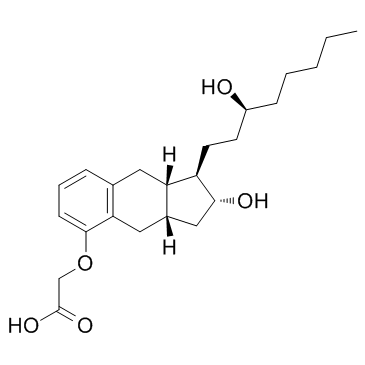
C([C@H]1[C@H](O)C[C@@H]2CC3C(OCC(=O)O)=CC=CC=3C[C@H]12)C[C@@H](O)CCCCC
|
| InChi Key |
PAJMKGZZBBTTOY-ZFORQUDYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H34O5/c1-2-3-4-7-17(24)9-10-18-19-11-15-6-5-8-22(28-14-23(26)27)20(15)12-16(19)13-21(18)25/h5-6,8,16-19,21,24-25H,2-4,7,9-14H2,1H3,(H,26,27)/t16-,17-,18+,19-,21+/m0/s1
|
| 化学名 |
2-[[(1R,2R,3aS,9aS)-2-hydroxy-1-[(3S)-3-hydroxyoctyl]-2,3,3a,4,9,9a-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[g]naphthalen-5-yl]oxy]acetic acid
|
| 别名 |
LRX15; LRX 15; LRX-15; Treprostinil; 81846-19-7; Rumodolin; Tyvaso; treprostinilo; UT15; UT-15; UT 15; BW 15AU; Uniprost; TU-62840; reprostinil; Orenitram; Remodulin; Tyvaso; LRX-15; UT-15;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ≥ 125 mg/mL (~320.1 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (5.33 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4242 mL | 12.1212 mL | 24.2424 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4848 mL | 2.4242 mL | 4.8485 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2424 mL | 1.2121 mL | 2.4242 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03045029 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Oral treprostinil | Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | United Therapeutics | July 18, 2017 | N/A |
| NCT05176951 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Treprostinil Palmitil Drug: Placebo |
Pulmonary Hypertension | Insmed Incorporated | December 22, 2022 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05060315 | Active Recruiting |
Combination Product: Remunity Pump for Remodulin |
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension | United Therapeutics | July 5, 2023 | N/A |
| NCT03835676 | Recruiting | Drug: Treprostinil | Pulmonary Hypertension | Magdi H. Yacoub | May 1, 2019 | Phase 4 |
| NCT04005469 | Recruiting | Drug: Treprostinil | Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Delayed Graft Function |
Rhode Island Hospital | November 13, 2020 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
|
|
|
|
|