| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
Bcl-2 (Ki = 0.01 nM); Bcl-xL (Ki = 48 nM); Bcl-W (Ki = 245 nM)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
ABT-199 对 Bcl-xL、Mcl-1 和 Bcl-w 的敏感性较低,Ki 分别为 48 nM、> 444 nM 和 245 nM。 ABT-199 对 FL5.12-Bcl-xL 细胞表现出弱活性,EC50 为 261 nM,但有效抑制 FL5.12-Bcl-2 细胞、RS4;11 细胞,EC50 为 4 nM 和 8 nM。在 RS4;11 细胞中,ABT-199 引起快速细胞凋亡,并伴有细胞色素 c 的释放、半胱天冬酶的激活、磷脂酰丝氨酸的外化以及亚 G0/G1 DNA 的积累。根据定量免疫印迹,NHL、DLBCL、MCL、AML 和 ALL 细胞系中的 Bcl-2 表达与 ABT-199 敏感性密切相关。 ABT-199 诱导 CLL 细胞凋亡的平均 EC50 为 3.0 nM。 [1]
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
ABT-199 (100 mg/kg) 在 RS4;11 异种移植物中引起最大 95% 的肿瘤生长抑制和 152% 的肿瘤生长延迟。 ABT-199 可单独使用或与其他药物(例如 SDX-105)联合使用,以抑制异种移植物的生长(DoHH2、Granta-519)。 [1]
在这里,我们报道了navitoclax的重组,以获得一种高效,口服生物利用和bcl -2选择性抑制剂ABT-199。该化合物在体内抑制bcl -2依赖性肿瘤的生长,并保护人类血小板。单剂量ABT-199治疗3例难治性慢性淋巴细胞白血病患者,24小时内肿瘤溶解[2] 。 为了在更类似于潜在临床应用的情况下研究VEN (Venetoclax)在个体白血病样本中的抗白血病活性,我们在不同个体、患者来源的小鼠异种移植ALL样本(N = 12)的临床前ii期样试验中研究了其抗白血病活性。移植到受体小鼠身上3周后,携带all的动物用VEN治疗10天,比较VEN (Venetoclax)或载药治疗后每一种白血病复发的次数。我们观察到VEN明显的体内抗白血病活性,这是由生存时间(“δ生存期”)的差异所表明的,从最小的影响到超过140天无ALL表现的延长生存期(图3a)。这种体内反应的变化与体外观察到的VEN敏感性的异质性相似,体外分析的EC50值显示与体内生存时间有中等程度的关联[3] 。 在出现白血病表现(受体外周血中存在5%的人ALL细胞)后,用VEN (Venetoclax)或载药治疗小鼠10天,然后评估无白血病生存,直到每个受体出现疾病表现。从更大的生物重复组中获得的这些结果精确地反映了临床前试验中看到的药物反应,重要的是,它清楚地对应于线粒体启动评估的BCL-2依赖程度:(i) PDX13显示出轻微的疾病表现延迟和低BCL-2依赖(图1)。3f,3f,平均生存差2.3天,BAD-HRK启动率18.6%),(ii)在PDX10中,我们观察到VEN治疗后明显延迟了显性白血病的发作,与明确的BCL-2依赖性一致(图。3g,3g,平均生存差43.2天,BAD-HRK启动率56.8%),(iii) VEN (Venetoclax)组在观察期内无白血病表现的PDX2生存期延长(图2)。3h,3h,超过70天生存时间优越,BAD-HRK启动率80.3%),对应于BCL-2的强依赖性。[3] |
| 酶活实验 |
ABT-199 对 Bcl-2 家族不同亚型的结合亲和力(Ki 或 IC50)通过竞争性荧光偏振测定来确定。使用的肽探针和蛋白质对如下::f-bad (1 nM) 和 Bcl-xL (6 nM)、f-Bax (1 nM) 和 Bcl-2 (10 nM)、f-Bax (1 nM) ) 和 Bcl-w (40 nM)、f-Noxa (2 nM) 和 Mcl-1 (40 nM)、f-Bax (1 nM) 和 Bcl-2-A1 (15 nM)。时间分辨荧光共振能量转移测定也用于确定 Bcl-xL 的结合亲和力。在室温下,将 Bcl-xL(1 nM,His 标记)、200 nM f-Bak、1 nM Tb 标记的抗 His 抗体和 ABT-199 混合 30 分钟。
|
| 细胞实验 |
RS4;11细胞在96孔板上以5 × 104 /孔的密度接种后,用ABT-199 (Venetoclax)稀释半对数步处理,从1 μM-0.05 nM开始。ABT-199 (Venetoclax)与白血病和淋巴瘤细胞系一起孵育48小时,每孔1.5-2 × 104个细胞。使用Cell TiterGlo试剂,评估对增殖的影响。使用非线性回归分析浓度-响应数据以确定EC50值[1]。
来自T-ALL细胞系的细胞(补充表1,可在Blood网站上获得)以每孔10万个细胞的速度在96孔板中进行镀。细胞在100µL含10%胎牛血清的培养基中孵育48小时,其中加入5µL适当的ABT-199 (Venetoclax)稀释剂或二甲亚砜(DMSO)。[2] 在添加20% FCS和1% l-谷氨酰胺的RPMI 1640中培养细胞,进行细胞活力测定。将细胞暴露于11种不同浓度的VEN (Venetoclax) (0.1 nM、1 nM、10 nM、50 nM、100 nM、250 nM、500 nM、1µM、3µM、5µM和10µM)中72 h (BCP-ALL细胞系)或24 h (BCP-ALL PDX细胞)。[3] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice: Nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient γ (NSG) mice are given a 150 µL injection of phosphate-buffered saline containing 5×106 luciferase-labeled LOUCY cells at the age of 6 weeks in the tail vein.
The IVIS Lumina II imaging system measures the bioluminescence at regular intervals. After the cells have engrafted and the mice have been randomly split into two groups at 6 weeks (each group contains an equal number of males and females), the treatment is initiated on day 0 of the experiment. Venetoclax (ABT-199) 100 mg/kg body weight or vehicle is administered orally to mice for 4 days in a row. Days 0, 2, and 4 are used to measure the bioluminescene.[1]
Nonobese diabetic/severe combined immunodeficient γ (NSG) mice were injected at 6 weeks of age in the tail vein with 150 µL phosphate-buffered saline containing 5 × 106 luciferase-labeled LOUCY cells. At regular time points, the bioluminescence was measured using the IVIS Lumina II imaging system. At 6 weeks, the cells were engrafted and the mice were randomly divided into 2 groups (with an equal number of males and females in both groups), and the treatment was started on day 0. Mice were treated with 100 mg ABT-199/kg body weight or with vehicle via oral gavage for 4 consecutive days. Venetoclax (ABT-199) was formulated in 60% phosal 50 propylene glycol, 30% polyethylene glycol 400, and 10% ethanol. At days 0, 2, and 4 the bioluminescene was measured. Before imaging, the mice were injected intraperitoneally with 200 µL of a 15 mg/mL firefly d-luciferin potassium salt solution and anesthetized by inhalation of 5% isoflurane. The mice were imaged 10 minutes after luciferin injection. The total bioluminescence signal in each mouse was calculated via the region of interest tool (total counts) in the Living Image software.[2] A xenograft of primary human T-ALL cells from patient 3 was established in NSG mice by retro-orbital injection. Upon establishment of disease, human leukemic cells were isolated from the spleen and retransplanted into secondary recipients. Next, tertiary xenograft injections were performed in a cohort of 10 NSG mice and leukemia engraftment was monitored by human CD45 staining in peripheral blood using FACS analysis with the S3 cell sorter. Upon detection of human CD45+ leukemic blasts in peripheral blood, mice were randomized in 2 groups and treated with vehicle or 100 mg Venetoclax (ABT-199)/kg body weight for 7 consecutive days. After treatment, animals were sacrificed and the percentage human CD45-positive leukemic blasts in bone marrow were determined by FACS as described above.[2] Upon transplantation of ALL cells, engraftment of human blasts was monitored in peripheral blood by flow cytometry surface staining for huCD19 and huCD4549,50. Mice were treated with vehicle (60% Phosal 50 PG, 30% polyethylene glycol and 10% ethanol) or VEN (Venetoclax) 100 mg/kg/day orally for 10 days. Treatment was initiated on day 21 post transplantation (Fig. (Fig.3a)3a) or upon engraftment of more than 5% blasts in the peripheral blood (Fig. 3f–h). Posttreatment survival times were defined as manifestation of clinically overt leukemia in recipient animals upon initiation of treatment. Manifestation of leukemia was confirmed by flow cytometry staining of bone marrow and spleen cells as described above showing high percentages of human ALL in the respective compartments. For the independent cohort (Fig. (Fig.4)4) treatment was carried out as previously described.[3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Following several oral administrations after a meal, the maximum plasma concentration of venetoclax was reached 5-8 hours after the dose. Venetoclax steady state AUC (area under the curve) increased proportionally over the dose range of 150-800 mg. After a low-fat meal, venetoclax mean (± standard deviation) steady-state Cmax was 2.1 ± 1.1 μg/mL and AUC0-24 was 32.8 ± 16.9 μg•h/mL at the 400 mg once daily dose. When compared with the fasted state, venetoclax exposure increased by 3.4 times when ingested with a low-fat meal and 5.2 times with a high-fat meal. When comparing low versus high fat, the Cmax and AUC were both increased by 50% when ingested with a high-fat meal. The FDA label indicataes that venetoclax should be taken with food,. After single oral administration of 200 mg radiolabeled [14C]-venetoclax dose to healthy subjects, >99.9% of the dose was found in feces and <0.1% of the dose was excreted in urine within 9 days, suggesting that hepatic elimination is responsible for the clearance of venetoclax from systemic circulation. Unchanged venetoclax accounted for 20.8% of the radioactive dose excreted in feces. The population estimate for apparent volume of distribution (Vdss/F) of venetoclax ranged from 256-321 L. Mainly hepatic. Metabolism / Metabolites In vitro studies demonstrated that venetoclax is predominantly metabolized as a substrate of CYP3A4/5,,. Biological Half-Life The half-life of venetoclax is reported to be 19-26 hours, after administration of a single 50-mg dose,. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Hepatotoxicity
In clinical trials in 240 patients with CLL, serum aminotransferase elevations occurred in 20% of subjects treated with venetoclax, but the elevations were generally transient, mild and not associated with jaundice or symptoms. In the preregistration trials, no cases of clinically apparent liver injury attributed to venetoclax were reported and few patients required drug discontinuation for liver test abnormalities. Since approval, venetoclax has had limited clinical use, but has not been implicated in cases of clinically apparent liver injury. Venetoclax decreases total white blood cell counts and can cause lymphopenia in addition to neutropenia. As a consequence, venetoclax may be capable of inducing immune reactions including reactivation of hepatitis B. However, instances of reactivation have not been reported, but neither has detailed information on the effects of venetoclax on hepatitis B virus levels in patients with preexisting hepatitis B or evidence of previous infection. Likelihood score: E (unlikely cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of venetoclax during breastfeeding. Because venetoclax is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is 26 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. Most sources consider breastfeeding to be contraindicated during maternal antineoplastic drug therapy. The manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding be discontinued during vemurafenib therapy and for 1 week after the final dose. Chemotherapy may adversely affect the normal microbiome and chemical makeup of breastmilk. Women who receive chemotherapy during pregnancy are more likely to have difficulty nursing their infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Protein Binding Venetoclax is highly bound to human plasma protein with unbound fraction in plasma <0.01 across a concentration range of 1-30 µM (0.87-26 µg/mL). The mean blood-to-plasma ratio was 0.57. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Venetoclax induces rapid and potent onset apoptosis of CLL cells, powerful enough to act within 24h and to lead to tumor lysis syndrome,,. Selective targeting of BCL2 with venetoclax has demonstrated a manageable safety profile and has been shown to induce significant response in patients with relapsed CLL (chronic lymphocytic leukemia) or SLL (small lymphocytic leukemia), including patients with poor prognostic features. This drug is not expected to have a significant impact on the cardiac QT interval. Venetoclax has demonstrated efficacy in various types of lymphoid malignancies, including relapsed/ refractory CLL harboring deletion 17p, with an overall response rate of approximately 80%. |
| 分子式 |
C45H50CLN7O7S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
868.44
|
|
| 精确质量 |
867.318
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 62.24; H, 5.80; Cl, 4.08; N, 11.29; O, 12.90; S, 3.69
|
|
| CAS号 |
1257044-40-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Venetoclax-d8;1257051-06-1
|
|
| PubChem CID |
49846579
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.644
|
|
| LogP |
10.88
|
|
| tPSA |
186.58
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
12
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
61
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1640
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
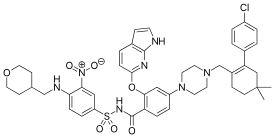
O=C(NS(=O)(C1=CC=C(NCC2CCOCC2)C([N+]([O-])=O)=C1)=O)C3=CC=C(N4CCN(CC5=C(C6=CC=C(Cl)C=C6)CC(C)(C)CC5)CC4)C=C3OC7=CN=C(NC=C8)C8=C7
|
|
| InChi Key |
LQBVNQSMGBZMKD-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C45H50ClN7O7S/c1-45(2)15-11-33(39(26-45)31-3-5-34(46)6-4-31)29-51-17-19-52(20-18-51)35-7-9-38(42(24-35)60-36-23-32-12-16-47-43(32)49-28-36)44(54)50-61(57,58)37-8-10-40(41(25-37)53(55)56)48-27-30-13-21-59-22-14-30/h3-10,12,16,23-25,28,30,48H,11,13-15,17-22,26-27,29H2,1-2H3,(H,47,49)(H,50,54)
|
|
| 化学名 |
4-[4-[[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohexen-1-yl]methyl]piperazin-1-yl]-N-[3-nitro-4-(oxan-4-ylmethylamino)phenyl]sulfonyl-2-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~115.1 mM)
Water: <1 mg/mL(slightly soluble or insoluble) Ethanol: <1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 5 mg/mL (5.76 mM) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液。
*生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (2.88 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀; 然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀; 加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (2.88 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 通过加热和超声助溶。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 5% DMSO+50% PEG 300+5% Tween 80+ddH2O: 5 mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 20 mg/mL (23.03 mM) in 60% phosal 50 propylene glycol (PG), 30% polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG400), 10% ethanol (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1515 mL | 5.7575 mL | 11.5149 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2303 mL | 1.1515 mL | 2.3030 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1151 mL | 0.5757 mL | 1.1515 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05464836 | Not yetrecrulting | Drug: CB-103/Drug:Venetoclax | LeukemiaLymphoblastic]Leukemta | M.D.Anderson Cancer Center | December 30 2022 | Phase 2 |
| NCT05360160 | Recruiting | DrugSNDX-5613DrugVenetoclax]Drug-ASTX727 | LeukemiaLymphoblastic]Leukemta | M.D.Anderson Cancer Centerastex PharmaceuticalsIncSyndax Pharmaceutic als inc |
December 30 2022 | Phase 2 |