| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
sPLA2 ( Ki = 15 nM ); 5-HT3A Receptor ( Ki = 3.7 nM ); Human 5-HT7 Receptor ( Ki = 19 nM ); SERT ( Ki = 1.6 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Lu-AA21004 抑制重组人 CYP1A2、CYP2C9、CYP2D6 和 CYP3A4,IC50 分别为 40 μM、39 μM、9.8 μM 和 10 μM。 Lu AA21004 是一种 h5-HT1B 受体部分激动剂,基于全细胞 cAMP 的检测,EC50 为 460 nM,内在活性为 22%。 Lu AA21004 与 r5-HT7 受体结合,Ki 值为 200 nM,是 r5-HT7 受体的功能性拮抗剂,在体外全细胞 cAMP 测定中,IC50 为 2 μM。激酶测定:Vortioxetine(化合物 5m)是一种多模式血清素能药物,抑制 5-HT1A、5-HT1B、5-HT3A、5-HT7 受体和 SERT,Ki 值为 15 nM、33 nM、3.7 nM、19 nM 和 1.6分别为nM。沃替西汀对 5-HT3A 和 5-HT7 受体表现出拮抗特性,对 5-HT1B 受体表现出部分激动剂特性,对 5-HT1A 受体表现出激动特性,并对 SERT 具有有效抑制作用。细胞测定:Vortioxetine 是一种 h5-HT1B 受体部分激动剂,基于全细胞 cAMP 测定,EC50 为 460 nM,内在活性为 22%。 Vortioxetine 与 r5-HT7 受体结合的 Ki 值为 200 nM,是 r5-HT7 受体的功能性拮抗剂,在体外全细胞 cAMP 测定中 IC50 为 2 μM。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
对于 Lu-AA21004,大鼠的肝脏清除率和口服生物利用度为 7.1 (L/h)/kg 和 16%。 Lu-AA21004(2.5 mg/kg、5 mg/kg 或 10 mg/kg sc)可增加清醒大鼠腹侧海马的细胞外 5-HT 水平。治疗 3 天后,Lu-AA21004(5 mg/kg 或 10 mg/kg sc)还会导致内侧前额皮质 (mPFC) 中 5-HT 基础水平显着升高。 Lu-AA21004在大鼠内侧前额叶皮层中用5mg/kg或10mg/kg治疗3天后,占据SERT的43%和57%。 Lu AA21004 剂量依赖性地占据 5-HT1B 受体,大鼠皮下给药 1 小时后 SERT 的 ED50 分别为 3.2 mg/kg 和 0.4 mg/kg。 Lu AA21004 剂量依赖性地影响大鼠的 Bezold-Jarisch 反射,抑制短暂性心动过缓,ED50 为 0.11 mg/kg。 Lu AA21004 (2.5-10.0 mg/kg sc) 增加大鼠内侧前额皮质和腹侧海马中 5-HT、DA 和 NA 的细胞外水平。 Lu AA21004(5 mg/kg sc)可增加大鼠腹侧海马中 5-HT 的细胞外水平(200%),SERT 占用率为 41%。 Lu AA21004 (7.8 mg/kg sc) 显着减少 FSL 大鼠的不动时间,但不减少 FRL 大鼠的不动时间。 Lu AA21004(8.0 mg/kg po)可增加大鼠的社交互动,并小幅但显着地增加大鼠的运动活动。 Lu AA21004 (7.9 mg/kg sc) 在大鼠条件性恐惧测定中显示出剂量依赖性抗焦虑样作用。沃替西汀 (10 mg/kg) 显着增加雄性 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠采集前 60 分钟的冻结,表明在采集和/或巩固过程中情境记忆形成增强。沃替西汀(5 mg/kg)还会导致保留期间的冻结率增加,这种效应通过事后测试达到了统计显着性。采集前的沃替西汀(2.5 mg/kg 或 5 mg/kg)显示新物体的平均探索时间分别为 29 秒和 33 秒。沃替西汀 (10 mg/kg) 显着降低大鼠的伤害感受,评估为缩爪潜伏期延长。注射后 20 分钟,5 和 10 mg/kg 的沃替西汀使乙酰胆碱水平增加至基线的 224% 和 204%。
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
Vortioxetine (Compound 5m) 是一种多模式血清素能药物,可抑制 SERT,抑制值分别为 1.6 nM、33 nM、3.7 nM、19 nM 以及 5-HT1A、5-HT1B 和 5-HT7 受体。 Vortioxetine 表现出强烈的 SERT 抑制作用以及对 5-HT3A 和 5-HT7 受体的拮抗作用、对 5-HT1B 受体的部分激动作用以及对 5-HT1A 受体的激动作用。
Vortioxetine/化合物5m (Lu AA21004)是先导化合物,对重组人5-HT(1A) (K(i) = 15 nM)、5-HT(1B) (K(i) = 33 nM)、5-HT(3A) (K(i) = 3.7 nM)、5-HT(7) (K(i) = 19 nM)、去甲肾上腺素能β(1) (K(i) = 46 nM)受体和SERT (K(i) = 1.6 nM)具有高亲和力。化合物5m对5-HT(3A)和5-HT(7)受体具有拮抗作用,对5-HT(1B)受体具有部分激动作用,对5-HT(1A)受体具有激动作用,对SERT具有有效抑制作用[1]。 体外SERT和5-HT3受体占用率测定[2] 用载体、氟西汀或沃替西汀(急性给药后1小时或第14次或第21次注射后24小时)处理小鼠的大脑,快速冷冻,用低温恒温器冠状切片,然后装在载玻片上冷冻待用。切片厚度为20 μm,从距bregma正前方约1.2 mm处开始测定SERT受体占用,从距bregma正前方约2.7 mm处开始测定5-HT3受体占用(Franklin and Paxinos, 2008)。在用于放射自显影实验之前,载玻片在- 20°C下保存至少24小时。[2] |
||
| 细胞实验 |
Vortioxetine 是一种 h5-HT1B 受体部分激动剂,在基于 cAMP 的全细胞测定中,EC50 为 460 nM,内在活性为 22%。在体外全细胞 cAMP 测定中,vortioxetine 与 r5-HT7 受体结合,Ki 值为 200 nM,并且是 r5-HT7 受体的功能性拮抗剂,IC50 为 2 μM。
SERT占用率评估[2] 载玻片在含有4.5 nM [3H]-escitalopram的缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, pH = 7.4)中室温孵育60 min。用1 μM艾司西酞普兰检测非特异性结合。载玻片在冷缓冲液中短暂洗涤,干燥,并在Beta成像仪中暴露16小时。SERT检测的感兴趣区域(ROI)包括外侧和内侧隔膜、伏隔核和嗅结节。SERT检测的ROI示例图像可以在补充图2A中找到。 5-HT3受体占用率的评价[2] 载玻片在由50 mM Tris和150 mM NaCl组成的缓冲液中预孵育5分钟。载玻片在空气流下干燥30-45分钟。随后,载玻片在含有1 nM [3H]LY278584的缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, pH = 7.4)中室温孵育60分钟。用1 μM昂丹司琼测定非特异性结合。载玻片在冷缓冲液中短暂洗涤,干燥,并在Beta成像仪中暴露24小时。5-HT3受体占用试验的ROI由海马组成。5-HT3受体占用测定的示例图像可以在补充图2B中找到。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The maximal plasma vortioxetine concentration (Cmax) after dosing is reached within 7 to 11 hours postdose. Absolute bioavailability is 75%. No effect of food on the pharmacokinetics was observed. Following a single oral dose of [14C]labeled vortioxetine, approximately 59% and 26% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine and feces, respectively as metabolites. Negligible amounts of unchanged vortioxetine were excreted in the urine up to 48 hours. The apparent volume of distribution of vortioxetine is approximately 2600 L, indicating extensive extravascular distribution. /MILK/ It is not known whether vortioxetine is present in human milk. Vortioxetine is present in the milk of lactating rats. Vortioxetine is a new multi-modal drug against major depressive disorder with high affinity for a range of different serotonergic targets in the CNS. We report the (11)C-labeling of vortioxetine with (11)C-MeI using a Suzuki-protocol that allows for the presence of an unprotected amine. Preliminary evaluation of (11)C-vortioxetine in a Danish Landrace pig showed rapid brain uptake and brain distribution in accordance with the pharmacological profile, all though an unexpected high binding in cerebellum was also observed. (11)C-vortioxetine displayed slow tracer kinetics with peak uptake after 60 min and with limited wash-out from the brain. Further studies are needed but this radioligand may prove to be a valuable tool in unraveling the clinical effects of vortioxetine. Vortioxetine and related material was mainly excreted by faeces in mice (84%), rats (69%) and dogs (59-65% in two separate studies), whereas humans showed prominent urinary excretion (59%) compared to faeces (26%). In excretion studies, the recovery of (14)C-Vortioxetine and related material was close to 100% in rodents. Dogs and humans exhibited a protracted excretion and the recovery was approximately 90% and 85% after 168 hours and 360 hours, respectively. The objective was to describe the pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine and evaluate the effect of intrinsic and extrinsic factors in the healthy population. Data from 26 clinical pharmacology studies were pooled. A total of 21,758 vortioxetine quantifiable plasma concentrations were collected from 887 subjects with corresponding demography. The doses ranged from 2.5 to 75 mg (single dose) and 2.5-60 mg (multiple QD doses). The pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine was best characterised by a two-compartment model with first-order absorption, lag-time and linear elimination, with interindividual error terms for absorption rate constant, oral clearance and central volume of distribution. The population mean was 32.7 L/hr for oral clearance and 1.97*10(3) L for the central volume of distribution. The average elimination half-life was 65.8 hr. CYP2D6 inferred metabolic status (ultra, extensive, intermediate or poor metabolisers) and age on oral clearance and height on central volume of distribution were identified as statistically significant covariate-parameter relationships. For CYP2D6 poor metabolizers, CL/F was approximately 50% to that seen in CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers. The impact of height on V2/F and age on CL/F was low and not considered to be clinically relevant. The final model was found to be reliable, stable and predictive. A reliable, stable and predictive pharmacokinetic model was developed to characterize pharmacokinetics of vortioxetine in the healthy population. For more Absorption, Distribution and Excretion (Complete) data for VORTIOXETINE (10 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Metabolism / Metabolites Vortioxetine is extensively metabolized primarily through oxidation via cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2A6, CYP2C8 and CYP2B6 and subsequent glucuronic acid conjugation. CYP2D6 is the primary enzyme catalyzing the metabolism of vortioxetine to its major, pharmacologically inactive, carboxylic acid metabolite, and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 have approximately twice the vortioxetine plasma concentration of extensive metabolizers. Vortioxetine is extensively metabolized primarily through oxidation via cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2A6, CYP2C8 and CYP2B6 and subsequent glucuronic acid conjugation. CYP2D6 is the primary enzyme catalyzing the metabolism of vortioxetine to its major, pharmacologically inactive, carboxylic acid metabolite, and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 have approximately twice the vortioxetine plasma concentration of extensive metabolizers. All metabolites detected in human hepatocytes were also present in dogs, mice and rats (plasma and/or urine) in vivo, except for a glucuronide conjugate of monohydroxy-Vortioxetine which was not found in mice or rats. Among all species tested, rabbit hepatocytes appeared to have the metabolite profile closer to human hepatocyte metabolite profile. Biological Half-Life Mean terminal halflife is approximately 66 hours The oral absolute bioavailability was approximately 10% in the rat, 48% in the dog and 75% in patients, with terminal elimination half-life values of 3.0, 7.9 and 66 hours, respectively. ... Data from 26 clinical pharmacology studies were pooled. A total of 21,758 vortioxetine quantifiable plasma concentrations were collected from 887 subjects with corresponding demography. The doses ranged from 2.5 to 75 mg (single dose) and 2.5-60 mg (multiple QD doses). ... The average elimination half-life was 65.8 hr. ... The mean elimination half-life and oral clearance are 66 hours and 33 L/hr, respectively. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Vortioxetine is a white to very slightly beige powder formulated into film-coated tablets. It is used for the management of major depressive disorders in adults. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: There is limited clinical trial experience regarding human overdosage with vortioxetine. In pre-marketing clinical studies, cases of overdose were limited to patients who accidentally or intentionally consumed up to a maximum dose of 40 mg of vortioxetine. The maximum single dose tested was 75 mg in men. Ingestion of vortioxetine in the dose range of 40 to 75 mg was associated with increased rates of nausea, dizziness, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, generalized pruritus, somnolence, and flushing. Toxicity may also occur at therapeutic dosage levels of vortioxetine. Potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with serotonergic antidepressants, including vortioxetine, when used alone, but particularly with concurrent use of other serotonergic drugs (including serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) type 1 receptor agonists ("triptans"), tricyclic antidepressants, buspirone, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, and St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)) and with drugs that impair the metabolism of serotonin (particularly monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, both those used to treat psychiatric disorders and others, such as linezolid and methylene blue). Manifestations of serotonin syndrome may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, and hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, and incoordination), seizures, and/or GI symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea). Concurrent or recent (i.e., within 2 weeks) therapy with MAO inhibitors intended to treat psychiatric disorders is contraindicated. Use of an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders within 3 weeks of vortioxetine discontinuance also is contraindicated. Vortioxetine also should not be initiated in patients who are being treated with other MAO inhibitors such as linezolid or IV methylene blue. If concurrent therapy with vortioxetine and other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, the patient should be made aware of the potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation of therapy or when dosage is increased. Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies. These studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant use in patients over age 24; there was a trend toward reduced risk with antidepressant use in patients aged 65 and older. Vortioxetine was not genotoxic in an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in cultured human lymphocytes. ANIMAL STUDIES: The acute oral single dose toxicity of vortioxetine is relatively low with a maximum tolerated dose (MTD) in mice and rats of 300 and 500 mg/kg, respectively. Clinical signs consisted of marked sensitivity to touch and disturbance, rapid breathing, and brown perinasal staining in rats administered 500 mg/kg. In mice, tremors, sensitivity to touch, eyes partly closed, and hypoactivity were seen after 200 and 300 mg/kg, as well as rapid, noisy and/or labored breathing, incoordination, unsteady gait, leaning, salivation, and hyperactivity after 400 and 500 mg/kg. When administered as two vortioxetine doses given an hour apart (200 mg/kg), clinical signs included convulsions, and resulted in death. Carcinogenicity studies were conducted in which mice and rats were given oral doses of vortioxetine up to 50 and 100 mg/kg/day for male and female mice, respectively, and 40 and 80 mg/kg/day for male and female rats, respectively, for 2 years. In rats, the incidence of benign polypoid adenomas of the rectum was statistically significantly increased in females. These were considered related to inflammation and hyperplasia and possibly caused by an interaction with a vehicle component of the formulation used for the study. The finding did not occur in male rats. In mice, vortioxetine was not carcinogenic in males or females. Vortioxetine caused developmental delays when administered during pregnancy to rats and rabbits. Developmental delays were also seen after birth in rats treated with vortioxetine during pregnancy and through lactation. There were no teratogenic effects in rats or rabbits treated with the drug during organogenesis. Treatment of rats with vortioxetine at doses up to 120 mg/kg/day had no effect on male or female fertility. Vortioxetine was not genotoxic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) and in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay. Hepatotoxicity Liver test abnormalities occur in a small proportion of patients ( Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Amounts of vortioxetine in milk appear to be low. If vortioxetine is required by the mother, it is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. However, until more data are available, vortioxetine should be used with careful infant monitoring during breastfeeding. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Three lactating mothers were taking vortioxetine for depression, two were taking 10 mg once daily and one was taking 20 mg once daily. All mothers were exclusively breastfeeding their infants aged 1, 2 and 6 months of age. No mothers reported any unusual behavior in their infants. A woman who was taking a vortioxetine dose of 76.1 mcg/kg daily partially breastfed her infant. She did not observe any adverse effects in her infant. A postpartum Japanese woman with depression was taking vortioxetine 20 mg zolpidem 10 mg, duloxetine 20 mg, rebamipide 100 mg and the Asian herbal medicine Kami-kihi-tou 2.5 grams daily. She partially (over 50%) breastfed her infant for 3 months. The infant had no detectable drug-related adverse effects on routine follow-up at 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9-months postpartum. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Vortioxetine has caused hyperprolactinemia and galactorrhea in some patients. An observational study looked at outcomes of 2859 women who took an antidepressant during the 2 years prior to pregnancy. Compared to women who did not take an antidepressant during pregnancy, mothers who took an antidepressant during all 3 trimesters of pregnancy were 37% less likely to be breastfeeding upon hospital discharge. Mothers who took an antidepressant only during the third trimester were 75% less likely to be breastfeeding at discharge. Those who took an antidepressant only during the first and second trimesters did not have a reduced likelihood of breastfeeding at discharge. The antidepressants used by the mothers were not specified. A retrospective cohort study of hospital electronic medical records from 2001 to 2008 compared women who had been dispensed an antidepressant during late gestation (n = 575) to those who had a psychiatric illness but did not receive an antidepressant (n = 1552) and mothers who did not have a psychiatric diagnosis (n = 30,535). Women who received an antidepressant were 37% less likely to be breastfeeding at discharge than women without a psychiatric diagnosis, but no less likely to be breastfeeding than untreated mothers with a psychiatric diagnosis. None of the mothers were taking vortioxetine. In a study of 80,882 Norwegian mother-infant pairs from 1999 to 2008, new postpartum antidepressant use was reported by 392 women and 201 reported that they continued antidepressants from pregnancy. Compared with the unexposed comparison group, late pregnancy antidepressant use was associated with a 7% reduced likelihood of breastfeeding initiation, but with no effect on breastfeeding duration or exclusivity. Compared with the unexposed comparison group, new or restarted antidepressant use was associated with a 63% reduced likelihood of predominant, and a 51% reduced likelihood of any breastfeeding at 6 months, as well as a 2.6-fold increased risk of abrupt breastfeeding discontinuation. Specific antidepressants were not mentioned. Protein Binding The plasma protein binding of vortioxetine in humans is 98%, independent of plasma concentrations. No apparent difference in the plasma protein binding between healthy subjects and subjects with hepatic (mild, moderate) or renal (mild, moderate, severe, ESRD) impairment is observed. Interactions Potentially serious, sometimes fatal adverse reactions may occur in patients who are receiving or have recently received a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor and then initiate therapy with serotonergic antidepressants or in those who received SSRI or SNRI therapy shortly before initiation of an MAO inhibitor. Concomitant use of MAO inhibitors intended to treat psychiatric disorders with vortioxetine is contraindicated. In addition, at least 2 weeks should elapse between discontinuance of an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of vortioxetine and at least 3 weeks should elapse between discontinuance of vortioxetine and initiation of an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders. Concomitant use of vortioxetine and a selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) or selective serotonin- and norepinephrine-reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) is associated with a risk of serious, sometimes fatal, serotonin syndrome. If concomitant use of vortioxetine and an SSRI or SNRI is clinically warranted, patients should be advised of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage increases. If serotonin syndrome manifestations occur, treatment with vortioxetine and the concurrently administered SSRI or SNRI should be discontinued immediately and supportive and symptomatic treatment should be initiated. Concomitant use of vortioxetine and diuretics may increase the risk of hyponatremia. When vortioxetine is administered concurrently with carbamazepine (a potent CYP inducer) for longer than 14 days, increasing the dosage of vortioxetine should be considered. The manufacturer recommends that the maximum dosage of vortioxetine not exceed 3 times the original dosage. Following discontinuance of carbamazepine, the original vortioxetine dosage should be resumed within 14 days. For more Interactions (Complete) data for VORTIOXETINE (26 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
Therapeutic Uses
Anti-Anxiety Agents; Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Agonists; Serotonin 5-HT1 Receptor Antagonists; Serotonin 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonists; Serotonin Uptake Inhibitors /CLINICAL TRIALS/ ClinicalTrials.gov is a registry and results database of publicly and privately supported clinical studies of human participants conducted around the world. The Web site is maintained by the National Library of Medicine (NLM) and the National Institutes of Health(NIH). Each ClinicalTrials.gov record presents summary information about a study protocol and includes the following: Disease or condition; Intervention (for example, the medical product, behavior, or procedure being studied); Title, description, and design of the study; Requirements for participation (eligibility criteria); Locations where the study is being conducted; Contact information for the study locations; and Links to relevant information on other health Web sites, such as NLM's MedlinePlus for patient health information and PubMed for citations and abstracts for scholarly articles in the field of medicine. Vortioxetine is included in the database. Brintellix is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). The efficacy of Brintellix was established in six 6 to 8 week studies (including one study in the elderly) and one maintenance study in adults. /Included in US product label/ Drug Warnings /BOX WARNING/ WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS. Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies. These studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant use in patients over age 24; there was a trend toward reduced risk with antidepressant use in patients aged 65 and older. In patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy, monitor closely for worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors. Advise families and caregivers of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Brintellix has not been evaluated for use in pediatric patients. Potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with serotonergic antidepressants, including vortioxetine, when used alone, but particularly with concurrent use of other serotonergic drugs (including serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) type 1 receptor agonists ("triptans"), tricyclic antidepressants, buspirone, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, and St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)) and with drugs that impair the metabolism of serotonin (particularly monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, both those used to treat psychiatric disorders and others, such as linezolid and methylene blue). Manifestations of serotonin syndrome may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or GI symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Patients receiving vortioxetine should be monitored for the development of serotonin syndrome. Concurrent or recent (i.e., within 2 weeks) therapy with MAO inhibitors intended to treat psychiatric disorders is contraindicated. Use of an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders within 3 weeks of vortioxetine discontinuance also is contraindicated. Vortioxetine also should not be initiated in patients who are being treated with other MAO inhibitors such as linezolid or IV methylene blue. If concurrent therapy with vortioxetine and other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, the patient should be made aware of the potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation of therapy or when dosage is increased. If manifestations of serotonin syndrome occur, treatment with vortioxetine and any concurrently administered serotonergic agents should be immediately discontinued and supportive and symptomatic treatment initiated. Serotonergic antidepressants, including vortioxetine, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents (NSAIAs), warfarin, and other anticoagulants may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiologic studies have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of GI bleeding. Bleeding events related to drugs that inhibit serotonin reuptake have ranged from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages. The manufacturer recommends that patients be advised of the increased risk of bleeding associated with concomitant use of vortioxetine and aspirin or other NSAIAs, warfarin, or other drugs that affect coagulation or bleeding. Treatment with serotonergic drugs, including vortioxetine, may result in hyponatremia. In many cases, hyponatremia appears to be due to the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). One case of hyponatremia with a serum sodium concentration lower than 110 mmol/L has been reported with vortioxetine in a premarketing study. Geriatric individuals and patients receiving diuretics or who are otherwise volume depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with serotonergic antidepressants. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls; more severe and/or acute cases have been associated with hallucinations, syncope, seizures, coma, respiratory arrest, and death. Vortioxetine should be discontinued and appropriate medical intervention should be instituted in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia. For more Drug Warnings (Complete) data for VORTIOXETINE (18 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Pharmacodynamics Vortioxetine binds with high affinity to the human serotonin transporter (Ki=1.6 nM), but not to the norepinephrine (Ki=113 nM) or dopamine (Ki>1000 nM) transporters. Vortioxetine potently and selectively inhibits reuptake of serotonin by inhibition of the serotonin transporter (IC50=5.4 nM). Specifically, vortioxetine binds to 5HT3 (Ki=3.7 nM), 5HT1A (Ki=15 nM), 5HT7 (Ki=19 nM), 5HT1D (Ki=54 nM), and 5HT1B (Ki=33 nM), receptors and is a 5HT3, 5HT1D, and 5HT7 receptor antagonist, 5HT1B receptor partial agonist, and 5HT1A receptor agonist. |
| 分子式 |
C18H22N2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
298.45
|
|
| 精确质量 |
298.15
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 72.44; H, 7.43; N, 9.39; S, 10.74
|
|
| CAS号 |
508233-74-7
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Vortioxetine hydrobromide; 960203-27-4; Vortioxetine-d8; 2140316-62-5; 1253056-29-9 (lactate)
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9966051
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Light yellow to yellow solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.2±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
424.8±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
210.7±28.7 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.643
|
|
| LogP |
4.26
|
|
| tPSA |
40.57
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
21
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
316
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| SMILES |
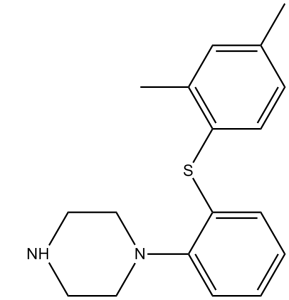
S(C1C([H])=C([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=C([H])C=1C([H])([H])[H])C1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C1N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H]
|
|
| InChi Key |
YQNWZWMKLDQSAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H22N2S/c1-14-7-8-17(15(2)13-14)21-18-6-4-3-5-16(18)20-11-9-19-10-12-20/h3-8,13,19H,9-12H2,1-2H3
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanylphenyl]piperazine
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.38 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (8.38 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 悬浊液; 超声助溶。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.38 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 15% Captisol, pH 9: 10 mg/mL 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3506 mL | 16.7532 mL | 33.5064 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6701 mL | 3.3506 mL | 6.7013 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3351 mL | 1.6753 mL | 3.3506 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Vortioxetine for the Treatment of Hoarding Disorder
CTID: NCT04035850
Phase: Phase 3 Status: Withdrawn
Date: 2024-02-02
 |
|---|
 |
 |