| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
sPLA2 ( Ki = 15 nM ); 5-HT3A Receptor ( Ki = 3.7 nM ); 5-HT7 Receptor ( Ki = 19 nM ); SERT ( Ki = 1.6 nM )
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:Lu-AA21004 抑制重组人 CYP1A2、CYP2C9、CYP2D6 和 CYP3A4,IC50 分别为 40 μM、39 μM、9.8 μM 和 10 μM。 Lu AA21004 是一种 h5-HT1B 受体部分激动剂,基于全细胞 cAMP 的检测,EC50 为 460 nM,内在活性为 22%。 Lu AA21004 与 r5-HT7 受体结合,Ki 值为 200 nM,是 r5-HT7 受体的功能性拮抗剂,在体外全细胞 cAMP 测定中,IC50 为 2 μM。激酶测定:Vortioxetine(化合物 5m)是一种多模式血清素能药物,抑制 5-HT1A、5-HT1B、5-HT3A、5-HT7 受体和 SERT,Ki 值为 15 nM、33 nM、3.7 nM、19 nM 和 1.6分别为nM。沃替西汀对 5-HT3A 和 5-HT7 受体表现出拮抗特性,对 5-HT1B 受体表现出部分激动剂特性,对 5-HT1A 受体表现出激动特性,并对 SERT 具有有效抑制作用。细胞测定:Vortioxetine 是一种 h5-HT1B 受体部分激动剂,基于全细胞 cAMP 测定,EC50 为 460 nM,内在活性为 22%。 Vortioxetine 与 r5-HT7 受体结合的 Ki 值为 200 nM,是 r5-HT7 受体的功能性拮抗剂,在体外全细胞 cAMP 测定中 IC50 为 2 μM。
|
||
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
对于 Lu-AA21004,大鼠的肝脏清除率和口服生物利用度为 7.1 (L/h)/kg 和 16%。 Lu-AA21004(2.5 mg/kg、5 mg/kg 或 10 mg/kg sc)可增加清醒大鼠腹侧海马的细胞外 5-HT 水平。治疗 3 天后,Lu-AA21004(5 mg/kg 或 10 mg/kg sc)还会导致内侧前额皮质 (mPFC) 中 5-HT 基础水平显着升高。 Lu-AA21004在大鼠内侧前额叶皮层中用5mg/kg或10mg/kg治疗3天后,占据SERT的43%和57%。 Lu AA21004 剂量依赖性地占据 5-HT1B 受体,大鼠皮下给药 1 小时后 SERT 的 ED50 分别为 3.2 mg/kg 和 0.4 mg/kg。 Lu AA21004 剂量依赖性地影响大鼠的 Bezold-Jarisch 反射,抑制短暂性心动过缓,ED50 为 0.11 mg/kg。 Lu AA21004 (2.5-10.0 mg/kg sc) 增加大鼠内侧前额皮质和腹侧海马中 5-HT、DA 和 NA 的细胞外水平。 Lu AA21004(5 mg/kg sc)可增加大鼠腹侧海马中 5-HT 的细胞外水平(200%),SERT 占用率为 41%。 Lu AA21004 (7.8 mg/kg sc) 显着减少 FSL 大鼠的不动时间,但不减少 FRL 大鼠的不动时间。 Lu AA21004(8.0 mg/kg po)可增加大鼠的社交互动,并小幅但显着地增加大鼠的运动活动。 Lu AA21004 (7.9 mg/kg sc) 在大鼠条件性恐惧测定中显示出剂量依赖性抗焦虑样作用。沃替西汀 (10 mg/kg) 显着增加雄性 Sprague-Dawley 大鼠采集前 60 分钟的冻结,表明在采集和/或巩固过程中情境记忆形成增强。沃替西汀(5 mg/kg)还会导致保留期间的冻结率增加,这种效应通过事后测试达到了统计显着性。采集前的沃替西汀(2.5 mg/kg 或 5 mg/kg)显示新物体的平均探索时间分别为 29 秒和 33 秒。沃替西汀 (10 mg/kg) 显着降低大鼠的伤害感受,评估为缩爪潜伏期延长。注射后 20 分钟,5 和 10 mg/kg 的沃替西汀使乙酰胆碱水平增加至基线的 224% 和 204%。
|
||
| 酶活实验 |
Vortioxetine (Compound 5m) 是一种多模式血清素能药物,可抑制 SERT,抑制值分别为 1.6 nM、33 nM、3.7 nM、19 nM 以及 5-HT1A、5-HT1B 和 5-HT7 受体。 Vortioxetine 表现出强烈的 SERT 抑制作用以及对 5-HT3A 和 5-HT7 受体的拮抗作用、对 5-HT1B 受体的部分激动作用以及对 5-HT1A 受体的激动作用。
Vortioxetine/化合物5m (Lu AA21004)是先导化合物,对重组人5-HT(1A) (K(i) = 15 nM)、5-HT(1B) (K(i) = 33 nM)、5-HT(3A) (K(i) = 3.7 nM)、5-HT(7) (K(i) = 19 nM)、去甲肾上腺素能β(1) (K(i) = 46 nM)受体和SERT (K(i) = 1.6 nM)具有高亲和力。化合物5m对5-HT(3A)和5-HT(7)受体具有拮抗作用,对5-HT(1B)受体具有部分激动作用,对5-HT(1A)受体具有激动作用,对SERT具有有效抑制作用[1]。 体外SERT和5-HT3受体占用率测定[2] 用载体、氟西汀或沃替西汀(急性给药后1小时或第14次或第21次注射后24小时)处理小鼠的大脑,快速冷冻,用低温恒温器冠状切片,然后装在载玻片上冷冻待用。切片厚度为20 μm,从距bregma正前方约1.2 mm处开始测定SERT受体占用,从距bregma正前方约2.7 mm处开始测定5-HT3受体占用(Franklin and Paxinos, 2008)。在用于放射自显影实验之前,载玻片在- 20°C下保存至少24小时。[2] |
||
| 细胞实验 |
Vortioxetine 是一种 h5-HT1B 受体部分激动剂,在基于 cAMP 的全细胞测定中,EC50 为 460 nM,内在活性为 22%。在体外全细胞 cAMP 测定中,vortioxetine 与 r5-HT7 受体结合,Ki 值为 200 nM,并且是 r5-HT7 受体的功能性拮抗剂,IC50 为 2 μM。
SERT占用率评估[2] 载玻片在含有4.5 nM [3H]-escitalopram的缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, pH = 7.4)中室温孵育60 min。用1 μM艾司西酞普兰检测非特异性结合。载玻片在冷缓冲液中短暂洗涤,干燥,并在Beta成像仪中暴露16小时。SERT检测的感兴趣区域(ROI)包括外侧和内侧隔膜、伏隔核和嗅结节。SERT检测的ROI示例图像可以在补充图2A中找到。 5-HT3受体占用率的评价[2] 载玻片在由50 mM Tris和150 mM NaCl组成的缓冲液中预孵育5分钟。载玻片在空气流下干燥30-45分钟。随后,载玻片在含有1 nM [3H]LY278584的缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM KCl, pH = 7.4)中室温孵育60分钟。用1 μM昂丹司琼测定非特异性结合。载玻片在冷缓冲液中短暂洗涤,干燥,并在Beta成像仪中暴露24小时。5-HT3受体占用试验的ROI由海马组成。5-HT3受体占用测定的示例图像可以在补充图2B中找到。 |
||
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
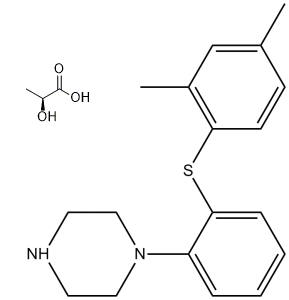
Vortioxetine is an N-arylpiperazine in which the aryl group is specified as 2-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanyl]phenyl. Used (as its hydrobromide salt) for treatment of major depressive disorder. It has a role as an antidepressant, an anxiolytic drug, a serotonergic agonist and a serotonergic antagonist. It is a N-arylpiperazine and an aryl sulfide. It is a conjugate base of a vortioxetine(1+).
Vortioxetine is an antidepressant medication indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). It is classified as a serotonin modulator and stimulator (SMS) as it has a multimodal mechanism of action towards the serotonin neurotransmitter system whereby it simultaneously modulates one or more serotonin receptors and inhibits the reuptake of serotonin. More specifically, vortioxetine acts via the following biological mechanisms: as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) through inhibition of the serotonin transporter, as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1B receptor, an agonist of 5-HT1A, and an antagonist of the 5-HT3, 5-HT1D, and 5-HT7 receptors. SMSs were developed because there are many different subtypes of serotonin receptors, however, not all of these receptors appear to be involved in the antidepressant effects of SRIs. Some serotonin receptors seem to play a relatively neutral or insignificant role in the regulation of mood, but others, such as 5-HT1A autoreceptors and 5-HT7 receptors, appear to play an oppositional role in the efficacy of SRIs in treating depression. Vortioxetine is a serotonergic antidepressant used for major depression disorders. Vortioxetine has been associated with a low rate of minor serum aminotransferase elevations during treatment, but has not been linked to instances of clinically apparent acute liver injury. A piperazine derivative that acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor, as a 5-HT3 receptor antagonist, and 5-HT1A receptor agonist. It is used for the treatment of anxiety and depression. Vortioxetine (Lu AA21004) is an investigational novel antidepressant with multimodal activity that functions as a 5-HT3, 5-HT7 and 5-HT(1D) receptor antagonist, 5-HT(1B) receptor partial agonist, 5-HT(1A) receptor agonist and inhibitor of the 5-HT transporter in vitro. Here we explore its anxiolytic and antidepressant potential in adult mice. Vortioxetine was assessed in BalB/cJ@RJ mice using the open-field and forced-swim tests (acute: p.o. 1 h, repeated: daily p.o. 21 days), and in 129S6/SvEvTac mice using the novelty suppressed feeding paradigm (acute: p.o. 1 h, sustained: daily p.o. 14 or 21 days). Fluoxetine and diazepam were controls. Acute and repeated dosing of vortioxetine produced more pronounced anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like activities than fluoxetine. Vortioxetine significantly increased cell proliferation and cell survival and stimulated maturation of immature granule cells in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus after 21 days of treatment. After 14 days, a high dose of vortioxetine increased dendritic length and the number of dendrite intersections, suggesting that vortioxetine accelerates the maturation of immature neurons. Vortioxetine displays an antidepressant and anxiolytic profile following repeated administration associated with increased neurogenesis at several stages. Vortioxetine effects were observed at low levels of 5-HT transporter occupancy, suggesting an alternative mechanism of action to 5-HT reuptake inhibition.[2] View MoreThe aim of this study was to assess the effects of a novel antidepressant, vortioxetine 10 mg, on driving, cognitive, and psychomotor performance in 24 healthy subjects in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, three-way crossover design. Mirtazapine 30 mg was included as an active comparator. Drugs were administered in the evening of 15 consecutive days. Performance was measured in the morning of days 2 and 16, using standardized tests measuring on-the-road driving, memory, tracking, divided attention, and vigilance. The statistical analysis on the primary measure of driving, i.e., SD of lateral position showed noninferiority of vortioxetine on days 2 and 16, and inferiority for mirtazapine on day 2. Vortioxetine did not cause cognitive or psychomotor impairment. Mirtazapine, however, impaired cognitive and psychomotor performance on day 2. Most of these effects disappeared after multiple doses of mirtazapine. To conclude, vortioxetine did not impair driving, cognitive, or psychomotor performance after single or multiple doses.[3] Pharmacodynamics Vortioxetine binds with high affinity to the human serotonin transporter (Ki=1.6 nM), but not to the norepinephrine (Ki=113 nM) or dopamine (Ki>1000 nM) transporters. Vortioxetine potently and selectively inhibits reuptake of serotonin by inhibition of the serotonin transporter (IC50=5.4 nM). Specifically, vortioxetine binds to 5HT3 (Ki=3.7 nM), 5HT1A (Ki=15 nM), 5HT7 (Ki=19 nM), 5HT1D (Ki=54 nM), and 5HT1B (Ki=33 nM), receptors and is a 5HT3, 5HT1D, and 5HT7 receptor antagonist, 5HT1B receptor partial agonist, and 5HT1A receptor agonist. Absorption The maximal plasma vortioxetine concentration (Cmax) after dosing is reached within 7 to 11 hours postdose. Absolute bioavailability is 75%. No effect of food on the pharmacokinetics was observed. Route of Elimination Following a single oral dose of [14C]labeled vortioxetine, approximately 59% and 26% of the administered radioactivity was recovered in the urine and feces, respectively as metabolites. Negligible amounts of unchanged vortioxetine were excreted in the urine up to 48 hours. Volume of Distribution The apparent volume of distribution of vortioxetine is approximately 2600 L, indicating extensive extravascular distribution. Metabolism / Metabolites Vortioxetine is extensively metabolized primarily through oxidation via cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2A6, CYP2C8 and CYP2B6 and subsequent glucuronic acid conjugation. CYP2D6 is the primary enzyme catalyzing the metabolism of vortioxetine to its major, pharmacologically inactive, carboxylic acid metabolite, and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 have approximately twice the vortioxetine plasma concentration of extensive metabolizers. NIH; DailyMed. Current Medication Information for Brintellix (Vortioxetine Hydrobromide) Tablet, Film Coated (Updated: July 2014). Available from, as of June 30, 2015: https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=4b0700c9-b417-4c3a-b36f-de461e125bd3 All metabolites detected in human hepatocytes were also present in dogs, mice and rats (plasma and/or urine) in vivo, except for a glucuronide conjugate of monohydroxy-Vortioxetine which was not found in mice or rats. Among all species tested, rabbit hepatocytes appeared to have the metabolite profile closer to human hepatocyte metabolite profile. Biological Half-Life Mean terminal halflife is approximately 66 hours The oral absolute bioavailability was approximately 10% in the rat, 48% in the dog and 75% in patients, with terminal elimination half-life values of 3.0, 7.9 and 66 hours, respectively. Mechanism of Action Vortioxetine is classified as a serotonin modulator and simulator (SMS) as it has a multimodal mechanism of action towards the serotonin neurotransmitter system whereby it simultaneously modulates one or more serotonin receptors and inhibits the reuptake of serotonin. More specifically, vortioxetine acts via the following biological mechanisms: as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) through inhibition of the serotonin transporter, while also acting as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1B receptor, an agonist of 5-HT1A, and antagonist of the 5-HT3, 5-HT1D, and 5-HT7 receptors. 1-(2-(2,4-Dimethylphenyl-sulfanyl)-phenyl)-piperazine (Lu AA21004) is a human (h) serotonin (5-HT)(3A) receptor antagonist (K(i) = 3.7 nM), h5-HT(7) receptor antagonist (K(i) = 19 nM), h5-HT(1B) receptor partial agonist (K(i) = 33 nM), h5-HT(1A) receptor agonist (K(i) = 15 nM), and a human 5-HT transporter (SERT) inhibitor (K(i) = 1.6 nM) (J Med Chem 54:3206-3221, 2011). Here, we confirm that Lu AA21004 is a partial h5-HT(1B) receptor agonist [EC(50) = 460 nM, intrinsic activity = 22%] using a whole-cell cAMP-based assay and demonstrate that Lu AA21004 is a rat (r) 5-HT(7) receptor antagonist (K(i) = 200 nM and IC(50) = 2080 nM). In vivo, Lu AA21004 occupies the r5-HT(1B) receptor and rSERT (ED(50) = 3.2 and 0.4 mg/kg, respectively) after subcutaneous administration and is a 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist in the Bezold-Jarisch reflex assay (ED(50) = 0.11 mg/kg s.c.). In rat microdialysis experiments, Lu AA21004 (2.5-10.0 mg/kg s.c.) increased extracellular 5-HT, dopamine, and noradrenaline in the medial prefrontal cortex and ventral hippocampus. Lu AA21004 (5 mg/kg per day for 3 days; minipump subcutaneously), corresponding to 41% rSERT occupancy, significantly increased extracellular 5-HT in the ventral hippocampus. Furthermore, the 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist, ondansetron, potentiated the increase in extracellular levels of 5-HT induced by citalopram. Lu AA21004 has antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like effects in the rat forced swim (Flinders Sensitive Line) and social interaction and conditioned fear tests (minimal effective doses: 7.8, 2.0, and 3.9 mg/kg). In conclusion, Lu AA21004 mediates its pharmacological effects via two pharmacological modalities: SERT inhibition and 5-HT receptor modulation. In vivo, this results in enhanced release of several neurotransmitters and antidepressant- and anxiolytic-like profiles at doses for which targets in addition to the SERT are occupied. The multimodal activity profile of Lu AA21004 is distinct from that of current antidepressants. The monoaminergic network, including serotonin (5-HT), norepinephrine (NE), and dopamine (DA) pathways, is highly interconnected and has a well-established role in mood disorders. Preclinical research suggests that 5-HT receptor subtypes, including 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT3, and 5-HT7 receptors as well as the 5-HT transporter (SERT), may have important roles in treating depression. This study evaluated the neuropharmacological profile of Lu AA21004, a novel multimodal antidepressant combining 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 receptor antagonism, 5-HT1B receptor partial agonism, 5-HT1A receptor agonism, and SERT inhibition in recombinant cell lines. Extracellular 5-HT, NE and DA levels were evaluated in the ventral hippocampus (vHC), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) and nucleus accumbens (NAc) after acute and subchronic treatment with Lu AA21004 or escitalopram. The acute effects of LuAA21004 on NE and DA neuronal firing were also evaluated in the locus coeruleus (LC) and ventral tegmental area (VTA), respectively. Acute Lu AA21004 dose-dependently increased 5-HT in the vHC, mPFC and NAc. Maximal 5-HT levels in the vHC were higher than those in the mPFC. Furthermore, mPFC 5-HT levels were increased at low SERT occupancy levels. In the vHC and mPFC, but not the NAc, high Lu AA21004 doses increased NE and DA levels. Lu AA21004 slightly decreased LC NE neuronal firing and had no effect on VTA DA firing. Results are discussed in context of occupancy at 5-HT3, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1A receptors and SERT. In conclusion, Lu AA21004, acting via two pharmacological modalities, 5-HT receptor modulation and SERT inhibition, results in a brain region-dependent increase of multiple neurotransmitter concentrations. and ECNP. All rights reserved. PMID:22612991 PMID:22612991 Pehrson AL et al; Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 23 (2): 133-45 (2013) Vortioxetine, a novel antidepressant with multimodal action, is a serotonin (5-HT)3, 5-HT7 and 5-HT1D receptor antagonist, a 5-HT1B receptor partial agonist, a 5-HT1A receptor agonist and a 5-HT transporter (SERT) inhibitor. Vortioxetine has been shown to improve cognitive performance in several preclinical rat models and in patients with major depressive disorder. Here we investigated the mechanistic basis for these effects by studying the effect of vortioxetine on synaptic transmission, long-term potentiation (LTP), a cellular correlate of learning and memory, and theta oscillations in the rat hippocampus and frontal cortex. Vortioxetine was found to prevent the 5-HT-induced increase in inhibitory post-synaptic potentials recorded from CA1 pyramidal cells, most likely by 5-HT3 receptor antagonism. Vortioxetine also enhanced LTP in the CA1 region of the hippocampus. Finally, vortioxetine increased fronto-cortical theta power during active wake in whole animal electroencephalographic recordings. In comparison, the selective SERT inhibitor escitalopram showed no effect on any of these measures. Taken together, our results indicate that vortioxetine can increase pyramidal cell output, which leads to enhanced synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Given the central role of the hippocampus in cognition, these findings may provide a cellular correlate to the observed preclinical and clinical cognition-enhancing effects of vortioxetine. Clinical Laboratory Methods In this work, a simple, sensitive and fast ultra performance liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method was developed and validated for the quantitative determination of vortioxetine in rat plasma. Plasma samples were processed with a protein precipitation. The separation was achieved by an Acquity UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1mmx50mm, 1.7um) column with a gradient mobile phase consisting of 0.1% formic acid in water and acetonitrile. Detection was carried out using positive-ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry via multiple reaction monitoring (MRM). The validated method had an excellent linearity in the range of 0.05-20ng/mL (R2>0.997) with a lower limit of quantification (0.05ng/mL). The extraction recovery was in the range of 78.3-88.4% for vortioxetine and 80.3% for carbamazepine (internal standard, IS). The intra- and inter-day precision was below 8.5% and accuracy was from -11.2% to 9.5%. No notable matrix effect and astaticism was observed for vortioxetine. The method has been successfully applied to a pharmacokinetic study of vortioxetine in rats for the first time, which provides the basis for the further development and application of vortioxetine. PMID:26094207 Gu EM et al; J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 997: 70-74 (2015) Toxicity Summary IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Vortioxetine is a white to very slightly beige powder formulated into film-coated tablets. It is used for the management of major depressive disorders in adults. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: There is limited clinical trial experience regarding human overdosage with vortioxetine. In pre-marketing clinical studies, cases of overdose were limited to patients who accidentally or intentionally consumed up to a maximum dose of 40 mg of vortioxetine. The maximum single dose tested was 75 mg in men. Ingestion of vortioxetine in the dose range of 40 to 75 mg was associated with increased rates of nausea, dizziness, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, generalized pruritus, somnolence, and flushing. Toxicity may also occur at therapeutic dosage levels of vortioxetine. Potentially life-threatening serotonin syndrome has been reported with serotonergic antidepressants, including vortioxetine, when used alone, but particularly with concurrent use of other serotonergic drugs (including serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) type 1 receptor agonists ("triptans"), tricyclic antidepressants, buspirone, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, and St. John's wort (Hypericum perforatum)) and with drugs that impair the metabolism of serotonin (particularly monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, both those used to treat psychiatric disorders and others, such as linezolid and methylene blue). Manifestations of serotonin syndrome may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, and hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, and incoordination), seizures, and/or GI symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea). Concurrent or recent (i.e., within 2 weeks) therapy with MAO inhibitors intended to treat psychiatric disorders is contraindicated. Use of an MAO inhibitor intended to treat psychiatric disorders within 3 weeks of vortioxetine discontinuance also is contraindicated. Vortioxetine also should not be initiated in patients who are being treated with other MAO inhibitors such as linezolid or IV methylene blue. If concurrent therapy with vortioxetine and other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, the patient should be made aware of the potential increased risk for serotonin syndrome, particularly during initiation of therapy or when dosage is increased. Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies. These studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior with antidepressant use in patients over age 24; there was a trend toward reduced risk with antidepressant use in patients aged 65 and older. Vortioxetine was not genotoxic in an in vitro chromosome aberration assay in cultured human lymphocytes. ANIMAL STUDIES: The acute oral single dose toxicity of vortioxetine is relatively low with a maximum tolerated dose (MTD) in mice and rats of 300 and 500 mg/kg, respectively. Clinical signs consisted of marked sensitivity to touch and disturbance, rapid breathing, and brown perinasal staining in rats administered 500 mg/kg. In mice, tremors, sensitivity to touch, eyes partly closed, and hypoactivity were seen after 200 and 300 mg/kg, as well as rapid, noisy and/or labored breathing, incoordination, unsteady gait, leaning, salivation, and hyperactivity after 400 and 500 mg/kg. When administered as two vortioxetine doses given an hour apart (200 mg/kg), clinical signs included convulsions, and resulted in death. Carcinogenicity studies were conducted in which mice and rats were given oral doses of vortioxetine up to 50 and 100 mg/kg/day for male and female mice, respectively, and 40 and 80 mg/kg/day for male and female rats, respectively, for 2 years. In rats, the incidence of benign polypoid adenomas of the rectum was statistically significantly increased in females. These were considered related to inflammation and hyperplasia and possibly caused by an interaction with a vehicle component of the formulation used for the study. The finding did not occur in male rats. In mice, vortioxetine was not carcinogenic in males or females. Vortioxetine caused developmental delays when administered during pregnancy to rats and rabbits. Developmental delays were also seen after birth in rats treated with vortioxetine during pregnancy and through lactation. There were no teratogenic effects in rats or rabbits treated with the drug during organogenesis. Treatment of rats with vortioxetine at doses up to 120 mg/kg/day had no effect on male or female fertility. Vortioxetine was not genotoxic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) and in the in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay. Hepatotoxicity Liver test abnormalities occur in a small proportion of patients (Likelihood score: E* (unproven but suspected rare cause of clinically apparent liver injury). Protein Binding The plasma protein binding of vortioxetine in humans is 98%, independent of plasma concentrations. No apparent difference in the plasma protein binding between healthy subjects and subjects with hepatic (mild, moderate) or renal (mild, moderate, severe, ESRD) impairment is observed. |
| 分子式 |
C21H28N2O3S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
388.523624420166
|
|
| 精确质量 |
388.18
|
|
| CAS号 |
1253056-29-9
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
75293775
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Typically exists as solid at room temperature
|
|
| tPSA |
98.1Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
27
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
375
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
KJXWEKCEAVJWHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H22N2S.C3H6O3/c1-14-7-8-17(15(2)13-14)21-18-6-4-3-5-16(18)20-11-9-19-10-12-20;1-2(4)3(5)6/h3-8,13,19H,9-12H2,1-2H3;2,4H,1H3,(H,5,6)
|
|
| 化学名 |
1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanylphenyl]piperazine;2-hydroxypropanoic acid
|
|
| 别名 |
Vortioxetine lactate; Vortioxetine DL-lactate; Vortioxetine-DL-lactate; UNII-V39BK25ME9; V39BK25ME9; 1253056-29-9; Vortioxetine lactate [WHO-DD]; Q27291485
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
注意: 如下所列的是一些常用的体内动物实验溶解配方,主要用于溶解难溶或不溶于水的产品(水溶度<1 mg/mL)。 建议您先取少量样品进行尝试,如该配方可行,再根据实验需求增加样品量。
注射用配方
注射用配方1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline)(IP/IV/IM/SC等) *生理盐水/Saline的制备:将0.9g氯化钠/NaCl溶解在100 mL ddH ₂ O中,得到澄清溶液。 注射用配方 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 400 μL PEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) 注射用配方 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (如: 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) 示例: 以注射用配方 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) 为例说明, 如果要配制 1 mL 2.5 mg/mL的工作液, 您可以取 100 μL 25 mg/mL 澄清的 DMSO 储备液,加到 900 μL Corn oil/玉米油中, 混合均匀。 View More
注射用配方 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline = 10 : 90 [如:100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline)] 口服配方
口服配方 1: 悬浮于0.5% CMC Na (羧甲基纤维素钠) 口服配方 2: 悬浮于0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose (羧甲基纤维素) 示例: 以口服配方 1 (悬浮于 0.5% CMC Na)为例说明, 如果要配制 100 mL 2.5 mg/mL 的工作液, 您可以先取0.5g CMC Na并将其溶解于100mL ddH2O中,得到0.5%CMC-Na澄清溶液;然后将250 mg待测化合物加到100 mL前述 0.5%CMC Na溶液中,得到悬浮液。 View More
口服配方 3: 溶解于 PEG400 (聚乙二醇400) 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5739 mL | 12.8694 mL | 25.7387 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5148 mL | 2.5739 mL | 5.1477 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2574 mL | 1.2869 mL | 2.5739 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05814640 | Recruiting | Drug: Vortioxetine Drug: Duloxetine |
Depression Sequestra |
First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University |
February 20, 2023 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT04818099 | Recruiting | Drug: Vortioxetine 10 mg Other: Placebo |
Radiation Injuries | Sun Yat-Sen Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-Sen University |
October 10, 2020 | Phase 3 |
| NCT04301492 | Recruiting | Drug: Vortioxetine | Depression | IRCCS San Raffaele Roma | November 20, 2019 | Phase 4 |
| NCT02357797 | Active Recruiting |
Other: Placebo Drug: Vortioxetine |
Schizophrenia Negative Symptoms |
Northwell Health | February 2016 | Phase 4 |
| NCT06025474 | Recruiting | Drug: Vortioxetine 20Mg Tab Drug: Sertraline 50 MG |
Burning Mouth Syndrome | Federico II University | January 1, 2023 | Phase 3 |
 |
|---|
|
 |