| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Human Endogenous Metabolite
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在饥饿的 U2OS 细胞中,乙酰辅酶 A 三钠促进细胞质蛋白乙酰化,同时减少饥饿诱导的自噬通量。 (稳定表达 GFP-LC3 的 U2OS 细胞显微注射乙酰辅酶 A 三钠;然后在缺乏营养物的情况下用 100 nM BafA1 培养,三小时后固定)[2]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在小鼠心脏压力超负荷模型中,乙酰辅酶 A 三钠通过抑制适应不良的自噬来减轻压力超负荷引起的心肌病[2][3]。小鼠一整天不进食(但允许无限量饮水),其心脏和肌肉中总乙酰辅酶 A 三钠的水平显着降低,这与较低水平的蛋白质乙酰化相关。然而,相同的实验设置实际上提高了蛋白质乙酰化和乙酰辅酶 A 三钠的肝脏水平,同时对大脑中酶的浓度没有明显影响[4]。
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Acetyl CoA participates in the biosynthesis of fatty acids and sterols, in the oxidation of fatty acids and in the metabolism of many amino acids. It also acts as a biological acetylating agent.
Lysine acetylation is a conserved protein post-translational modification that links acetyl-coenzyme A metabolism and cellular signalling. Recent advances in the identification and quantification of lysine acetylation by mass spectrometry have increased our understanding of lysine acetylation, implicating it in many biological processes through the regulation of protein interactions, activity and localization. In addition, proteins are frequently modified by other types of acylations, such as formylation, butyrylation, propionylation, succinylation, malonylation, myristoylation, glutarylation and crotonylation. The intricate link between lysine acylation and cellular metabolism has been clarified by the occurrence of several such metabolite-sensitive acylations and their selective removal by sirtuin deacylases. These emerging findings point to new functions for different lysine acylations and deacylating enzymes and also highlight the mechanisms by which acetylation regulates various cellular processes.[1] Acetyl-coenzyme A (AcCoA) is a major integrator of the nutritional status at the crossroads of fat, sugar, and protein catabolism. Here we show that nutrient starvation causes rapid depletion of AcCoA. AcCoA depletion entailed the commensurate reduction in the overall acetylation of cytoplasmic proteins, as well as the induction of autophagy, a homeostatic process of self-digestion. Multiple distinct manipulations designed to increase or reduce cytosolic AcCoA led to the suppression or induction of autophagy, respectively, both in cultured human cells and in mice. Moreover, maintenance of high AcCoA levels inhibited maladaptive autophagy in a model of cardiac pressure overload. Depletion of AcCoA reduced the activity of the acetyltransferase EP300, and EP300 was required for the suppression of autophagy by high AcCoA levels. Altogether, our results indicate that cytosolic AcCoA functions as a central metabolic regulator of autophagy, thus delineating AcCoA-centered pharmacological strategies that allow for the therapeutic manipulation of autophagy.[2] Cardiac hypertrophy is a major predictor of heart failure and a prevalent disorder with high mortality. Little is known, however, regarding mechanisms governing the transition from stable cardiac hypertrophy to decompensated heart failure. Here, we tested the role of autophagy, a conserved pathway mediating bulk degradation of long-lived proteins and cellular organelles that can lead to cell death. To quantify autophagic activity, we engineered a line of "autophagy reporter" mice and confirmed that cardiomyocyte autophagy can be induced by short-term nutrient deprivation in vivo. Pressure overload induced by aortic banding induced heart failure and greatly increased cardiac autophagy. Load-induced autophagic activity peaked at 48 hours and remained significantly elevated for at least 3 weeks. In addition, autophagic activity was not spatially homogeneous but rather was seen at particularly high levels in basal septum. Heterozygous disruption of the gene coding for Beclin 1, a protein required for early autophagosome formation, decreased cardiomyocyte autophagy and diminished pathological remodeling induced by severe pressure stress. Conversely, Beclin 1 overexpression heightened autophagic activity and accentuated pathological remodeling. Taken together, these findings implicate autophagy in the pathogenesis of load-induced heart failure and suggest it may be a target for novel therapeutic intervention.[3] Acetyl-coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) is a central metabolic intermediate. The abundance of acetyl-CoA in distinct subcellular compartments reflects the general energetic state of the cell. Moreover, acetyl-CoA concentrations influence the activity or specificity of multiple enzymes, either in an allosteric manner or by altering substrate availability. Finally, by influencing the acetylation profile of several proteins, including histones, acetyl-CoA controls key cellular processes, including energy metabolism, mitosis, and autophagy, both directly and via the epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Thus, acetyl-CoA determines the balance between cellular catabolism and anabolism by simultaneously operating as a metabolic intermediate and as a second messenger.[4] |
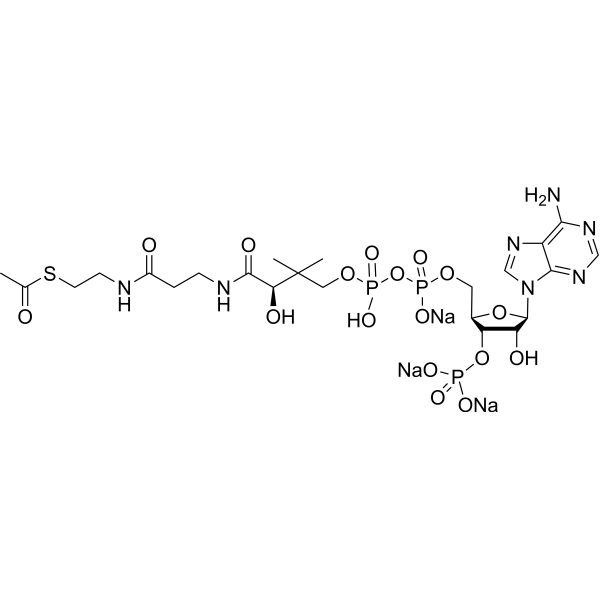
| 分子式 |
C23H35N7NA3O17P3S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
875.52
|
| 精确质量 |
809.125
|
| CAS号 |
102029-73-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Acetyl coenzyme A lithium;32140-51-5;Acetyl coenzyme A;72-89-9
|
| PubChem CID |
6302
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 折射率 |
1.718
|
| LogP |
-3.89
|
| tPSA |
418.36
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
9
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
22
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
20
|
| 重原子数目 |
51
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
1380
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
O[C@@H]1[C@@H]([C@@H](COP(O)(=O)OP(O)(=O)OCC(C)(C)[C@@H](O)C(=O)NCCC(=O)NCCSC(=O)C)O[C@H]1N1C=NC2C(=NC=NC1=2)N)OP(O)(O)=O.[Na+].[Na+].[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
ZSLZBFCDCINBPY-KMYLAXNMSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C23H38N7O17P3S/c1-12(31)51-7-6-25-14(32)4-5-26-21(35)18(34)23(2,3)9-44-50(41,42)47-49(39,40)43-8-13-17(46-48(36,37)38)16(33)22(45-13)30-11-29-15-19(24)27-10-28-20(15)30/h10-11,13,16-18,22,33-34H,4-9H2,1-3H3,(H,25,32)(H,26,35)(H,39,40)(H,41,42)(H2,24,27,28)(H2,36,37,38)/t13-,16-,17-,18?,22-/m1/s1
|
| 化学名 |
S-[2-[3-[[4-[[[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-phosphonooxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-2-hydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]ethyl] ethanethioate
|
| 别名 |
Acetyl coenzyme A sodium salt; 102029-73-2; Coenzyme A, S-acetate, trisodium salt (9CI); Acetyl Coenzyme A Trisodium Salt; Acetyl-CoA sodium; XGCDESRMLMCTPI-UHFFFAOYSA-N;
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : 83.33 mg/mL (95.18 mM)
DMSO : < 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (114.22 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1422 mL | 5.7109 mL | 11.4218 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2284 mL | 1.1422 mL | 2.2844 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1142 mL | 0.5711 mL | 1.1422 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。