| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| 25g |
|
||
| 50g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 靶点 |
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (M1-M5) and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) [1]
- Acetylcholine receptors on cultured sweat gland epithelial cells (subtype unspecified) [3] - Receptors mediating proinflammatory cytokine regulation in sepsis-related cell models (subtype unspecified) [4] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
无钙心肌中汗腺上皮细胞荧光值和细胞内游离钙降低,而高钙心肌中氯化心脏胆碱(ACh氯化物;10μM)钙通道、荧光值和细胞内游离钙显着升高[3]。
用氯化乙酰胆碱(10⁻⁸ M 至 10⁻⁴ M)处理培养的汗腺上皮细胞,可诱导胞内钙浓度([Ca²⁺]i)呈浓度依赖性升高;该反应可被毒蕈碱受体拮抗剂部分抑制,提示毒蕈碱受体参与介导 [3] - 氯化乙酰胆碱(5 mM、10 mM)在体外可抑制p53突变肽的聚集,10 mM浓度时最大抑制率约为40%;动态光散射分析显示,处理后p53突变肽聚集体的平均粒径减小 [5] - 无直接体外促炎或抗炎细胞因子产生相关作用报道,相关活性仅在体内脓毒症模型中观察到 [4] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在小鼠中,氯化乙酰胆碱(ACh氯化物;SC;20 mg/kg;单剂量)显着增加胆碱能刺激和发病率[4]。
在盲肠结扎穿孔(CLP)诱导的小鼠脓毒症模型中,CLP后30分钟腹腔注射氯化乙酰胆碱(10 μg/kg),可显著降低72小时内的死亡率(死亡率从约80%降至约40%)[4] - 与未处理的脓毒症对照组相比,脓毒症小鼠经氯化乙酰胆碱处理后,血清中肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)和白细胞介素-6(IL-6)等促炎细胞因子水平降低 [4] - 在饥饿大鼠(禁食72小时)中,可观察到回肠高分泌现象,给予氯化乙酰胆碱可增强胆碱能介导的肠道分泌,表现为回肠液体和电解质排泄增加 [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
毒蕈碱型乙酰胆碱受体结合实验:从相关组织中制备含M1-M5受体的膜组分,将其与不同浓度的氯化乙酰胆碱在放射性标记乙酰胆碱激动剂存在下共同孵育。孵育后通过过滤去除未结合配体,检测结合组分的放射性,以确定结合亲和力和特异性 [1]
- 烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体结合实验:从神经或肌肉组织中纯化烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体,将其与氯化乙酰胆碱及荧光标记的烟碱拮抗剂混合。通过荧光偏振法监测结合反应,利用氯化乙酰胆碱对标记拮抗剂的置换作用计算结合参数 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
培养汗腺上皮细胞钙浓度检测实验:将汗腺上皮细胞接种于培养板,加载钙敏感荧光探针。稳定后,加入浓度为10⁻⁸ M 至 10⁻⁴ M的氯化乙酰胆碱,连续5-10分钟检测荧光强度,评估胞内钙浓度变化。同时设置毒蕈碱受体拮抗剂处理组,验证受体亚型的介导作用 [3]
- p53突变肽聚集抑制实验:将重组p53突变肽溶解于缓冲液,加入氯化乙酰胆碱使其终浓度达到5 mM和10 mM。混合物在37°C孵育24小时后,通过动态光散射法检测粒径分布,采用SDS-PAGE检测聚集体形成情况 [5] |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Male and female inbred albino mice weighing 18-22 grams (sepsis) [4]
Doses: 20 mg/kg Route of Administration: subcutaneous injection; single dose Experimental Results: Dramatically diminished intraperitoneal (ip) injection of 2×109 large intestine Mortality of mice with sepsis caused by bacilli and blood levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6. Mouse sepsis model: Male mice were anesthetized, and sepsis was induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). Thirty minutes after CLP, Acetylcholine Chloride was administered via intraperitoneal injection at a dose of 10 μg/kg. Control groups received equal volumes of normal saline. Mice were monitored for mortality over 72 hours, and serum samples were collected at 24 hours post-CLP to measure proinflammatory cytokine levels [4] - Rat starvation-induced ileal hypersecretion model: Male rats were fasted for 72 hours to induce ileal hypersecretion. The ileum was excised and mounted in Ussing chambers, then Acetylcholine Chloride was added to the mucosal or serosal side of the ileal tissue at unspecified concentrations. Transepithelial electrical resistance and short-circuit current were measured to evaluate intestinal secretion function [2] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
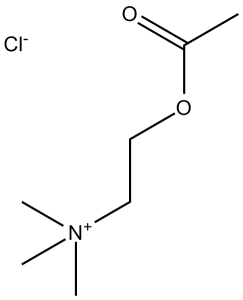
Acetylcholine chloride is the chloride salt of acetylcholine, and a parasympatomimetic drug. It contains an acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine Chloride is the chloride salt form of acetylcholine, a synthetic, quaternary amino alcohol with cholinergic properties. Acetylcholine chloride mimics the parasympathomimetic effect of the endogenous compound acetylcholine. Administered as an ophthalmic solution, this drug stimulates the cholinoceptors in the sphincter muscle of the iris, causing the pupil to constrict. (NCI05) A neurotransmitter found at neuromuscular junctions, autonomic ganglia, parasympathetic effector junctions, a subset of sympathetic effector junctions, and at many sites in the central nervous system. See also: Acetylcholine (has active moiety); Chloride Ion (has part); Acetylcholine Chloride; Histamine; Serotonin (component of) ... View More ... Acetylcholine Chloride is an endogenous neurotransmitter that acts as a ligand for cholinergic receptors (muscarinic and nicotinic subtypes) to mediate signal transmission in the central and peripheral nervous systems [1] - Its biological functions include regulating glandular secretion (e.g., sweat gland, intestinal gland), smooth muscle contraction, neurotransmission, and immune response modulation [1][3][2][4] - As a cationic osmolyte, Acetylcholine Chloride exhibits the ability to inhibit protein aggregation, which may have potential implications for diseases associated with abnormal protein aggregation [5] - The cholinergic system, with Acetylcholine Chloride as the key mediator, plays a crucial role in maintaining intestinal epithelial barrier function and regulating inflammatory responses [1][2][4] |
| 分子式 |
C7H16NO2.CL
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
181.66
|
|
| 精确质量 |
181.086
|
|
| CAS号 |
60-31-1
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Acetylcholine iodide;2260-50-6;Acetylcholine bromide;66-23-9;Acetylcholine-d4 chloride;344298-94-8;Acetylcholine-d9 chloride;344298-95-9
|
|
| PubChem CID |
6060
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 熔点 |
146-150 °C(lit.)
|
|
| tPSA |
26.3
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
11
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
115
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
|
| InChi Key |
JUGOREOARAHOCO-UHFFFAOYSA-M
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C7H16NO2.ClH/c1-7(9)10-6-5-8(2,3)4;/h5-6H2,1-4H3;1H/q+1;/p-1
|
|
| 化学名 |
2-acetyloxyethyl(trimethyl)azanium;chloride
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (11.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (11.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 20.8 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (11.45 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 23.33 mg/mL (128.43 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.5048 mL | 27.5239 mL | 55.0479 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.1010 mL | 5.5048 mL | 11.0096 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5505 mL | 2.7524 mL | 5.5048 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT06219590 | Recruiting | Procedure: Acetylcholine Iontophoresis Procedure: Shame Acetylcholine Iontophoresis |
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Peripheral Neuropathy |
South Valley University | October 28, 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT01137656 | Completed | Drug: Acetylcholine and Blood | Healthy | Mark Gladwin | April 2010 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03636100 | Terminated | Device: Cryoballoon ablation | Atrial Fibrillation | Saint Luke's Health System | August 15, 2018 | |
| NCT05618132 | Recruiting | Diagnostic Test: Acetylcholine rechallenge | Angina Pectoris, Variant Angina Pectoris; Spasm-Induced Angina Pectoris With Normal Coronary Arteriogram | University Hospital, Antwerp | January 9, 2023 | Not Applicable |
| NCT06180252 | Completed | Diagnostic Test: PET with 11C MP4 | Alzheimer Disease | IRCCS San Raffaele | May 12, 2004 |