| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
ETA (IC50 = 3.4 nM); ETA (pA2 = 6.7); ETB (IC50 = 987 nM); ETB (pA2 = 5.5)
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
当应用于非重组细胞(主要人肺平滑肌细胞、大鼠主动脉平滑肌细胞系 A10 和小鼠成纤维细胞系 3T3)时,aproticentan (ACT-132577) 完全抑制 ET-1 引起的细胞内钙升高[1]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在大鼠中,aprobicitentan (ACT-132577) 比其母体化学物质具有更长的半衰期,并且分布体积大于血浆体积[1]。 Aprocitentan (ACT-132577) 在大鼠血浆中的平均回收率范围为 82.6% 至 90.6%,而 Aprocitentan (ACT-132577) 在大鼠血浆中的基质效应范围为 101.4% 至 115.2%[2]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
Macitentan,也被称为Actelion-1或ACT-064992 [N-[5-(4-溴苯基)-6-(2-(5-溴嘧啶-2-氧基)乙氧基)-嘧啶-4-基]-N'-丙基氨基磺酰胺],是一种新型的ET(a)/ET(B)内皮素(ET)受体双拮抗剂,用于组织靶向。马西坦的选择是基于对ET受体的抑制效力和优化物理化学性质,以达到对亲脂环境的高亲和力。在体内,马西坦被代谢成一种主要的、具有药理活性的代谢物ACT-132577。马西坦及其代谢物可拮抗ET-1在过表达ET(A)和ET(B)受体的细胞膜上的特异性结合,并在多种天然细胞系中减弱ET-1诱导的钙动员,抑制常数在纳摩尔范围内。在功能试验中,马西坦和ACT-132577抑制ET-1诱导的离体内皮剥离大鼠主动脉(ET(A)受体)收缩和萨拉福毒素s6c诱导的离体大鼠气管(ET(B)受体)收缩。在肺动脉高压大鼠中,马西坦既能抑制肺动脉压升高,又能抑制右心室肥厚,显著提高生存率。在糖尿病大鼠中,长期给药马西坦可以降低血压和蛋白尿,防止终末器官损伤(肾血管肥大和结构损伤)。综上所述,马西坦通过其组织靶向特性和对ET受体的双重拮抗作用,保护糖尿病终末器官损伤,提高肺动脉高压大鼠的生存率。这一特点使得马西坦成为治疗慢性组织ET系统激活相关心血管疾病的新药物。[1]
|
| 细胞实验 |
校准标准和质量控制样品[2]
以甲醇-水(50:50,v/v)配制ACT-132577 (1.0 mg/mL)和地西泮(IS)(100µg/mL)原液。用甲醇稀释IS原液,制得0.25µg/mL IS工作标准液;用同样的方法从原液中制备用于校准和控制的工作溶液。所有的溶液在4°C下保存,使用前带到室温。 在空白大鼠血浆中加入适量的工作溶液制备ACT-132577校准标准品。校正图偏移到大鼠血浆中ACT-132577(10、20、50、100、200、500、1000、2000和4000 ng/mL)的10-4000 ng/mL范围内。按照与校准标准品相同的方法制备三种不同血浆浓度(20、1800和3600 ng/mL)的质量控制(QC)样品。分析标准品和QC样品保存在-20℃ 通过分析空白大鼠血浆、空白血浆加标ACT-132577和IS以及大鼠血浆样品来评价该方法的选择性。 通过分析三天的加标样品,构建了校准曲线。act -132577- is的峰面积比随分析物浓度绘制。在10-4000 ng/mL浓度范围内,以浓度倒数(1/x)为权重因子,得到的标准曲线与方程拟合良好。定量下限(LLOQ)定义为校准曲线上的最低浓度。 通过分析不同条件下浓度分别为20和3600 ng/mL的血浆样品,评价ACT-132577在大鼠血浆中的稳定性。这些结果与新鲜制备的血浆样品进行了比较。将加标样品在室温下暴露2小时后测定短期稳定性,将待注射样品(蛋白质沉淀后)在HPLC自进样器中于室温下放置24小时。在连续3天的完整冻融循环(-20至25°C)后评估冻融稳定性。标准加标血浆样品在-20°C下保存20天后,评估其长期稳定性。对IS (50 ng/mL)的稳定性进行了类似的评价。 |
| 动物实验 |
Pharmacokinetic study[2]
Twelve Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200-220 g) were used. The ethical number of the experiment animals was wydw2013-0071. All experimental procedures and protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Wenzhou Medical University. Diet was prohibited for 12 h before the experiment but water was freely available. Blood samples (0.2 mL) were collected from the caudal vein into heparinized 1.5 mL tapered plastic centrifuge tubes at 0.0333, 0.15, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h after oral (15 mg/kg, n=6) and intravenous (5 mg/kg, n=6) administration of macitentan, respectively. The caudal vein of rat was cleaned by 75% alcohol, after that the end of caudal vein was cut by scissors. A 1.5 mL tapered plastic centrifuge tube was used to collect the blood which dropped from the end of caudal vein by squeezing and massaging gently. The samples were immediately centrifuged at 3000 × g for 10 min. The plasma as-obtained (50 µL) was stored at -20°C until UPLC-MS/MS analysis. Plasma ACT-132577 concentration versus time data for each rat was analyzed by DAS (Drug and Statistics) software. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Aprocitentan was well tolerated across all doses. No serious adverse events (AEs) occurred. The most frequently reported AE was headache. Small increases in body weight were recorded in subjects receiving 100 mg qd. Plasma concentration–time profiles of aprocitentan were similar after single- and multiple-dose administration, and support a qd dosing regimen based on a half-life of 44 hours. After multiple doses, PK was dose proportional. Accumulation at steady state, reached by Day 8, was 3-fold. Only minor differences in exposure between healthy females and males, healthy elderly and adult subjects, and fed and fasted conditions were observed. Plasma ET-1 concentrations, reflecting ETB receptor antagonism, significantly increased with doses ≥25 mg. Time-matched analysis of electrocardiogram (ECG) parameters did not suggest drug-induced ECG effects. Exposure–response analysis indicated no QTc prolongations at plasma levels up to 10 µg/mL.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019; 13: 949–964.
|
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the clinical use of aprocitentan during breastfeeding. Because aprocitentan is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins, the amount in milk is likely to be low. However, its half-life is 41 hours and it might accumulate in the infant. Because no information is available on the use of aprocitentan during breastfeeding, an alternate drug may be preferred, especially while nursing a newborn or preterm infant. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
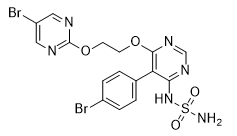
ACT-132577 is a member of the class of sulfamides in which one of the amino groups of sulfonamide is substituted by a 5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-{2-[(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]ethoxy}pyrimidin-4-yl group. An active metabolite of macitentan (obtained by oxidative depropylation), an orphan drug used for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. It has a role as an antihypertensive agent, an endothelin receptor antagonist, a drug metabolite and a xenobiotic metabolite. It is an aromatic ether, an organobromine compound, a member of pyrimidines and a member of sulfamides. It is functionally related to an ethylene glycol.
Aprocitentan is under investigation in clinical trial NCT03541174 (A Research Study to Show the Effect of Aprocitentan in the Treatment of Difficult to Control (Resistant) High Blood Pressure (Hypertension) and Find Out More About Its Safety). Drug Indication Treatment of hypertension. Macitentan, also called Actelion-1 or ACT-064992 [N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-(2-(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yloxy)ethoxy)-pyrimidin-4-yl]-N'-propylaminosulfonamide], is a new dual ET(A)/ET(B) endothelin (ET) receptor antagonist designed for tissue targeting. Selection of macitentan was based on inhibitory potency on both ET receptors and optimization of physicochemical properties to achieve high affinity for lipophilic milieu. In vivo, macitentan is metabolized into a major and pharmacologically active metabolite, ACT-132577. Macitentan and its metabolite antagonized the specific binding of ET-1 on membranes of cells overexpressing ET(A) and ET(B) receptors and blunted ET-1-induced calcium mobilization in various natural cell lines, with inhibitory constants within the nanomolar range. In functional assays, macitentan and ACT-132577 inhibited ET-1-induced contractions in isolated endothelium-denuded rat aorta (ET(A) receptors) and sarafotoxin S6c-induced contractions in isolated rat trachea (ET(B) receptors). In rats with pulmonary hypertension, macitentan prevented both the increase of pulmonary pressure and the right ventricle hypertrophy, and it markedly improved survival. In diabetic rats, chronic administration of macitentan decreased blood pressure and proteinuria and prevented end-organ damage (renal vascular hypertrophy and structural injury). In conclusion, macitentan, by its tissue-targeting properties and dual antagonism of ET receptors, protects against end-organ damage in diabetes and improves survival in pulmonary hypertensive rats. This profile makes macitentan a new agent to treat cardiovascular disorders associated with chronic tissue ET system activation.[1] It was reported that macitentan was metabolized predominantly by cytochrome P450 3A4, and ACT-132577, its pharmacologically active metabolite, is fivefold less potent at blocking ET receptors than macitentan. In this work, a sensitive and selective ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) method for determination of ACT-132577 in rat plasma was developed and validated. After addition of diazepam as an internal standard (IS), protein precipitation by acetonitrile was used to prepare samples. Chromatographic separation was achieved on a UPLC BEH C18 column (2.1 mm × 100 mm, 1.7 μm) with 0.2% formic acid and methanol as the mobile phase with gradient elution. An electrospray ionization source was applied and operated in positive ion mode; multiple reactions monitoring (MRM) mode was used for quantification using target fragment ions m/z 546.9→200.6 for ACT-132577, and m/z 285.1→193.1 for IS. Calibration plots were linear throughout the range 10-4000 ng/mL for ACT-132577 in rat plasma. Mean recovery of ACT-132577 in rat plasma ranged from 82.6% to 90.6%, matrix effect of ACT-132577 in rat plasma ranged from 101.4% to 115.2%. RSD of intra-day and inter-day precision were both less than 11%. The accuracy of the method ranged from 96.1% to 103.5%. The method was successfully applied to pharmacokinetic study of ACT-132577 after oral and intravenous administration of macitentan. [2] |
| 分子式 |
C₁₆H₁₀D₄BR₂N₆O₄S
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
546.194
|
| 精确质量 |
543.916
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 35.18; H, 2.58; Br, 29.26; N, 15.39; O, 11.72; S, 5.87
|
| CAS号 |
1103522-45-7
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Aprocitentan-d4
|
| PubChem CID |
25099191
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
| LogP |
4.385
|
| tPSA |
150.59
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
10
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
597
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
C1=CC(=CC=C1C2=C(N=CN=C2OCCOC3=NC=C(C=N3)Br)NS(=O)(=O)N)Br
|
| InChi Key |
DKULOVKANLVDEA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H14Br2N6O4S/c17-11-3-1-10(2-4-11)13-14(24-29(19,25)26)22-9-23-15(13)27-5-6-28-16-20-7-12(18)8-21-16/h1-4,7-9H,5-6H2,(H2,19,25,26)(H,22,23,24)
|
| 化学名 |
N-[5-(4-bromophenyl)-6-{2-[(5-bromopyrimidin-2-yl)oxy]ethoxy}pyrimidin-4-yl]sulfuric diamide
|
| 别名 |
ACT 132577; ACT-132577; Aprocitentan; ACT132577; N-Despropyl-macitentan; Tryvio; Aprocitentan [USAN]; Macitentan metabolite m6; MZI81HV01P; Despropyl Macitentan.
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~25 mg/mL (~45.77 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.58 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8309 mL | 9.1543 mL | 18.3086 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3662 mL | 1.8309 mL | 3.6617 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1831 mL | 0.9154 mL | 1.8309 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。