| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
B16F10细胞条件培养基的活性成分相对分子质量小于5,000,可强烈减少L-抗坏血酸钠(10 mM)诱导的细胞凋亡[4]。
|
|---|---|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
与未用L-抗坏血酸钠(Sodium L-ascorbate)治疗的Tg大鼠相比,用L-抗坏血酸钠(15.4%)治疗的Tg大鼠的癌症发病率更高(29.6%)。即使没有 L-抗坏血酸钠盐治疗,转基因大鼠也会出现多种器官癌症 [5]。 PEITC 治疗 12 周后,所有动物均出现单纯性增生和乳头状或结节性 (PN) 增生;然而,无论是否进行钠盐(L-抗坏血酸)治疗,大多数病变都会在 48 周后消退。到第 48 周,即经过 24 周的 PEITC 治疗后,少数病例中相同的病变已进展为不典型增生和癌症;然而,大鼠单纯性增生和PN增生是L-抗坏血酸钠盐治疗显示出增强作用的唯一情况。 [6]。
|
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Ascorbic acid, the reduced form of vitamin C, functions as a potent antioxidant as well as in cell differentiation. Ascorbate is taken up by mammalian cells through the specific sodium/ascorbate co-transporters SVCT1 and SVCT2. Although skeletal muscle contains about 50% of the whole-body vitamin C, the expression of SVCT transporters has not been clearly addressed in this tissue. ... This work ... analyzed the expression pattern of SVCT2 during embryonic myogenesis using the chick as model system. ... Immunohistochemical analyses showed that SVCT2 is preferentially expressed by type I slow-twitch muscle fibers throughout chick myogenesis as well as in post-natal skeletal muscles of several species, including human... Humans use two sodium-ascorbate cotransporters (hSVCT1 and hSVCT2) for transporting the dietary essential micronutrient ascorbic acid, the reduced and active form of vitamin C. Although the human liver plays a pivotal role in regulating and maintaining vitamin C homeostasis, vitamin C transport physiology and regulation of the hSVCT systems in this organ have not been well defined. Thus, this research used a human hepatic cell line (HepG2), confirming certain results with primary human hepatocytes and determined the initial rate of ascorbic acid uptake to be Na(+) gradient, pH dependent, and saturable as a function of concentration over low and high micromolar ranges. Additionally, hSVCT2 protein and mRNA are expressed at higher levels in HepG2 cells and native human liver, and the cloned hSVCT2 promoter has more activity in HepG2 cells. Results using short interfering RNA suggest that in HepG2 cells, decreasing hSVCT2 message levels reduces the overall ascorbic acid uptake process more than decreasing hSVCT1 message levels. Activation of PKC intracellular regulatory pathways caused a downregulation in ascorbic acid uptake not mediated by a single predicted PKC-specific amino acid phosphorylation site in hSVCT1 or hSVCT2. However, PKC activation causes internalization of hSVCT1 but not hSVCT2. Examination of other intracellular regulatory pathways on ascorbic acid uptake determined that regulation also potentially occurs by PKA, PTK, and Ca(2+)/calmodulin, but not by nitric oxide-dependent pathways... Metabolism / Metabolites ... Adrenal cortex is closely associated with ascorbate metabolism ... Hydrocortisone was reported ... to stimulate synthesis of ascorbate from gluconolactone, but deoxycorticosterone or aldosterone caused ... increase in ascorbate excretion in normal or adrenalectomized rats... |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Vitamin C is a normal component of human milk and is a key milk antioxidant. The recommended vitamin C intake in lactating women is 120 mg daily, and for infants aged 6 months or less is 40 mg daily. High daily doses up to 1000 mg increase milk levels, but not enough to cause a health concern for the breastfed infant and is not a reason to discontinue breastfeeding. Nursing mothers may need to supplement their diet to achieve the recommended intake or to correct a known deficiency. Maternal doses of vitamin C in prenatal vitamins at or near the recommended intake do not alter milk levels. Freezing (-20 degrees C) freshly expressed mature milk from hospitalized mothers of term and preterm infants does not change milk vitamin C levels for at least 3 months of freezer storage. After 6 to 12 months of freezing (-20 degrees C), vitamin C levels can decrease by 15 to 30%. Storage at -80 degrees C preserves vitamin C levels for up to 8 months, with 15% loss by 12 months. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Sixty healthy lactating women between 1 and 6 months postpartum exclusively breastfeeding their infants were given vitamin C 500 mg plus vitamin E 100 IU once daily for 30 days, or no supplementation. Infants of supplemented mothers had increased biochemical markers of antioxidant activity in their urine. Clinical outcomes were not reported. Eighteen preterm infants, seven of whom were less than 32 weeks gestational age, who were fed pooled, Holder-pasteurized donor milk beginning during the first three days of life had their average blood plasma ascorbic acid concentrations decrease from 15.5 mg/L at birth to 5.4 mg/L by 1 week of age, and to 4.1 mg/L by 3 weeks of age. The authors described the 1- and 3-week levels as subtherapeutic (<6 mg/L) and indicative of inadequate intake, potentially jeopardizing postnatal growth potential. Although this study was conducted before advances in the provision of parenteral nutrition and enteral milk fortification for preterm infants, contemporary studies suggest that inadequate vitamin C intake from pooled, pasteurized donor milk may be a potential health problem for preterm infants receiving donor milk. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. Interactions Tissues exposed to Na ascorbate responded more vigorously than untreated muscles when graded concentrations of calcium chloride added to bathing solution minus Ca2+ ions but with acetylcholine. The effects of sodium ascorbate with or without Vitamin K3 was studied in vitro using cultured human neoplastic cell lines MCF-7 (breast carcinoma), KB (oral epidermal carcinoma), and AN3-CA (endometrial adenocarcinoma) at concentrations of 0.198 ug/mL to 1.98 mg/mL. Culture media without sodium ascorbate and the vitamin were used as a control. At 50%confluence, different combinations of sodium ascorbate and Vitamin K3 were added to the cultures for a 1 hr incubation. DNA determinations were made. Sodium Ascorbate supplemented media had a growth inhibiting action only at high concentrations (5 x 10+3 mol/L). Combined administration demonstrated a synergisitic inhibition of cell growth at 10 to 50 times lower concentrations. These results are for all three cell types ... Sodium ascorbate and/or sodium nitrite /was administered/ for 6 months to male and female Wistar rats (5 rats/group). The control group was fed a basal diet and water only. Treated groups were administered the following: 0.075%, 0.15%, or 0.3% sodium nitrite dissolved in water; 1%, 2%, or 4% sodium ascorbate; or a combination with both chemicals at low + low, middle + middle, and high + high doses. Body weight gain was significantly decreased in the combined-high dose group. Significant decreases of serum total protein, increase of BUN (blood urea nitrogen) and relative kidney weight were also found in the combined-high dose group. Histopathological examination showed moderate or severe squamous cell hyperplasia of the forestomach in the combined-high dose group and slight hyperplasia in the combined-middle dose group. No differences were seen between the sexes. The minimum toxic dose was 0.15% sodium nitrite+2% sodium ascorbate ... |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Minute crystals or white powder. pH of aqueous solutions 5.6 to 7.0 or even higher (a 10% solution, made from a commercial grade, may have a pH of 7.4 to 7.7). (NTP, 1992)
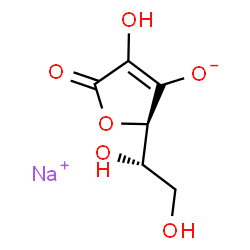
Sodium ascorbate is an organic sodium salt resulting from the replacement of the proton from the 3-hydroxy group of ascorbic acid by a sodium ion. It has a role as a food antioxidant, a flour treatment agent, a coenzyme, a plant metabolite, a human metabolite, a Daphnia magna metabolite and a reducing agent. It is an organic sodium salt and a vitamin C. It contains a L-ascorbate. A six carbon compound related to glucose. It is found naturally in citrus fruits and many vegetables. Ascorbic acid is an essential nutrient in human diets, and necessary to maintain connective tissue and bone. Its biologically active form, vitamin C, functions as a reducing agent and coenzyme in several metabolic pathways. Vitamin C is considered an antioxidant. See also: Ascorbic Acid (has active moiety) ... View More ... Mechanism of Action Mechanism of action of ascorbate is a superoxide radical scavenger. ... Sodium ascorbate decreases cellular iron uptake by melanoma cells in a dose- and time-dependent fashion, indicating that intracellular iron levels may be a critical factor in sodium ascorbate-induced apoptosis. Indeed, sodium ascorbate-induced apoptosis is enhanced by the iron chelator, desferrioxamine (DFO) while it is inhibited by the iron donor, ferric ammonium citrate (FAC). Moreover, the inhibitory effects of sodium ascorbate on intracellular iron levels are blocked by addition of transferrin, suggesting that transferrin receptor (TfR) dependent pathway of iron uptake may be regulated by sodium ascorbate. Cells exposed to sodium ascorbate demonstrated down-regulation of TfR expression and this precedes sodium ascorbate-induced apoptosis. Taken together, sodium ascorbate-mediated apoptosis appears to be initiated by a reduction of TfR expression, resulting in a down-regulation of iron uptake followed by an induction of apoptosis... Humans use two sodium-ascorbate cotransporters (hSVCT1 and hSVCT2) for transporting the dietary essential micronutrient ascorbic acid, the reduced and active form of vitamin C. Although the human liver plays a pivotal role in regulating and maintaining vitamin C homeostasis, vitamin C transport physiology and regulation of the hSVCT systems in this organ have not been well defined. Thus, this research used a human hepatic cell line (HepG2), confirming certain results with primary human hepatocytes and determined the initial rate of ascorbic acid uptake to be Na(+) gradient, pH dependent, and saturable as a function of concentration over low and high micromolar ranges. Additionally, hSVCT2 protein and mRNA are expressed at higher levels in HepG2 cells and native human liver, and the cloned hSVCT2 promoter has more activity in HepG2 cells. Results using short interfering RNA suggest that in HepG2 cells, decreasing hSVCT2 message levels reduces the overall ascorbic acid uptake process more than decreasing hSVCT1 message levels. Activation of PKC intracellular regulatory pathways caused a downregulation in ascorbic acid uptake not mediated by a single predicted PKC-specific amino acid phosphorylation site in hSVCT1 or hSVCT2. However, PKC activation causes internalization of hSVCT1 but not hSVCT2. Examination of other intracellular regulatory pathways on ascorbic acid uptake determined that regulation also potentially occurs by PKA, PTK, and Ca(2+)/calmodulin, but not by nitric oxide-dependent pathways... Therapeutic Uses Antioxidants; Free Radical Scavengers Ascorbic acid and calcium and sodium ascorbates are used as antoxidants in pharmaceutical manufacturing and in the food industry. In 20 patients in acute asthmatic crisis, 16 recovered promptly after receiving 6 g sodium ascorbate iv. Chronic oral treatment (0.6-1 g/day/60 days) with Na ascorbate prevented asthmatic symptoms in 18/25 asthmatic patients. 8 patients with hyphema were treated with iv glycerin in combination with sodium ascorbate. The results showed that glycerol in combination with sodium ascorbate diminished the hemorrhage in eye within 12-24 hr. For more Therapeutic Uses (Complete) data for Sodium ascorbate (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. Drug Warnings Each gram of sodium ascorbate contains approximately 5 mEq of sodium; this should be considered when the drug is used in patients on salt-restricted diets. |
| 分子式 |
C6H7NAO6
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
198.11
|
| 精确质量 |
198.014
|
| CAS号 |
134-03-2
|
| 相关CAS号 |
L-Ascorbic acid;50-81-7;L-Ascorbic acid (GMP Like);50-81-7
|
| PubChem CID |
23667548
|
| 外观&性状 |
Off-white to light yellow solid powder
|
| 密度 |
1.799 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
552.7ºC at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
220 °C (dec.)(lit.)
|
| 闪点 |
238.2ºC
|
| 蒸汽压 |
1.62E-14mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
105.5 ° (C=10, H2O)
|
| tPSA |
110.05
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
3
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
| 重原子数目 |
13
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
237
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
2
|
| SMILES |
[Na+].O1C(C(=C([C@@]1([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])O[H])O[H])[O-])O[H])=O
|
| InChi Key |
PPASLZSBLFJQEF-RXSVEWSESA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C6H8O6.Na/c7-1-2(8)5-3(9)4(10)6(11)12-5;/h2,5,7-10H,1H2;/q;+1/p-1/t2-,5+;/m0./s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium;(2R)-2-[(1S)-1,2-dihydroxyethyl]-4-hydroxy-5-oxo-2H-furan-3-olate
|
| 别名 |
Ascorbate Vitamin C sodium Sodium Ascorbate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中(例如氮气保护),避免吸湿/受潮和光照。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~504.77 mM)
DMSO : ~1 mg/mL (~5.05 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 50 mg/mL (252.39 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0477 mL | 25.2385 mL | 50.4770 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0095 mL | 5.0477 mL | 10.0954 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5048 mL | 2.5239 mL | 5.0477 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT03508726 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Ascorbate | Soft Tissue Sarcoma | Mohammed Milhem | 2019-06-27 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT04877587 | WITHDRAWN | Drug: Ascorbate Drug: Gemcitabine |
Bone Sarcoma Metastatic Bone Sarcoma Metastatic Soft-tissue Sarcoma Soft Tissue Sarcoma |
David Dickens | 2023-01 | Early Phase 1 |
| NCT02420314 | COMPLETEDWITH RESULTS | Drug: Paclitaxel Drug: Carboplatin Drug: Ascorbic Acid |
Carcinoma, Non-Small-Cell Lung | Joseph J. Cullen, MD, FACS | 2015-04 | Phase 2 |
| NCT06433791 | NOT YET RECRUITING | Drug: Ascorbate-Meglumine | Safety | LadeRx LLC | 2024-06-17 | Phase 1 |
| NCT04634227 | RECRUITING | Drug: Ascorbate | Bone Sarcoma Metastatic Bone Tumor Sarcoma Soft Tissue Sarcoma Unresectable Soft Tissue Sarcoma |
Mohammed Milhem, MBBS | 2020-11-24 | Early Phase 1 |
|
|
|