| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Chk1 (IC50 = 5 nM); Chk2 (IC50 = 5 nM)
AZD7762 targets checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1) with an IC50 value of 1.3 nM and checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2) with an IC50 value of 7.6 nM in recombinant kinase assays [1] AZD7762 shows moderate selectivity, with IC50 values > 1 μM for 28 other tested kinases (including CDK1, Aurora A, ATM, ATR) [1] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
AZD7762 是一种更具选择性的 Chk1 抑制剂,通过可逆地结合 Chk1 的 ATP 结合位点来抑制 cdc25C 肽的 Chk1 磷酸化,IC50 为 5 nM,Ki 为 3.6 nM。 AZD7762 通过阻断 Cdc25A 的 chk1 依赖性降解和细胞周期蛋白 A 的激活,诱导细胞停滞,EC50 为 0.620 μM,并显着消除喜树碱诱导的 G2 停滞,EC50 为 10 nM。AZD7762 (300 nM) 增强吉西他滨的抗肿瘤功效通过将 GI50 值从 24.1 nM 和 2.25 μM 分别降低至 1.08 nM 和 0.15 μM,针对 SW620 和拓扑替康针对 MDA-MB-231。 AZD7762 对多种带有 p53 野生型、p53 突变、Mdm2 扩增或 p14 缺失的神经母细胞瘤细胞系显示出细胞毒性,IC50 值范围为 82.6-505.9 nM。激酶测定:使用杆状病毒载体将重组人 Chk1 在昆虫细胞中表达为谷胱甘肽 S-转移酶融合体,并通过谷胱甘肽亲和层析进行纯化。合成了 Chk1 的合成肽底物(N-生物素氨基己酰基-KKVRSSGLYRSPMPENLNRPR)。肽和 ATP(冷 + 40 nCi [33P]ATP)的最终测定浓度分别为 0.8 和 1 μM。将不同浓度的 AZD7762、含有肽、chk1 激酶和 ATP 的缓冲液依次添加到 384 孔测定板中。将板孵育 2 小时,通过添加含有 EDTA 和闪烁邻近分析珠的缓冲液来终止反应,并使用 TopCount 读数器读取板。进行数据分析以确定剂量反应(IC50)。细胞测定:对于检查点废除测定,用喜树碱(拓扑异构酶 I 抑制剂;0.07 μg/mL)处理 HT29 细胞 2 小时以诱导 G2 检查点。然后用 AZD7762(12.5 μM 至 6 nM)加诺考达唑的 12 点滴定处理细胞 20 小时。将细胞用 3.7% 甲醛固定 1 小时,用含有 0.05% Triton X 的 PBS 透化,并与抗 phH3 抗体一起孵育 1 小时,然后用 Alexa Fluor 488 抗兔和 Hoechst 染色 1 小时。有丝分裂指数在ArrayScan上测定并表示为经历有丝分裂的细胞的百分比。对于增强测定,SW620 或 MDA-MB-231 细胞给药 24 小时,吉西他滨的 9 点滴定范围为 0.01 至 100 nM,AZD7762 (300 nM) 的恒定剂量。 24小时后,除去培养基,并将AZD7762单独添加回孔中,再继续培养24小时。然后将细胞在不含 AZD7762 的培养基中再孵育 72 小时。通过MTT测定对细胞增殖的影响。
在多种人类癌细胞系(HCT116、A2780、MCF-7、PC3、HeLa)中,AZD7762 表现出抗增殖活性,IC50 值范围为 25 nM 至 150 nM [1] - 50 nM AZD7762 可废除 DNA 损伤剂(顺铂、多柔比星)在 HCT116 细胞中诱导的 G2/M 检查点,使 G2/M 期细胞积累比例从 62% 降至 28% [1] - 100 nM AZD7762 单独处理 A2780 细胞仅诱导轻度凋亡(12% 凋亡细胞),但与顺铂(1 μM)联合处理 72 小时后,凋亡率升高至 58% [1] - Western blot 检测显示,AZD7762 可抑制 HCT116 细胞中 Chk1 介导的 CDC25C(Ser216)磷酸化及 Chk2 介导的 p53(Ser20)磷酸化 [1] - AZD7762 与 DNA 靶向治疗药物联合使用时表现出协同抗增殖效应:在 HCT116 细胞中,与顺铂联合的协同指数(CI)= 0.4,与多柔比星联合 CI = 0.35,与紫杉醇联合 CI = 0.5,与吉西他滨联合 CI = 0.45 [1] - 75 nM AZD7762 可增强顺铂处理细胞中的 DNA 双链断裂,表现为 γ-H2AX 灶点形成增加(较顺铂单独处理高 3.2 倍)[1] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
单独使用 25 mg/kg 的 AZD7762 在 H460-DNp53 异种移植小鼠和 SW620 异种移植小鼠中显示出很少的抗肿瘤活性,但当与吉西他滨 (60 mg/kg) 联合给药时,AZD7762 在两种异种移植小鼠中显示出显着的抗肿瘤功效,其即使在 12.5 mg 的低剂量下,细胞杀灭率仍为 0.9 或治疗/对照百分比 (%T/C) 为 26。在 H460-DNp53 异种移植大鼠中,AZD7762 与吉西他滨 (10 mg/kg) 组合给药以剂量依赖性方式抑制肿瘤体积,10 和 20 mg/kg AZD7762 的%T/C 值为 48 和 32,分别。 AZD7762 (25 mg/kg) 与伊立替康 (25 或 50 mg/kg) 组合可导致 SW620 异种移植小鼠的肿瘤完全消退,%T/C 分别显着增加至 -66% 和 -67%。
在 HCT116 人结直肠癌异种移植模型(nu/nu 小鼠)中,AZD7762 腹腔给药(10 mg/kg,每日一次,连续 5 天)联合顺铂(5 mg/kg,腹腔给药,第 1 天和第 5 天)的肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达 89%,而顺铂单独处理的 TGI 为 41% [1] - 在 A2780 人卵巢癌异种移植模型(nu/nu 小鼠)中,AZD7762 腹腔给药(15 mg/kg,每日一次,连续 5 天)联合紫杉醇(10 mg/kg,静脉给药,第 1 天和第 5 天)的 TGI 为 92%,荷瘤小鼠中位生存期较紫杉醇单独处理延长 65% [1] - AZD7762 与顺铂联合处理组的肿瘤组织中,TUNEL 阳性凋亡细胞增加(45% vs 顺铂单独处理组 18%),Ki-67 增殖指数降低(22% vs 顺铂单独处理组 56%)[1] |
| 酶活实验 |
通过谷胱甘肽亲和层析纯化,重组人 Chk1 通过杆状病毒载体在昆虫细胞中表达为谷胱甘肽 S-转移酶融合体。对于 Chk1,N-生物素氨基己酰基-KKVRSSGLYRSPMPENLNRPR 是一种合成肽底物。最终检测肽和 ATP 浓度分别为 0.8 和 1 μM(冷 + 40 nCi [ 33 P]ATP)。具有 384 个孔的检测板充满不同浓度的 AZD7762,这是一种含有 ATP、chk1 激酶和肽的缓冲液。使用 TopCount 读数器,在孵育两小时后对板进行读数,在此期间通过添加含有 EDTA 和闪烁邻近分析珠的缓冲液来停止反应。通过进行数据分析确定剂量反应 (IC50)。
重组 Chk1/Chk2 激酶活性测定:反应体系包含重组 Chk1/Chk2、ATP(10 μM)和荧光标记肽底物,加入系列浓度的 AZD7762(0.1 nM 至 1 μM),30°C 孵育 60 分钟。通过荧光共振能量转移(FRET)检测磷酸化底物,非线性回归计算 IC50 值 [1] - 激酶选择性面板测定:采用相同的 FRET 方法,在 1 μM 浓度下测试 AZD7762 对 30 种人类激酶的抑制作用。相对于溶媒对照组计算抑制率,对抑制率 > 20% 的激酶计算 IC50 值 [1] |
| 细胞实验 |
在检查点废除试验中,用喜树碱(一种拓扑异构酶 I 抑制剂;0.07 μg/mL)处理 HT29 细胞两小时,以触发 G2 检查点。之后,除诺考达唑外,对细胞进行 AZD7762(12.5 μM 至 6 nM)的 12 点滴定,持续 20 小时。在 3.7% 甲醛中固定一小时,在含有 0.05% Triton X 的 PBS 中透化细胞,并在抗 phH3 抗体、Alexa Fluor 488 抗兔和 Hoechst 染色剂中孵育细胞一小时,将细胞留置又一个小时。进行有丝分裂的细胞百分比由有丝分裂指数表示,该指数是使用 ArrayScan 计算的。为了进行增强测定,将 SW620 或 MDA-MB-231 细胞用恒定剂量的 AZD7762 (300 nM) 处理 24 小时,然后对吉西他滨进行 9 点滴定,浓度范围为 0.01 至 100 nM。 24小时后除去培养基,然后将AZD7762单独添加回孔中再继续培养24小时。此后,将细胞在不含 AZD7762 的培养基中再培养 72 小时。 MTT测定对细胞增殖的影响。
抗增殖实验:癌细胞接种于 96 孔板(5×103 个细胞 / 孔),用系列浓度的 AZD7762(10 nM 至 1 μM)单独或与 DNA 靶向药物联合处理 72 小时。基于四唑盐还原的比色法评估细胞活力,计算 IC50 值及协同指数 [1] - 细胞周期分析:细胞用 AZD7762(50 nM)联合顺铂(1 μM)处理 24 小时后,收集细胞,70% 乙醇固定,碘化丙啶染色,流式细胞术测定细胞周期分布 [1] - 凋亡实验:细胞经 AZD7762(100 nM)和 / 或多柔比星(0.5 μM)处理 72 小时后,用膜联蛋白 V-FITC 和碘化丙啶染色,流式细胞术分析 [1] - Western blot 分析:细胞用 RIPA 缓冲液裂解,蛋白经 SDS-PAGE 分离后转移至膜上,与抗磷酸化 CDC25C(Ser216)、磷酸化 p53(Ser20)、γ-H2AX、剪切型半胱天冬酶 -3、PARP 及 β- 肌动蛋白抗体孵育。化学发光法检测信号,密度计量法定量 [1] - γ-H2AX 灶点实验:细胞用 AZD7762(75 nM)和顺铂(1 μM)处理 24 小时后,固定,用 γ-H2AX 抗体和 DAPI 染色,荧光显微镜观察。手动计数每个细胞的灶点数量 [1] |
| 动物实验 |
Mice and Rats: Male RNU rats and male NCr mice are employed. Tumor cells are removed from mice used as xenograft models, centrifuged for five minutes to pellet the cells, and then resuspended in sterile PBS. Using a 25-gauge needle, cells (3×10 3 -6×10 6 ) are s.c. implanted into the right flank of the mice in a volume of 0.1 to 0.2 mL. Before compound is administered, tumors are allowed to grow to the specified size of 100 to 200 mm 3 . Rat xenograft models involve cell harvesting, centrifugation for 5 minutes to pellet the cells, and resuspension in a 50% sterile PBS and 50% Matrigel solution. Five days prior to cell implantation, rats undergo a whole-body radiation dose of 5 Gy with the goal of enhancing tumor growth. With a 25-gauge needle, H460-DNp53 cells (1×10 7 ) are s.c. implanted into the rats' right flanks in a volume of 0.2 mL. Before administering AZD-7762, tumors are allowed to grow to the specified size of 100 to 200 mm 3 . The tail vein is used to administer intravenous injections of AZD-7762 (10 and 20 mg/kg). Treatments were administered in cycles of three to five, according to cyclic schedules. Every three days, AZD-7762 is delivered after a standard agent (NSC 613327 or CPT-11) has been administered. Electronic calipers are used to measure and compute tumor volumes.
Mice: Pharmacological inhibitors are administered to C57Bl/6 mice eight days after they receive an intravenous injection of 2×10 5 Eμ-Myc B-lymphoma cells in PBS. Treatment is administered to the mice until an ethical endpoint, such as a hunched posture, ruffled fur, enlarged lymph nodes, labored breathing, weight loss of more than 20% of the initial body weight, limited mobility, or paralysis, is achieved. On weekdays, 20 mg/kg of AZD7762 is administered intraperitoneally in a solution of 10.3% -hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and 0.9% saline.
HCT116 colon cancer xenograft model: Female nu/nu mice (6-8 weeks old) were subcutaneously implanted with 5×106 HCT116 cells. When tumors reached 100-150 mm3, mice were randomized into groups (n=6/group) and treated with: (1) vehicle (5% DMSO + 20% Cremophor EL + 75% saline) i.p., (2) AZD7762 (10 mg/kg) i.p. once daily for 5 days, (3) cisplatin (5 mg/kg) i.p. on days 1 and 5, (4) AZD7762 + cisplatin. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every 2 days [1] - A2780 ovarian cancer xenograft model: Female nu/nu mice (6-8 weeks old) were subcutaneously implanted with 5×106 A2780 cells. Tumors reaching 100-150 mm3 were randomized (n=6/group) and treated with: (1) vehicle i.p., (2) AZD7762 (15 mg/kg) i.p. once daily for 5 days, (3) paclitaxel (10 mg/kg) i.v. on days 1 and 5, (4) AZD7762 + paclitaxel. Tumor volume and survival were monitored [1] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
In mice, intraperitoneal administration of AZD7762 (10 mg/kg) resulted in a Cmax of 2.8 μM, AUC0-24h of 16.5 μM·h, and terminal half-life (t1/2) of 4.2 hours [1]
- AZD7762 exhibited moderate aqueous solubility (35 μM at pH 7.4) and high human plasma protein binding (91%) [1] - Oral administration of AZD7762 (25 mg/kg) in mice showed low oral bioavailability (12%), with a Cmax of 0.3 μM and AUC0-24h of 2.1 μM·h [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
In single-dose toxicity studies in mice, AZD7762 had a maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of 20 mg/kg i.p., with lethal toxicity observed at 30 mg/kg (50% mortality) [1]
- Repeat-dose administration of AZD7762 (10 mg/kg i.p., q.d. for 5 days) in mice caused mild myelosuppression (reduced white blood cell count by 23%) and transient weight loss (≤8%), which recovered within 7 days [1] - AZD7762 did not inhibit human cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP3A4) at concentrations up to 10 μM [1] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
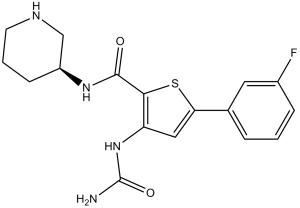
3-(carbamoylamino)-5-(3-fluorophenyl)-N-[(3S)-3-piperidinyl]-2-thiophenecarboxamide is an aromatic amide and a member of thiophenes.
AZD7762 has been investigated for the treatment of Cancer, Solid Tumors, and Advanced Solid Malignancies. Checkpoint Kinase Inhibitor AZD7762 is a synthetic small molecule inhibitor of checkpoint kinases (Chks) with potential chemosensitizing activity. AZD7762 binds to and inhibits Chks, which may prevent cell cycle arrest and subsequent nucleotide excision repair in DNA-damaged tumor cells, resulting in tumor cell apoptosis. This agent may enhance the cytotoxicity of DNA-damaging agents. Chks are protein kinases that regulate either G1/S or G2/M transitions in the cell cycle. In the presence of DNA damage or incomplete DNA replication, Chks become activated and initiate cell cycle arrest to allow DNA repair or the completion of DNA replication. Insights from cell cycle research have led to the hypothesis that tumors may be selectively sensitized to DNA-damaging agents resulting in improved antitumor activity and a wider therapeutic margin. The theory relies on the observation that the majority of tumors are deficient in the G1-DNA damage checkpoint pathway resulting in reliance on S and G2 checkpoints for DNA repair and cell survival. The S and G2 checkpoints are regulated by checkpoint kinase 1, a serine/threonine kinase that is activated in response to DNA damage; thus, inhibition of checkpoint kinase 1 signaling impairs DNA repair and increases tumor cell death. Normal tissues, however, have a functioning G1 checkpoint signaling pathway allowing for DNA repair and cell survival. Here, we describe the preclinical profile of AZD7762, a potent ATP-competitive checkpoint kinase inhibitor in clinical trials. AZD7762 has been profiled extensively in vitro and in vivo in combination with DNA-damaging agents and has been shown to potentiate response in several different settings where inhibition of checkpoint kinase results in the abrogation of DNA damage-induced cell cycle arrest. Dose-dependent potentiation of antitumor activity, when AZD7762 is administered in combination with DNA-damaging agents, has been observed in multiple xenograft models with several DNA-damaging agents, further supporting the potential of checkpoint kinase inhibitors to enhance the efficacy of both conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy and increase patient response rates in a variety of settings.[1] AZD7762 is a novel small-molecule inhibitor of Chk1 and Chk2, key regulators of the DNA damage response and cell cycle checkpoints [1] The mechanism of action of AZD7762 involves abrogating G2/M and S-phase checkpoints, forcing cancer cells with unrepaired DNA to proceed through mitosis, leading to mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis [1] AZD7762 is designed to potentiate the efficacy of DNA-targeted chemotherapies by preventing cancer cells from repairing drug-induced DNA damage [1] AZD7762 shows greater activity in p53-deficient cancer cells, as these cells rely more heavily on Chk1/Chk2-mediated checkpoints for survival [1] |
| 分子式 |
C17H19FN4O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
362.42
|
|
| 精确质量 |
362.12
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.34; H, 5.28; F, 5.24; N, 15.46; O, 8.83; S, 8.85
|
|
| CAS号 |
860352-01-8
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
AZD-7762 hydrochloride;1246094-78-9
|
|
| PubChem CID |
11152667
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.38
|
|
| 沸点 |
547.6ºC at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 闪点 |
285ºC
|
|
| LogP |
4.821
|
|
| tPSA |
124.49
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
4
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
495
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
C(C1=C(NC(=O)N)C=C(C2C=CC=C(F)C=2)S1)(=O)N[C@@H]1CNCCC1
|
|
| InChi Key |
IAYGCINLNONXHY-LBPRGKRZSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C17H19FN4O2S/c18-11-4-1-3-10(7-11)14-8-13(22-17(19)24)15(25-14)16(23)21-12-5-2-6-20-9-12/h1,3-4,7-8,12,20H,2,5-6,9H2,(H,21,23)(H3,19,22,24)/t12-/m0/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
3-(carbamoylamino)-5-(3-fluorophenyl)-N-[(3S)-piperidin-3-yl]thiophene-2-carboxamide
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.90 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10 mg/mL (27.59 mM) in 10% HP-β-CD (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7592 mL | 13.7961 mL | 27.5923 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5518 mL | 2.7592 mL | 5.5185 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2759 mL | 1.3796 mL | 2.7592 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT00413686 | Completed | Drug: AZD7762 Drug: Gemcitabine |
Solid Tumors | AstraZeneca | December 2006 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00473616 | Terminated | Drug: AZD7762 Drug: Irinotecan |
Advanced Solid Tumors Cancer |
AstraZeneca | May 2007 | Phase 1 |
| NCT00937664 | Terminated | Drug: AZD7762 Drug: gemcitabine |
Cancer Solid Tumors |
AstraZeneca | July 2009 | Phase 1 |
|
|---|
|
|
 Effect of AZD7762 on cell cycle proteins following treatment of cells with DNA-damaging agents.Mol Cancer Ther.2008 Sep;7(9):2955-66. |
|---|
 AZD7762 potentiated gemcitabine and topotecan.Mol Cancer Ther.2008 Sep;7(9):2955-66. |
 AZD7762 potentiated gemcitabine in rodent xenograft efficacy models.Mol Cancer Ther.2008 Sep;7(9):2955-66. |