| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
GABABR/GABAB receptor
|
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在表达野生型或异质亨廷顿蛋白的纹状体细胞(HD19 或 HD43)中,暴露于 1、10 μM 巴氯芬 24 小时后,乳酸脱氢酶 (LDH) 活性显着降低。这表明细胞更有活力。在 HD43 细胞中,巴氯芬可显着提高细胞存活率和胰凝乳蛋白酶样胰体活性 [3]。
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在 YAC128 HD 按钮中,巴氯芬(腹腔注射;10 μg/g;每天两次,持续三天)可改善运动缺陷 [3]。
|
| 酶活实验 |
蛋白酶体活性测定[3]
通过测量由肽AMC连接的底物产生的7-氨基-4-甲基香豆素(AMC;激发380nm,发射460nm)的荧光来测定蛋白酶体活性。反应在最终体积为200μl的缓冲液中进行,缓冲液包括50 mM Tris–HCl(pH 7.5)和1 mM EDTA。在将样品添加到反应混合物中后,通过添加底物Suc-Leu-Leu-Val-Try-AMC(65μM)来启动反应,以测量糜蛋白酶样活性。反应在25°C下进行360分钟。酶活性以蛋白质的荧光单位(FU)/mg/min表示。 |
| 细胞实验 |
细胞培养和体外巴氯芬治疗[3]
在补充有10%胎牛血清(Hyclone)、2mM l-谷氨酰胺(Sigma,St.Louis,MO)、青霉素和链霉素的Dulbecco改良鹰氏培养基(DMEM;Hyclone,Logan,UT)中,在33°C下培养Tet-off诱导型野生型(HD19,26CAG重复序列)和突变型(HD43105CAG重复)纹状体细胞。通过给予多西环素(1μg/ml)24小时来诱导亨廷顿基因的表达。将选择性GABAB受体激动剂巴氯芬(RS-巴氯芬;密苏里州Ellisville市Tocris-Cookson)以指定浓度给予培养细胞。给药24小时后,收集细胞培养基用于细胞活力测定。收获细胞并在含有以下蛋白酶和磷酸酶抑制剂的均化缓冲液(50mM Tris(pH 8.0)、150mM NaCl、5mM EDTA、1%Triton X-100)中裂解,用于蛋白质样品制备:10μg/ml抑肽酶、25μg/ml亮蛋白肽、10μg/ml pepstatin、10μg/ml苯甲磺酰氟、50mM氟化钠、50mM原钒酸钠) 细胞活力测定[3] 我们根据制造商的说明(Roche,Mannheim,Germany),通过对收集的细胞培养基进行乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)测定来测定细胞活力。通过在490nm处的吸光度测量对照或巴氯芬处理的纹状体细胞的LDH活性。 |
| 动物实验 |
Animal/Disease Models: Wild type (WT) and mutant (MT) male YAC128 mice 13-18 months old [3]
Doses: 10 μg/g Route of Administration: IP; twice (two times) daily at 9:00 AM and 5:00 PM , for 3 days; then a single dose was administered at 9:00 am on the fourth day. Experimental Results: Motor deficits in YAC128 HD transgenic mice were improved. Increased proteasome activity and diminished neuronal intranuclear inclusions (NII) in YAC128 HD transgenic mice. |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
Baclofen has an oral bioavailability of 70% to 85%. Following oral administration, it is rapidly absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract with peak plasma concentrations being reached two to three hours after ingestion. Peak effect is observed about four hours after intrathecal administration. The absorption is dose-dependent and increases with higher doses. There is intersubject variation in absorption. Administration of oral baclofen suspension with a high-fat meal resulted in 9% decrease in AUC and 33% decrease in Cmax compared to the fasted state. About 70-80% of baclofen is eliminated in an unchanged form by renal excretion within 72 hours of administration. About 5% of the dose is excreted via the kidneys as metabolites. There is intersubject variation in elimination. The volume of distribution of baclofen is 0.7 L/kg. As baclofen is mainly water-soluble, it does not readily cross the blood-brain barrier. Drug concentrations of baclofen in the cerebrospinal fluid are approximately 8.5 times lower than in the plasma. The systemic clearance (CL/F) was 180 mL/min and the renal clearance was 103 mL/min following oral administration. Metabolism / Metabolites Approximately 15% of the oral dose is metabolized in the liver, mainly by deamination. Deamination yields the main metabolite, β-(p-chlorophenyl)-4-hydroxybutyric acid, which is pharmacologically inactive. ~ 15% of the dose is metabolized in the liver, primarily by deamination. 70-80% of the dose is excreted unchanged or as metabolites in urine and the remainder is excreted in feces. Oral Baclofen is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. After oral administration, baclofen appears in the blodd within half an our. It is fairly distributed in most organs and body tissues. After oral administration of baclofen, about 85% is excreted unchanged in the urine and feces and the remainder is oxidatively dearninated in the liver to produce beta-(p-chlorophenyl)-gamma-hydroxybutyric acid as a major metabolite. (L1322). Route of Elimination: In a study using radiolabeled baclofen, approximately 85% of the dose was excreted unchanged in the urine and feces. Baclofen is excreted primarily by the kidney as unchanged drug; 70 - 80% of a dose appears in the urine as unchanged drug. The remainder is excreted as unchanged drug in the feces or as metabolites in the urine and feces. Half Life: 2.5-4 hours Biological Half-Life The half-life is 2-6 hours after oral administration and 1-5 hours following intrathecal administration. The apparent elimination half-life of baclofen oral suspension or granules is about 5.6 hours. |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Toxicity Summary
Baclofen is a direct agonist at GABAB receptors. The precise mechanism of action of Baclofen is not fully known. It is capable of inhibiting both monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes at the spinal level, possibly by hyperpolarization of afferent terminals, although actions at supraspinal sites may also occur and contribute to its clinical effect. Toxicity Data LD50: 45 mg/kg (Intravenous, Mouse) (A308) LD50: 78 mg/kg (Intravenous, Rat) (A308) |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Pharmacodynamics
Baclofen is an antispasmodic agent that induces muscle relaxation. It reduces the release of excitatory neurotransmitters in the pre-synaptic neurons and stimulates inhibitory neuronal signals in the post-synaptic neurons. Oral formulations of baclofen are the most commonly used form of the drug. In one cross-section study, intrathecal baclofen was more effective than oral baclofen in relieving spasticity directly at the level of the spinal cord. Baclofen has CNS depression properties and can cause sedation with tolerance, somnolence, ataxia, and respiratory and cardiovascular depression. Baclofen also mediates some antinociceptive effects and stimulates gastric acid secretion. Baclofen exhibits anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective activities: it inhibits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines from microglia and astrocytes, and decreases oxidative stress in rats. |
| 分子式 |
C10H12CLNO2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
213.66
|
| 精确质量 |
213.055
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 56.21; H, 5.66; Cl, 16.59; N, 6.56; O, 14.98
|
| CAS号 |
1134-47-0
|
| 相关CAS号 |
(R)-Baclofen;69308-37-8;Baclofen-d4;1189938-30-4;(R)-Baclofen hydrochloride;63701-55-3;Baclofen hydrochloride;28311-31-1
|
| PubChem CID |
2284
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white soild
|
| 密度 |
1.3±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
364.3±32.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 熔点 |
208-210°C
|
| 闪点 |
174.1±25.1 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.9 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.577
|
| LogP |
1.56
|
| tPSA |
63.32
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
3
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
4
|
| 重原子数目 |
14
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
191
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
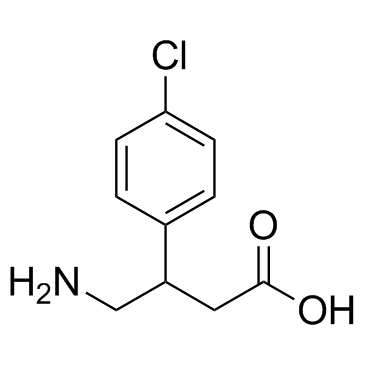
O=C(O)CC(C1=CC=C(Cl)C=C1)CN
|
| InChi Key |
KPYSYYIEGFHWSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C10H12ClNO2/c11-9-3-1-7(2-4-9)8(6-12)5-10(13)14/h1-4,8H,5-6,12H2,(H,13,14)
|
| 化学名 |
4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl)butanoic acid
|
| 别名 |
Baclofen Lioresal, Liofen, Gablofen Baclon Kemstro
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~4.81 mg/mL (~22.51 mM)
H2O : ~2 mg/mL (~9.36 mM) 0.1 M HCL: ~10 mg/mL (~46.8 mM) |
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 2.5 mg/mL (11.70 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。 (<60°C).
配方 2 中的溶解度: ~2.5 mg/mL (11.7 mM) in PBS 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.6803 mL | 23.4017 mL | 46.8033 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.9361 mL | 4.6803 mL | 9.3607 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4680 mL | 2.3402 mL | 4.6803 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Baclofen as a Perioperative Analgesic Adjuvant
CTID: NCT03720717
Phase: Phase 4 Status: Terminated
Date: 2024-09-05