| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
| 靶点 |
ATR ( IC50 = 7 nM )
- Ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3-related protein (ATR) kinase (IC₅₀ = 1.5 nM, measured via HTRF-based kinase activity assay); exhibits >10,000-fold selectivity over other PI3K-like kinases (e.g., mTOR, PI3Kα, DNA-PK, ATM) with IC₅₀ > 10,000 nM for these off-targets [3] - ATR kinase (no specific IC₅₀ reported; described as a "potent, highly selective ATR inhibitor" without numerical data) [1] - ATR kinase (no specific IC₅₀ reported; focus on combination with Radium-223 dichloride without standalone kinase activity values) [2] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
体外活性:在体外,BAY 1895344 是一种非常有效且高度选择性的 ATR 抑制剂,IC50 为 7 nM。它能有效抑制多种人类肿瘤细胞系的增殖(中位 IC50 = 78 nM)。在细胞机制测定中,BAY 1895344 有效抑制羟基脲诱导的 H2AX 磷酸化 (IC50 = 36 nM)。激酶测定:Elimusertib (BAY1895344) 抑制 ATR,IC50 为 7 nM。细胞测定:在细胞机制测定中,BAY 1895344 抑制羟基脲诱导的 H2AX 磷酸化。在细胞机制测定中,BAY 1895344 有效抑制羟基脲诱导的 H2AX 磷酸化 (IC50=36 nM)。
1. ATR激酶抑制与选择性:Elimusertib (BAY1895344) 强效抑制重组人ATR-ATRIP复合物活性,IC₅₀为1.5 nM(HTRF实验)。对456种人类激酶(含PI3Kα、PI3Kβ、mTOR、ATM、DNA-PK)的选择性测试显示,仅对ATR有显著抑制作用,10 μM浓度下对其他所有激酶的抑制率均<10%,证实脱靶激酶活性极低 [3] 2. 肿瘤细胞抗增殖活性:Elimusertib (BAY1895344) 在多种人类肿瘤细胞系中表现出剂量依赖性抗增殖作用,EC₅₀范围为8 nM(ATM缺陷型HCT116结肠癌细胞)至120 nM(ATM正常型A549肺癌细胞)。ATM缺陷或DNA修复缺陷细胞(如BRCA1突变型MDA-MB-436乳腺癌细胞,EC₅₀ = 12 nM)对其敏感性显著高于ATM正常细胞 [3] 3. DNA损伤反应(DDR)信号通路抑制:HCT116细胞经Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(25 nM,处理4小时)处理后,ATR下游底物的磷酸化水平降低,其中Chk1磷酸化(p-Chk1 S345)较对照减少80%,H2AX磷酸化(p-γH2AX)减少40%(Western blot验证),证实ATR-Chk1 DDR通路被阻断 [3] 4. 克隆形成存活抑制:在HCT116 ATM-/-细胞中,Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(10 nM)处理14天后,克隆形成存活率降低90%;而在相同浓度下,ATM正常型HCT116细胞的存活率仅降低30% [3] 5. 与氯化镭-223联合作用:在PC-3前列腺癌细胞(骨转移模型)中,Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(5 nM)与氯化镭-223(100 kBq/mL)联合使用表现出协同抗增殖作用(联合指数CI = 0.6),而单独使用两种药物的CI均>1.0(无协同作用)[2] 6. 与化疗/放疗联合作用:在A2780卵巢癌细胞中,Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(15 nM)与顺铂(1 μM)联合处理使凋亡细胞比例增加60%(Annexin V/PI染色),而单独使用两种药物的凋亡率分别为25%和20%;与2 Gy放疗联合使用时,DNA双链断裂(γH2AX焦点)较单独放疗增加3.5倍 [3] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
BAY1895344 表现出显着改善的水溶性、跨物种的生物利用度,并且在 hERG 膜片钳测定中没有活性。它还在 DNA 损伤缺陷肿瘤模型的单一疗法以及与 DNA 损伤诱导疗法的联合治疗中显示出非常有前景的功效。 BAY 1895344在以DDR缺陷为特征的各种不同适应症的异种移植模型中单药治疗表现出强大的体内抗肿瘤功效,诱导卵巢癌和结直肠癌疾病稳定,甚至在套细胞淋巴瘤模型中诱导肿瘤完全缓解。
1. ATM缺陷肿瘤异种移植模型单药疗效:雌性裸鼠(荷HCT116 ATM-/-结肠癌细胞异种移植瘤,皮下接种5×10⁶细胞)口服Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(25 mg/kg,每日一次[qd],连续21天),肿瘤生长抑制率(TGI)达85%,且肿瘤缩小15%;载体对照组同期肿瘤体积增长200%,未观察到显著体重下降(较基线<5%)[1, 3] 2. 卵巢癌异种移植模型单药疗效:荷A2780卵巢癌细胞异种移植瘤的裸鼠口服Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(50 mg/kg,qd,连续14天),TGI达90%,肿瘤体积基本稳定(增长<10%);对照组肿瘤体积增长300%。肿瘤组织免疫组化(IHC)证实DDR通路抑制(p-Chk1 S345较对照减少75%)[3] 3. 骨转移模型中与氯化镭-223联合疗效:雄性SCID小鼠(经胫骨注射1×10⁵ PC-3细胞建立前列腺癌骨转移模型)随机分为载体组、Elimusertib (BAY1895344)组(10 mg/kg,口服,每周两次[biw])、氯化镭-223组(100 kBq/kg,单次静脉注射[iv])及联合组。Elimusertib (BAY1895344)治疗4周,氯化镭-223在治疗第0天给药。微计算机断层扫描(micro-CT)显示联合组肿瘤负荷减少92%,中位生存期延长45天(氯化镭-223单药组为28天,Elimusertib (BAY1895344)单药组为30天)[2] 4. 肺癌同系移植模型中与顺铂联合疗效:雌性C57BL/6小鼠(荷LLC1肺癌同系移植瘤,皮下接种1×10⁶细胞)口服Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(20 mg/kg,qd,连续10天)联合顺铂(5 mg/kg,iv,每周一次,连续2周),TGI达95%;顺铂单药组TGI为60%,Elimusertib (BAY1895344)单药组为70%。肿瘤组织Western blot显示凋亡标志物切割型caspase-3较单药组增加3倍 [3] |
| 酶活实验 |
1. ATR激酶活性实验(基于HTRF):将重组人ATR-ATRIP复合物(0.5 nM)与生物素化肽底物(来源于Chk1,含ATR磷酸化位点S345)及ATP(10 μM)在激酶缓冲液(50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5、10 mM MgCl₂、1 mM DTT、0.01% BSA)中于30°C孵育60分钟。Elimusertib (BAY1895344)的添加浓度范围为0.01 nM至1000 nM(载体为0.1% DMSO)。孵育后,加入Eu³⁺-穴状化合物偶联的抗磷酸化Chk1(S345)抗体与链霉亲和素偶联的XL665混合物,室温孵育30分钟。检测615 nm(Eu³⁺发射光)和665 nm(XL665发射光)处的荧光共振能量转移(FRET)信号,665/615 nm比值与激酶活性成正比。通过四参数逻辑模型拟合剂量-反应曲线计算IC₅₀ [3]
2. 激酶选择性实验:采用放射活性或荧光法检测Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(1 μM和10 μM)对456种人类激酶(含PI3Kα、PI3Kβ、mTOR、ATM、DNA-PK)的抑制活性。每种激酶的反应体系包含重组酶、特异性肽/蛋白底物及ATP(浓度为各激酶的Km值)。孵育后量化激酶活性,计算相对于载体对照的抑制百分比。结果显示,10 μM Elimusertib (BAY1895344)对除ATR外的所有激酶抑制率均<10% [3] |
| 细胞实验 |
BAY 1895344 在细胞机制测定中抑制羟基脲诱导的 H2AX 磷酸化。 BAY 1895344 在细胞机制测定中显着抑制羟基脲诱导的 H2AX 磷酸化 (IC50=36 nM)。
1. 抗增殖实验(CellTiter-Glo法):将肿瘤细胞(如HCT116、A2780、PC-3)以5×10³个细胞/孔(ATM缺陷细胞)或1×10⁴个细胞/孔(ATM正常细胞)接种于96孔板,在完全培养基(DMEM/RPMI + 10% FBS)中培养24小时。加入浓度范围为0.001 nM至1000 nM的Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(载体为0.1% DMSO),于37°C(5% CO₂)孵育72小时。加入与培养基等体积的CellTiter-Glo试剂,室温孵育10分钟后检测发光值,计算抑制50%细胞活力的浓度(EC₅₀)[1, 2, 3] 2. DDR标志物Western blot实验:将HCT116细胞以2×10⁵个细胞/孔接种于6孔板,培养24小时。用Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(0.1–100 nM)处理4小时后,用冷PBS洗涤细胞,以含蛋白酶/磷酸酶抑制剂的RIPA缓冲液裂解。取20 μg总蛋白进行10% SDS-PAGE电泳,转移至PVDF膜,用5%脱脂牛奶封闭1小时。膜与抗p-ATR(S428)、p-Chk1(S345)、总ATR、总Chk1及β-肌动蛋白(内参)一抗在4°C孵育过夜,再与HRP偶联的二抗室温孵育1小时。检测化学发光信号,通过密度定量(归一化至β-肌动蛋白)分析条带强度 [3] 3. 克隆形成存活实验:将HCT116 ATM-/-和ATM正常细胞以200个细胞/孔(低密度)接种于6孔板,培养24小时。加入Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(1–100 nM),培养14天(每3天换液一次)。用4%多聚甲醛固定克隆,0.1%结晶紫染色,手动计数(>50个细胞的克隆视为存活)。存活分数计算为(处理组克隆数/对照组克隆数)× 100% [3] 4. Annexin V/PI凋亡实验:将A2780细胞以3×10⁵个细胞/孔接种于6孔板,培养24小时后,用Elimusertib (BAY1895344)(15 nM)、顺铂(1 μM)或两者联合处理48小时。胰酶消化收集细胞,冷PBS洗涤,重悬于结合缓冲液。加入Annexin V-FITC和碘化丙啶(PI)(每100 μL细胞悬液各加1 μL),室温避光孵育15分钟。通过流式细胞术量化凋亡细胞(Annexin V⁺/PI⁻和Annexin V⁺/PI⁺)比例 [3] |
| 动物实验 |
Female C.B-17 SCID mice, SU-DHL-8 GCB-DLBCL xenograft model
50 mg/kg Oral administration, b.i.d., 3 days on/4 days off, for 11 days In vivo studies in CDX models [2] The in vivo antitumor efficacy and tolerability of Elimusertib (BAY1895344) as monotherapy/combination therapy were evaluated in CDX subcutaneous or orthotopic xenograft models in mice. Monotherapy experiments were performed in GRANTA-519 (in female SCID beige mice), REC-1 (in female C.B-17 SCID mice), PC-3 (in male NMRI nude mice), LOVO, and A2780 (both in female NMRI nude mice) models treated with BAY 1895344 at 50 mg/kg [all models; twice daily, 3 days on/4 days off (3on/4off), per os/orally] or at 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg (GRANTA-519; twice daily, 3on/4off, per os/orally), ibrutinib (REC-1; 20 mg/kg, once daily, per os/orally), AZD6738 (GRANTA-519, REC-1; 50 mg/kg, once daily, per os/orally), M6620 (GRANTA-519 and REC-1; 100 mg/kg, once daily, per os/orally), or 5-FU (LOVO; 50 mg/kg, once weekly, intraperitoneally). The combination of BAY 1895344 at 10 or 20 mg/kg [once daily, 2 days on/5 days off (2on/5off), per os/orally.] or 50 mg/kg (twice daily, 3on/4off, per os/orally) and carboplatin (50 mg/kg, once weekly, intraperitoneally) was investigated in IGROV-1 tumor–bearing female nude (nu/nu) mice. The combination of 20 or 50 mg/kg BAY 1895344 (twice daily, 2on/5off, per os/orally) and EBRT (5 Gy, 7.7 minutes, once daily on days 12 and 27) was investigated in LOVO tumor–bearing female NMRI nude mice. Combination therapy experiments with 20 or 50 mg/kg BAY 1895344 (twice daily, 3on/4off, per os/orally) and 20 or 50 mg/kg olaparib (once daily, intraperitoneally) were performed in MDA-MB-436 and 22Rv1 models in female NOD/SCID and male SCID mice, respectively. Combination experiments with 20 mg/kg BAY 1895344 (twice daily, 3on/4off, per os/orally) and 100 mg/kg darolutamide (once daily, per os/orally) were performed in the hormone-dependent LAPC-4 prostate cancer model in male C.B-17 SCID mice. Castrated mice served here as a control. For a triple combination treatment, mice received EBRT (5 Gy, every 7 days twice) in addition to treatment with BAY 1895344 and darolutamide. To elucidate the in vivo mode of action of Elimusertib (BAY1895344), ATR and H2AX phosphorylation was determined in lysed GRANTA-519 xenograft tumor samples. For the quantification of circulating ATRis, plasma samples were taken from mice and measured by LC-MS/MS. 1. Subcutaneous xenograft model (HCT116 ATM-/- colon cancer): Female nude mice (6–8 weeks old, n=6 per group) were acclimated for 7 days. HCT116 ATM-/- cells (5×10⁶ in 100 μL PBS + 100 μL Matrigel) were injected subcutaneously into the right dorsal flank. When tumors reached 100–150 mm³ (volume = length × width² / 2), mice were randomized into groups: vehicle (0.5% hydroxypropyl methylcellulose [HPMC] + 0.1% Tween 80, 10 mL/kg) or Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (10, 25, 50 mg/kg). Drugs were administered orally (po) once daily (qd) for 21 days. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every 3 days. At study end, mice were euthanized, tumors were excised and weighed, and tumor tissues were fixed in 10% formalin for IHC analysis [1, 3] 2. Bone metastasis model (PC-3 prostate cancer): Male SCID mice (7–9 weeks old, n=8 per group) were anesthetized with isoflurane. PC-3 cells (1×10⁵ in 20 μL PBS) were injected intratibially into the left hind limb. Two weeks post-injection, mice were randomized into groups: vehicle, Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (10 mg/kg po biw), Radium-223 (100 kBq/kg iv single dose), or combination. Elimusertib (BAY1895344) was administered for 4 weeks; Radium-223 was given once on day 0 of treatment. Tumor burden was assessed by micro-CT (bone lesion volume) at 2 and 4 weeks. Survival was monitored daily, and median survival was calculated [2] 3. Syngeneic graft model (LLC1 lung cancer): Female C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old, n=7 per group) were injected subcutaneously with LLC1 cells (1×10⁶ in 200 μL PBS) into the left flank. When tumors reached 80–100 mm³, mice were randomized into groups: vehicle, Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (20 mg/kg po qd for 10 days), cisplatin (5 mg/kg iv once weekly for 2 weeks), or combination. Tumor volume and body weight were measured every 2 days. At study end, tumors were collected for Western blot analysis of cleaved caspase-3 [3] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
1. Oral bioavailability: In mice, oral administration of Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (25 mg/kg) resulted in an oral bioavailability (F) of 65%, with peak plasma concentration (Cmax) = 2.8 μg/mL and time to Cmax (Tmax) = 1 hour. In rats (5 mg/kg po), F = 58%, Cmax = 1.5 μg/mL, Tmax = 1.5 hours. In beagle dogs (2 mg/kg po), F = 72%, Cmax = 0.9 μg/mL, Tmax = 2 hours [3]
2. Plasma pharmacokinetics (PK): In mice, intravenous Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (5 mg/kg) showed a terminal half-life (t₁/₂) = 4.2 hours, volume of distribution (Vdss) = 1.8 L/kg, and clearance (CL) = 0.3 L/h/kg. Oral administration (25 mg/kg) resulted in area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC₀-24h) = 18 μg·h/mL [3] 3. Tissue distribution: In mice given Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (25 mg/kg po), tissue/plasma concentration ratios at 1 hour post-dose were: tumor (HCT116 ATM-/-) = 3.2, liver = 5.1, kidney = 2.8, brain = 0.3 (minimal blood-brain barrier penetration). Tumor concentrations remained above the cellular EC₅₀ (8 nM) for 12 hours post-dose [3] 4. Metabolism and excretion: In rats, Elimusertib (BAY1895344) was primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) to two major metabolites (M1: O-demethylation; M2: aliphatic hydroxylation), accounting for 60% of plasma radioactivity. After oral administration of [¹⁴C]-labeled Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (5 mg/kg), 70% of radioactivity was excreted in feces and 15% in urine within 48 hours; unchanged parent drug accounted for 25% of fecal radioactivity [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
1. Acute toxicity: Single oral administration of Elimusertib (BAY1895344) to mice (up to 200 mg/kg) and rats (up to 100 mg/kg) caused no mortality or severe clinical signs (e.g., lethargy, ataxia). The approximate lethal dose (LD₅₀) was >200 mg/kg in mice [3]
2. Repeat-dose toxicity (28-day study): In rats (n=5/sex/group), oral Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (10, 25, 50 mg/kg qd for 28 days) showed a no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) of 25 mg/kg. At 50 mg/kg, males showed mild leukopenia (white blood cell count = 4.2 × 10⁹/L vs. control = 6.5 × 10⁹/L) and slight increases in reticulocytes (12% vs. control = 8%), with no changes in liver enzymes (ALT, AST) or renal function (creatinine, BUN). No histopathological lesions were observed in liver, kidney, or bone marrow [3] 3. Plasma protein binding: In human plasma, Elimusertib (BAY1895344) showed high protein binding (98.5%), measured via ultrafiltration. Binding was similar in rat (97.8%) and dog (98.2%) plasma [3] 4. Drug-drug interaction potential: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) (10 μM) did not inhibit human CYP1A2, 2C9, 2C19, or 2D6 (inhibition <10% vs. controls) and only weakly inhibited CYP3A4 (IC₅₀ = 15 μM). It did not induce CYP1A2, 2B6, or 3A4 in human hepatocytes, indicating low risk of pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions [3] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Elimusertib is an orally available ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR)-specific kinase inhibitor, with potential antineoplastic activity. Upon oral administration, elimusertib selectively binds to and inhibits the activity of ATR, which prevents ATR-mediated signaling. This inhibits DNA damage checkpoint activation, disrupts DNA damage repair and induces apoptosis in ATR-overexpressing tumor cells. ATR, a serine/threonine protein kinase upregulated in a variety of cancer cell types, plays a key role in DNA repair, cell cycle progression and cell survival.
The integrity of the genome of eukaryotic cells is secured by complex signaling pathways, known as DNA damage response (DDR). Recognition of DNA damage activates DDR pathways resulting in cell cycle arrest, suppression of general translation, induction of DNA repair, cell survival or even cell death. Proteins that directly recognize aberrant DNA structures recruit and activate kinases of the DDR pathway, such as ATR (ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related). ATR responds to a broad spectrum of DNA damage, including double-strand breaks (DSB) and lesions derived from interference with DNA replication as well as increased replication stress (e.g. in oncogene-driven tumor cells). Therefore, inhibition of ATR kinase activity could be the basis for a novel anti-cancer therapy in tumors with increased DNA damage, deficiency in DNA damage repair or replication stress. Herein we report the identification of the potent, highly selective and orally available ATR inhibitor BAY 1895344 by a collaborative effort involving medicinal chemistry, pharmacology, DMPK and computational chemistry. The chemical structures of lead compound BAY-937 and clinical candidate BAY 1895344 as well as the main SAR trends within this novel class of naphthyridine derivatives will be disclosed for the first time. The novel lead compound BAY-937 revealed promising inhibition of ATR (IC50 = 78 nM) and high kinase selectivity in vitro. In cellular mechanistic assays BAY-937 inhibited hydroxyurea-induced H2AX phosphorylation (IC50 = 380 nM) demonstrating the anticipated mode of action. Moreover, BAY-937 was shown to inhibit proliferation of a variety of tumor cell lines with low- to sub-micromolar IC50 values. In initial xenograft studies, BAY-937 revealed moderate activity in monotherapy and in combination with cis-platin. However, BAY-937 also revealed low aqueous solubility, low bioavailability (rat) and activity in the hERG patch clamp assay. Extensive lead optimization efforts led to the identification of the novel, orally available ATR inhibitor BAY 1895344. In vitro, BAY 1895344 was shown to be a very potent and highly selective ATR inhibitor (IC50 = 7 nM), which potently inhibits proliferation of a broad spectrum of human tumor cell lines (median IC50 = 78 nM). In cellular mechanistic assays BAY 1895344 potently inhibited hydroxyurea-induced H2AX phosphorylation (IC50 = 36 nM). Moreover, BAY 1895344 revealed significantly improved aqueous solubility, bioavailability across species and no activity in the hERG patch-clamp assay. BAY 1895344 also demonstrated very promising efficacy in monotherapy in DNA damage deficient tumor models as well as combination treatment with DNA damage inducing therapies. The start of clinical investigation of BAY 1895344 is planned for early 2017. [1] The DNA damage response (DDR) secures the integrity of the genome of eukaryotic cells. DDR deficiencies can promote tumorigenesis but concurrently may increase dependence on alternative repair pathways. The ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) kinase plays a central role in the DDR by activating essential signaling pathways of DNA damage repair. Here, we studied the effect of the novel selective ATR kinase inhibitor BAY 1895344 on tumor cell growth and viability. Potent antiproliferative activity was demonstrated in a broad spectrum of human tumor cell lines. BAY 1895344 exhibited strong monotherapy efficacy in cancer xenograft models that carry DNA damage repair deficiencies. The combination of BAY 1895344 with DNA damage-inducing chemotherapy or external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) showed synergistic antitumor activity. Combination treatment with BAY 1895344 and DDR inhibitors achieved strong synergistic antiproliferative activity in vitro, and combined inhibition of ATR and PARP signaling using olaparib demonstrated synergistic antitumor activity in vivo Furthermore, the combination of BAY 1895344 with the novel, nonsteroidal androgen receptor antagonist darolutamide resulted in significantly improved antitumor efficacy compared with respective single-agent treatments in hormone-dependent prostate cancer, and addition of EBRT resulted in even further enhanced antitumor efficacy. Thus, the ATR inhibitor BAY 1895344 may provide new therapeutic options for the treatment of cancers with certain DDR deficiencies in monotherapy and in combination with DNA damage-inducing or DNA repair-compromising cancer therapies by improving their efficacy.[2] 1. Mechanism of action: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) binds to the ATP-binding pocket of ATR kinase with high affinity, preventing ATP hydrolysis and subsequent phosphorylation of downstream DDR substrates (Chk1, H2AX). This blocks cell cycle checkpoint activation (G2/M and S-phase checkpoints), leading to unresolved DNA damage and selective cell death in tumor cells—especially those with defective DNA repair (e.g., ATM deficiency), which rely on ATR for survival [1, 3] 2. Preclinical therapeutic advantages: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) combines three key properties for clinical translation: (1) high oral bioavailability (>50% across species) enabling convenient oral dosing; (2) exceptional ATR selectivity (>10,000-fold vs. off-target kinases) minimizing off-target toxicity; (3) synergistic activity with standard-of-care treatments (chemotherapy, radiotherapy, Radium-223) in preclinical models, supporting combination therapy strategies [2, 3] 3. Indications focus: Preclinical data support Elimusertib (BAY1895344) for treatment of solid tumors with DNA repair defects, including ATM-mutant colon/ovarian cancer, BRCA-mutant breast/ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer with bone metastases (especially in combination with Radium-223) [1, 2, 3] #### Additional Info 1. Mechanism of action: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) binds to the ATP-binding pocket of ATR kinase with high affinity, preventing ATP hydrolysis and subsequent phosphorylation of downstream DDR substrates (Chk1, H2AX). This blocks cell cycle checkpoint activation (G2/M and S-phase checkpoints), leading to unresolved DNA damage and selective cell death in tumor cells—especially those with defective DNA repair (e.g., ATM deficiency), which rely on ATR for survival [1, 3] 2. Preclinical therapeutic advantages: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) combines three key properties for clinical translation: (1) high oral bioavailability (>50% across species) enabling convenient oral dosing; (2) exceptional ATR selectivity (>10,000-fold vs. off-target kinases) minimizing off-target toxicity; (3) synergistic activity with standard-of-care treatments (chemotherapy, radiotherapy, Radium-223) in preclinical models, supporting combination therapy strategies [2, 3] 3. Indications focus: Preclinical data support Elimusertib (BAY1895344) for treatment of solid tumors with DNA repair defects, including ATM-mutant colon/ovarian cancer, BRCA-mutant breast/ovarian cancer, and prostate cancer with bone metastases (especially in combination with Radium-223) [1, 2, 3] 4. Development context: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) was developed as a second-generation ATR inhibitor to address limitations of first-generation compounds (e.g., poor oral bioavailability, low selectivity). Its preclinical efficacy and safety profile led to clinical trials (not reported in these studies) for advanced solid tumors [3] |
| 分子式 |
C20H23CL2N7O
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
447.13
|
|
| 精确质量 |
448.35
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 53.58; H, 5.17; Cl, 15.81; N, 21.87; O, 3.57
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
1876467-74-1
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
Yellow solid powder
|
|
| tPSA |
84.8 Ų
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
2
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
6
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
3
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
29
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
537
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
C[C@@H]1COCCN1C2=NC3=C(C=CN=C3C4=CC=NN4)C(=C2)C5=CC=NN5C.Cl
|
|
| InChi Key |
KWQNBYGUBHMRPY-BTQNPOSSSA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C20H21N7O.ClH/c1-13-12-28-10-9-27(13)18-11-15(17-5-8-23-26(17)2)14-3-6-21-20(19(14)24-18)16-4-7-22-25-16;/h3-8,11,13H,9-10,12H2,1-2H3,(H,22,25);1H/t13-;/m1./s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
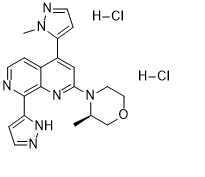
(3R)-3-methyl-4-[4-(2-methylpyrazol-3-yl)-8-(1H-pyrazol-5-yl)-1,7-naphthyridin-2-yl]morpholine;hydrochloride
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|---|
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2365 mL | 11.1824 mL | 22.3649 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4473 mL | 2.2365 mL | 4.4730 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2236 mL | 1.1182 mL | 2.2365 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
| NCT Number | Recruitment | interventions | Conditions | Sponsor/Collaborators | Start Date | Phases |
| NCT05071209 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Elimusertib | Recurrent Lymphoma Refractory Lymphoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
December 22, 2021 | Phase 1 Phase 2 |
| NCT04267939 | Active Recruiting |
Drug: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) Drug: Niraparib |
Advanced Ovarian Carcinoma Advanced Fallopian Tube Carcinoma |
Bayer | February 26, 2020 | Phase 1 |
| NCT04491942 | Recruiting | Drug: Elimusertib Drug: Cisplatin |
Advanced Gastric Carcinoma Advanced Penile Carcinoma |
National Cancer Institute (NCI) |
August 25, 2021 | Phase 1 |
| NCT03188965 | Completed | Drug: Elimusertib (BAY1895344) |
Advanced Solid Tumor Mantle Cell Lymphoma |
Bayer | July 6, 2017 | Phase 1 |