| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
- 醋酸诱导的扭体实验: 灌胃给予CAT(100和200 mg/kg)能显著减少小鼠的腹部扭体次数。200 mg/kg的剂量产生的镇痛作用可持续至给药后240分钟。该模型中的半数有效剂量(ED50)估计为74.42 mg/kg(95%置信区间:67.65 – 81.88 mg/kg)。[1]
- 福尔马林诱导的舔爪实验: CAT(100和200 mg/kg,灌胃)能显著减少小鼠在福尔马林试验早期(神经源性,0-5分钟)和晚期(炎性,20-25分钟)两个阶段的舔爪时间。[1] - 谷氨酸诱导的舔爪实验: CAT(100和200 mg/kg,灌胃)能显著抑制小鼠足底注射谷氨酸诱导的伤害性行为(舔爪时间)。[1] - 辣椒素诱导的伤害性感受实验: CAT(100和200 mg/kg,灌胃)能剂量依赖性地减弱小鼠足底注射辣椒素(TRPV1激动剂)诱导的伤害性行为(舔爪时间)。[1] - 薄荷醇诱导的伤害性感受实验: CAT(100和200 mg/kg,灌胃)能显著抑制小鼠足底注射薄荷醇(TRPM8激动剂)诱导的伤害性行为。[1] - 酸化生理盐水诱导的伤害性感受实验: CAT(100和200 mg/kg,灌胃)能显著抑制小鼠足底注射酸化生理盐水(pH 2.04,ASIC激活剂)诱导的伤害性行为。[1] - PMA诱导的伤害性感受实验: CAT(200 mg/kg,灌胃)能显著减少小鼠足底注射PMA(PKC激活剂)诱导的伤害性行为。[1] - 8-Br-cAMP诱导的伤害性感受实验: CAT(200 mg/kg,灌胃)能显著减少小鼠足底注射8-Br-cAMP(PKA激活剂)诱导的伤害性行为。[1] - 肉桂醛诱导的伤害性感受实验: CAT(100和200 mg/kg,灌胃)并未显著改变小鼠足底注射肉桂醛(TRPA1激动剂)诱导的伤害性行为,提示TRPA1不参与其作用机制。[1] - 作用机制研究(L-精氨酸/NO通路): 在醋酸扭体实验中,预先给予L-精氨酸并未逆转CAT(200 mg/kg)的镇痛作用,提示L-精氨酸-NO通路不参与。[1] - 作用机制研究(KATP通道): 在醋酸扭体实验中,预先给予格列本脲(KATP通道阻断剂)部分逆转了CAT(200 mg/kg)的镇痛作用,提示KATP通道的参与。[1] |
|---|---|
| 动物实验 |
- Animals and Housing: Male Swiss mice (4 weeks old, 26-32 g) were used. They were housed in a temperature-controlled room (25 ± 2 °C) with a 12/12 h light/dark cycle and free access to food and water. Animals were fasted for 8 hours before experiments with free access to water. [1]
- Drug Formulation and Administration: Citronellyl acetate is an oily substance. For administration, it was emulsified in a solution of 2% Tween 80 in distilled water using sonic agitation for 5 minutes. The drug was administered intragastrically (by gavage) at doses of 25, 50, 75, 100, and 200 mg/kg. The control group received an equivalent volume of the vehicle (2% Tween 80 in distilled water). [1] - Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test: Mice were pretreated with vehicle, CAT, or indomethacin (positive control, 10 mg/kg, p.o.). After a predetermined time (e.g., 60 minutes for dose-response), 0.6% acetic acid was injected intraperitoneally (10 µL/g body weight). Ten minutes later, the number of writhing episodes (abdominal constriction and hind leg extension) was counted over a 20-minute period. [1] - Paw Licking Tests (Formalin, Glutamate, etc.): Mice were pretreated with vehicle or CAT. After a set time (30 or 60 minutes), they received a 20 µL intraplantar injection into the right hind paw of one of the following: 1% formalin, glutamate (10 µmol/paw), capsaicin (1.6 µg/paw), menthol (1.2 µmol/paw), cinnamaldehyde (10 µmol/paw), acidified saline (2% acetic acid in saline, pH 2.04), PMA (500 pmol/paw), or 8-Br-cAMP (500 nmol/paw). The duration of paw licking was recorded over specific time windows post-injection (e.g., 0-5 min for formalin early phase, 20-25 min for late phase). [1] - Locomotor Activity Tests (Open Field and Rotarod): To rule out motor impairment, mice were treated with vehicle or CAT (25-200 mg/kg, p.o.). After 60 minutes, spontaneous locomotor activity was assessed for 5 minutes in an open field arena (number of quadrants crossed). Motor coordination was assessed using a rotarod apparatus (time spent on a rotating rod at 12 rpm, with a maximum of three attempts). [1] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
- Acute Behavioral Toxicity: In the rotarod and open field tests, CAT at antinociceptive doses (up to 200 mg/kg, intragastric) did not significantly alter motor coordination or spontaneous locomotor activity in mice 60 minutes after administration, indicating no acute sedative or motor-impairing effects at these doses. [1]
|
| 参考文献 | |
| 其他信息 |
Citronellol acetate is a monoterpenoid that is the acetate ester of citronellol. It has been isolated from Citrus hystrix. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is an acetate ester and a monoterpenoid. It is functionally related to a citronellol.
Citronellyl acetate has been reported in Alpinia latilabris, Alpinia hainanensis, and other organisms with data available. Citronellyl acetate is a metabolite found in or produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. See also: Java citronella oil (part of). - Citronellyl acetate is a monoterpene ester found in plants like Eucalyptus citriodora. It is chemically similar to citronellol and citronellal, which have known biological activities. [1] - Prior to this study, CAT was known to possess fungicidal, larvicidal, bactericidal, insecticidal, and antitumor (pro-apoptotic in hepatoma cells) activities, but its antinociceptive properties had not been investigated. [1] - The study concludes that the systemic (intragastric) administration of CAT produces pronounced antinociceptive effects in mouse models of acute pain. Its mechanism involves, at least in part, the modulation of TRPV1, TRPM8, ASIC channels, glutamate receptors, KATP channels, and the inhibition of PKC and PKA signaling pathways. TRPA1 channels and the L-arginine-NO pathway do not appear to be involved. [1] |
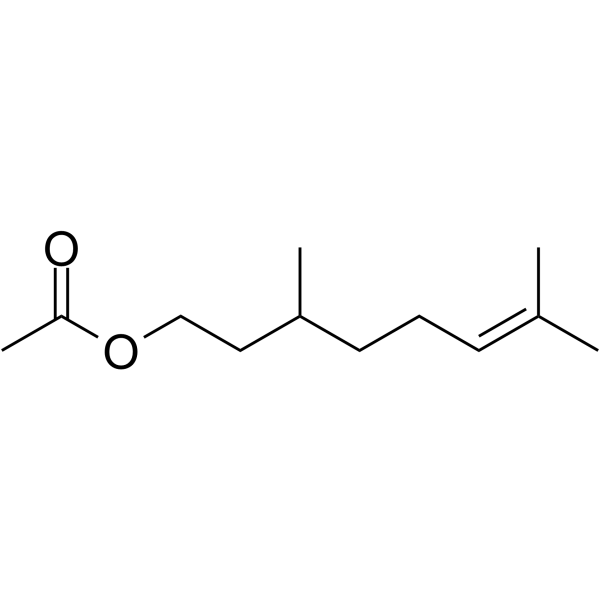
| 分子式 |
C12H22O2
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
198.3019
|
| 精确质量 |
198.161
|
| CAS号 |
150-84-5
|
| PubChem CID |
9017
|
| 外观&性状 |
Colorless to light yellow liquid
|
| 密度 |
0.9±0.1 g/cm3
|
| 沸点 |
258.5±19.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
| 闪点 |
88.2±19.9 °C
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
| 折射率 |
1.442
|
| LogP |
4.28
|
| tPSA |
26.3
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
0
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
2
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
7
|
| 重原子数目 |
14
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
191
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
0
|
| SMILES |
O(C(C([H])([H])[H])=O)C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])/C(/[H])=C(\C([H])([H])[H])/C([H])([H])[H]
|
| InChi Key |
JOZKFWLRHCDGJA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C12H22O2/c1-10(2)6-5-7-11(3)8-9-14-12(4)13/h6,11H,5,7-9H2,1-4H3
|
| 化学名 |
3,7-dimethyloct-6-enyl acetate
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~504.29 mM)
|
|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (12.61 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (12.61 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (12.61 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.0429 mL | 25.2143 mL | 50.4286 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0086 mL | 5.0429 mL | 10.0857 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5043 mL | 2.5214 mL | 5.0429 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。