| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|

| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
在所有三个 CYP2C19 基因型组中,(R)-兰索拉唑的血浆浓度均显着高于相应的 (S)-对映体。对于所有三个基因型组,(R)-兰索拉唑的 AUC0-∞ Cmax 和消除半衰期分别比 (S)-对映体更长和更高[3]。
|
||
|---|---|---|---|
| 动物实验 |
|
||
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion
The dual delayed-release formulation of dexlansoprazole results in a plasma concentration-time profile with two distinct peaks; the first peak occurs one to two hours after administration, followed by a second peak within four to five hours. About 25% of the dose is released at the pH level of 5.5 in the proximal duodenum, while the other 75% is released in the distal small intestine at the pH level of 6.75. After oral administration of dexlansoprazole 30 or 60 mg to healthy subjects and symptomatic GERD patients, mean Cmax and AUC values of dexlansoprazole increased approximately dose-proportionally. Following administration of 30 mg in healthy adults, the mean (%CV) Cmax and AUC were 658 (40%) ng/mL and 3275 (47%) ng x h/mL, respectively. At a dose of 60 mg, the mean (%CV) Cmax and AUC were 1397 (51%) ng/mL and 6529 (60%) ng x h/mL, respectively. In healthy subjects, food increased Cmax by 12 to 55% and AUC by 9 to 37%. The effect of food on Tmax varied, as both an increase and a decrease was observed. Dexlansoprazole does not appear to be eliminated unchanged in the urine. Following the administration of [14C] dexlansoprazole to six healthy male subjects, approximately 50.7% (standard deviation (SD): 9.0%) of the administered radioactivity was excreted in urine and 47.6% (SD: 7.3%) in the feces. The apparent volume of distribution (Vz/F) after multiple doses in symptomatic GERD patients was 40 L. Apparent clearance (CL/F) in healthy subjects was 11.4 to 11.6 L/hour, respectively, after five days of 30 or 60 mg once daily administration. Metabolism / Metabolites Dexlansoprazole is extensively metabolized in the liver. It undergoes oxidation and reduction, followed by subsequent sulfation, glucuronidation, and glutathione conjugation to form inactive metabolites. Oxidative metabolites are formed from CYP2C19-mediated hydroxylation and CYP3A4-mediated oxidation to the sulfone. CYP2C19 is a polymorphic liver enzyme which exhibits three phenotypes in the metabolism of CYP2C19 substrates: extensive metabolizers (*1/*1), intermediate metabolizers (*1/mutant) and poor metabolizers (mutant/mutant). Dexlansoprazole is the major circulating component in plasma regardless of CYP2C19 metabolizer status. In CYP2C19 intermediate and extensive metabolizers, the major plasma metabolites are 5-hydroxy dexlansoprazole and its glucuronide conjugate, while in CYP2C19 poor metabolizers dexlansoprazole sulfone is the major plasma metabolite. Lansoprazole has known human metabolites that include 5-Hydroxylansoprazole and Lansoprazole Sulfone. Biological Half-Life Dexlansoprazole is eliminated with a half-life of approximately one to two hours. |
||
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Dexlansoprazole is the R-enantiomer of the proton-pump inhibitor, lansoprazole. No information is available on the use of dexlansoprazole or lansoprazole during breastfeeding. However, lansoprazole has been used safely in newborn infants, so it is unlikely that the amount of dexlansoprazole in breastmilk would be harmful. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk A retrospective claims database study in the United States found that users of proton pump inhibitors had an increased risk of gynecomastia. A review article reported that a search of database from the European Pharmacovigilance Centre found 1 case of gynecomastia, no cases of galactorrhea, 1 cases of breast pain and 1 case of breast enlargement associated with dexlansoprazole. A search of the WHO global pharmacovigilance database found 2 cases of gynecomastia, no cases of galactorrhea, 4 cases of breast pain and 1 case of breast enlargement associated with dexlansoprazole. Protein Binding Plasma protein binding of dexlansoprazole ranged from 96 to 99% in healthy subjects and was independent of concentration from 0.01 to 20 mcg/mL. |
||
| 参考文献 |
|
||
| 其他信息 |
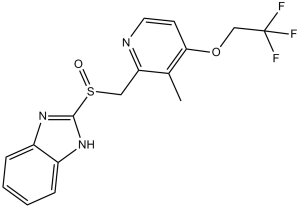
Dexlansoprazole is a sulfoxide and a member of benzimidazoles.
Dexlansoprazole is a new-generation proton pump inhibitor (PPI) used for the management of symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and erosive esophagitis. Dexlansoprazole is the R-enantiomer of [DB00448], which is composed of a racemic mixture of the R- and S-enantiomers. Compared to the older generation of PPIs (which includes [DB00213], [DB00338], and [DB00448]), dexlansoprazole has a unique pharmacokinetic profile due to its delayed-release and dual-delivery release system: This aims to address some limitations of the older-generation PPIs, such as short plasma half-life and the need for meal-associated dosing. Dexlansoprazole inhibits the final step in gastric acid production by blocking the (H+, K+)-ATPase enzyme. Dexlansoprazole is a Proton Pump Inhibitor. The mechanism of action of dexlansoprazole is as a Proton Pump Inhibitor. Dexlansoprazole is the R-isomer of lansoprazole and a substituted benzimidazole prodrug with selective and irreversible proton pump inhibitor activity. As a weak base, dexlansoprazole accumulates in the acidic environment of the secretory canaliculus of the gastric parietal cell where it is converted to an active sulfenamide form that binds to cysteine sulfhydryl groups on the luminal aspect of the proton pump hydrogen-potassium adenosine triphosphatase (H+/K+ ATPase), thereby inhibiting the pump's activity and the parietal cell secretion of H+ ions into the gastric lumen, the final step in gastric acid production. The R-isomer of lansoprazole that is used to treat severe GASTROESOPHAGEAL REFLUX DISEASE. See also: Dexlansoprazole Sesquihydrate (is active moiety of); Lansoprazole (annotation moved to). Drug Indication Dexlansoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) indicated for the: - Healing of all grades of erosive esophagitis (EE) for up to eight weeks in patients 12 years of age and older. - Maintenance of healed EE and relief of heartburn for up to six months in adults and 16 weeks in patients 12 to 17 years of age. - Treatment of heartburn associated with symptomatic non-erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) for four weeks in patients 12 years of age and older. Mechanism of Action Dexlansoprazole suppresses gastric acid secretion by blocking the final step of acid production. It inhibits the H/K ATPase at the secretory surface of the gastric parietal cell, which is involved in the secretion of hydrochloric acid. H/K ATPase is a proton pump responsible for hydrolyzing ATP and exchanging H+ ions from the cytoplasm for K+ ions in the secretory canaliculus: this action results in hydrochloric acid secretion into the gastric lumen. Pharmacodynamics Dexlansoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) that suppresses both basal and stimulated gastric acid secretion. PPIs are associated with a risk for a rebound effect and a short-term increase in hypersecretion; thus, such risk cannot be excluded with dexlansoprazole. With long-term use, PPIs are also associated with a risk of increased susceptibility to bacterial infections, vitamin B12 and iron deficiency, and hypomagnesemia and hypocalcemia, possibly leading to osteoporosis and bone fractures. Dexlansoprazole is reported to interfere with the secretin stimulation test and create false positive urine screening tests for tetrahydrocannabinol. Dexlansoprazole can increase gastrin levels, which can cause enterochromaffin-like cell hyperplasia and increase serum CgA levels. Increased CgA levels may cause false positive results in diagnostic investigations for neuroendocrine tumours. |
| 分子式 |
C16H14F3N3O2S
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
369.36
|
|
| 精确质量 |
369.075
|
|
| CAS号 |
138530-94-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Lansoprazole;103577-45-3;(R)-Lansoprazole-d4;(S)-Lansoprazole;138530-95-7
|
|
| PubChem CID |
9578005
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid powder
|
|
| 密度 |
1.5±0.1 g/cm3
|
|
| 沸点 |
555.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg
|
|
| 熔点 |
66-68?C
|
|
| 闪点 |
289.9±32.9 °C
|
|
| 蒸汽压 |
0.0±1.5 mmHg at 25°C
|
|
| 折射率 |
1.635
|
|
| LogP |
2.76
|
|
| tPSA |
87.08
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
8
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
5
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
25
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
480
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
CC1=C(C=CN=C1C[S@@](=O)C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3N2)OCC(F)(F)F
|
|
| InChi Key |
MJIHNNLFOKEZEW-RUZDIDTESA-N
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C16H14F3N3O2S/c1-10-13(20-7-6-14(10)24-9-16(17,18)19)8-25(23)15-21-11-4-2-3-5-12(11)22-15/h2-7H,8-9H2,1H3,(H,21,22)/t25-/m1/s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
(R)-2-(((3-methyl-4-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)pyridin-2-yl)methyl)sulfinyl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole
|
|
| 别名 |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.77 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 25.0 mg/mL澄清DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;然后向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.77 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 25.0 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入到 900 μL 玉米油中并混合均匀。 请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7074 mL | 13.5369 mL | 27.0739 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5415 mL | 2.7074 mL | 5.4148 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2707 mL | 1.3537 mL | 2.7074 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
Phase 1 Dexlansoprazole Delayed-Release Capsules for Acid-Related Disorders in Infants Aged 1 to 11 Months
CTID: NCT02442752
Phase: Phase 1 Status: Withdrawn
Date: 2020-04-15