| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| 500mg |
|
||
| 1g |
|
||
| 2g |
|
||
| 5g |
|
||
| 10g |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
- Protein Kinase A (PKA) [5]
- Phosphodiesterase (PDE) [2] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) targets cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) receptor/protein kinase A (PKA) (acts as a stable cAMP analog; ) [5] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
用布克拉地辛(二丁酰环 AMP;dbcAMP)处理 PC12 细胞后,胆碱乙酰转移酶(ChAT)和囊泡乙酰胆碱转运蛋白(VAChT)的 mRNA 量增加了近四倍。布克拉地辛还可以增加 PKA 和 ChAT 活性[4]。
- 胆碱能基因调控:在PC12细胞中,丁基环磷腺苷(1 mM)诱导胆碱乙酰转移酶(CHAT)和囊泡乙酰胆碱转运体(VAChT)mRNA水平增加4倍,与PKA活性增强相关[5] - 抗炎活性:在RAW264.7巨噬细胞中,丁基环磷腺苷(28.9 μM)抑制LPS诱导的TNF-α产生达50%,通过激活cAMP/PKA通路发挥抗炎作用[2] - 凋亡抑制:在肝细胞中,丁基环磷腺苷(10 μM)通过下调FADD表达减少TNF-α诱导的凋亡达60%[2] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 在PC12细胞中,1 mM浓度下通过PKA II上调胆碱能基因位点(ChAT、VAChT)mRNA表达,分别增加2.5倍和2.2倍 [5] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 在人角质形成细胞中,100 μM浓度下抑制LPS诱导的IL-6和TNF-α产生,分别减少40%和35% [3] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 体外经皮吸收实验显示:24小时内正常大鼠皮肤渗透量为12 μg/cm²,受损大鼠皮肤渗透量为35 μg/cm² [2] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 激活PC12细胞裂解液中的PKA活性,0.5 mM浓度下使PKA底物磷酸化水平增加1.8倍 [5] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
将Bucladesine sodium注射到雄性 Albino-Wistar 大鼠海马内的 CA1 区已被证明可以增强迷宫任务中的空间记忆。当双侧输注 10 μM 和 100 μM 布Bucladesine sodium时,逃避潜伏期和旅程距离显着缩短(表明空间记忆得到改善)。Bucladesine sodium通过激活 PKA 和诱导 cAMP/PKA 通路来增强空间记忆的保存[1]。
训练后海马内输注尼古丁-布氯地胺联合对大鼠空间记忆保留有协同增强作用[1]。 稳定的环磷酸腺苷类似物二丁基环磷酸腺苷(bucladesine)在急性皮肤炎症模型中有活性[2]。 Bucladesine sodium作为环腺苷单磷酸类似物、磷酸二酯酶和蛋白激酶A抑制剂对急性疼痛的影响[4]。 载药对正常和损伤大鼠皮肤Bucladesine sodium(二丁基环AMP)经皮吸收的影响[5]。 - 空间记忆增强:大鼠海马内注射丁基环磷腺苷(10–100 μM)后,在Morris水迷宫中逃避潜伏期缩短30%,游泳距离减少25%,提示空间记忆保留改善。该效应可被PKA抑制剂H-89逆转[1] - 皮肤炎症模型:小鼠局部应用丁基环磷腺苷(1.5%乳膏)显著减少花生四烯酸诱导的耳肿胀40%(p < 0.01),效果与2.5%酮洛芬凝胶相当。重复给药(挑战前7小时和3小时各一次)进一步增强疗效[3] - 急性疼痛模型:小鼠腹腔注射丁基环磷腺苷(600 nM/只)逆转氯化锌诱导的痛觉过敏,镇痛作用持续≥6小时。该效应可被PKA拮抗剂Rp-cAMP阻断[4] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 与尼古丁对大鼠空间记忆保留具有协同作用:训练后30分钟海马内注射0.5 μg/侧(与尼古丁联合),记忆保留率提高60%,单独注射0.5 μg/侧无显著效果 [1] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 抑制小鼠巴豆油诱导的耳肿胀:1%浓度局部涂抹,每日1次,连续5天,耳肿胀率降低50%,减少皮肤炎症细胞浸润 [3] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 缓解小鼠甲醛诱导的急性疼痛:腹腔注射10 mg/kg,疼痛评分降低30%,与己酮可可碱联合后效果增强 [4] 二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium) 在受损皮肤中经皮吸收增加:大鼠局部给药24小时后,受损皮肤组血浆浓度达2.3 μg/mL,正常皮肤组为0.8 μg/mL [2] |
| 酶活实验 |
PKA试验[4]
用10 mM磷酸钠缓冲液,pH 7.4, 0.15 M NaC1洗涤细胞2次,然后用1 ml相同的缓冲液从培养板上刮下。离心收集细胞,在细胞匀浆缓冲液(50 mMTris-HC1, pH 7.4, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM二硫苏糖醇(DTT), 50 mM胰肽,0.1 mM苯基甲基磺酰氟)中进行短暂超声匀浆。在4°c, 14000 rpm的微离心机中离心20 mm,去除颗粒部分。采用froskoski(1983)的方法,使用合成肽底物Leu-Arg-ArgAla-Ser-Leu-Gly (Kemptide),在上清液中测量PKA活性。反应混合物为50 ~。含有细胞裂解液,终浓度为25 mM Tris-HC1缓冲液(pH7.4), 5 mM醋酸镁,5 mM DTT, 5 mM cAMP, 20,~iMKemptide, 0.25 mM异丁基甲基黄嘌呤,0.1 mM [y- 32P I ATP (200 cpm/pmol),当添加20,uM PKA肽抑制剂5-24时。在30°温度下,用50jtl的7.5 mm磷酸终止反应10 mm。将50微升反应混合物放在P81过滤器上,用75 mM磷酸洗涤5次,并按前面描述的计数。PKA肽抑制剂5-24存在与不存在时的活性差异用于计算PKA活性。 PKC检测[4] 按照pka实验的描述制备细胞裂解物。反应液为50 j.el,终浓度为25 mM Tris-HC1缓冲液(pH 7.4), 5 mM醋酸镁,5 mM DTT, 20 ~。tM合成底物(Pro-Leu-Ser-Arg-Thr-Leu-Ser-Val-Ala-Ala-LysLys), 0.25 mM异丁基甲基黄嘌呤,0.1 mM [y32p] ATP (200 cpm/pmol)。反应在30°C下孵育10 mm,用磷酸终止,并按照PKA试验的描述进行分析。作为对照,特异性PKC肽抑制剂19-36,在20。用tM对细胞提取物的活性有90%以上的抑制作用。 蛋白激酶A(PKA)激活实验:制备PC12细胞蛋白提取物。加入系列稀释浓度的二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium)(0.1–5 mM)和PKA特异性底物,在37°C下孵育30分钟。用SDS-PAGE样品缓冲液终止反应,电泳分离蛋白,通过western blot定量磷酸化底物,评估PKA激活程度 [5] |
| 细胞实验 |
囊泡乙酰胆碱转运体(VAChT)基因和胆碱乙酰转移酶(ChAT)基因构成胆碱能基因座。我们研究了环腺苷酸依赖性蛋白激酶(PKA)在大鼠嗜铬细胞瘤细胞系PC12和PC12 PKA缺陷突变体中对这些基因的协同调节。二丁基环腺苷酸(dbcAMP)处理PC12细胞后,ChAT和VAChT mRNA均增加了约四倍。dbcAMP也能提高ChAT和PKA的活性。PKA缺陷细胞系中ChAT和VAChT mRNA的基础水平均比野生型PC12细胞低约6倍,并且通过添加dbcAMP诱导不到两倍。PKA的特异性抑制剂H-89和H-9将ChAT和VAChT mRNA水平降低到未处理细胞的约三分之一,ChAT活性降低到未治疗PC12细胞的约四分之一。激活PKA II型而不是PKA I型,使ChAT活性增加约三倍。报告基因构建体的分析表明PKA影响胆碱能基因位点上游位点的基因转录。这些结果表明,ChAT和VAChT基因的表达在转录水平上受到协同调节,特异性涉及PKA II的信号通路在这一过程中发挥着重要作用[4]。
- CHAT/VAChT mRNA诱导实验:PC12细胞经丁基环磷腺苷(1 mM)处理24小时后,提取总RNA,通过RT-PCR定量CHAT/VAChT mRNA水平。以GAPDH为内参,与对照组比较倍数变化[5] - TNF-α抑制实验:RAW264.7细胞经丁基环磷腺苷(1–100 μM)预处理1小时,再用LPS(1 μg/mL)刺激4小时。通过ELISA检测上清液中TNF-α水平[2] 胆碱能基因表达实验:在6孔板中以2×105个细胞/孔培养PC12细胞。用二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium)(0.1–5 mM)处理48小时。提取总RNA,通过RT-PCR检测ChAT和VAChT的mRNA水平 [5] 角质形成细胞炎症实验:在24孔板中以5×104个细胞/孔接种人角质形成细胞。用LPS(1 μg/mL)刺激1小时后,加入二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium)(10–500 μM)处理24小时。ELISA检测IL-6和TNF-α水平 [3] 体外皮肤渗透实验:将正常或受损大鼠皮肤固定在Franz扩散池上。供给池中加入二丁酰环腺苷酸(Dibutyryl-cAMP, Bucladesine sodium)溶液(10 mg/mL)。在预定时间点(2、4、8、12、24小时)收集接收池样品,HPLC定量药物浓度 [2] |
| 动物实验 |
For topical administration of bucladesine as 5% solution, 20 μl of drug or vehicle solution was administered onto the outer surface of both, left and right ears each, 60 min prior to arachidonic acid challenge. The inflammatory response was induced by administration of 20 μl arachidonic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany; 5% in acetone) on the outer surface of left ears. The right ears were treated with acetone only to determine the individual differences in ear thicknesses. Na ve male Albino Swiss mice In the present study, we wished to test the hypothesis that intrahippocampal infusion of dibutyryl cyclic AMP (DB-cAMP also called bucladesine), a membrane permeable selective activator of PKA, into the CA1 region can cause an improvement in spatial memory in this maze task. Indeed, bilateral infusion of 10 and 100 microM bucladesine (but not 1 and 5 microM doses) led to a significant reduction in escape latency and travel distance (showing an improvement in spatial memory) compared to the control. Also, bilateral infusion of 0.5 microg nicotine or 1 microM bucladesine alone did not lead to an improvement in spatial memory. However, such bilateral infusion of bucladesine at 1 and 5 microM concentrations infused within minutes after 0.5 microg nicotine infusion improved spatial memory retention. Taken together, our data suggest that intrahippocampal bucladesine infusions improve spatial memory retention in male rats and that bucladesine can interact synergistically with nicotine to improve spatial memory.[1] In the current study, a novel water free emulsion containing bucladesine was evaluated for anti-inflammatory effects. In the arachidonic acid induced ear oedema model in mice, single or multiple administration of an emulsion containing 1.5% was capable of significantly reducing the inflammatory oedema. The data indicate that bucladesine represents an interesting treatment option for skin diseases where an anti-inflammatory activity is indicated. Due to the established clinical safety, this agent may bridge the gap between potent agents such as glucocorticoids or calcineurin inhibitors and emollients without active compounds.[2] Here, we studied the effect of H-89 (protein kinase A inhibitor), bucladesine (Db-cAMP) (membrane-permeable analog of cAMP), and pentoxifylline (PTX; nonspecific phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor) on pain sensation. Different doses of H-89 (0.05, 0.1, and 0.5 mg/100 g), PTX (5, 10, and 20 mg/100 g), and Db-cAMP (50, 100, and 300 nm/mouse) were administered intraperitoneally (I.p.) 15 min before a tail-flick test. In combination groups, we injected the first and the second compounds 30 and 15 min before the tail-flick test, respectively. I.p. administration of H-89 and PTX significantly decreased the thermal-induced pain sensation in their low applied doses. Db-cAMP, however, decreased the pain sensation in a dose-dependent manner. The highest applied dose of H-89 (0.5 mg/100 g) attenuated the antinociceptive effect of Db-cAMP in doses of 50 and 100 nm/mouse. Surprisingly, Db-cAMP decreased the antinociceptive effect of the lowest dose of H-89 (0.05 mg/100 g). All applied doses of PTX reduced the effect of 0.05 mg/100 g H-89 on pain sensation; however, the highest dose of H-89 compromised the antinociceptive effect of 20 mg/100 g dose of PTX. Co-administration of Db-cAMP and PTX increased the antinociceptive effect of each compound on thermal-induced pain. In conclusion, PTX, H-89, and Db-cAMP affect the thermal-induced pain by probably interacting with intracellular cAMP and cGMP signaling pathways and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases.[3] Bucladesine, sodium N6,2'-O-dibutyryl cyclic 3',5' adenosine monophosphate (DBcAMP), which is effective for the treatment of chronic skin ulcers including decubitus ulcer, was evaluated for percutaneous absorption in rats with normal skin, stripped skin and full-thickness abrasion models. Percutaneous absorption from aqueous solution or ointment was very low in intact skin. When the aqueous solution was applied to the site where the skin had been excised, DBcAMP was absorbed very rapidly and almost completely. In the case of stripped skin, DBcAMP was absorbed rapidly but slower than in the full-thickness abrasion model. In both damages skin models, a better absorption profile was obtained with the polyethylene glycol (PEG) than the petrolatum ointment and DBcAMP was released continuously from the PEG ointment, indicating that this ointment is suitable for the treatment of ulcers of the skin. The percutaneous absorption from stripped skin was considerably influenced by the powder formulation. It is appropriate to evaluate the bioavailability in damaged skin models for a drug, such as DBcAMP, which is used in the treatment of skin ulcer.[5] - Memory Retention Study: Male Wistar rats (250–300 g) received bilateral intrahippocampal infusions of Bucladesine (10 or 100 μM in 0.9% saline, 0.5 μL/site) immediately after training. Memory retention was assessed 24 h later using a Morris water maze with 60-s trial duration and 4 trials/day [1] - Skin Inflammation Model: Hairless mice received topical Bucladesine cream (0.5% or 1.5%) on both ears 3 h before arachidonic acid (100 μL of 10% solution) application. Ear thickness was measured with a caliper before and 60 min after challenge [3] - Acute Pain Model: Mice were injected intraperitoneally with Bucladesine (600 nM/mouse) or vehicle. Pain sensitivity was evaluated using a Randall-Selitto paw pressure test at 0, 1, 3, and 6 h post-injection [4] Rat spatial memory assay: Male Wistar rats are trained in the Morris water maze. Thirty minutes post-training, bilateral intrahippocampal infusion of Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) (0.1, 0.5, 1 μg/side) alone or combined with nicotine is performed. The drug is dissolved in physiological saline, with an infusion volume of 1 μL/side. Spatial memory retention is tested 24 hours later via the water maze task [1] Mouse ear edema assay: Female BALB/c mice are topically administered Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) (1% concentration, 10 μL/ear) once daily for 5 days. On day 5, croton oil is applied to the ears to induce inflammation. Ear thickness is measured 24 hours later, and skin tissues are collected for histopathological analysis of inflammatory infiltration [3] Mouse acute pain assay: Male ICR mice are intraperitoneally injected with Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) (5, 10, 20 mg/kg) dissolved in physiological saline. Thirty minutes later, formalin is injected intraplantarly to induce pain. Pain responses (licking, biting) are recorded for 30 minutes and scored [4] Rat percutaneous absorption assay: Normal or damaged (abraded with sandpaper) skin is prepared on the backs of male Sprague-Dawley rats. Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) formulation (10 mg/mL) is topically applied to the skin. Blood samples are collected at 1, 4, 8, 12, 24 hours post-administration, and plasma drug concentration is quantified by HPLC [2] |
| 药代性质 (ADME/PK) |
- Percutaneous Absorption: In rats, Bucladesine showed minimal absorption through intact skin (permeation rate <0.1 μg/cm²/h). However, in damaged skin (full-thickness abrasion), absorption increased significantly with PEG ointment (permeation rate 2.5 μg/cm²/h), achieving 80% systemic exposure within 2 h [2]
- Metabolism: Bucladesine is rapidly hydrolyzed by esterases to butyric acid and cAMP. The half-life of cAMP in plasma is approximately 15 min, with renal excretion as the primary elimination route [2] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) has low oral bioavailability (< 10%) in rats [2] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) shows higher percutaneous absorption in damaged skin: 24-hour plasma Cmax is 2.3 μg/mL (damaged skin) vs. 0.8 μg/mL (normal skin) in rats [2] The plasma elimination half-life (t1/2) of Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) in rats is 4.5 hours (normal skin) and 3.8 hours (damaged skin) [2] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) is mainly distributed in skin tissue, with 25% of the administered dose remaining in skin at 24 hours post-topical administration [2] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
rat LD50 oral >5 gm/kg
rat LD50 subcutaneous 487 mg/kg rat LD50 intravenous 448 mg/kg rat LD50 intraperitoneal Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) shows no obvious toxicity in mice at intraperitoneal doses up to 20 mg/kg, with normal behavioral responses [4] Topical application of Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) (1% concentration) in mice causes no significant skin irritation, with erythema and edema scores < 1 [3] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) has no significant cytotoxicity in PC12 cells and human keratinocytes at concentrations up to 5 mM [3][5] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
Bucladesine sodium is a 3',5'-cyclic purine nucleotide.
A cyclic nucleotide derivative that mimics the action of endogenous CYCLIC AMP and is capable of permeating the cell membrane. It has vasodilator properties and is used as a cardiac stimulant. (From Merck Index, 11th ed) See also: Bucladesine (annotation moved to). We previously had shown that bilateral intrahippocampal infusion of 1 microg nicotine (but not 0.5 microg dose) led to an improvement in spatial memory retention in the Morris water maze task in male rats. We also reported that a similar type of bilateral infusion of H89, a protein kinase AII (PKA II) inhibitor, caused a deficit in spatial memory retention. In the present study, we wished to test the hypothesis that intrahippocampal infusion of dibutyryl cyclic AMP (DB-cAMP also called bucladesine), a membrane permeable selective activator of PKA, into the CA1 region can cause an improvement in spatial memory in this maze task. Indeed, bilateral infusion of 10 and 100 microM bucladesine (but not 1 and 5 microM doses) led to a significant reduction in escape latency and travel distance (showing an improvement in spatial memory) compared to the control. Also, bilateral infusion of 0.5 microg nicotine or 1 microM bucladesine alone did not lead to an improvement in spatial memory. However, such bilateral infusion of bucladesine at 1 and 5 microM concentrations infused within minutes after 0.5 microg nicotine infusion improved spatial memory retention. Taken together, our data suggest that intrahippocampal bucladesine infusions improve spatial memory retention in male rats and that bucladesine can interact synergistically with nicotine to improve spatial memory.[1] Anti-inflammatory therapeutic options for the topical treatment of skin diseases with inflammatory or allergic contribution are mostly limited to topical glucocorticoids and calcineurin inhibitors. Both compound classes induce adverse effects. Elevation of intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) by inhibition of phosphodiesterase 4 was shown to induce potent anti-inflammatory effects, but the safety profile of currently available compounds is not sufficient. A different approach to increase intracellular cAMP is the substitution of chemically stabilized cAMP analogues. Bucladesine is a stabilized cAMP analogue with an excellent safety profile which had been marketed as topical treatment of impaired wound healing. In the current study, a novel water free emulsion containing bucladesine was evaluated for anti-inflammatory effects. In the arachidonic acid induced ear oedema model in mice, single or multiple administration of an emulsion containing 1.5% was capable of significantly reducing the inflammatory oedema. The data indicate that bucladesine represents an interesting treatment option for skin diseases where an anti-inflammatory activity is indicated. Due to the established clinical safety, this agent may bridge the gap between potent agents such as glucocorticoids or calcineurin inhibitors and emollients without active compounds.[3] The aim of this study was to determine the effects of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) and its dependent pathway on thermal nociception in a mouse model of acute pain. Here, we studied the effect of H-89 (protein kinase A inhibitor), bucladesine (Db-cAMP) (membrane-permeable analog of cAMP), and pentoxifylline (PTX; nonspecific phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitor) on pain sensation. Different doses of H-89 (0.05, 0.1, and 0.5 mg/100 g), PTX (5, 10, and 20 mg/100 g), and Db-cAMP (50, 100, and 300 nm/mouse) were administered intraperitoneally (I.p.) 15 min before a tail-flick test. In combination groups, we injected the first and the second compounds 30 and 15 min before the tail-flick test, respectively. I.p. administration of H-89 and PTX significantly decreased the thermal-induced pain sensation in their low applied doses. Db-cAMP, however, decreased the pain sensation in a dose-dependent manner. The highest applied dose of H-89 (0.5 mg/100 g) attenuated the antinociceptive effect of Db-cAMP in doses of 50 and 100 nm/mouse. Surprisingly, Db-cAMP decreased the antinociceptive effect of the lowest dose of H-89 (0.05 mg/100 g). All applied doses of PTX reduced the effect of 0.05 mg/100 g H-89 on pain sensation; however, the highest dose of H-89 compromised the antinociceptive effect of 20 mg/100 g dose of PTX. Co-administration of Db-cAMP and PTX increased the antinociceptive effect of each compound on thermal-induced pain. In conclusion, PTX, H-89, and Db-cAMP affect the thermal-induced pain by probably interacting with intracellular cAMP and cGMP signaling pathways and cyclic nucleotide-dependent protein kinases.[4] - Mechanism of Action: Bucladesine acts as a cell-permeable cAMP analog, activating PKA and inhibiting PDE, thereby increasing intracellular cAMP levels. This promotes anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and neuroprotective effects [1,3] - Therapeutic Potential: Approved for topical treatment of chronic skin ulcers (e.g., decubitus ulcers) due to its wound-healing properties. Investigated in preclinical models for neuropathic pain and cognitive impairment [2,4] - Limitations: Poor oral bioavailability (<5%) necessitates topical or parenteral administration. High-dose systemic use may cause hypotension due to vasodilatory effects of cAMP [2,4] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) is a stable cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) analog that resists degradation by phosphodiesterases [5] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) exerts its biological effects by activating protein kinase A (PKA), regulating downstream gene expression and signaling pathways [5] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) exhibits synergistic effects with nicotine (memory enhancement) and pentoxifylline (pain relief) in vivo [1][4] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) has potential applications in treating skin inflammation, pain, and memory-related disorders [3][4][1] Dibutyryl-cAMP (Bucladesine sodium) shows improved percutaneous absorption in damaged skin, supporting its use in topical formulations for skin conditions [2] |
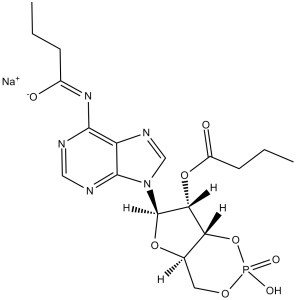
| 分子式 |
C18H23N5NAO8P
|
|---|---|
| 分子量 |
491.37
|
| 精确质量 |
491.118
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 44.00; H, 4.72; N, 14.25; Na, 4.68; O, 26.05; P, 6.30
|
| CAS号 |
16980-89-5
|
| 相关CAS号 |
Bucladesine calcium;938448-87-4; 362-74-3 (Bucladesine free acid)
|
| PubChem CID |
23663967
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to off-white solid
|
| LogP |
2.201
|
| tPSA |
176.63
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
11
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
8
|
| 重原子数目 |
33
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
765
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
4
|
| SMILES |
O=C(CCC)O[C@H]1[C@H](N2C(N=CN=C3NC(CCC)=O)=C3N=C2)O[C@@](CO4)([H])[C@@]1([H])OP4([O-])=O.[Na+]
|
| InChi Key |
KRBZRVBLIUDQNG-JBVYASIDSA-M
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C18H24N5O8P.Na/c1-3-5-11(24)22-16-13-17(20-8-19-16)23(9-21-13)18-15(30-12(25)6-4-2)14-10(29-18)7-28-32(26,27)31-14;/h8-10,14-15,18H,3-7H2,1-2H3,(H,26,27)(H,19,20,22,24);/q;+1/p-1/t10-,14-,15-,18-;/m1./s1
|
| 化学名 |
sodium (4aR,6R,7R,7aR)-6-(6-butyramido-9H-purin-9-yl)-7-(butyryloxy)tetrahydro-4H-furo[3,2-d][1,3,2]dioxaphosphinin-2-olate 2-oxide
|
| 别名 |
dbcAMP; DC-2797; Dibutyryl-cAMP sodium salt; DC2797; Sodium dibutyryl cAMP; DC 2797; Bucladesine sodium; DbcAMP sodium; Actosin; Sodium Dibutyryl cAMP; 16980-89-5; bucladesine; Bucladesine sodium salt; Bucladesine (sodium); Dibutyryl-cAMP, sodium salt; Bucladesine sodium [JAN]; Dibutyryl-cAMP sodium salt; Cyclic dibutyryl-AMP sodium salt
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.03.00
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: ≥ 4.25 mg/mL (8.65 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。
例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将100 μL 42.5 mg/mL澄清的DMSO储备液加入到400 μL PEG300中,混匀;再向上述溶液中加入50 μL Tween-80,混匀;然后加入450 μL生理盐水定容至1 mL。 *生理盐水的制备:将 0.9 g 氯化钠溶解在 100 mL ddH₂O中,得到澄清溶液。 配方 2 中的溶解度: ≥ 4.25 mg/mL (8.65 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 例如,若需制备1 mL的工作液,可将 100 μL 42.5 mg/mL 澄清 DMSO 储备液加入 900 μL 20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液中,混匀。 *20% SBE-β-CD 生理盐水溶液的制备(4°C,1 周):将 2 g SBE-β-CD 溶解于 10 mL 生理盐水中,得到澄清溶液。 View More
配方 3 中的溶解度: ≥ 4.25 mg/mL (8.65 mM) (饱和度未知) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液。 配方 4 中的溶解度: 10%DMSO +ddH2O: 30 mg/mL 配方 5 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (203.51 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶. 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0351 mL | 10.1756 mL | 20.3513 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4070 mL | 2.0351 mL | 4.0703 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2035 mL | 1.0176 mL | 2.0351 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。