| 规格 | 价格 | 库存 | 数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM * 1 mL in DMSO |
|
||
| 1mg |
|
||
| 5mg |
|
||
| 10mg |
|
||
| 25mg |
|
||
| 50mg |
|
||
| 100mg |
|
||
| 250mg |
|
||
| Other Sizes |
|
| 靶点 |
Endogenous Metabolite; α-KG-dependent dioxygenases
Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate targets α-ketoglutarate (α-KG)-dependent dioxygenases (including JmjC histone demethylases: JMJD2A Ki = 1.5 mM; TET family 5-methylcytosine hydroxylases: TET2 Ki = 0.8 mM) [1] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate targets ATP Synthase (IC50 = 5 mM) [2] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate interferes with HIF-1α stability [4] |
|---|---|
| 体外研究 (In Vitro) |
异柠檬酸脱氢酶 (IDH) 1 和 2 基因突变会导致人类恶性肿瘤中 D-α-羟基戊二酸二钠 ((R)-2-羟基戊二酸) 的积累 [1][2]。当存在 50 mMD-2-HG 和 100 μM α-酮戊二酸 (α-KG) 时,KDM7A 部分抑制 H3K9me2 和 H3K27me2 肽。如果添加300 μM α-KG,可以抵消50 mM D-2-HG对CeKDM7A的抑制作用,证明D-α-羟基戊二酸二钠只是α-KG针对CeKDM7A去甲基酶的弱竞争性抑制剂。 1]。 D-α-羟基戊二酸二钠对 TET 羟化酶有微弱的抑制作用。当在 0.1 mM α-KG 存在的情况下添加 10 mMD-α-羟基戊二酸时,TET2 受到部分抑制 (33%),而当添加 50 mMD-α-羟基戊二酸时观察到更高的抑制 (83%)。 D-α-羟基戊二酸对TET1的抑制作用不太明显[1]。
Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 以10 mM浓度处理HeLa细胞48小时,通过抑制JmjC去甲基化酶和TET羟化酶,使组蛋白H3K9me3水平升高2倍,DNA 5-羟甲基胞嘧啶(5-hmC)含量降低30% [1] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 以10 mM浓度处理HeLa细胞24小时,抑制线粒体ATP合酶活性,使细胞ATP生成量减少40%,mTOR磷酸化水平(p-mTOR/mTOR比值)降低50% [2] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 以5 mM浓度处理小鼠CD4+ T细胞72小时,使HIF-1α蛋白稳定性降低60%,细胞代谢向氧化磷酸化偏移(耗氧率升高2.5倍),并抑制Th17细胞极化(IL-17A+细胞比例减少35%)[4] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 以2 mM浓度处理大鼠原代大脑皮层细胞24小时,诱导氧化应激:活性氧(ROS)生成增加1.8倍,丙二醛(MDA)含量升高1.5倍,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性降低40% [5] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 以20 mM浓度处理原代大脑皮层细胞24小时,细胞毒性较低,存活率仍达80% [5] |
| 体内研究 (In Vivo) |
在大鼠大脑皮层、人骨骼肌和牛心脏线粒体颗粒中,D-α-羟基戊二酸显着抑制葡萄糖利用、CO2 生成和呼吸链,表明有氧代谢下降[5]。由于其能够刺激特定的 NMDA 谷氨酸受体,D-α-羟基戊二酸也被认为是一种内源性兴奋毒性有机酸,因为它严重降低了鸡胚端脑和新生大鼠海马神经元培养物中的细胞存活率[5]。在 30 日龄大鼠皮质上清液 (TAR) 值中,D-α-羟基戊二酸二钠 (0.01-1 mM) 显着降低总体抗氧化反应性并增强化学发光和硫代巴比妥酸反应物质 (TBA-RS)[5 ]。
Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 以100 mg/kg/天的剂量腹腔注射7日龄Wistar大鼠,持续7天,诱导大脑皮层氧化应激:ROS水平升高2倍,MDA含量增加1.7倍,过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性降低35% [5] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 以50 mg/kg的剂量每周两次静脉注射C57BL/6小鼠,持续2周,使脾脏中HIF-1α表达降低55%,Th17细胞比例减少40% [4] 在L2HGDH基因敲除小鼠(2-羟基戊二酸尿症模型)中,Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠) 内源性累积导致神经发育迟缓(翻身、爬行能力延迟3天),4周龄时出现大脑白质脱髓鞘病变 [3] |
| 酶活实验 |
酶实验[1]< br >
为了检测人JHDM1A/KDM2A对H3K36me2的去甲基化酶活性,首先将pET28a-JHDM1A转化到大肠杆菌BL21中获得His标记的JHDM1A,当细胞密度达到0.5 OD600单位时,在30°C下加入1 mM IPTG诱导蛋白表达。超声裂解细胞,用Ni-NTA琼脂糖纯化His-JHDM1A融合蛋白。在组蛋白去甲基化缓冲液[50 mM HEPES (pH 8.0), 625 μM Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2, 0.1-0.5 mM α-KG, 2 mM抗坏血酸]中,37℃孵育2个μg寡核小体,4个μg纯化His-JHDM1A和/或10-50 mM L-或D-2-HG], 2- 3小时,加入SDS上样缓冲液停止反应,随后使用抗h3k36me2抗体进行western blotting分析。为了测定CeKDM7A对H3K9me2和H3K27me2的去甲基化酶活性,以两种合成的二甲基化肽H3K9me2 [ARTKQTARK (me2)STGGKA]和H3K27me2 [QLATKAARK (me2)SAPAS]为底物。在20 μl缓冲液(20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)、150 mM NaCl、50 μM (NH4)2Fe(SO4)2、100 μM α-KG、2 mM Vc、10 mM PMSF)存在下,在10 μg酶、1 μg肽存在下进行脱甲基酶测定,时间为3小时。脱甲基反应混合物通过C18 ZipTip (Millipore)脱盐。为了检验2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)的抑制作用,在加入其他反应混合物之前,将不同浓度的2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)与KDM7A短暂孵育。样品采用MALDI-TOF/TOF质谱仪进行分析。
如前所述(Ito et al., 2010),并在补充实验程序中详细描述了tet催化的5mc到5hmc的体外转化。简单地说,5 μg纯化蛋白与0.5 μg双链寡核苷酸底物在50 mM HEPES (pH 8)、75 μM Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2、2 mM抗坏血酸和0.1 mM α-KG中与或不加不同量的2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)中孵育3小时,37℃下纯化寡核苷酸底物并用MspI消化。用小牛碱性磷酸酶处理DNA的5′端,用[γ-32P]ATP和T4多核苷酸激酶标记。标记的片段用乙醇沉淀,在15 mM MgCl2、2 mM CaCl2存在下,用10 μg DNase I和10 μg磷酸二酯酶I在37℃下消化,1微升消化产物在peg -纤维素TLC板上定位,在异丁酸/水/氢氧化铵(66:20:2)流动缓冲液中分离。 α-KG依赖性双加氧酶活性实验:重组JMJD2A(JmjC去甲基化酶)或TET2(羟化酶)与α-KG、Fe²+、抗坏血酸及肽/DNA底物共同孵育;加入不同浓度的Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠)(0.1–20 mM),37°C孵育1小时;通过荧光光谱法检测去甲基化/羟化产物,经竞争性抑制曲线计算Ki值 [1] ATP合酶活性实验:从HeLa细胞中分离线粒体并重悬于反应缓冲液;加入Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠)(1–20 mM),随后加入ADP和无机磷酸;通过化学发光法检测ATP生成量,根据发光强度抑制率确定IC50值 [2] ROS检测实验:原代大脑皮层细胞加载DCFH-DA探针后,用Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠)(1–5 mM)处理24小时;通过流式细胞术(激发波长488 nm)定量ROS水平 [5] |
| 细胞实验 |
最近发现,中心代谢物α-酮戊二酸(α-KG)通过抑制ATP合成酶和TOR信号传导延长秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命。在这里,我们意外地发现(R)-2-羟基戊二酸酯(R)-2HG),一种干扰各种α- kg介导过程的肿瘤代谢物,同样延长了蠕虫的寿命。(R)-2HG在携带异柠檬酸脱氢酶(IDH) 1和2基因新形态突变的人类癌症中积累。我们发现,像α-KG一样,(R)-2HG和(S)-2HG结合并抑制ATP合酶,抑制mTOR信号传导。这些作用在IDH1突变细胞中得到了反映,表明(R)-2HG具有生长抑制功能。一直以来,胶质母细胞瘤细胞中2-HG或α-KG对ATP合酶的抑制足以在葡萄糖限制条件下抑制生长和杀死肿瘤细胞,例如,当酮体(而不是葡萄糖)提供能量时。这些发现为研究2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)和代谢物在生物学和疾病中的作用提供了治疗策略和途径。[3]
d -2-羟基戊二酸酯(D-2HG)由多种类型的恶性细胞释放,包括携带异柠檬酸脱氢酶(IDH)功能获得突变的急性髓性白血病(AML)原细胞。D-2HG作为肿瘤代谢物,以自分泌的方式促进造血细胞的增殖、变异和分化阻断。然而,IDH突变和高D-2HG水平的预后影响仍然存在争议,可能取决于整体突变背景。越来越多的研究关注AML细胞创造的促进免疫逃避的宽松环境。D-2HG对免疫细胞的影响尚不完全清楚。在这里,我们试图研究D-2HG作为抗aml免疫的关键介质对t细胞的影响。D-2HG在体外被t细胞有效吸收,这与从携带IDH突变的AML患者分离的t细胞中测量到的高2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG)水平一致。D-2HG对t细胞活化有轻微影响。然而,D-2HG引发HIF-1a蛋白不稳定,导致代谢偏向氧化磷酸化,增加调节性T细胞(Treg)频率,减少辅助性T细胞17 (Th17)极化。我们的数据首次表明,D-2HG可能有助于免疫反应的微调。[4] 组蛋白/DNA修饰实验:HeLa细胞接种于6孔板(1×10⁶细胞/孔),用Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠)(5–20 mM)处理48小时;提取组蛋白进行蛋白质印迹分析H3K9me3水平,分离基因组DNA通过点印迹检测5-hmC含量 [1] ATP/mTOR信号实验:HeLa细胞接种于96孔板(5×10³细胞/孔),用Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠)(5–15 mM)处理24小时;通过化学发光试剂检测ATP水平,细胞裂解液经蛋白质印迹检测p-mTOR和总mTOR表达 [2] T细胞极化与代谢实验:从小鼠脾脏分离CD4+ T细胞,接种于24孔板(2×10⁵细胞/孔),在Th17极化条件下加入Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠)(2–10 mM)培养72小时;通过流式细胞术(膜联蛋白V-FITC/IL-17A-PE染色)分析IL-17A+细胞,Seahorse细胞外通量分析仪检测氧化磷酸化水平 [4] 氧化应激实验:大鼠原代大脑皮层细胞接种于6孔板,用Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate((R)-2-羟基戊二酸二钠)(1–5 mM)处理24小时;通过硫代巴比妥酸反应检测MDA含量,比色法(黄嘌呤氧化酶法测SOD,过氧化氢分解法测CAT)检测SOD/CAT活性 [5] |
| 动物实验 |
Large amounts of d-2-hydroxyglutaric acid (DGA) accumulate in d-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (D-2-OHGA), an inherited neurometabolic disorder characterized by severe neurological dysfunction and cerebral atrophy. Despite the significant brain abnormalities, the neurotoxic mechanisms of brain injury in this disease are virtually unknown. In this work, the in vitro effect of DGA on various parameters of oxidative stress was investigated; namely chemiluminescence, thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBA-RS), total radical-trapping antioxidant potential (TRAP), total antioxidant reactivity (TAR) and the activities of the antioxidant enzymes catalase, glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase in cerebral cortex from 30-day-old-rats. DGA significantly increased chemiluminescence and TBA-RS and decreased TAR values in the cortical supernatants. In contrast, TRAP and the antioxidant enzyme activities were not altered by the metabolite. Furthermore, the DGA-induced increase of TBA-RS was fully prevented by the free radical scavengers ascorbic acid plus Trolox (water-soluble alpha-tocopherol) and attenuated by the inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase Nomega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), suggesting the role of superoxide, hydroxyl and nitric oxide radicals in this action. The data indicate a stimulation of lipid peroxidation through the production of free radicals and a reduction of the brain capacity to efficiently modulate the damage associated with the enhanced generation of free radicals by DGA. In the case that these findings also occur in human D-2-OHGA, it is feasible that oxidative stress may be involved in the pathophysiology of the brain injury observed in patients with this disease.[5]
Cerebral oxidative stress model: 7-day-old Wistar rats were randomly divided into control and treatment groups; the treatment group received Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate (100 mg/kg/day, dissolved in normal saline) via intraperitoneal injection for 7 days, while the control group received equal volume of normal saline; 24 hours after the last administration, rats were sacrificed, and cerebral cortex tissues were dissected for oxidative stress index detection [5] T-cell metabolism model: C57BL/6 mice (6–8 weeks old) were administered Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate (50 mg/kg, dissolved in PBS) via intravenous injection twice weekly for 2 weeks; 3 days after the final injection, mice were euthanized, and spleen tissues were collected to isolate CD4+ T cells for flow cytometry and metabolism analysis [4] 2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria model: L2HGDH-knockout mice were bred under specific pathogen-free conditions; no exogenous Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate was administered, and endogenous drug accumulation was monitored; neurodevelopmental milestones (crawling) were recorded weekly, and cerebral tissues were harvested at 4 weeks of age for histopathological examination [3] |
| 毒性/毒理 (Toxicokinetics/TK) |
Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate induced oxidative stress-related neurotoxicity in young rats, characterized by increased lipid peroxidation and decreased antioxidant enzyme activity in the cerebral cortex [5]
Endogenous accumulation of Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate in L2HGDH-knockout mice led to progressive neurofunctional deficits (motor and cognitive impairment) and cerebral white matter abnormalities [3] In vitro, Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate showed low cytotoxicity to primary cerebral cortex cells, with 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) > 20 mM [5] No significant hepatotoxicity or nephrotoxicity was observed in mice and rats after short-term administration (≤2 weeks) of Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate [3][5] |
| 参考文献 |
|
| 其他信息 |
IDH1 and IDH2 mutations occur frequently in gliomas and acute myeloid leukemia, leading to simultaneous loss and gain of activities in the production of α-ketoglutarate (α-KG) and 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG), respectively. Here we demonstrate that 2-HG is a competitive inhibitor of multiple α-KG-dependent dioxygenases, including histone demethylases and the TET family of 5-methlycytosine (5mC) hydroxylases. 2-HG occupies the same space as α-KG does in the active site of histone demethylases. Ectopic expression of tumor-derived IDH1 and IDH2 mutants inhibits histone demethylation and 5mC hydroxylation. In glioma, IDH1 mutations are associated with increased histone methylation and decreased 5-hydroxylmethylcytosine (5hmC). Hence, tumor-derived IDH1 and IDH2 mutations reduce α-KG and accumulate an α-KG antagonist, 2-HG, leading to genome-wide histone and DNA methylation alterations.[1]
The organic acidurias D: -2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (D-2-HGA), L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (L-2-HGA), and combined D,L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria (D,L-2-HGA) cause neurological impairment at young age. Accumulation of D-2-hydroxyglutarate (D-2-HG) and/or L-2-hydroxyglutarate (L-2-HG) in body fluids are the biochemical hallmarks of these disorders. The current review describes the knowledge gathered on 2-hydroxyglutaric acidurias (2-HGA), since the description of the first patients in 1980. We report on the clinical, genetic, enzymatic and metabolic characterization of D-2-HGA type I, D-2-HGA type II, L-2-HGA and D,L-2-HGA, whereas for D-2-HGA type I and type II novel clinical information is presented which was derived from questionnaires.[3] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate is an oncometabolite produced by mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1/2 (IDH1/2) enzymes in gliomas, acute myeloid leukemia, and other cancers [1] It exerts biological effects primarily by competitively binding to the α-KG-binding pocket of α-KG-dependent dioxygenases, displacing α-KG and inhibiting their catalytic activity [1] Mutations in L2HGDH (L-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase) or D2HGDH (D-2-hydroxyglutarate dehydrogenase) lead to endogenous accumulation of Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate, causing 2-hydroxyglutaric acidurias—rare inherited metabolic disorders characterized by neurodevelopmental abnormalities [3] Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate disrupts cellular energy metabolism by inhibiting ATP Synthase, leading to reduced ATP production and suppressed mTOR signaling [2] In T cells, it modulates metabolic phenotype and polarization, suggesting potential roles in immune regulation and autoimmune diseases [4] |
| 分子式 |
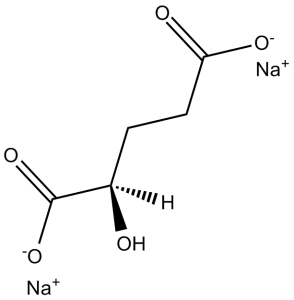
C5H6NA2O5
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 分子量 |
192.08
|
|
| 精确质量 |
192.001
|
|
| 元素分析 |
C, 31.27; H, 3.15; Na, 23.94; O, 41.65
|
|
| CAS号 |
103404-90-6
|
|
| 相关CAS号 |
|
|
| PubChem CID |
51051608
|
|
| 外观&性状 |
White to light yellow solid powder
|
|
| 熔点 |
>291°C (dec.)
|
|
| tPSA |
100.49
|
|
| 氢键供体(HBD)数目 |
1
|
|
| 氢键受体(HBA)数目 |
5
|
|
| 可旋转键数目(RBC) |
2
|
|
| 重原子数目 |
12
|
|
| 分子复杂度/Complexity |
130
|
|
| 定义原子立体中心数目 |
1
|
|
| SMILES |
C(CC(=O)[O-])[C@H](C(=O)[O-])O.[Na+].[Na+]
|
|
| InChi Key |
DZHFTEDSQFPDPP-HWYNEVGZSA-L
|
|
| InChi Code |
InChI=1S/C5H8O5.2Na/c6-3(5(9)10)1-2-4(7)8;;/h3,6H,1-2H2,(H,7,8)(H,9,10);;/q;2*+1/p-2/t3-;;/m1../s1
|
|
| 化学名 |
2R-hydroxy-pentanedioic acid, disodium salt
|
|
| 别名 |
D-alpha-Hydroxyglutaric acid disodium salt; Disodium (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate; 103404-90-6; Sodium (R)-2-hydroxypentanedioate; Disodium (R)-2-Hydroxyglutarate; D-2-Hydroxypentanedioic acid disodium salt; MDK4906; D-alpha-Hydroxyglutaric acid disodium; disodium (2R)-2-hydroxypentanedioate; MFCD00069573; D-2-HGA; 2R-hydroxy-pentanedioic acid, disodium salt
|
|
| HS Tariff Code |
2934.99.9001
|
|
| 存储方式 |
Powder -20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month 注意: 请将本产品存放在密封且受保护的环境中,避免吸湿/受潮。 |
|
| 运输条件 |
Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs)
|
| 溶解度 (体外实验) |
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 溶解度 (体内实验) |
配方 1 中的溶解度: 100 mg/mL (520.62 mM) in PBS (这些助溶剂从左到右依次添加,逐一添加), 澄清溶液; 超声助溶。 (<60°C).
请根据您的实验动物和给药方式选择适当的溶解配方/方案: 1、请先配制澄清的储备液(如:用DMSO配置50 或 100 mg/mL母液(储备液)); 2、取适量母液,按从左到右的顺序依次添加助溶剂,澄清后再加入下一助溶剂。以 下列配方为例说明 (注意此配方只用于说明,并不一定代表此产品 的实际溶解配方): 10% DMSO → 40% PEG300 → 5% Tween-80 → 45% ddH2O (或 saline); 假设最终工作液的体积为 1 mL, 浓度为5 mg/mL: 取 100 μL 50 mg/mL 的澄清 DMSO 储备液加到 400 μL PEG300 中,混合均匀/澄清;向上述体系中加入50 μL Tween-80,混合均匀/澄清;然后继续加入450 μL ddH2O (或 saline)定容至 1 mL; 3、溶剂前显示的百分比是指该溶剂在最终溶液/工作液中的体积所占比例; 4、 如产品在配制过程中出现沉淀/析出,可通过加热(≤50℃)或超声的方式助溶; 5、为保证最佳实验结果,工作液请现配现用! 6、如不确定怎么将母液配置成体内动物实验的工作液,请查看说明书或联系我们; 7、 以上所有助溶剂都可在 Invivochem.cn网站购买。 |
| 制备储备液 | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2062 mL | 26.0308 mL | 52.0616 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0412 mL | 5.2062 mL | 10.4123 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5206 mL | 2.6031 mL | 5.2062 mL |
1、根据实验需要选择合适的溶剂配制储备液 (母液):对于大多数产品,InvivoChem推荐用DMSO配置母液 (比如:5、10、20mM或者10、20、50 mg/mL浓度),个别水溶性高的产品可直接溶于水。产品在DMSO 、水或其他溶剂中的具体溶解度详见上”溶解度 (体外)”部分;
2、如果您找不到您想要的溶解度信息,或者很难将产品溶解在溶液中,请联系我们;
3、建议使用下列计算器进行相关计算(摩尔浓度计算器、稀释计算器、分子量计算器、重组计算器等);
4、母液配好之后,将其分装到常规用量,并储存在-20°C或-80°C,尽量减少反复冻融循环。
计算结果:
工作液浓度: mg/mL;
DMSO母液配制方法: mg 药物溶于 μL DMSO溶液(母液浓度 mg/mL)。如该浓度超过该批次药物DMSO溶解度,请首先与我们联系。
体内配方配制方法:取 μL DMSO母液,加入 μL PEG300,混匀澄清后加入μL Tween 80,混匀澄清后加入 μL ddH2O,混匀澄清。
(1) 请确保溶液澄清之后,再加入下一种溶剂 (助溶剂) 。可利用涡旋、超声或水浴加热等方法助溶;
(2) 一定要按顺序加入溶剂 (助溶剂) 。
 2-HG extends the lifespan of adultC. elegans.Cell Metab.2015 Sep 1;22(3):508-15. |
|---|
2-HG binds and inhibits ATP synthase.Cell Metab.2015 Sep 1;22(3):508-15. |
Inherent vulnerability, or the loss of cell viability, characteristic of cells with ATP5B knockdown, 2-HG accumulation, or IDH mutations.Cell Metab.2015 Sep 1;22(3):508-15. |